当前位置:网站首页>Deep understanding of MySQL lock and transaction isolation level
Deep understanding of MySQL lock and transaction isolation level
2022-06-26 18:05:00 【Time is light, you are safe】
1、 Lock definition
A lock is a mechanism by which a computer coordinates multiple processes or threads to access a resource concurrently .
In the database , In addition to traditional computing resources ( Such as CPU、RAM、I/O etc. ) Beyond contention , Data is also a resource for users to share .
How to ensure the consistency of data concurrent access 、 effectiveness It's a problem that all databases have to solve , Lock conflicts also affect the performance of database concurrent access Important factors .
2、 Lock classification
(1)、 from On the performance It is divided into Optimism lock ( Use version comparison to achieve ) and Pessimistic locking
Optimism lock ( Use version comparison to achieve ). For example, using a database to maintain a version , Add a field to the table version
For example, there is a piece of data , The initialized version is V1,id Fields, too 1.
Find out this data , The version number obtained is V1, When you want to update this field in the current transaction , You need to determine whether the updated record is the same as the one found in the database , Will be updated . If it has been updated by other threads , The current update cannot be executed .
In short, it is : Other threads have been updated , On this basis, it is not clear whether it has been updated , Direct updates are likely to cause the data of other threads to be overwritten .
Optimistic lock for pessimistic lock , Performance is very good . Optimistic locks that cannot be updated will return directly , No need to wait , Pessimistic locking involves waiting
(2)、 from Type of database operation branch , It is divided into Read the lock and Write lock ( All belong to pessimistic lock )
Read the lock ( Shared lock ): For the same data , Multiple read operations can be performed simultaneously without affecting each other ( If a thread wants to write data , no )
Write lock ( Exclusive lock ): Before the current write operation is completed , It blocks other write and read locks
(3)、 from Granularity of data operations branch , It is divided into Table locks and Row lock
3、 Table locks
Every operation Lock the whole watch .
characteristic :
① Low overhead , Locked fast ;ps: Lock the whole table at one time , You don't need to navigate to a specific line . The whole table will only have one table lock , Not as many as row locks , Low overhead
② A deadlock will not occur ;ps: Yes mysql Come on , A deadlock is actually a process in which several threads operate on different rows , You want to lock the row data that other threads are working on . For table locks , There will always be only one thread operating , If you can get the current table, there will be no deadlock
③ Large locking size , The highest probability of lock collisions , Lowest degree of concurrency ;ps: After a thread gets the table , The operation must be completed , Release the lock , Other threads can continue to operate , So the concurrency is low , Only one thread operation can be supported at a time
3.1 Basic operation
-- Build table SQL
CREATE TABLE `mylock` (
`id` INT (11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`NAME` VARCHAR (20) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE = MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8;
-- insert data
INSERT INTO`test`.`mylock` (`id`, `NAME`) VALUES ('1', 'a');
INSERT INTO`test`.`mylock` (`id`, `NAME`) VALUES ('2', 'b');
INSERT INTO`test`.`mylock` (`id`, `NAME`) VALUES ('3', 'c');
INSERT INTO`test`.`mylock` (`id`, `NAME`) VALUES ('4', 'd');
Add meter lock by hand
lock table The name of the table read(write), The name of the table 2 read(write);
View the lock added to the table
show open tables;
Delete table lock
unlock tables;
3.2 Add watch lock

Now we are right mylock The watch is locked , You can open one more mysql The window of , To read mylock Table data for , See how it turns out ?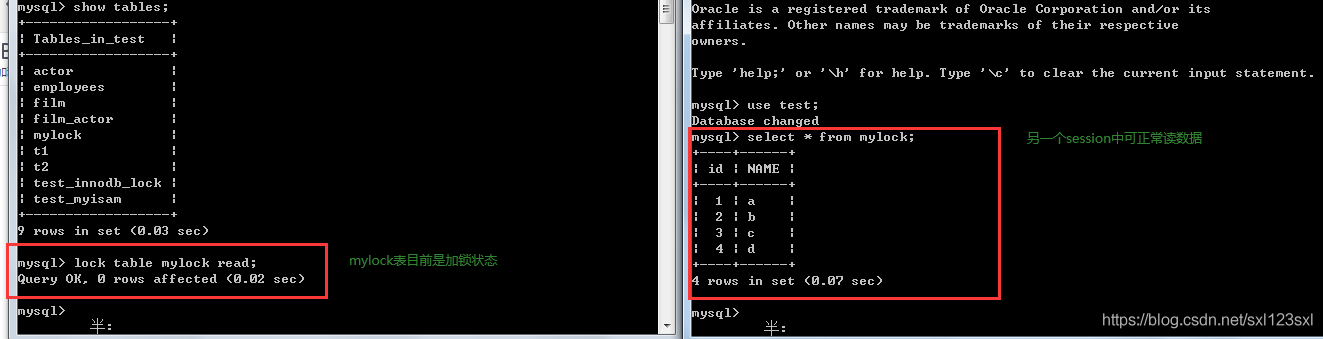
You can see , In a session After the read lock of table lock is added in , other session The read data in can be executed normally .
