当前位置:网站首页>Redis learning notes
Redis learning notes
2022-06-22 21:15:00 【fate _ zore】
redis
NoSql
Technology development
The classification of Technology
Solve functional problems :Java、Jsp、RDBMS、Tomcat、HTML、Linux、JDBC、SVN
Solve the problem of scalability :Struts、Spring、SpringMVC、Hibernate、Mybatis
Solve performance problems :NoSQL、Java Threads 、Hadoop、Nginx、MQ、ElasticSearch
redis Brief introduction and installation
- Redis It's an open source key-value The storage system .
- and Memcached similar , It supports storage value There are more types , Include string( character string )、list( Linked list )、set( aggregate )、zset(sorted set -- Ordered set ) and hash( Hash type ).
- These data types support push/pop、add/remove And take intersection, union and difference sets and more abundant operations , And these operations are atomic .
- On this basis ,Redis Support various sorts of sorting .
- And memcached equally , To ensure efficiency , The data is cached in memory .
- The difference is Redis Periodically, updated data is written to disk or changes are written to an appended log file .
- And on this basis to achieve master-slave( Master-slave ) Sync .
Application scenarios
Cache with relational database
- High frequency , Hot access data , Lower the database IO
- Distributed architecture , do session share
A variety of data structures store persistent data

install
Five data types are commonly used
key (key) operation
keys * View all of the current library key ( matching :keys *1)
exists key Judge a certain key Whether there is
type key View your key What type is it
del key Delete specified key data
unlink key according to value Select non blocking delete
Only will keys from keyspace Delete from metadata , The real deletion will be done asynchronously later .
expire key 10 10 Second : For a given key Set expiration time
ttl key See how many seconds are left to expire ,-1 Never expire ,-2 Indicates that it has expired
select Command switch database
dbsize Check the... Of the current database key The number of
flushdb Empty the current library
flushall Kill all the warehouses
Redis character string (String)
brief introduction
- string yes redis Most basic types , And mencached Basically the same type , One key Corresponding to one value
- string It's binary safe ,redis Of string Can contain any data , Such as pictures or serialized objects
- string Of value Maximum attainable 512M
Common commands :
set key valueAdd key value pair
get <key>Query the corresponding key value
append <key><value>Will be given Append to the end of the original value
strlen <key>Get the length of the value
setnx <key><value>Only in key When there is no Set up key Value
incr <key>take key Increase the value of the number stored in 1, Can only operate on numeric values , If it is empty , The new value added is 1
decr <key>take key The number stored in minus 1 Can only operate on numeric values , If it is empty , The new value added is -1
incrby / decrby <key>< step >take key Increase or decrease the number value stored in . Custom step size .
mset <key1><value1><key2><value2>.....Set one or more... At the same time key-value Yes
mget <key1><key2><key3> .....Get one or more at the same time value
msetnx <key1><value1><key2><value2> .....Set one or more... At the same time key-value Yes , If and only if all given key It doesn't exist .
getrange <key>< The starting position >< End position >Get the range of values , similar java Medium substring, Front bag , Back bag
setrange <key>< The starting position ><value>use Overwrite the stored string value , from < The starting position > Start ( Index from 0**** Start ).
setex <key>< Expiration time ><value>While setting the key value , Set expiration time , Unit second .
getset <key><value>Trade in new for old , Set the new value and get the old value .
data structure
String The data structure is simple Dynamic string (Simple Dynamic String, abbreviation SDS). Is a string that can be modified , The internal structure is similar to Java Of ArrayList, use Pre allocate redundant space to reduce frequent memory allocation .

As shown in the picture , Space actually allocated internally for the current string capacity Generally higher than the actual string length len. When the string length is less than 1M when , Expansion is to double the existing space , If exceeded 1M, When expanding, it will only expand more at one time 1M Space . Note that the maximum string length is 512M.
Redis list (List)
brief introduction
Single bond multi value
- Redis List is a simple list of strings , Sort by insertion order .
- You can add an element to the head of the list ( On the left ) Or tail ( On the right ).
- Its bottom layer is actually a two-way linked list , High performance on both ends , The performance of the nodes in the middle of the index subscript operation will be poor .

Common commands :
lpush/rpush <key><value1><value2><value3> ....From the left / Insert one or more values... To the right .
lpop/rpop <key>From the left / Spit out a value on the right . Value at key at , The value of the light key .
rpoplpush <key1><key2>Spit out a value from the right side of the list , Insert to the left of the list .
lrange <key><start><stop>Get elements according to index subscript ( From left to right )
lrange mylist 0 -10 The first one on the left ,-1 The first one on the right ,(0-1 To get all )
linsert <key> before <value><newvalue>Insert the value after the
lrem <key><n><value>Delete from the left n individual value( From left to right )
lset<key><index><value>Will list key Subscript to be index Replace the value of with value
data structure :
List The data structure of is fast linked list quickList.
First, in the case of fewer list elements will use a block of continuous memory storage , This structure is ziplist, That is, compressed list .
It stores all the elements next to each other , Allocated is a continuous block of memory .
When there is a large amount of data, it will be changed to quicklist.
Because ordinary linked list needs too much additional pointer space , It's a waste of space . For example, what's in this list is just int Data of type , Two additional pointers are required for the structure prev and next.

