当前位置:网站首页>Advanced thinking on application scenarios of standardization, maximum normalization and mean normalization
Advanced thinking on application scenarios of standardization, maximum normalization and mean normalization
2022-06-22 15:44:00 【A day or two】
This article belongs to the summary of knowledge points , The content belongs to excerpt and sorting
One 、 Basic concepts


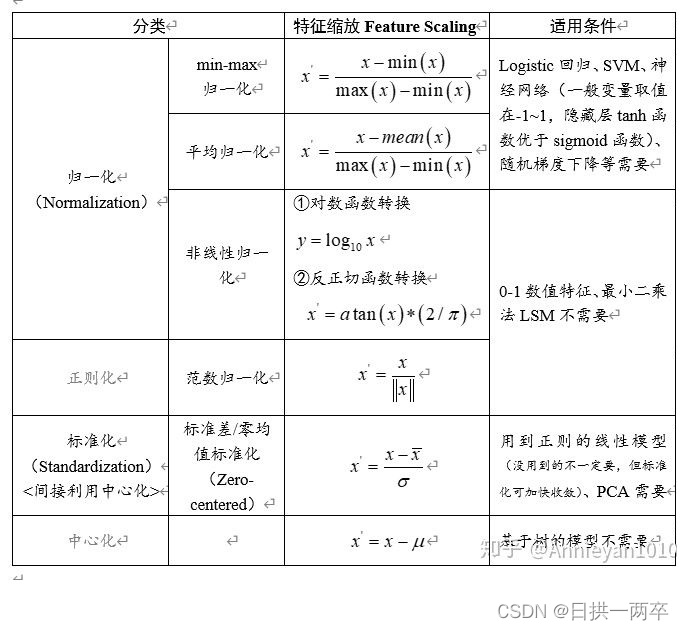
Two 、 Different normalization methods are described :
2.1 Maximum normalization
The method of linearizing the original data is transformed into [0 1] The scope of the , This method realizes the equal scaling of the original data . By using the maximum and minimum values of variable values ( Or the maximum ) Convert raw data into data bounded by a specific range , So as to eliminate the influence of dimension and order of magnitude , Change the weight of variables in the analysis to solve the problem of different measures . Because the extremum method is only related to the two extreme values of the maximum and minimum of the variable in the process of dimensionless variable , It has nothing to do with other values , This makes the method rely too much on two extreme values when changing the weight of each variable .

2.2 Mean normalization
Mean normalization and maximum normalization are basically the same , Only the denominator is x-mean(x), The data will be compressed in [-1,1] The range of

2.3 Standardization method
That is, the value of each variable and its average value μ Divided by the standard deviation of the variable σ. Although this method makes use of all the data information in the dimensionless process , However, this method not only makes the mean values of the transformed variables the same after dimensionless , And the standard deviation is the same , That is, dimensionless, it also eliminates the difference in the degree of variation of each variable , Thus, the importance of the transformed variables in the cluster analysis is the same . And in the actual analysis , The importance of each variable in the analysis is often determined according to the difference of its value in different units , If the difference is large, the analysis weight is relatively large .

2.4 Nonlinear normalization
- Logarithmic function conversion :y = log10(x)
- Inverse cotangent function conversion :y = atan(x) * 2 / π
- It is often used in scenarios with large data differentiation , Some values are very large , Some are very small . Through some mathematical functions , Mapping the original values . The method includes log、 Index , Tangent, etc . According to the distribution of data , The curve that determines the nonlinear function , such as log(V, 2) still log(V, 10) etc. .
2.5 Centralization
The value of each variable and its mean μ The difference between the

2.6 Icon
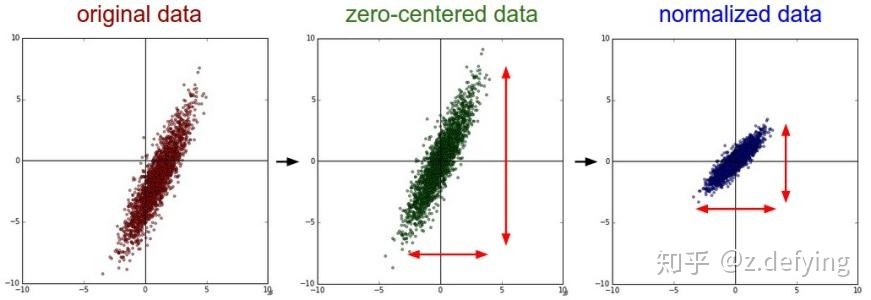
Raw data distribution 、 Zero mean data distribution 、 Normalized data distribution