Then can we do it in another session Write to the data table in ??
You can see another session The write operation in is blocked , Watch lock is waiting ( Mentioned above , If there is a watch waiting , It turns out to be a pessimistic lock ), That is to say, only release the watch lock , Write data to execute normally .
We can first look at the locking status of the database table 
Release the watch lock , At the same time, observe whether the update statement changes 
Conclusion :
At present session And others session You can read the watch
At present session Insert or update locked tables in will report errors , other session Insert or update will wait
Come here , Guys, think about it , What are the general usage scenarios for table locks ? What kind of business scenario will use ??
Generally, data migration or full table operation is required ,, It's better to lock the watch in advance , To prevent being migrated by others session Or the thread modifies the data .
3.3 Conclusion
MyISAM In the execution of the query statement (SELECT) front , Will automatically lock all tables involved ,
In the implementation of addition, deletion and modification Before operation , Will automatically lock the tables involved .
1、 Yes MyISAM surface Of Read operations ( Add read lock ) , It will not block other processes from reading the same table , But it blocks write requests to the same table . Only when the read lock is released , To perform other process write operations .
2、 Yes MylSAM surface Of Write operations ( Add write lock ) , Will block other processes to read and write to the same table , Only When the write lock is released , Will perform read and write operations of other processes
summary :
In short , Namely Reading locks block writing , But it doesn't block reading . A write lock blocks both reading and writing .
4、 Row lock
Every operation Lock a row of data .
characteristic :
① Spending big , Lock the slow ;ps: You need to navigate to a specific line , Then lock it , So locking is slow . The whole table will have many row locks , So it costs a lot
② A deadlock occurs ;
③ Locking granularity minimum , Occurrence of lock The probability of conflict is the lowest , Highest concurrency ;ps: Many thread operations can be supported at one time , As long as the operation is different , Different row locks are added , Therefore, the concurrency is higher than that of table lock
InnoDB And MYISAM There are two big differences :
Support transactions (TRANSACTION)
Row level locking is supported
4.1 Basic operation
-- Create table statement
CREATE TABLE `account` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`balance` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- insert data
INSERT INTO `test`.`account` (`name`, `balance`) VALUES ('lilei', '450');
INSERT INTO `test`.`account` (`name`, `balance`) VALUES ('hanmei', '16000');
INSERT INTO `test`.`account` (`name`, `balance`) VALUES ('lucy', '2400');
Query existing data 
Open transaction :( The general implementation of a SQL sentence , By default, it is submitted automatically , I don't want to submit by default now , have access to begin operation )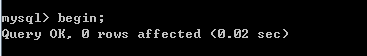
Now update the data :
Show successful execution , Query the data again , It also proves that the update was successful 
However, the transaction is not committed , Don't submit now , On the other side session Operation in , Update the records of different rows first 
You can see that the modification is successful , Then let's modify the same record , Check the effect 
Found after execution SQL blocked , in other words id=3 This data is first session The transaction in is locked .
At this time, we will submit the transaction to see the effect 
4.2 Row lock support transaction
4.2.1 Business (Transaction) And its ACID attribute
The business is made up of a group of SQL A logical processing unit made up of statements , The transaction has the following 4 Attributes , Usually referred to as transaction ACID attribute .
Atomicity (Atomicity)
A transaction is an atomic unit of operation , Its modification of data , Or all of them That's ok , Or none of them .
Uniformity (Consistent)
At the beginning and end of the transaction , Data must be consistent . This means It means that all relevant data rules must be applied to the modification of transactions , To maintain the integrity of the data ; End of transaction when , All internal data structures ( Such as B Tree index or double linked list ) They have to be right .
Isolation, (Isolation)
The database system provides a certain isolation mechanism , Ensure that transactions are not externally affected and The effect of operation “ Independent ” Environmental execution . This means that the intermediate state in the transaction process is Invisible , vice versa .
persistence (Durable)
After the transaction completes , Its modification of data is permanent , Even if the system System failure can also be maintained .