Redis Linking lists and ziplist Combined to form quicklist. That is to say, multiple ziplist Use two-way pointer string to use . This not only satisfies the fast insertion and deletion performance , There will not be too much space redundancy .
Redis aggregate (Set)
brief introduction :
- Redis set The functions and list Similar to a list function , What's special is set Yes. Automatic weight removal Of , When you need to store a list of data , You don't want duplicate data ,set Is a good choice , also set Provides a way to determine whether a member is in a set Important interfaces within a collection , This is also list What cannot be provided .
- Redis Of Set yes string Unordered collection of type . The bottom of it is actually a value by null Of hash surface , So add the , Delete , Look for The complexity is O(1).
- An algorithm , As data increases , The length of execution , If it is O(1), Data increase , The time to find the data remains the same
Common commands :
sadd <key><value1><value2> .....-> Put one or more member Elements are added to the collection key in , What already exists member Elements will be ignored
smembers <key>-> Take all the values of the set .
sismember <key><value>-> Determine whether the set contains the value , Yes 1, No, 0
scard<key>-> Returns the number of elements in the collection .
srem <key><value1><value2> ....-> Delete an element in the collection .
spop <key>-> Spit a value out of the set at random .
srandmember <key><n>-> Randomly take... From the set n It's worth . Will not be removed from the collection .
smove <source><destination>value-> Move a value in a set from one set to another
sinter <key1><key2>-> Returns the intersection element of two sets .
sunion <key1><key2>-> Returns the union element of two sets .
sdiff <key1><key2>-> Returns two sets of Difference set Elements (key1 Medium , It doesn't contain key2 Medium )
data structure :
Set The data structure is dict Dictionaries , Dictionaries are implemented with hash tables .
Java in HashSet The internal implementation of HashMap, It's just all value They all point to the same object .Redis Of set The structure is the same , It's also used internally hash structure , be-all value All point to the same internal value .
Redis Hash (Hash)
brief introduction :
Redis hash It's a collection of key-value pairs .
Redis hash It's a string Type of field and value Mapping table ,hash Ideal for storing objects .
similar Java Inside Map<String,Object>
user ID For searching key, Stored value User object contains name , Age , Birthday and other information , If you use ordinary key/value Structure to store
There are mainly the following 2 Storage methods :
Common commands :
hset <key><field><value>-> Give... In the set Key assignment
hget <key1><field>-> Take... Out of the collection value
hmset <key1><field1><value1><field2><value2>...-> Batch settings hash Value
hexists<key1><field>-> Look at the hash table key in , Given domain field Whether there is .
hkeys <key>-> List the hash All of the collection field
hvals <key>-> List the hash All of the collection value
hincrby <key><field><increment>-> Hash table key In the domain field Plus the increment 1 -1
hsetnx <key><field><value>Hash table key In the domain field Is set to value , If and only if domain field non-existent .
data structure :
Hash There are two kinds of data structures corresponding to types :ziplist( Compressed list ),hashtable( Hashtable ). When field-value When the length is short and the number is small , Use ziplist, Otherwise use hashtable.
Redis Ordered set Zset
brief introduction :
- Redis Ordered set zset With the common set set Very similar , Is a collection of strings without repeating elements .
- The difference is that each member of an ordered set is associated with a score (****score), This score (score) Used to sort the members of a set from the lowest score to the highest score . Members of a collection are unique , But the score can be repeated .
- Because the elements are ordered , So you can also quickly rate (score) Or order (position) To get a range of elements .
- Accessing intermediate elements of ordered collections is also very fast , So you can use ordered sets as a smart list without duplicate members .
Common commands :
zadd <key><score1><value1><score2><value2>…Put one or more member Elements and score Value added to ordered set key among .
zrange <key><start><stop> [WITHSCORES]Return to ordered set key in , The subscript is
Between the elements belt WITHSCORES, You can return scores and values together to the result set .
zrangebyscore key minmax [withscores] [limit offset count]Return to ordered set key in , all score The value is between min and max Between ( Including equal to min or max ) Members of . Members of the ordered set press score Value increment ( From small to large ) Order .
zrevrangebyscore key maxmin [withscores] [limit offset count]ditto , Change to big to small .
zincrby <key><increment><value>For the elements score Plus the increment
zrem <key><value>Delete... Under this collection , The element that specifies the value
zcount <key><min><max>Count the set , The number of elements in the fraction range
zrank <key><value>Returns the rank of the value in the collection , from 0 Start .
data structure :
SortedSet(zset) yes Redis A very special data structure provided , On the one hand, it is equivalent to Java Data structure of Map<String, Double>, You can give each element value Give a weight score, On the other hand, it is similar to TreeSet, Internal elements are weighted score Sort , You can get the rank of each element , You can also use score To get a list of elements .
zset The bottom layer uses two data structures
(1)hash,hash The role of is to associate elements value And weight score, Guarantee elements value Uniqueness , You can use the element value Find the appropriate score value .
(2) Skip list , The purpose of jump tables is to give elements value Sort , according to score Scope get element list for .
Redis Compression meter 、 Skip list ? Here you go - Nuggets (juejin.cn)
The configuration file
units Company
Configure size units , Some basic units of measurement are defined at the beginning , Only support bytes, I won't support it bit
Case insensitive

INCLUDES
similar jsp Medium include, In the case of multiple instances, the common configuration file can be extracted

Network related configuration
bind
- By default bind=127.0.0.1 Only local access requests can be accepted
- Without writing , Unlimited acceptance of any ip Address access
- Production environment must write the address of your application server ; The server needs remote access , So you need to comment it out
- If it's on protected-mode, Then there's no setting bind ip And without a password ,Redis Only local responses are allowed
protected-mode
Native access protection mode

port
Port number , Default 6379

tcp-backlog
- Set up tcp Of backlog,backlog It's actually a connection queue ,backlog The sum of the queues = Three handshake queues not completed + Three handshake queues have been completed .
- In a high concurrency environment you need a high backlog Value to avoid slow client connection problems .
- Be careful Linux The kernel will reduce this value to /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn Value (128), So we need to confirm the increase /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn and /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog(128) Two values to achieve the desired effect

timeout
How many seconds will an idle client be shut down ,0 Indicates that the feature is turned off . namely Never close .

tcp-keepalive
- A heartbeat detection for accessing clients , Every n Check once per second .
- The unit is in seconds , If set to 0, It won't go on Keepalive testing , It is suggested to set it to 60

GENERAL Universal
daemonize
Whether to start background process , Off by default
pidfile
Deposit pid The location of the file , Each instance produces a different pid file
loglevel
Set the level of the log

logfile
The output file address of the log

databases
Set the number of Libraries Default 16, The default database is 0 Number , have access to SELECT The command specifies the database on the connection id

SECURITY
Set the password

Access password view 、 Set and cancel
Set the password in the command , It's just temporary . restart redis The server , The password is restored .
Permanent settings , It needs to be set in the configuration file .

LIMITS Limit
Publish and subscribe
What is publish and subscribe
Redis Publish subscribe (pub/sub) It's a message communication mode : sender (pub) Send a message , subscriber (sub) receive messages .
Redis Clients can subscribe to any number of channels .
Redis Publish and subscribe to
The client can subscribe to channels, as shown in the figure below

When you post a message to this channel , The message is sent to the subscribing client

Publish and subscribe command line implementation
- Open a client subscription channel1

- command :
SUBSCRIBE channel1 - Open another client , to channel1 Release the news

- command :
publish channel1 hello 
New data types
Bitmaps
brief introduction
Modern computers use binary ( position ) As the basic unit of information , 1 Bytes are equal to 8 position , for example “abc” Strings are created by 3 Byte composition , But it is actually represented in binary when stored in the computer , “abc” Respectively corresponding ASCII The codes are 97、 98、 99, The corresponding binaries are 01100001、 01100010 and 01100011, Here's the picture

Reasonable use of operation bits can effectively improve memory utilization and development efficiency .
Redis Provides Bitmaps This “ data type ” Can achieve the operation of the bit :
- Bitmaps Itself is not a data type , It's actually a string (key-value) , But it can operate on the bits of a string .
- Bitmaps A separate set of commands is provided , So in Redis Use in Bitmaps It's not quite the same as using strings . You can put Bitmaps Think of it as an array of bits , Each unit of an array can only store 0 and 1, The subscript of the array is in Bitmaps It's called offset .

command
setbit<key><offset><value>Set up Bitmaps The value of an offset in (0 or 1)
example :
Whether each individual user has visited the website and stored in Bitmaps in , Record the user you visited as 1, Do not visit users remember to do 0, Use offset as user's id.
Set the number of the key offset The value of a bit ( from 0 Count up ) , Suppose there are now 20 Users ,userid=1, 6, 11, 15, 19 's users visited the site , Then the current Bitmaps The initialization result is shown in Figure
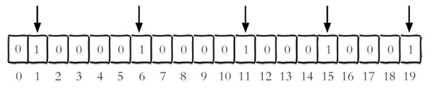