You can see mean Both normalization and standardization move the data distribution center to the origin , Normalization does not change the shape of the data distribution , Standardization makes the distribution of sample data approximate to a certain distribution .
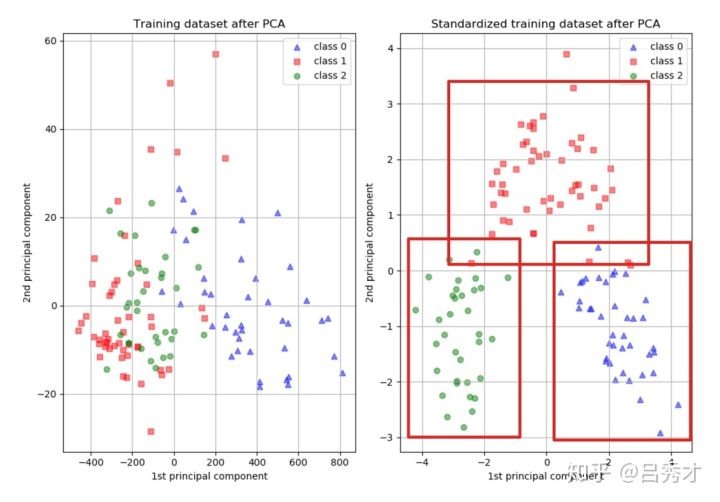
Standardization is good for PCA The impact of dimensionality reduction
3、 ... and 、 How to choose
The difference between normalization and Standardization : Normalization is to convert the eigenvalues of samples to the same dimension and map the data to [0,1] perhaps [-1, 1] Within the interval , Only determined by the extreme value of the variable , Because the interval scaling method is a kind of normalization . Standardization deals with data according to the columns of characteristic matrix , It is through seeking. z-score Methods , Convert to standard normal distribution , Related to the overall sample distribution , Each sample point can have an impact on Standardization . What they have in common is that they can eliminate the errors caused by different dimensions ; It's all a linear transformation , It's all about vectors X Compress to scale and then translate .
The difference between standardization and centralization : Standardization is the original score minus the mean and then divided by the standard deviation , Centralization is the original score minus the average . Therefore, the general process is to centralize first and then standardize .
When to use normalization ? When to use standardization ?
- If there is a requirement for the output range , Use normalization .
- If the data is stable , There is no extreme maximum or minimum , Use normalization .
- If the data has outliers and more noise , Use standardization , The influence of outliers and extremes can be avoided indirectly through centralization .
Generally speaking , It is recommended to give priority to the use of standardization .
3.1 Which models must be normalized / Standardization
3.1.1 SVM
Different models have different assumptions about the distribution of features . such as SVM With Gaussian kernels , All dimensions share one variance , This assumes that the characteristic distribution is circular , If you input an ellipse, it's a hole , So simple normalization is not good enough .
3.1.2 KNN、PCA、Kmeans
Models that need to measure distance , Generally, when the eigenvalue difference is large , Will be normalized / Standardization . Otherwise it will appear “ Large numbers take decimals ”.
In the classification 、 Clustering algorithm , When distance is needed to measure similarity 、 Or use PCA Technology for dimensionality reduction , Standardization performs better . When it comes to distance measurement 、 Covariance calculation 、 When the data does not conform to the positive distribution , The normalization method can be used . For example, in image processing , take RGB After the image is converted to a grayscale image, its value is limited to [0 255] The scope of the . occasionally , We have to feature in 0 To 1 Between , At this point, we can only use normalization .
3.1.3 neural network
1) Numerical problems
normalization / Standardization can avoid some unnecessary numerical problems . The order of magnitude of the input variable does not cause numerical problems , But in fact, it's not so difficult to cause . because tanh The nonlinear interval of is about [-1.7,1.7]. It means making neurons work ,tanh( w1x1 + w2x2 +b) Inside w1x1 +w2x2 +b The order of magnitude should be 1 (1.7 The order of magnitude ) about . In this case, the input is larger , It means that the weights have to be smaller , A larger , A smaller one , Multiply the two , And that leads to numerical problems .
2) Solving the problem requires
a. initialization : In initialization, we want each neuron to initialize to a valid state ,tanh Function in [-1.7, 1.7] There is good nonlinearity in the range , So we hope that the input of the function and the initialization of the neuron can be in a reasonable range so that each neuron is effective at the beginning .
b. gradient : To input - Cryptic layer - Output such three layers BP For example , We know that for input - The gradient of hidden layer weights is 2ew(1-a^2)*x In the form of (e It's the error ,w It's the weight from the hidden layer to the output layer ,a It's the value of the neurons in the hidden layer ,x It's input ), If the order of magnitude of the output layer is very large , Can cause e It's an order of magnitude , Empathy ,w In order to make the hidden layer ( The order of magnitude is 1) Reflected in the output layer ,w It's going to be big , Plus x If it's too big , We can see from the gradient formula that , Multiply the three , The gradient is very big . This will bring numerical problems to the update of gradient .
c. Learning rate : from (2) in , You know, the gradient is very large , The learning rate has to be very small , therefore , Learning rate ( The initial value of learning rate ) The selection needs to refer to the range of input , It's better to normalize the data directly , In this way, the learning rate does not have to be adjusted according to the data range . The weight gradient from hidden layer to output layer can be written as 2ea, The weight gradient from input layer to hidden layer is 2ew(1-a^2)x , suffer x and w Influence , The order of magnitude of each gradient is different , therefore , They need different orders of magnitude of learning rates . Yes w1 Appropriate learning rate , Maybe relative to w2 It's too small for me , If it is suitable for use w1 Learning rate of , It will lead to w2 Step very slowly in the direction , It takes a lot of time , And it's suitable for w2 Learning rate of , Yes w1 It's too big for me , No search for w1 Solution . If you use a fixed learning rate , And the data is not normalized , The consequences can be imagined .
3.2 Which algorithms in machine learning can not be normalized
Probability models don't need to be normalized , Because they don't care about the value of variables , It's about the distribution of variables and the conditional probabilities between variables . image svm、 Optimization problems such as linear regression require normalization . The decision tree belongs to the former . Normalization is also one of the necessary abilities to improve the application ability of the algorithm .
Is there any measurement of distance in the model algorithm , There is no measure of the standard deviation between variables . such as decision tree Decision tree , He used the algorithm, which did not involve any distance and other related , So when making a decision tree model , There is usually no need to standardize variables .
Four 、 The relationship between different normalization and different activation functions
4.1 sigmoid function
First of all Sigmoid For the activation function as an example ,Sigmoid The image of the function , The formula is as follows :



