当前位置:网站首页>Deep learning: numpy
Deep learning: numpy
2022-06-26 18:17:00 【Little fox dreams of going to fairy tale town】
【 Knowledge framework 】
Deep learning Numpy piece
One 、ndarray Array
1、 establish ndarray Array
array function
This function converts the list to an array
import numpy as np
a = [0,1,2,3,4]
b = np.array(a)
print(b)

arange function
Create an array , The array is a set range 、 Determine the interval 、 Incremental array
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10,2)# from 0 Start to 10 end ( barring 10), The increment interval is 2
print(a)
【 Running results 】
zeros function
Creates the full length of a shape of a specified length 0 Array
import numpy as np
a = np.zeros([3,3])# Create a 3*3 Of all the 0 Array
print(a)
【 Running results 】

ones function
Creates a full... Of the specified length and shape 1 Array
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])# Create a 3*3 Of all the 1 Array
print(a)
【 Running results 】
2、ndarray Properties of array
shape
The shape of the array
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])# Create a 3*3 Of all the 1 Array
print(a.shape)
【 Running results 】
dtype
Data type of array
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
print(a.dtype)
【 Running results 】
size
The number of elements in the array , Its size is equal to the product of each dimension
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
print(a.size)
【 Running results 】
ndim
The dimension size of the array , Its size is equal to shape The number of elements contained
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
print(a.ndim)
【 Running results 】
Change the shape and data type of the array
Change shape with reshape( Slice of array )
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
print(' Original array shape ',a.shape)
a = a.reshape([1,9])
print(' Current array shape ',a.shape)
【 Running results 】
Change the data type with astype
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
print(' Original array type ',a.dtype)
a = a.astype(np.int64)
print(' Current array type ',a.dtype)
【 Running results 】
3、 Scalar sum ndarray Operations between arrays
Scalar and array 4 Operations ( Add, subtract, multiply and divide )
Scalars operate on every element in an array
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
b = 2.0+a
c = 2.0-a
d = 2.0*a
e = 2.0/a
print(' The original array is :\n',a)
print('2+ Array :\n',b)
print('2- Array :\n',c)
print('2* Array :\n',d)
print('2/ Array :\n',e)
【 Running results 】
Array and array operation
Operation between corresponding elements
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
b = np.zeros([3,3])
c = a+b
d = a*b
print(' Array a:\n',a,'\n Array b:\n',b)
print('a+b:\n',c)
print('a*b:\n',d)
【 Running results 】
4、ndarray Statistical method of array
mean
Calculate the arithmetic mean
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
# Two expressions
print(np.mean(a))
print(a.mean())
【 Running results 】
std var
std: Standard deviation var: variance
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10,2)
print(' The test array is :\n',a)
print(' The standard deviation is :',a.std())
print(' The variance of :',a.var())
【 Running results 】
sum
Sum up
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10,2)
print(' The test array is :\n',a)
print(' Sum for :',a.sum())
【 Running results 】
max min
max: Maximum min: minimum value
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10,2)
print(' The test array is :\n',a)
print(' The maximum value is :',a.max())
print(' The minimum value is :',a.min())
【 Running results 】