Be careful :
Set up Bitmaps The value of an offset in (0 or 1) Be careful : Users of many applications id With a specified number ( for example 10000) start , Direct users id and Bitmaps A certain amount of offset is bound to cause waste , The usual practice is to do it every time setbit The user will be id Subtract the specified number .
At first initialization Bitmaps when , If the offset is very large , Then the whole initialization process will be slow , It may cause Redis The block .
getbit<key><offset>obtain Bitmaps The value of an offset in
example :
obtain id=8 Is the user of 2020-11-06 I visited , return 0 I haven't visited :

bitcount<key>[start end]Statistics character string Set to 1 Of bit Count . In general , The whole string given will be counted , By specifying additional start or end Parameters , You can make the count only on specific bits .start and end Parameter settings , You can use negative values : such as -1 Represents the last bit , and -2 The second last bit ,start、end Refer to bit Subscript number of bytes of the Group , Both include .
bitop and(or/not/xor) <destkey> [key…]bitop It's a composite operation , It can do more than one Bitmaps Of and( intersection ) 、 or( Combine ) 、 not( Not ) 、 xor( Exclusive or ) Operate and save the result in destkey in .
example
2020-11-04 Visit the website on userid=1,2,5,9.
setbit unique:users:20201104 1 1
setbit unique:users:20201104 2 1
setbit unique:users:20201104 5 1
setbit unique:users:20201104 9 1
2020-11-03 Visit the website on userid=0,1,4,9.
setbit unique:users:20201103 0 1
setbit unique:users:20201103 1 1
setbit unique:users:20201103 4 1
setbit unique:users:20201103 9 1
Calculate the number of users who visited the website in two days
bitop and unique:users:and:20201104_03
unique:users:20201103unique:users:20201104

Bitmaps And set contrast
Suppose the website has 1 Billion users , The users who visit independently every day are 5 Ten million , If you use set type and Bitmaps Store active users separately and get tables
| set and Bitmaps Store a day's active user comparison | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| data type | Each user id Occupancy space | Number of users to store | Total memory |
| aggregate type | 64 position | 50000000 | 64 position *50000000 = 400MB |
| Bitmaps | 1 position | 100000000 | 1 position *100000000 = 12.5MB |
Obviously , Use... In this case Bitmaps Can save a lot of memory space , In particular, the memory savings over time are considerable
| set and Bitmaps Store independent user space comparison | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| data type | One day | A month | A year |
| Collection types | 400MB | 12GB | 144GB |
| Bitmaps | 12.5MB | 375MB | 4.5GB |
but Bitmaps It's not a panacea , If the website has few independent visitors every day , For example, only 10 ten thousand ( A lot of zombie users ) , Then the comparison between the two is shown in the table below , Obviously , Use at this time Bitmaps Not really , Because most of the bits are 0
HyperLogLog
At work , We often encounter functional requirements related to statistics , For example, statistical websites PV(PageView Page visits ), have access to Redis Of incr、incrby Make it easy .
But like UV(UniqueVisitor, Independent visitor )、 Independent IP Count 、 How to solve the problems that need to be de duplicated and counted, such as the number of search records ? The problem of finding the number of non repeating elements in a set is called the cardinality problem .
There are many solutions to the cardinality problem :
(1) The data is stored in MySQL In the table , Use distinct count Calculate the number of non duplicates
(2) Use Redis Provided hash、set、bitmaps And other data structures
The results of the above scheme are accurate , But as the data increases , Resulting in more and more occupied space , It is impractical for very large data sets .
Whether it can reduce a certain accuracy to balance the storage space ?Redis Launched HyperLogLog
Redis HyperLogLog It's an algorithm for cardinality statistics ,HyperLogLog The advantages of , When the number or volume of input elements is very, very large , The space needed to calculate the cardinality is always fixed 、 And it's very small .
stay Redis Inside , Every HyperLogLog Keys only cost 12 KB Memory , So we can calculate the proximity 2^64 Cardinality of different elements . This is the same as calculating the cardinality , The more elements consume memory, the more collections there are .
however , because HyperLogLog Only the input elements will be used to calculate the cardinality , Instead of storing the input elements themselves , therefore HyperLogLog It can't be like a collection , Return the various elements of the input .
What is the cardinality ?
Like data sets {1, 3, 5, 7, 5, 7, 8}, So the cardinality set of this dataset is {1, 3, 5 ,7, 8}, base ( Don't repeat elements ) by 5. Cardinality estimation is within the range of acceptable error , Fast base calculation .
command
pfadd
pfadd <key>< element> [element ...]
Add specified elements to HyperLogLog in

Adds all elements to the specified HyperLogLog In the data structure . If after executing the command HLL The approximate cardinality of the estimate changes , Then return to 1, Otherwise return to 0.
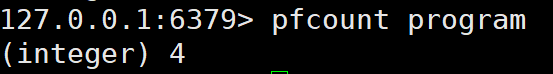
pfcount
pfcount<key> [key ...]
Calculation HLL The approximate cardinality of , Multiple can be calculated HLL, For example, use HLL Store daily UV, Calculate a week's UV have access to 7 Days of UV Consolidation calculation is enough
pfmerge
pfmerge<destkey><sourcekey> [sourcekey ...]
Put one or more HLL The merged results are stored in another HLL in , For example, monthly active users can use daily active users to consolidate and calculate the available

Geospatial
Redis 3.2 Added right to GEO Type of support .GEO,Geographic, Abbreviation for geographic information . This type of , It's elemental 2 Dimensional coordinates , On the map is latitude and longitude .redis Based on this type , Longitude and latitude settings are provided , Inquire about , Range queries , Distance inquiry , Longitude and latitude Hash And so on .
command
geoadd
geoadd<key>< longitude><latitude><member> [longitude latitude member...]
Add location ( longitude , latitude , name )
example

Be careful : Two poles can't be added directly , City data is usually downloaded , Directly through Java The program is imported once .
Effective longitude from -180 C to 180 degree . Effective latitude from -85.05112878 C to 85.05112878 degree .
When the coordinate position is beyond the specified range , The command will return an error .
Added data , You can't add it again .
geopos
geopos <key><member> [member...]
Get the coordinate value of the specified area

geodist
geodist<key><member1><member2> [m|km|ft|mi ]
Get the linear distance between two positions
example

Company :
- m Expressed in meters [ The default value is ].
- km Expressed in kilometers .
- mi In miles .
- ft In feet .
If the user does not explicitly specify the unit parameter , that GEODIST The default is meters
georadius
georadius<key>< longitude><latitude>radius m|km|ft|mi
Centered on a given latitude and longitude , Find the elements in a certain radius

Jedis operation Redis6
test
rely on
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
</dependency>
Connect the test ( Error model )
public static void main(String[] args) {
// establish jedis object
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.150.111",6379);
// Test whether it can be linked to
String ping = jedis.ping();
System.out.println(ping);
}

resolvent
Ban Linux The firewall of :Linux(CentOS7) To carry out an order
systemctl stop firewalld.service
redis.conf Note out bind 127.0.0.1 , then protected-mode no
Correct result

