This paper proposes a fine-grained classification solution CAP, Through the context aware attention mechanism to help the model find subtle feature changes . In addition to the pixel level attention mechanism , There are also regional attention mechanisms and local feature coding methods , Very different from previous visual schemes , It's worth seeing.
source : Xiaofei's algorithm Engineering Notes official account
The paper : Context-aware Attentional Pooling (CAP) for Fine-grained Visual Classification

- Address of thesis :https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.06635
- Paper code :https://github.com/ArdhenduBehera/cap
Introduction
This paper considers that most of the excellent fine-grained image recognition methods assist in recognition by exploring the local features of the target , However, the local information is not marked , However, weak supervision or unsupervised method is adopted to locate the local feature location . And most methods use pre - trained detectors , Unable to capture the relationship between the target and local features . In order to better describe the picture content , The information from pixel to target to scene needs to be considered more carefully , Not only to locate local features / The location of the target , It also describes its rich and complementary features from multiple dimensions , To get a complete picture / The content of the goal .
This paper considers how to describe the target from the perspective of convolution network , Put forward context-aware attentional pooling(CAP) modular , It can efficiently encode the position information and appearance information of local features . The module takes the output characteristics of convolution network as input , Learn to adjust the importance of different areas in the feature , Thus we can get the rich appearance characteristics and spatial characteristics of local areas , And then carry out accurate classification .
The main contributions of this paper are as follows :
- An extension module in the field of fine-grained image recognition is proposed CAP, It can be simply applied to various convolution networks , Bring considerable fine-grained classification performance improvement .
- To capture the target / Nuances between scenes , A context - sensitive method guided by regional features is proposed attention features .
- Propose a learnable pool operation , It is used to automatically select the hidden state of the circular network to form the space and appearance features .
- The proposed algorithm is used in 8 Test on a fine-grained data set , get SOTA result .
- Analyze different basic networks , expand CAP Application scope of the module .
Proposed Approach
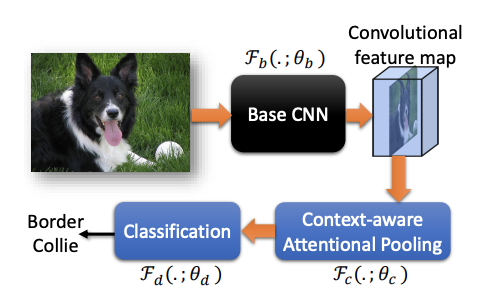
The overall flow of the algorithm in this paper is shown in the figure above , Input picture , Output specific dependent categories , contain 3 A component (3 Group parameters ):
- Basics CNN The Internet \(\mathcal{F}(.;\theta_b)\)
- CAP modular \(\mathcal{F}(.;\theta_c)\)
- Classification module \(\mathcal{F}(.;\theta_d)\)
Context-aware attentional pooling (CAP)

The output characteristic of convolution network is defined as \(x=\mathcal{F}_b(I_n;\theta_b)\),CAP The module takes pixel level features into account 、 Small area characteristics 、 The context information of large area features and picture level features .
pixel-level contextual information

The context information of pixel level features mainly learns the correlation degree between pixels \(p(x_i|x_j;\theta_p)\), In the calculation \(j\) The output of the position synthesizes all other pixel features according to the correlation degree , Use it directly self-attention Realization , Feature conversion uses \(1\times 1\) Convolution . This step directly operates on the output characteristics of the backbone network , But it is not reflected in the overall flow chart .
Proposing integral regions
In order to learn context information more efficiently , The paper is on the characteristic diagram \(o\) Define basic areas of different granularity levels on the , The granularity level is determined by the size of the area . hypothesis \((i,j)\) The smallest area on the location is \(r(i,j\Delta_x,\Delta_y)\) For example , A series of areas can be derived by enlarging the width and height \(R=\{r(i,j,m\Delta_x,n\Delta_y)\}\),\(i < i + m \Delta_x \le W\),\(j < j + n \Delta_y \le H\). Produce similar sets of regions at different locations \(R\), Get the final set of regions \(\mathcal{R}=\{R\}\).\(\mathcal{R}\) Areas with different aspect ratios covering all locations , Provides comprehensive contextual information , Help provide subtle features at different levels of the picture .
Bilinear pooling
Follow the previous step , Get... On the characteristic graph \(|\mathcal{R}|\) Regions , The size ranges from the smallest \(\Delta_x\times\Delta_y\times C\) To the biggest \(W\times H\times C\), The goal of this paper is to represent different size regions as fixed size features , Bilinear interpolation is mainly used . Definition \(T_{\psi}(y)\) Is a coordinate conversion function ,\(y=(i,j)\in \mathbb{R}^c\) Is the area coordinate , The corresponding eigenvalue is \(R(y)\in \mathbb{R}^C\), Then the converted picture \(\tilde{R}\) Of \(\tilde{y}\) The value on the coordinates is :