4.2.2 Problems caused by concurrent transaction processing
Update missing (Lost Update)
When two or more transactions select the same row , When the row is then updated based on the originally selected value , Because each transaction does not know the existence of other transactions , There will be lost updates – The last update covers by its Updates from his office .
eg: There are two threads working on the inventory table , The inventory quantity found by the first thread is 10, Minus stock 5, The remaining inventory should be 5. At the same time , The second thread also found that the inventory is 10, Minus stock 1, The remaining inventory is 9, At this time, if the first thread updates first , Update after the second thread , Then the inventory will be 9 Update back to database , The result of the second thread overwrites the result of the first thread
Dirty reading (Dirty Reads)
A transaction is modifying a record , Before this transaction is completed and committed , The data of this record is in an inconsistent state ; At this time , Another transaction also reads the same record , If not controlled , The second transaction reads these “ dirty ” data , And further processing based on it , Uncommitted data dependency will be generated . This phenomenon is called by image “ Dirty reading ”.
In a word : Business A Transaction read B Data that has been modified but not yet submitted , On the basis of this data, we have done the operation . here , If B Transaction rollback ,A Invalid data read , Does not meet conformance requirements .
eg: Open transaction , There are two threads working on the inventory table , The inventory quantity found by the first thread is 10, Minus stock 2, Remaining inventory 8, But the transaction has not been committed yet . At the same time , When the second thread in the transaction reads again , The inventory was found to be 8, Minus inventory 5, Remaining inventory 3. At this time, the first thread has an exception , the rollback Rollback operation , Finally, the inventory will be 3 Update to database .
Don't reread (Non-Repeatable Reads)
A time after a transaction reads some data , Read the previously read data again , But found The data it reads has changed 、 Or some records have been deleted ! This phenomenon is called “ It can't be read repeatedly ”.
In a word : Business A Transaction read B Submitted modify data , Nonconformance isolation
Fantasy reading (Phantom Reads)
A transaction re reads the previously retrieved data according to the same query criteria , But I found that other affairs were involved Enter the new data that meets the query conditions , This phenomenon is called “ Fantasy reading ”.
In a word : Business A Transaction read B The submitted newly added data , Nonconformance isolation .
4.2.3 Transaction isolation level
Dirty reading 、 No repeated reading or phantom reading , In fact, it's all about database read consistency , The database must provide some transaction isolation mechanism to solve .
| Isolation level | Dirty reading (Dirty Reads) | Don't reread (Non-Repeatable Reads) | Fantasy reading (Phantom Reads) |
| Read uncommitted (Read uncommitted) | Probably | Probably | Probably |
| Read submitted (Read committed) | impossible | Probably | Probably |
| Repeatable (Repeatable red) | impossible | impossible | Probably |
| Serializable (serializable) | impossible | impossible | impossible |
The more strict the transaction isolation of the database , The less side effects , But the more it costs , Because transactions are separated In essence, separation is to make affairs to a certain extent “ Serialization ” Conduct , This is obviously related to “ Concurrent ” Is contradictory .
meanwhile , Different applications have different requirements for read consistency and transaction isolation , For example, many applications Yes “ It can't be read repeatedly " and “ Fantasy reading ” It's not sensitive , Perhaps more concerned about the ability of concurrent data access .
View the transaction isolation level of the current database :
show variables like 'tx_isolation';
Set the transaction isolation level :
set tx_isolation='REPEATABLE-READ';
MySQL The default transaction level is :REPEATABLE-READ
More , You can go to Case study of row lock and isolation level see
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
无需人工先验!港大&同济&LunarAI&旷视提出基于语义分组的自监督视觉表征学习,显著提升目标检测、实例分割和语义分割任务!
二分查找-2
力扣每日一题-第28天-566.重塑矩阵
判断某个序列是否为栈的弹出序列
深入理解MySQL锁与事务隔离级别
KDD 2022 | 如何在跨域推荐中使用对比学习?
博云,站在中国容器潮头
Several key points in divorce agreement
Get and set settings in 26class
数据加密标准(DES)概念及工作原理
临时关闭MySQL缓存
MySql 导出数据库中的全部表索引
QPushButton 样式使用示例(以及按钮setmenu添加下拉菜单的方法)
股票开账户如何优惠开户?现在在线开户安全么?
Properties file garbled
Lm06 the mystery of constructing the bottom and top trading strategy only by trading volume
transforms.RandomCrop()的输入只能是PIL image 不能是tensor
【代码随想录-动态规划】T583、两个字符串的删除操作
Ethereum技术架构介绍
[dynamic planning] Jianzhi offer II 091 Paint the house