Data type testing
@Test
public void string(){
// Batch addition
jedis.mset("k1","v1","k2","v2","k3","v3");
// Batch query ( return list)
jedis.mget("k1","k2","k3").forEach(System.out::println);
}
@Test
public void list(){
jedis.lpush("lk","lv1","lv2","lv3");
List<String> lk = jedis.lrange("lk", 0, -1);
System.out.println(lk);
}
@Test
public void set(){
jedis.sadd("sk1","sv1","sv1","sv2","sv3","sv4","sv5");
Set<String> sk1 = jedis.smembers("sk1");
System.out.println(sk1);
}
@Test
public void hash(){
jedis.hset("user","age","20");
String hget = jedis.hget("user", "age");
System.out.println(hget);
}
@Test
public void zSet(){
jedis.zadd("zk1", 100d,"zv1");
jedis.zadd("zk1", 200d,"zv2");
jedis.zadd("zk1", 50d,"zv3");
Set<String> zk1 = jedis.zrange("zk1", 0, -1);
System.out.println(zk1);
}
}
Analog mobile phone verification code
Ideas

package com.fate.jedis;
import org.junit.Test;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import java.util.Random;
/** * @author m */
public class CodeController {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.150.111",6379);
public Boolean isCode(String code,String id) {
String rightCode = jedis.get(id + "_code");
return rightCode.equals(code);
}
public String getCode() {
Random random = new Random();
StringBuilder code = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
int r= random.nextInt(10);
code.append(r);
}
return code.toString();
}
public String setCode(String id) {
String code = getCode();
jedis.incrBy(id,1);
String count = jedis.get(id);
if (count == null) {
jedis.setex(id,24*60*60,"1");
}else if (Integer.parseInt(count)<3){
jedis.incrBy(id,1);
jedis.setex(id+ "_code",120*2 ,code);
return code;
}else {
System.out.println(" The maximum number of times ");
}
return code;
}
@Test
public void t(){
String code = setCode("18848312652");
Boolean aBoolean = isCode(code, "18848312652");
System.out.println(aBoolean);
}
}
Redis6 And Spring Boot Integrate
Introduce dependencies
<!-- redis Integrate -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Connection pool -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
<version>2.6.0</version>
</dependency>
The configuration file
#Redis Server address
spring.redis.host=192.168.150.111
#Redis Server connection port
spring.redis.port=6379
#Redis Database index ( The default is 0)
spring.redis.database= 0
# Connection timeout ( millisecond )
spring.redis.timeout=1800000
# Maximum number of connections in connection pool ( Use a negative value to indicate that there is no limit )
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=20
# Maximum blocking waiting time ( A negative number means no limit )
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=-1
# The maximum free connection in the connection pool
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=5
# The smallest free connection in the connection pool
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=0
Configuration class
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.time.Duration;
/** * @author m */
@EnableCaching
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
@Bean
@SuppressWarnings({
"rawtypes", "unchecked" })
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory){
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<String, Object>();
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//Json Serialization configuration
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
//String Serial number configuration
StringRedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
//key and hash Of key All use String The serialization configuration of
template.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
template.setHashKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
//value and hash Of value use Json The serialization configuration of
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
// Solve the problem of query cache conversion exception
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// Configure serialization ( Solve the problem of garbled code ), Expiration time 600 second
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(600))
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisSerializer))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer))
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.build();
return cacheManager;
}
}
test
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/** * @author m */
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/redisTest")
public class RedisTestController {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
@GetMapping()
public String test(){
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name","lucy");
return (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
}
}
RedisTemplate
All the methods
// Configure the default serialization and deserialization tool classes
1.afterPropertiesSet
// Execute relevant functions according to parameters operation operation , for example , Business
2.execute
// perform pipelining Pipeline related operations
3.executePipelined
// Execute assignment connection Connection related operations
4.executeWithStickyConnection
// perform session Internal execute Method
5.executeSession
// establish RedisConnection proxy class
6.createRedisConnectionProxy
// connection Preprocessing of connections
7.preProcessConnection
// Post processing of results , Do nothing by default
8.postProcessResult
// Whether to RedisCallback Expose local connections
9.isExposeConnection
// Set whether to RedisCallback Expose local connections
10.setExposeConnection
// 12 To 26 Are to set and get the relevant serialization tool classes
11.isEnableDefaultSerializer
12.setEnableDefaultSerializer
13.getDefaultSerializer
14.setDefaultSerializer
15.setKeySerializer
16.getKeySerializer
17.setValueSerializer
18.getValueSerializer
19.getHashKeySerializer
20.setHashKeySerializer
21.getHashValueSerializer
22.setHashValueSerializer
23.getStringSerializer
24.setStringSerializer
25.setScriptExecutor
// 27 To 34 For private methods , Not available for external use
26.rawKey
27.rawString
28.rawValue
29.rawKeys
30.deserializeKey
31.deserializeMixedResults
32.deserializeSet
33.convertTupleValues
// Perform transactions
34.exec
35.execRaw
// Delete operation
36.delete
// Contact links
37.unlink
// Check whether it contains the specified key
38.hasKey
39.countExistingKeys
// Set expiration time
40.expire
41.expireAt
// Convert to byte stream and send to channel send out message
42.convertAndSend
// Get expiration time
43.getExpire
// Returns all... Based on the passed in regular expression key
44.keys
// Cancel designation key The expiration time of
45.persist
// Move the specified key and index To database
46.move
// Get a random... From the key space key
47.randomKey
// Will specify key Change to target key
48.rename
// key When there is no , Will specify key Change to target key
49.renameIfAbsent
// The settings are stored in the specified location key The type of
50.type
// Retrieval stored in key Serialized version of the value of
51.dump
// perform Redis Of restore The order of
52.restore
// Mark the beginning of transaction blocking
53.multi
// Discard all in multi The order issued later
54.discard
// Observe the specified key At the beginning of the transaction multi Subsequent modifications
55.watch
// Refresh all previously observed key
56.unwatch
// by key Element ordering
57.sort
// Close the client connection
58.killClient
// Request information and statistics about the connection client
59.getClientList
// Change the replication configuration to the new master
60.slaveOf
// Change this machine to master
61.slaveOfNoOne
// 64 To 79 Is to get the corresponding operation
62.opsForCluster
63.opsForGeo
64.boundGeoOps
65.boundHashOps
66.opsForHash
67.opsForHyperLogLog
68.opsForList
69.boundListOps
70.boundSetOps
71.opsForSet
72.opsForStream
73.boundStreamOps
74.boundValueOps
75.opsForValue
76.boundZSetOps
77.opsForZSet
// Set whether transactions are supported
78.setEnableTransactionSupport
// Set up bean Class loader for
79.setBeanClassLoader
spring-data-redis The following functions are provided :
Connection pool automatic management , Provides a highly encapsulated “RedisTemplate” class
It is classified and packaged , Encapsulate the same type of operation as operation Interface
ValueOperations: Simple K-V operation
SetOperations:set Type data operation
ZSetOperations:zset Type data operation
HashOperations: in the light of map Type of data operation
ListOperations: in the light of list Type of data operationProvide for the right to key Of “bound”( binding ) Convenient operation API, Can pass bound Encapsulate the specified key, And then do a series of operations without “ Explicit ” Re designation of Key, namely BoundKeyOperations
BoundValueOperations
BoundSetOperations
BoundListOperations
BoundSetOperations
BoundHashOperationsEncapsulate transaction operations , There's container control .
For data “ serialize / Deserialization ”, Provides a variety of alternative strategies (RedisSerializer)
- JdkSerializationRedisSerializer:POJO Object access scenarios , Use JDK The serialization mechanism itself , take pojo Class passing ObjectInputStream/ObjectOutputStream Do serialization , Final redis-server A sequence of bytes will be stored . Is currently the most commonly used serialization strategy .
- StringRedisSerializer:Key perhaps value For string scenarios , According to the designation charset Encode the byte sequence of data into string yes “newString(bytes,charset)” and “string.getBytes(charset)” The direct packaging of . It's the lightest and most efficient strategy .
- JacksonJsonRedisSerializer:jackson-json The tool provides javabean And json The ability to transform between , Can be pojo Examples are sequenced into json The format is stored in redis in , Can also be json Format data into pojo example . because jackson When the tool serializes and deserializes , You need to specify Class type , So this strategy is a little more complex to encapsulate .
- OxmSerializer: Provided will be javabean And xml The ability to transform between , Currently available tripartite support includes jaxb,apache-xmlbeans;redis The data stored will be xml Tools . But with this strategy , It's going to be difficult to program , And it's the least efficient ; Not recommended .【 need spring-oxm Module support 】
If your data needs to be parsed by a third party tool , So the data should use StringRedisSerializer instead of JdkSerializationRedisSerializer.
RedisTemplate Top level method
- Determine given key Whether there is , Go back if you have true, Return on no false
redisTemplate.hasKey(K key)
- Delete the given key
redisTemplate.delete(K key)
- Delete given key Set
redisTemplate.delete(Collection<K> keys)
- perform Redis Dump the command and return the result , hold key The values are sequenced into byte[] type
redisTemplate.dump(K key)
- The incoming key Value sets the expiration time 、 Will be given key The expiration time of is set to the date timestamp
redisTemplate.expire(K key, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
redisTemplate.expireAt(K key, Date date)
- Find all that match the given pattern key , Returns a non repeating Set type
redisTemplate.keys(K pattern)
- take oldKey Rename it to newKey.
redisTemplate.rename(K oldKey, K newKey)
- obtain key The type of value
redisTemplate. type(K key)
