当前位置:网站首页>Detailed explanation of spark specification
Detailed explanation of spark specification
2022-06-25 11:21:00 【pyiran】
Why speculation
We all know ,Spark job in , One stage When to finish , Depending on stage Next last task The completion time of .task The completion time of is also affected by many factors , such as partition The distribution of ,executor Resource usage of ,host Operating state , Cluster network, etc . In many cases, it is caused by the operating environment task Running too slowly , Give Way task Running again can alleviate this problem , therefore Spark It supports speculation( speculation ) function . In this article, we will introduce in detail what is spark Of speculation.
Spark.Speculation
stay spark Of configuration in , About speculation The parameters of are as follows :
| property name | default | meaning |
|---|---|---|
| spark.speculation | false | If set to "true", Would be right. tasks Execute the speculation mechanism . That is to say, in one stage Slow down tasks There will be a chance to be restarted |
| spark.speculation.interval | 100ms | Spark testing tasks The interval between speculative mechanisms |
| spark.speculation.multiplier | 1.5 | One task The runtime is all task Several times the median running time of ( Threshold value ) Will be considered as task Reboot required |
| spark.speculation.quantile | 0.75 | When one stage What percentage of tasks The speculation mechanism will not be enabled until the operation is completed |
We noticed that , The speculation mechanism is based on a stage Next on , Different stage Under the task Will not affect each other , It is also aimed at the running task. When speculation execution is started ,spark Will get the first completed task Results and will task Mark as done .
Speculation Workflow
from spark About speculation Configuration parameters for , It is not difficult for us to judge spark The speculative workflow of .

Spark Source code
TaskScheduler Start function of , stay sparkContext Called during initialization .
override def start() {
backend.start()
if (!isLocal && conf.getBoolean("spark.speculation", false)) {
logInfo("Starting speculative execution thread")
speculationScheduler.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.tryOrStopSparkContext(sc) {
checkSpeculatableTasks()
}
}, SPECULATION_INTERVAL_MS, SPECULATION_INTERVAL_MS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
}
}
stay TaskSetManager in , Detection needs to be started speculation The mechanism task
/** * Check for tasks to be speculated and return true if there are any. This is called periodically * by the TaskScheduler. * */
override def checkSpeculatableTasks(minTimeToSpeculation: Int): Boolean = {
// Can't speculate if we only have one task, and no need to speculate if the task set is a
// zombie.
if (isZombie || numTasks == 1) {
return false
}
var foundTasks = false
val minFinishedForSpeculation = (SPECULATION_QUANTILE * numTasks).floor.toInt
logDebug("Checking for speculative tasks: minFinished = " + minFinishedForSpeculation)
if (tasksSuccessful >= minFinishedForSpeculation && tasksSuccessful > 0) {
val time = clock.getTimeMillis()
val medianDuration = successfulTaskDurations.median
val threshold = max(SPECULATION_MULTIPLIER * medianDuration, minTimeToSpeculation)
// TODO: Threshold should also look at standard deviation of task durations and have a lower
// bound based on that.
logDebug("Task length threshold for speculation: " + threshold)
for (tid <- runningTasksSet) {
val info = taskInfos(tid)
val index = info.index
if (!successful(index) && copiesRunning(index) == 1 && info.timeRunning(time) > threshold &&
!speculatableTasks.contains(index)) {
logInfo(
"Marking task %d in stage %s (on %s) as speculatable because it ran more than %.0f ms"
.format(index, taskSet.id, info.host, threshold))
speculatableTasks += index
sched.dagScheduler.speculativeTaskSubmitted(tasks(index))
foundTasks = true
}
}
}
foundTasks
}
DAGScheduler Chinese vs task Conduct re-launch, So this is taking advantage of event The mechanism goes on .
/** * Called by the TaskSetManager when it decides a speculative task is needed. */
def speculativeTaskSubmitted(task: Task[_]): Unit = {
eventProcessLoop.post(SpeculativeTaskSubmitted(task))
}
Reference resources
https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/configuration.html
边栏推荐
- try-catch-finally
- 数据库系列:MySQL索引优化总结(综合版)
- Bayes
- SQL injection vulnerability (bypass)
- Vulnérabilité à l'injection SQL (contournement)
- SystemVerilog (XIII) - enumerate data types
- 2022年PMP项目管理考试敏捷知识点(2)
- 金仓数据库 KingbaseES 插件DBMS_OUTPUT
- Course paper + code and executable EXE file of library information management system based on C language
- Application of global route guard
猜你喜欢

