当前位置:网站首页>Middle order clue binary tree
Middle order clue binary tree
2022-06-26 00:45:00 【Be nice 123】
Clue binary tree
The basic concept of clue binary tree
The clue of binary tree is to change the null pointer in the binary linked list to point to the precursor or subsequent clue . The precursor or successor information can only be obtained when traversing , Therefore, the implementation of threaded binary tree is to traverse the binary tree once
Taking the establishment of middle order clue binary tree as an example :
- Attached pointer pre Point to the node just visited , The pointer p Point to the node being accessed , namely pre Point to p The precursor of .
- In the process of middle order traversal , Check p Whether the left pointer of is null , If empty, point it to pre; Check pre Whether the right pointer of is null , If empty, point it to p
Construction of ordered clue binary tree
InThread
Recursive algorithm for binary tree cueing through middle order traversal ( It is to make the null pointer of the node point to the predecessor or successor node of its order traversal )
// Recursive algorithm for binary tree cueing through middle order traversal ( Is to make the null pointer of a node point to its predecessor or successor node )
// Construction of ordered clue binary tree , Left root right
void InThread(ThreadTree &p,ThreadTree &pre){
if(p != NULL){
InThread(p->lchild,pre);// recursive , Clue left subtree
if(p->lchild == NULL){
// The left subtree is empty , Establish precursor clues
p->lchild=pre;
p->ltag=1;
}
if(pre!=NULL && pre->rchild==NULL){
pre->rchild=p;// Establish the following clues of the precursor node
pre->rtag=1;
}
pre=p;// Mark the current node as the node just visited
InThread(p->rchild, pre);// recursive , Clue right subtree
}//if(p != NULL)
}
CreateInThread
The main process algorithm of establishing the middle order clue binary tree through the middle order traversal is as follows :
This function is used to build a medium order clue binary tree , call InThread function , And handle the last node traversed .
CreateInThread and InThread The specific relationship between : The former can be regarded as the foreman who commands the overall situation , The latter is a small worker who moves bricks
// The main process algorithm of establishing the middle order clue binary tree through the middle order traversal is as follows :
void CreateInThread(ThreadTree &T){
ThreadTree pre=NULL;
if(T){
// Nonempty binary tree , Clue
InThread(T,pre);// Clue binary tree
pre->rchild==NULL;// Process the last node traversed
pre->rtag=1;//@@@
}
}
Clue binary tree with leading node
If you don't want the first node traversed by the middle order lchild And the last node rchild by NULL, You must add a header node , Cannot point it to the tree root , Because as shown in the figure below , The predecessor and successor nodes of the root point to the root , If we traverse the first node of the middle order lchild And the last node rchild Point to the root node , The correctness of the result cannot be guaranteed during traversal .
In a word, i.e :
If we let the middle order traverse the first node lchild And the last node rchild Not for NULL, You must add an additional Head Head node , Cannot simply point to the root node
Traversal of ordered clue binary tree
The nodes of the middle order clue binary tree contain the precursor and successor information of the clue binary tree . When traversing it , Just find the first node in the sequence , Then find the successor of the node in turn , Until its successor is empty .
Firstnode
Find the middle order clue in the binary tree , The first node under the middle order sequence
// Find the middle order clue in the binary tree , The first node under the middle order sequence
ThreadNode *Firstnode(ThreadNode *p){
//printf("Firstnode:");
while(p->ltag==0){
p=p->lchild;// Bottom left node ( It doesn't have to be a leaf node )
}
return p;
}
Nextnode
Find the middle order clue in the binary tree , node p Successor under middle order sequence
// Find the middle order clue in the binary tree , node p Successor under middle order sequence
ThreadNode *Nextnode(ThreadNode *p){
if(p->rtag==0){
return Firstnode(p->rchild);
}
else{
return p->rchild;//rtag==1 Return directly to the follow-up clues
}
}
Inorder
We can write a middle order traversal algorithm of middle order clue binary tree without head node
// Using the above two algorithms ,
// We can write a middle order traversal algorithm of middle order clue binary tree without head node
void Inorder(ThreadNode *T){
for(ThreadNode *p=Firstnode(T);p!=NULL;p=Nextnode(p)){
visit(p);
}
}
Complete test code
Complete test code c++
Be careful :
- You still need to create a binary tree first , Then the binary tree is traversed in the middle order