- Only when the newKey When there is no , Key oldKey Rename it to newKey.
redisTemplate.renameIfAbsent(K oldKey, K newKey)
- Random from redis Get one of key
redisTemplate.randomKey()
- Get current key The remaining expiration time
redisTemplate.getExpire(K key)
- Get the remaining expiration time , Set the time unit at the same time
redisTemplate. getExpire(K key, TimeUnit timeUnit)
- Delete key The expiration time of
redisTemplate. persist(K key)
- Will be given key Move to an indexed database
redisTemplate. move(K key, int dbIndex)
RedisTemplate.opsForValue() Method
Set up key Follow value Value
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(K key, V value)obtain key Value
redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(Object key)Set up key Follow value Value , Also set expiration time
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(K key, V value, Duration timeout)stay start and end To get the substring of the key value
redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(K key, long start, long end)Set up key And returns its old value
redisTemplate.opsForValue().getAndSet(K key, V value)Get multiple key
redisTemplate.opsForValue().multiGet(Collection<K> keys)Get the original key Add a new string after the value of
redisTemplate.opsForValue().append(K key, String value)Incrementally increase double value
redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(K key, double increment)adopt increment(K key, long delta) Method to store... Incrementally long value ( A positive value increases itself , Negative values are self decreasing )
redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(K key, long increment)Only if provided key When there is no , Only by using the key value pairs provided in the collection key Set to multiple values .
redisTemplate.opsForValue().multiSetIfAbsent(Map<? extends K,? extends V> map)Use the key value pairs provided in the collection to set multiple key Set to multiple values
Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("1","1"); map.put("2","2"); map.put("3","3"); redisTemplate.opsForValue().multiSet(Map<? extends K,? extends V> map)Get specified key The length of the string of
redisTemplate.opsForValue().size(K key)Overwrite with the given value... Starting at the specified offset key Part of
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(K key, V value, long offset)If key non-existent , Is set key To save string values , There is returned false, Otherwise return to true
redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, value)To reset key And add the expiration time
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, timeout, unit)Put binary number offset The bit value becomes value
redisTemplate.opsForValue().setBit(K key, long offset, boolean value)Yes key String value stored , Gets the bit on the specified offset (bit)
redisTemplate.opsForValue().getBit(K key, long offset)
RedisTemplate.opsForHash() Method
- from key Situated hash Get the given hashKey Value , namely key field(hashKey) value
redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(H key, Object hashKey)
- Get stored in key The whole hash, That is, get all the values
redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(H key)
- Set up hash hashKey Value
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(H key, HK hashKey, HV value)
- Use m The data provided in will be multiple hash Field is set to multiple values , That is to use map Assign a value
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(H key, Map<? extends HK,? extends HV> m)
- Only when the hashKey Set when it doesn't exist hash hashKey Value .
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putIfAbsent(H key, HK hashKey, HV value)
- Delete the given hash hashKeys
redisTemplate.opsForHash().delete(H key, Object... hashKeys)
- Determine the given hash hashKey Whether there is
redisTemplate.opsForHash().hasKey(H key, Object hashKey)
- Increase by a given increment hash hashKey Value
redisTemplate.opsForHash().increment(H key, HK hashKey, double increment)
redisTemplate.opsForHash().increment(H key, HK hashKey, long increment)
- stay key Get hash Of hashKey Set ( Field )
redisTemplate.opsForHash().keys(H key)
- obtain key Of hash size .
redisTemplate.opsForHash().size(H key)
- stay key Get hash Value
redisTemplate.opsForHash().values(H key)
- View matching key value pairs
redisTemplate.opsForHash().scan(H key, ScanOptions options)
RedisTemplate.opsForList() Method
- from key Of list Get the element at the index in
redisTemplate.opsForList().index(K key, long index)
- from key Of list In order to get start and end Between the elements
redisTemplate.opsForList().range(K key, long start, long end)
- by key add value
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(K key, V value)
- Add a value to key in
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPushAll(K key, Collection<V> values)
- Only when the list In existence , To add values to key in
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPushIfPresent(K key, V value)
- stay pivot Before adding values to key in
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(K key, V pivot, V value)
- Attach a value to key
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush(K key, V value)
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll(K key, Collection<V> values)
- stay pivot Then add the value to key in
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush(K key, V pivot, V value)
- Set the value at the index of the list element
redisTemplate.opsForList().set(K key, long index, V value)
- Delete and return to stored in key The first element in the list of 、
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(K key)
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(K key, Duration timeout)
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(K key, long count)
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(K key, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
- Delete and return to stored in key The last element in the list of
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop(K key)
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop(K key, Duration timeout)
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop(K key, long count)
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop(K key, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
- from sourceKey Delete the last element from the list of , Attach it to destinationKey And return its value
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPopAndLeftPush(K sourceKey, K destinationKey)
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPopAndLeftPush(K sourceKey, K destinationKey, Duration timeout)
- From storage in key Delete the first... From the list of count The emergence of value
redisTemplate.opsForList().remove(K key, long count, Object value)
- stay start and end Between elements key Trim list at
redisTemplate.opsForList().trim(K key, long start, long end)
- Get stored in key The size of the list
redisTemplate.opsForList().size(K key)
RedisTemplate.opsForSet() Method
- stay key Of set Add the given value to
redisTemplate.opsForSet().add(K key, V... values)
- stay key Of set Deletes the given value and returns the number of deleted elements
redisTemplate.opsForSet().remove(K key, Object... values)
- from key Of set To remove and return a random member
redisTemplate.opsForSet(). pop(K key)
- stay key Get the size of the collection at
redisTemplate.opsForSet().size(K key)
- Check on key Of set Whether the contains a value
redisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember(K key, Object o)
- Back in the key and otherKeys And all given sets Intersecting members
redisTemplate.opsForSet().intersect(K key, Collection<K> otherKeys)
- stay key and otherKeys And all given sets The intersection , And store the results in destKey in
redisTemplate.opsForSet().intersectAndStore(K key, Collection<K> otherKeys, K destKey)
- stay key and otherKey Intersect all given sets, And store the results in destKey in
redisTemplate.opsForSet().intersectAndStore(K key, K otherKey, K destKey)
- Merge given key and otherKey All of the sets
redisTemplate.opsForSet().union(K key, K otherKey)
- Will be given key and otherKey All of you set Merge , And store the results in destKey in
redisTemplate.opsForSet().unionAndStore(K key, K otherKey, K destKey)
- Get the difference set
redisTemplate.opsForSet().difference(key, otherKeys)
- Get the difference set and store it in destKey
redisTemplate.opsForSet().differenceAndStore(key, otherKey, destKey)
- Randomly get an element in the set
redisTemplate.opsForSet().randomMember(key)
- Get all the elements in the collection
redisTemplate.opsForSet().members(key)
1
- Random acquisition in the set count It's worth
redisTemplate.opsForSet().randomMembers(key, count)
- Random acquisition in the set count It's worth , But weight removal
redisTemplate.opsForSet().distinctRandomMembers(key, count)
- Traverse set
redisTemplate.opsForSet().scan(key, options)
RedisTemplate.opsForZSet() Method
- Additive elements , Sort from small to large
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(key, value, score)
- To delete multiple values Value
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().remove(key, values)
- Add element score Value returns the increased value at the same time
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().incrementScore(key, value, delta)
- Returns the rank of elements in the set from small to large
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().rank(key, value)
- Returns the ranking of elements in the set from large to small
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRank(key, value)
- Get the element of the specified interval in the collection
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRangeWithScores(key, start,end)
- Query the elements in the collection and sort them from small to large
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRangeByScore(key, min, max)
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRangeByScoreWithScores(key, min, max)
- Sort from high to low , Then get the value between the minimum and maximum
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRangeByScore(key, min, max, start, end)
- according to score Value to get the number of elements
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().incrementScore(key, value, delta)
- Get the size of the collection
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().size(key)redisTemplate.opsForZSet().zCard(key)
- Get... In the collection key、value Elemental score value
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().score(key, value)
- Removes the specified index element
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().removeRange(key, start, end)
- Remove the specified score Collection members of the scope
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().removeRangeByScore(key, min, max)
- obtain key and otherKey Union of and stored in destKey in
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().unionAndStore(key, otherKey, destKey)
- obtain key and otherKey And stored in destKey in
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().intersectAndStore(key, otherKey, destKey)
Redis6 Transaction operation of
Redis The definition of the transaction