Z Type update
Of course, this is the case for the first floor , After the activation function of the first layer Sigmoid After output , All output values range from [0,1] Between , That is, they are greater than 0, So the second floor in the back 、 The third floor to the last floor , In back propagation , Because of the input x The symbols are all positive , Will appear Z Type renewal phenomenon , Make the network convergence speed very slow , This is it. Sigmoid Problems caused by non-zero mean function . So for Sigmoid In terms of functions , The first 2、3 To the last layer of neural network , Exist Z Type update problem , For zero averaging of input data , Can avoid the first layer of neural network Z Type update problem .
for fear of Z Type update , Zero the input , In this way, some input will be positive and negative doped input , Every ω Gradient symbols and inputs for x relevant , It won't be all the same , It won't be Z Type updated .
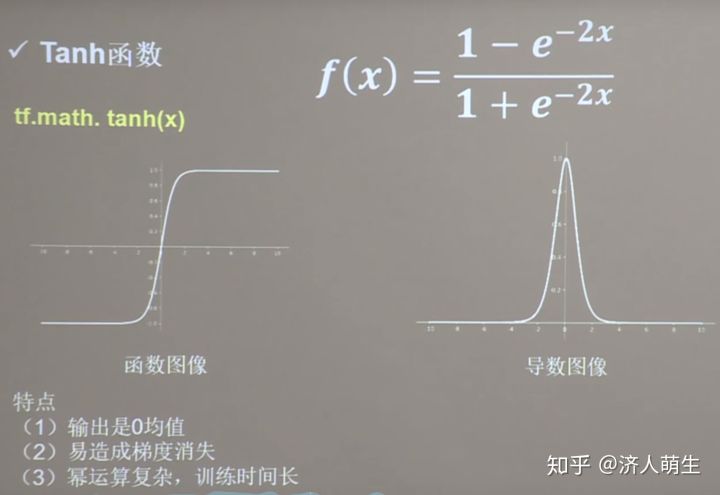
4.2 tanh function
tanh Function is also one of the classical activation functions , Function image , The formula is as follows :

4.3 ReLU function
ReLU It is the most common activation function at present , Function image 、 The formula is as follows :