- When you create a binary tree, you should correct ltag rtag Initialize to 0, Express lchild,rchild It points to the left / The right child ( Not the precursor / The subsequent ), And initialization cannot be initialized in the definition of structure , Because when defining a structure , It is not allocated memory , So the initial value cannot be stored . After the structure variable should be declared , Manual assignment . In the following code is malloc Then initialize
- Because after the threaded binary tree, each node is threaded into a ring , Therefore, in the functions of middle order recursive traversal and post order recursive destruction, we need to ltag rtag Judge .
// Clue binary tree
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define ElemType char
//tag by 0 Indicates pointing to the left / The right child , by 1 Indicates the precursor to the node / The subsequent
typedef struct ThreadNode{
ElemType data;// data elements
struct ThreadNode *lchild,*rchild;// Left and right child pointer
int ltag;// Because when defining a structure , It is not allocated memory , So the initial value cannot be stored . After the structure variable should be declared , Manual assignment
int rtag;// Left and right cue marks
}ThreadNode,*ThreadTree;
void visit(ThreadTree T){
printf("%c ",T->data);
}
// Construction of ordered clue binary tree , Left root right
void InThread(ThreadTree &p,ThreadTree &pre){
if(p != NULL){
InThread(p->lchild,pre);// recursive , Clue left subtree
if(p->lchild == NULL){
// The left subtree is empty , Establish precursor clues
p->lchild=pre;
p->ltag=1;
}
if(pre!=NULL && pre->rchild==NULL){
pre->rchild=p;// Establish the following clues of the precursor node
pre->rtag=1;
}
pre=p;// Mark the current node as the node just visited
InThread(p->rchild, pre);// recursive , Clue right subtree
}//if(p != NULL)
}
// The main process algorithm of establishing the middle order clue binary tree through the middle order traversal is as follows :
void CreateInThread(ThreadTree &T){
//ThreadNode *Head = (ThreadNode*)malloc(sizeof(ThreadNode));
// Head->lchild=T;
//Head->ltag=1;
//ThreadTree pre=T;
ThreadTree pre=NULL;
if(T){
// Nonempty binary tree , Clue
InThread(T,pre);// Clue binary tree
//Head->rchild=pre;
//Head->rtag=1;
pre->rchild==NULL;
//pre->rchild=T;// Process the last node traversed
pre->rtag=1;
}
}
// Find the middle order clue in the binary tree , The first node under the middle order sequence
ThreadNode *Firstnode(ThreadNode *p){
//printf("Firstnode:");
while(p->ltag==0){
p=p->lchild;// Bottom left node ( It doesn't have to be a leaf node )
}
return p;
}
// Find the middle order clue in the binary tree , node p Successor under middle order sequence
ThreadNode *Nextnode(ThreadNode *p){
if(p->rtag==0){
return Firstnode(p->rchild);
}
else{
return p->rchild;//rtag==1 Return directly to the follow-up clues
}
}
// Using the above two algorithms ,
// We can write a middle order traversal algorithm of middle order clue binary tree without head node
void Inorder(ThreadNode *T){
for(ThreadNode *p=Firstnode(T);p!=NULL;p=Nextnode(p)){
visit(p);
}
}
// Create a threaded binary tree , Enter... In the previous order , # Represents an empty node
bool CreateThreadTree(ThreadTree &T){
ElemType ch;
scanf("%c", &ch);
if(ch == '#'){
//printf(" Do you want to create an empty tree ?\n");
T=NULL;
return false;
}
else{
T=(ThreadTree)malloc(sizeof(ThreadNode));
T->ltag=T->rtag=0;
if(!T){
printf("malloc failure\n");
return false;
}
T->data = ch;
CreateThreadTree(T->lchild);
CreateThreadTree(T->rchild);
return true;
}
}
bool DestroyThreadTree(ThreadTree T){
if(T==NULL){
printf(" Blank nodes \n");
return false;
}
if(T->ltag!=1)
DestroyThreadTree(T->lchild);
if(T->rtag!=1)
DestroyThreadTree(T->rchild);
printf(" The destruction %c\n",T->data);
free(T);//@@@'
T=NULL;
return true;
}
// Traversing the clue binary tree in the middle order
void InOrder(ThreadTree T){
if(T){
if(T->ltag!=1)
InOrder(T->lchild);
visit(T);
if(T->rtag != 1)
InOrder(T->rchild);
}
}
int main(){
ThreadTree T=NULL;
printf(" Enter the values of the nodes in the binary tree in the previous order ( Input # Represents an empty node )\n");
CreateThreadTree(T);// Input preamble , Build a binary tree
CreateInThread(T);// Through the middle order traversal, the middle order clue binary tree is established
ThreadNode *p=Firstnode(T);// Find the first node under the middle order traversal
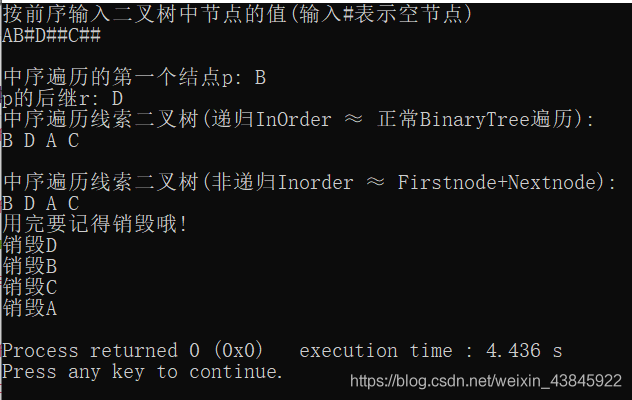
printf("\n The first node traversed in middle order p: %c\n",p->data);
ThreadNode* r=Nextnode(p);// Find the middle order to traverse p In the subsequent
printf("p In the subsequent r: %c\n",r->data);
printf(" Traversing the clue binary tree in the middle order ( recursive InOrder ≈ normal BinaryTree Traverse ): \n");
InOrder(T);
printf("\n");
printf("\n Traversing the clue binary tree in the middle order ( Non recursive Inorder ≈ Firstnode+Nextnode): \n");
Inorder(T);
printf("\n Remember to destroy it after use !\n");
DestroyThreadTree(T);
return 0;
}
sample input