Redis A transaction is a separate isolation operation : All commands in the transaction are serialized 、 To execute in order . Transaction is in the process of execution , Will not be interrupted by command requests from other clients .
Redis The main function of business is Concatenate multiple commands Prevent other orders from jumping in line .
Multi、Exec、discard
From input Multi Command start , All the entered commands will enter the command queue in turn , But will not execute , Until input Exec after ,Redis The previous commands in the command queue will be executed successively .
In the process of team formation, you can go through discard To give up team building .

Wrong handling of transactions
- There was a report error on a command in the team , During execution, all queues of the whole are cancelled

- If an error is reported in a command during execution , Only the wrong command will not be executed , And other orders will be executed , No rollback .

Transaction conflict
Example
A request wants to reduce the amount 8000
A request wants to reduce the amount 5000
A request wants to reduce the amount 1000

The idea of two locks

Pessimistic locking
Pessimistic locking (Pessimistic Lock), seeing the name of a thing one thinks of its function , Is very pessimistic , Every time I go to get the data, I think others will modify it , So every time I get the data, I lock it , So that if people want to take this data, they will block Until it gets the lock . There are many lock mechanisms used in traditional relational databases , such as Row lock , Table locks etc. , Read the lock , Write lock etc. , It's all locked before the operation .
Optimism lock
Optimism lock (Optimistic Lock), seeing the name of a thing one thinks of its function , Is very optimistic , Every time I go to get the data, I think other people won't modify it , So it won't lock , But in the process of updating, we will judge whether other people have updated this data during this period , You can use mechanisms like version numbers . Optimistic lock is suitable for multi read applications , This can improve throughput .Redis It's using this check-and-set The mechanism implements the .
WATCHkey [key …]
In execution multi Before , Execute first watch key1 [key2], You can watch one ( Or more ) key , If you're in business This before execution ( Or these ) key Altered by other orders , Then the business will be interrupted .
unwatch
Cancel WATCH Command to all key Surveillance .
If in execution WATCH After the command ,EXEC Order or DISCARD If the order is executed first , Then there's no need to execute UNWATCH 了 .
Redis Three characteristics of transaction
Ø Separate isolation operation
- All commands in the transaction are serialized 、 To execute in order . Transaction is in the process of execution , Will not be interrupted by command requests from other clients .
Ø There is no concept of isolation level
- The commands in the queue are not actually executed until they are submitted , Because no instruction is actually executed before the transaction is committed
Ø There is no guarantee of atomicity
- If a command fails in a transaction , Subsequent orders will still be executed , No rollback
Second kill case
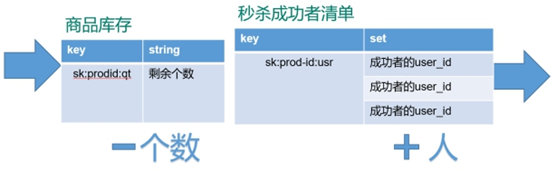
Ideas
- Pass in uid and prodid( And verify )
- according to uid and prodid Generate key
- Inventory judgment (null Not yet begun ,0 end ), Repeat second kill judgment
- Second kill of users , stock –
- The user enters the seckill success list
Code :
public static boolean doSecKill(String uid,String prodid) throws IOException {
//1 uid and prodid Judge not empty
if(uid == null || prodid == null) {
return false;
}
//2 Connect redis
//Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.44.168",6379);
// Get through connection pool jedis object
JedisPool jedisPoolInstance = JedisPoolUtil.getJedisPoolInstance();
Jedis jedis = jedisPoolInstance.getResource();
//3 Splicing key
// 3.1 stock key
String kcKey = "sk:"+prodid+":qt";
// 3.2 Second kill successful users key
String userKey = "sk:"+prodid+":user";
// Monitor inventory
jedis.watch(kcKey);
//4 Get inventory , If inventory null, The second kill hasn't started yet
String kc = jedis.get(kcKey);
if(kc == null) {
System.out.println(" The second kill hasn't started yet , Please wait ");
jedis.close();
return false;
}
// 5 Judge whether the user repeats the second kill operation
if(jedis.sismember(userKey, uid)) {
System.out.println(" It's a second kill , You can't repeat the second kill ");
jedis.close();
return false;
}
//6 Judge if the quantity of goods , Inventory quantity is less than 1, End of seckill
if(Integer.parseInt(kc)<=0) {
System.out.println(" The second kill is over ");
jedis.close();
return false;
}
//7 Second kill process
// With a transaction
Transaction multi = jedis.multi();
// Team operation
multi.decr(kcKey);
multi.sadd(userKey,uid);
// perform
List<Object> results = multi.exec();
if(results == null || results.size()==0) {
System.out.println(" The second kill failed ....");
jedis.close();
return false;
}
//7.1 stock -1
//jedis.decr(kcKey);
//7.2 Add successful users to the list
//jedis.sadd(userKey,uid);
System.out.println(" The second kill succeeded ..");
jedis.close();
return true;
}
You can solve the link timeout problem through the thread pool
public class JedisPoolUtil {
private static volatile JedisPool jedisPool = null;
private JedisPoolUtil() {
}
public static JedisPool getJedisPoolInstance() {
if (null == jedisPool) {
synchronized (JedisPoolUtil.class) {
if (null == jedisPool) {
JedisPoolConfig poolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig();