argmin argmax
minimum value 、 Maximum index
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10,2)
print(' The test array is :\n',a)
print(' The maximum index is :',a.argmax())
print(' The minimum index is :',a.argmin())
【 Running results 】
cumsum cumprod
Accumulation and accumulation ( Look at the results )
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10,2)
print(' The test array is :\n',a)
print(' Add up to :',a.cumsum())
print(' Accumulated as :',a.cumprod())
【 Running results 】
Two 、np.random random number
1、 Random array
Uniform distribution
import numpy as np
a = np.random.rand(10)
print(a)
【 Running results 】
Specify the value range and shape
import numpy as np
a = np.random.uniform(low=-1.0,high=1.0,size=(3,3))#low Lower limit ,high ceiling ,size shape
print(a)
【 Running results 】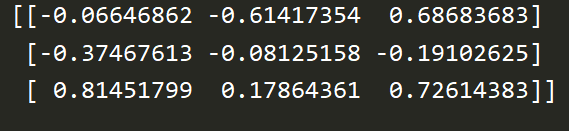
Normal distribution
import numpy as np
a = np.random.randn(9)
print(a)
【 Running results 】
Specified mean loc And variance scale
import numpy as np
a = np.random.normal(loc=2.0,scale=2.0,size=(3,3))
print(a)
【 Running results 】
2、 Random disorder order
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10)
print(' Original array a by :\n',a)
np.random.shuffle(a)
print(' After randomly disrupting the order :\n',a)
【 Running results 】
3、 Random selection of elements
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10)
print(' Original array a by :\n',a)
b = np.random.choice(a)
print(' The randomly selected elements are :',b)
【 Running results 】
3、 ... and 、 linear algebra
diag Find diagonal elements
Returns the diagonal elements of a square array in the form of a one-dimensional array
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(1,10)
a = a.reshape([3,3])
b = np.diag(a)
print(' The test matrix is :\n',a)
print(' The diagonal element is :',b)
【 Running results 】
dot Matrix multiplication
Matrix multiplication
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,12)
b = a.reshape([3,4])
c = a.reshape([4,3])
d = b.dot(c)
print(' matrix b:\n',b)
print(' matrix c:\n',c)
print(' matrix b* matrix c:\n',d)
【 Running results 】
trace Sum of diagonal elements
Calculate the sum of diagonal elements
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(1,10)
b = a.reshape([3,3])
c = np.trace(b)
print(' The test matrix is :\n',b)
print(' matrix b The sum of the diagonal elements of is :',c)
【 Running results 】
det Matrix determinants
Calculate the determinant of a matrix
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(1,10)
b = a.reshape([3,3])
c = np.linalg.det(b)
print(' matrix b The determinant of is :',c)
【 Running results 】
eig Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
Calculate the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a square matrix
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(1,10)
b = a.reshape([3,3])
c = np.linalg.eig(b)
print(' The test matrix is :\n',b)
print(' matrix b Eigenvalues and eigenvectors :\n',c)
【 Running results 】
inv The inverse of the square
Calculate the inverse of the square
import numpy as np
a = np.random.rand(3,3)
b = np.linalg.inv(a)
print(' The test matrix is :\n',a)
print(' matrix b The inverse matrix of is :\n',b)
【 Running results 】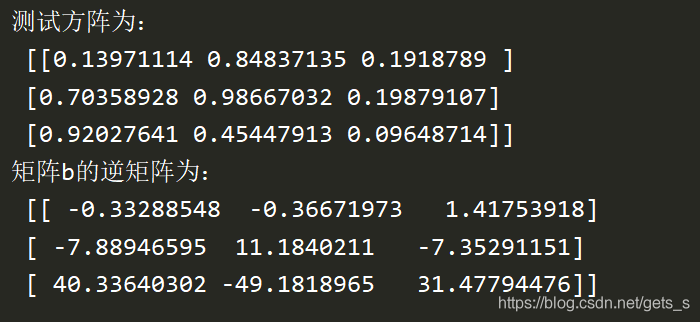
Remember the praise. 、 Focus on 、 Comment on 、 Collection 、 forward
边栏推荐
- I want to know. I am in Zhaoqing. Where can I open an account? Is it safe to open an account online?
- Clion编译catkin_ws(ROS工作空间包的简称)加载CMakeLists.txt出现的问题
- sql中的几种删除操作
- Class inheritance of 25class
- Detailed explanation of MySQL mvcc mechanism
- MySQL download and configuration MySQL remote control
- Chinese (Simplified) language pack
- 必须要掌握的面试重点——索引和事务(附讲B-树与B+树)
- Image binarization
- 行锁分析和死锁
猜你喜欢

博云,站在中国容器潮头

wm_concat()和group_concat()函数

LeetCode 238 除自身以外数组的乘积

DVD-数字通用光盘

Leetcode interview question 29 clockwise print matrix

Do you know how to compare two objects

成功解决之idea引用Lombok的@Slf4j后无法正常使用log

pycharm的plt.show()如何保持不关闭

MySQL download and configuration MySQL remote control

Class inheritance of 25class
随机推荐
交叉编译环境出现.so链接文件找不到问题
Chinese (Simplified) language pack
Union, intersection and difference operations in SQL
Leetcode interview question 29 clockwise print matrix
Publish message publishers and subscribe message subscribers of ROS
In and exceptions, count (*) query optimization
Ethereum技术架构介绍
Interview key points that must be mastered index and affairs (with B-tree and b+ tree)
临时关闭MySQL缓存
How about opening a flush account? Is it safe? How to open a stock trading account
Please advise tonghuashun which securities firm to choose for opening an account? Is it safe to open an account online now?
判断某个序列是否为栈的弹出序列
ISO文件
How to create and enforce indexes
50行代码爬取Top500图书导入TXT文档
带你解决哈希冲突,并实现一个简单hash表,
博云,站在中国容器潮头
成功解决之idea引用Lombok的@Slf4j后无法正常使用log
Case study of row lock and isolation level
Binary search-2