test result
边栏推荐
- 基于OpenVINOTM开发套件“无缝”部署PaddleNLP模型
- AD20(Altium Designer) PCB 高亮网络
- Performance leads the cloud native database market! Intel and Tencent jointly build cloud technology ecology
- Is camkiia the same as gcamp6f?
- CaMKIIa和GCaMP6f是一樣的嘛?
- 性能领跑云原生数据库市场!英特尔携腾讯共建云上技术生态
- Xiaohongshu microservice framework and governance and other cloud native business architecture evolution cases
- Redisson 3.17.4 发布
- Compile the telegraph desktop side (tdesktop) using vs2022
- Anti shake and throttling
猜你喜欢

Atlas200dk brush machine

【超能云终端创领先机】如何在48小时内交付一座方舱医院?

CaMKIIa和GCaMP6f是一樣的嘛?

从进程的角度来解释 输入URL后浏览器会发生什么?

机器视觉:照亮“智”造新“视”界
![[TSP problem] solving traveling salesman problem based on Hopfield neural network with matlab code](/img/a9/4fbe82fc77712f2e10119aacb99143.png)
[TSP problem] solving traveling salesman problem based on Hopfield neural network with matlab code

1-11solutions to common problems of VMware virtual machine

jarvisoj_level2_x64

C IO stream (II) extension class_ Packer

Apache基金会正式宣布Apache InLong成为顶级项目
随机推荐
从进程的角度来解释 输入URL后浏览器会发生什么?
【超能云终端创领先机】如何在48小时内交付一座方舱医院?
What do SMT operators do? operating duty?
Ad20 (Altium designer) PCB highlight network
Anti shake and throttling
Redux workflow explanation + small examples
Flink reports error: a JNI error has occurred, please check your installation and try again
EBS r12.2.0 to r12.2.6
【图像检测】基于高斯过程和Radon变换实现血管跟踪和直径估计附matlab代码
信号处理函数内必须使用可重入函数
Deploy Ogg on the same machine and test
Redisson 3.17.4 发布
"Seamless" deployment of paddlenlp model based on openvinotm development kit
Types of feeder and how to work
使用VS2022編譯Telegram桌面端(tdesktop)
Simulink求解器综合介绍
Dynamic verification code
Shenzhen Taipower: the way of "communication" of the United Nations
What are the red lines of open source that should not be trodden on?
Use js to obtain the last quarter based on the current quarter