5、 ... and 、 Some examples
5.1 Must logistic regression be standardized ?
It depends on whether our logistic regression is regular . If you don't use regular , that , Standardization is not necessary , If you use regular , Then standardization is necessary . Because when regular is not used , Our loss function only measures the difference between the prediction and the reality , Plus regular , In addition to measuring the gap above, our loss function , Also measure whether the parameter value is small enough . The magnitude of the parameter value, or the magnitude level, is related to the numerical range of the feature .
for instance , We use weight to predict height , Weight use kg When measuring , The trained model is : height = weight *x ,x These are the parameters we have trained . When we weigh in tons ,x The value of will be expanded to the original 1000 times .
If the numerical range of different characteristics is different , There are plenty of them 0 To 0.1, There are plenty of them 100 To 10000, that , The parameter size level corresponding to each feature will also be different , stay L1 When regular , We simply add the absolute values of the parameters , Because they have different size levels , It will lead to L1 Finally, it will only work on parameters with large levels , Those small parameters are ignored .
If not regular , So what are the benefits of standardization for logistic regression ? The answer is good , After standardization , The size of the parameter value we obtained can reflect the different characteristics of the sample label Contribution of , It is convenient for us to conduct feature screening . If there is no standardization , You can't filter features like this .
Are there any precautions for standardization ? The most important thing to note is to split test Set , Don't standardize on the whole data set , Because that will test The information of the set is introduced into the training set , It's a very easy mistake !
5.2 PCA Need standardization ?
Let's take a look at , If we will predict the variables of house prices , use PCA Methods to reduce dimensions , Will it have an impact on the results . We see that before standardization , One component can explain 99% The change of the variables of , And the standardized component explains 75% The change of . The main reason is that without standardization , We give too much weight to living space , It's the result .

5.3 Kmeans,KNN Need standardization ?
Kmeans,KNN Some distance related algorithms , Or clustering , We need to standardize the variables first .
give an example : We will 3 There are two types of cities , Variables include area and education level ; The three cities are like this :
City A, It's quite large , But robberies happen all day , Low education ;
City B, The area is also very large , Good law and order , Highly educated ;
City C, Medium size , Public security is also very good , Education is also very high ;


If we don't do Standardization , If you do the clustering model directly ,A Cities and B The cities are divided , Do you think , A city with good public security and a whole city of theft and robbery are separated together , It's a bit against common sense .
Reference link :
Standardization and normalization - nxf_rabbit75 - Blog Garden (cnblogs.com)
normalization 、 Standardization 、 Zero mean effect and difference - You know (zhihu.com)
The role of neural network image input zeroing _wtrnash The blog of -CSDN Blog _ Zero mean value
边栏推荐
- 『忘了再学』Shell流程控制 — 38、while循环和until循环介绍
- What does password security mean? What are the password security standard clauses in the ISO 2.0 policy?
- MongoDB在腾讯零售优码中的应用
- 问一下想获取到sqlserver的start_lsn有好的办法吗?
- Keil simulation and VSPD
- KEIL仿真和vspd
- 快速玩转CI/CD图形化编排
- Hello, big guys. Error reporting when using MySQL CDC for the first time
- Runmaide medical passed the hearing: Ping An capital was a shareholder with a loss of 630million during the year
- Database connection pool: Code Directory
猜你喜欢

After 17 years, Liu Yifei became popular again: ordinary people don't want to be eliminated, but they also need to understand this

Countdown to the conference - Amazon cloud technology innovation conference invites you to build a new AI engine!

Community article | mosn building subset optimization ideas sharing

关于 GIN 的路由树

Yilian technology rushes to Shenzhen Stock Exchange: annual revenue of RMB 1.4 billion, 65% of which comes from Ningde times

mysql的concat()函数如何用

Hongshi electric appliance rushes to the Growth Enterprise Market: the annual revenue is 600million yuan. Liujinxian's equity was frozen by Guangde small loan

How MySQL modifies a field to not null

推荐几个AI智能平台

UK considers listing arm in London based on national security
随机推荐
乱解码nlp
推进兼容适配,使能协同发展 GBase 5月适配速递
"Software defines the world, open source builds the future" 2022 open atom global open source summit will open at the end of July
类似attention nlp
[graduation project] Research on emotion analysis based on semi supervised learning and integrated learning
得物App数据模拟平台的探索和实践
Mitsubishi manipulator demo program
数据库连接池:连接池功能点的实现
What is the value of a website? Why build an independent station
接了个私活项目,一下赚了15250,还有必要做主业吗?
Exploration and practice of dewu app data simulation platform
向量3(静态成员)
"Forget to learn again" shell process control - 38. Introduction to while loop and until loop
Show me my personal work list for the past two years. I earn 6K a month in my spare time. It's so delicious to have a sideline
大佬们好,初次使用MySQL cdc 报错
"Forget to learn again" shell process control - 38. Introduction to while loop and until loop
问一下想获取到sqlserver的start_lsn有好的办法吗?
The IPO of Tian'an technology was terminated: Fosun and Jiuding were shareholders who planned to raise 350million yuan
希尔排序的简单理解
Ultimate efficiency is the foundation for the cloud native database tdsql-c to settle down