poolConfig.setMaxTotal(200);
poolConfig.setMaxIdle(32);
poolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(100*1000);
poolConfig.setBlockWhenExhausted(true);
poolConfig.setTestOnBorrow(true); // ping PONG
jedisPool = new JedisPool(poolConfig, "192.168.44.168", 6379, 60000 );
}
}
}
return jedisPool;
}
public static void release(JedisPool jedisPool, Jedis jedis) {
if (null != jedis) {
jedisPool.returnResource(jedis);
}
}
}
have access to lua To solve the remaining inventory problems
public class SecKill_redisByScript {
private static final org.slf4j.Logger logger =LoggerFactory.getLogger(SecKill_redisByScript.class) ;
public static void main(String[] args) {
JedisPool jedispool = JedisPoolUtil.getJedisPoolInstance();
Jedis jedis=jedispool.getResource();
System.out.println(jedis.ping());
Set<HostAndPort> set=new HashSet<HostAndPort>();
// doSecKill("201","sk:0101");
}
static String secKillScript ="local userid=KEYS[1];\r\n" +
"local prodid=KEYS[2];\r\n" +
"local qtkey='sk:'..prodid..\":qt\";\r\n" +
"local usersKey='sk:'..prodid..\":usr\";\r\n" +
"local userExists=redis.call(\"sismember\",usersKey,userid);\r\n" +
"if tonumber(userExists)==1 then \r\n" +
" return 2;\r\n" +
"end\r\n" +
"local num= redis.call(\"get\" ,qtkey);\r\n" +
"if tonumber(num)<=0 then \r\n" +
" return 0;\r\n" +
"else \r\n" +
" redis.call(\"decr\",qtkey);\r\n" +
" redis.call(\"sadd\",usersKey,userid);\r\n" +
"end\r\n" +
"return 1" ;
static String secKillScript2 =
"local userExists=redis.call(\"sismember\",\"{sk}:0101:usr\",userid);\r\n" +
" return 1";
public static boolean doSecKill(String uid,String prodid) throws IOException {
JedisPool jedispool = JedisPoolUtil.getJedisPoolInstance();
Jedis jedis=jedispool.getResource();
//String sha1= .secKillScript;
String sha1= jedis.scriptLoad(secKillScript);
Object result= jedis.evalsha(sha1, 2, uid,prodid);
String reString=String.valueOf(result);
if ("0".equals( reString ) ) {
System.err.println(" Empty !!");
}else if("1".equals( reString ) ) {
System.out.println(" Panic buying !!!!");
}else if("2".equals( reString ) ) {
System.err.println(" The user has robbed !!");
}else{
System.err.println(" Panic buying exception !!");
}
jedis.close();
return true;
}
}
Redis6 Persistence is RDB
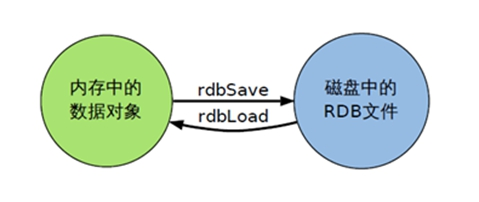
Write the data set snapshot in memory to disk within the specified time interval , That's what jargon says Snapshot snapshot , When it recovers, it reads the snapshot file directly into memory
How backups are performed
Redis Will create... Separately (fork) A subprocess to persist , Will first write data to In a temporary file , When the persistence process is over , Replace the last persistent file with this temporary file . The whole process , The main process is not going to do anything IO Operation of the , This ensures extremely high performance If large-scale data recovery is needed , And it's not very sensitive to the integrity of data recovery , that RDB The way is better than AOF It's more efficient .RDB The disadvantage is that the data may be lost after the last persistence .
Sketch Map

fork
- Fork Its function is to copy the same process as the current process . All the data for the new process ( Variable 、 environment variable 、 Program counter, etc ) The values are consistent with the original process , But it's a whole new process , And as a child of the original process
- stay Linux In the program ,fork() Will produce a child process that is exactly the same as the parent process , But the subprocesses are more likely to exec system call , For efficiency ,Linux Introduced in “ Copy on write technology ”
- Generally, the parent process and the child process share the same physical memory , Only when the content of each segment of the process space changes , Will copy the contents of the parent process to the child process .
Persistence process

dump.rdb file
stay redis.conf Name of the configuration file in , The default is dump.rdb

rdb Save path of file , You can also modify . The default is Redis At startup, the command line is in the same directory dir “/myredis/”

How to trigger RDB snapshot ; Retention strategy
The default snapshot configuration in the configuration file

command save VS bgsave
- save :save Just keep it , Nothing else , All blocked . Save manually . Don't suggest .
- bgsave**:Redis The snapshot operation will be performed asynchronously in the background ,** The snapshot can also respond to client requests .
Can pass lastsave Command gets the last time the snapshot was executed successfully
flushall command
perform flushall command , There will be dump.rdb file , But it's empty , meaningless
Save
Format :save Second Number of write operations
RDB It's the compression of the entire memory Snapshot,RDB Data structure of , You can configure composite snapshot trigger conditions ,
The default is 1 Changed in minutes 1 Ten thousand times ,
or 5 Changed in minutes 10 Time ,
or 15 Changed in minutes 1 Time .
Ban
Not set up save Instructions , Or to save Pass in an empty string
Dynamic stop RDB:
redis-cli config set save “”#save Give null value after , Indicates disable save policy
The configuration file
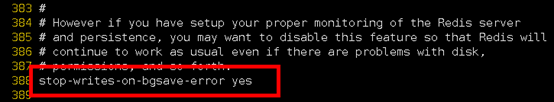
stop-writes-on-bgsave-erro
When Redis If you can't write to disk , Turn it off Redis Write operations for . recommend yes
rdbcompression
For snapshots stored on disk , You can set whether to compress storage . If so ,redis Will be used LZF Algorithm for compression .
If you don't want to consume CPU To compress , It can be set to turn off this function . recommend yes.