\(R(T_{\psi(y)})\) Is a sampling function ,\(K(\cdots)\) It's a kernel function , The most primitive method is adopted here , Map the target coordinates back to the original drawing , Take the nearest four points , Output by distance , Finally, the pooled fixed feature is obtained \(\bar{f}(w\times h\times C)\).
Context-aware attention

here , This paper uses a new attention mechanism to obtain context information , according to \(\bar{f}_r\) With other features \(\bar{f}_{r^{'}}(r, r^{'}\in \mathcal{R})\) The similarity of the weighted output , This allows the model to selectively focus on more relevant areas , So as to produce more comprehensive context information . To query items \(q(\bar{f}_r)\) And a set of keyword items \(k(\bar{f}_{r^{'}})\), Output context vector \(c_r\):

Parameter matrix \(W_{\beta}\) and \(W_{\beta^{'}}\) It is used to convert input features into key items of query items ,\(W_{\alpha}\) Is a nonlinear combination ,\(b_{\alpha}\) and \(b_{\beta}\) For the offset term , The overall learnable parameters are \(\{W_{\beta},W_{\beta^{'}},W_{\alpha},b_{\alpha},b_{\beta}\}\in\theta_c\), And attention items \(\alpha_{r,r^{'}}\) It represents the similarity between the two features . such , Context vector \(c_r\) Can represent the area \(\bar{f}_r\) Implied context information , This information is obtained according to its relevance to other regions , The whole calculation idea is similar to self-attention Basically similar .
Spatial structure encoding

Context vector \(c=\{c_r|r=1,\cdots|\mathcal{R}|\}\) The key degree and characteristics of the area are described , In order to further add structural information related to spatial arrangement , In this paper, the context vector of the region \(c\) Turn to area sequence ( Press the paper from top to bottom 、 Left to right ), Input into the recurrent neural network , Hidden units using recurrent neural networks \(h_r\in\mathbb{R}^n\) To express structural features .
Area \(r\) The intermediate feature of can be expressed as \(h_r=\mathcal{F}_h(h_{r-1},f_r;\theta_h)\),\(\mathcal{F}_h\) use LSTM,\(\theta_h\in\theta_c\) contain LSTM Related parameters of . In order to increase generalization ability and reduce computation , Contextual features \(f_r\in\mathbb{R}^{1\times C}\) from \(c_r\in\mathbb{R}^{w\times h\times C}\) Perform global average pooling to obtain , Finally, the context feature sequence is output \(f=(f_1,f_2,\cdots,f_r,\cdots,f_{|\mathcal{R}|})\) Corresponding hidden state sequence \(h=(h_1,h_2,\cdots,h_r,\cdots,h_{|\mathcal{R}|})\), Later, it is used in the classification module .
Classification

In order to further guide the model to distinguish subtle changes , This paper proposes a learnable pool operation , Can respond to similar hidden layers by combining \(h_r\) To integrate feature information . The paper draws lessons from NetVLAD Thought , A derivable clustering method is used to transform the response value of the hidden layer , First, the response of hidden layer to class cluster is calculated \(k\) The relevance of , And then weighted to the class cluster \(k\) Of VLAD encoding in :

Each class cluster has its learnable parameters \(W_i\) and \(b_i\), The whole idea is based on softmax, Press... For the response value of the hidden layer softmax The weight of is assigned to different clusters . After getting all the class clusters encoding After vector , Use learnable weights \(W_N\) and softmax Normalize . therefore , Classification module \(\mathcal{F}_d\) The learnable parameter of is \(\theta_d=\{W_i, b_i, W_N\}\).
Experiments and Discussion

On different datasets , Compare different methods .

Comparison of accuracy under different backbone networks .

Visualization of output characteristics of different modules , chart b It's to join CAP after , Characteristics of backbone network output .
Conclusion
This paper proposes a fine-grained classification solution CAP, Through the context aware attention mechanism to help the model find the subtle feature changes of the target . In addition to the pixel level attention mechanism , There are also regional attention mechanisms and local feature coding methods , Very different from previous visual schemes , It's worth seeing. .
If this article helps you , Please give me a compliment or watch it ~
More on this WeChat official account 【 Xiaofei's algorithm Engineering Notes 】