FPGA displays characters and pictures based on VGA

Jincang KFS data centralized scenario (many to one) deployment
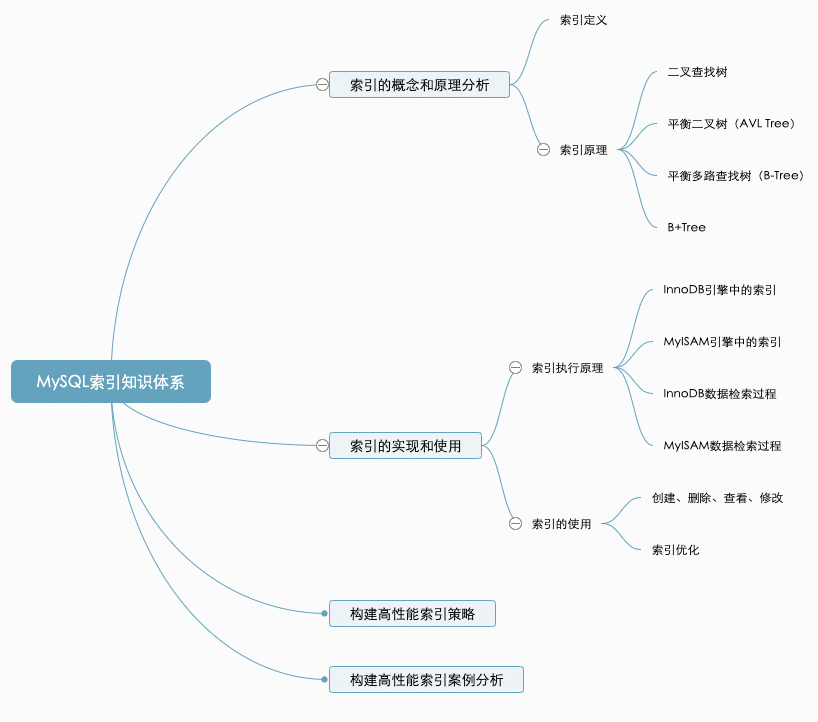
数据库系列:MySQL索引优化总结(综合版)

Android之Kotlin语法详解与使用
基于超算平台气象预警并行计算架构研究

Dragon Book tiger Book whale Book gnawing? Try the monkey book with Douban score of 9.5
![[observation] objectscale: redefining the next generation of object storage, reconstruction and innovation of Dell Technology](/img/82/8cac87231e51698ab17f1274b3a0bd.jpg)
[observation] objectscale: redefining the next generation of object storage, reconstruction and innovation of Dell Technology

Crawler scheduling framework of scratch+scratch+grammar

Explanation and use of kotlin syntax for Android

Redis6 note02 configuration file, publish and subscribe, new data type, jedis operation
随机推荐
try-catch-finally
龙书虎书鲸书啃不动?试试豆瓣评分9.5的猴书
Kingbasees plug-in ftutilx of Jincang database
基于超算平台气象预警并行计算架构研究
反应c语言程序结构特点的程序
wait()、notify()和notifyAll()、sleep()、Condition、await()、signal()
GaussDB 集群维护案例集-sql执行慢
Causes and solutions of over fitting
Dynamic programming to solve stock problems (Part 1)
10.1. Oracle constraint deferred, not deferred, initially deferred and initially deferred
16 种企业架构策略
手机上股票开户安全吗?找谁可以开户啊?
SQL注入漏洞(绕过篇)
Daily 3 questions (3) - check whether integers and their multiples exist
Course paper + code and executable EXE file of library information management system based on C language
从GEE中免费获取全球人类住区层 (GHSL) 数据集
中国信通院沈滢:字体开源协议——OFL V1.1介绍及合规要点分析
【上云精品】节能提效!加速纺织业“智造”转型
Arrays. asList()
An interesting logic SRC mining