rdbchecksum Check for integrity
After storing the snapshot , Can also let redis Use CRC64 Algorithm to check data ,
But doing so will add about 10% Performance consumption of , If you want to get the maximum performance improvement , You can turn it off
recommend yes.

rdb Backup of
Through the first config get dir Inquire about rdb File directory
take *.rdb Copy your files to other places
rdb The recovery of
- close Redis
- First copy the backup file to the working directory cp dump2.rdb dump.rdb
- start-up Redis, The backup data is loaded directly
Pros and
advantage
- Suitable for large-scale data recovery
- Data integrity and consistency requirements are not high, more suitable for use
- Save disk space
- Fast recovery
Inferiority
- Fork When , The data in memory is cloned , roughly 2 Double expansion needs to be considered
- although Redis stay fork When used Copy on write technology , But if the data is huge, it still consumes performance .
- Make a backup at a certain interval in the backup cycle , So if Redis accident down If you drop it , All changes since the last snapshot will be lost .

Redis6 Persistence is AOF
brief introduction
With journal To record each write operation ( Incremental save ), take Redis All written instructions executed are recorded ( Reading operation does not record ), Only files can be added but not rewritten ,redis At the beginning of startup, it will read the file and rebuild the data , In other words ,redis In case of restart, execute the write instruction from the front to the back according to the contents of the log file to complete the data recovery
Persistence process
- The client request write command will be append Append to AOF In the buffer
- AOF Buffer based on AOF Persistence strategy [always,everysec,no] Will operate sync Synced to disk AOF In file ;
- AOF When the file size exceeds the rewrite policy or manual rewrite , Would be right AOF file rewrite rewrite , Compress AOF File capacity ;
- Redis When the service is restarted , Will return load load AOF The write operation in the file achieves the purpose of data recovery ;

AOF Not on by default
Can be in redis.conf Name of the configuration file in , The default is appendonly.aof
AOF Save path of file , Same as RDB The path is the same .
AOF and RDB At the same time open
AOF and RDB At the same time open , The system defaults to AOF The data of ( There is no loss of data )
AOF start-up / Repair / recovery
- AOF Although the backup mechanism and performance are similar to RDB Different , But the operation of backup and recovery is the same as RDB equally , It's all copying backup files , Copy to when you need to recover Redis Working directory , Start the system and load .
- Normal recovery
- Modify the default appendonly no, Change it to yes
- There will be data aof Copy a file and save it to the corresponding directory ( View directory :config get dir)
- recovery : restart redis Then reload
- Abnormal recovery
- n Modify the default appendonly no, Change it to yes
- n If encountered AOF File corruption , adopt /usr/local/bin/redis-check-aof–fix appendonly.aof Resume
- n Backup is bad AOF file
- n recovery : restart redis, Then reload
AOF Synchronous frequency setting
appendfsync always
Always sync , Every time Redis All writes are immediately logged ; Poor performance but good data integrity
appendfsync everysec
A second synchronous , Log once per second , If it goes down , This second's data may be lost .
appendfsync no
redis Don't take the initiative to synchronize , Give the timing of synchronization to the operating system .
Rewrite Compress
brief introduction
AOF By means of document addition , The documents will become larger and larger to avoid this , New rewrite mechanism , When AOF When the file size exceeds the set threshold ,Redis Will start AOF The content of the file is compressed , Keep only the smallest instruction set that can recover data . You can use commands bgrewriteaof
Principle and implementation
AOF When files continue to grow and become too large , Meeting fork A new process to rewrite the file ( Also write temporary documents first and then rename),redis4.0 Post version rewriting , It means to put up rdb Snapshot , In the form of a two-tier system attached to the new aof Head , As historical data available , Replace the original daily account operation .
no-appendfsync-on-rewrite:
If no-appendfsync-on-rewrite=yes , Don't write aof Files are only written to the cache , User requests don't block , But in this period of time, if you lose the cache data in this period of time .( Reduce data security , Improve performance )
If no-appendfsync-on-rewrite=no, I'll still brush the data to the disk , But we're encountering an override operation , There could be a blockage .( Data security , But the performance degrades )
Trigger mechanism , When to rewrite
Redis It will record the last time it was rewritten AOF size , The default configuration is when AOF The file size is last rewrite Double the size and the file is larger than 64M Trigger when
Rewriting can save a lot of disk space , Reduce recovery time . But there's a burden to rewrite every time , So set Redis You have to meet certain conditions to rewrite .
auto-aof-rewrite-percentage: Set the overridden benchmark , The document reaches 100% Start rewriting ( The file is the original rewritten file 2 It's time to trigger )
auto-aof-rewrite-min-size: Set the overridden benchmark , The smallest file 64MB. Reach this value and start rewriting .
for example : The document reaches 70MB Start rewriting , drop to 50MB, When do you start rewriting next time ?100MB
When the system was loaded or last rewritten ,Redis It will be recorded at this time AOF size , Set to base_size,
If Redis Of AOF The current size >= base_size +base_size*100% ( Default ) And the current size >=64mb( Default ) Under the circumstances ,Redis Would be right AOF Rewrite .
Rewrite process
bgrewriteaof Trigger override , Judge whether there is bgsave or bgrewriteaof Running , If there is , Then wait for the end of the command to continue .
The main process fork Out of the child process to perform the rewrite operation , Make sure the main process doesn't block .
Subprocess traversal redis Data in memory to temporary file , The client's write request is written at the same time aof_buf Buffers and aof_rewrite_buf Rewriting the buffer ensures that the original AOF The file is complete and new AOF New data modification actions during file generation will not be lost .
1). The subprocess writes a new AOF After the document , Signal the main process , Parent process update statistics .
2). The main process puts aof_rewrite_buf Write the data in to the new AOF file .
Use the new AOF The file covers the old AOF file , complete AOF rewrite .

Pros and
advantage

- The backup mechanism is more robust , Lower probability of data loss .
- Readable log text , By manipulating the AOF steady , It can handle misoperation .
Inferiority
- Compared with RDB Take up more disk space .
- Recovery of backup is slower .
- If every read and write is synchronized , There is a certain performance pressure .
- There are individual problems Bug, It can't recover .

Choose suggestions
- The official recommendation is to use both .
- If you're not sensitive to data , You can use the menu alone RDB.
- It is not recommended to use it alone AOF, Because there may be Bug.
- If it's just a pure memory cache , You don't have to .
Redis6 Master-slave replication of
brief introduction
After the host data is updated, according to the configuration and Policy , Automatic synchronization to the standby machine master/slaver Mechanism ,Master Write first ,Slave Mainly reading
effect
- Read / write separation , Performance expansion
- Rapid disaster recovery

Specific operation
- Copy multiple redis.conf file include( Write absolute path )
- Turn on daemonize yes
- Pid File name pidfile
- Designated port port
- Log File name
- dump.rdb name dbfilename
- Appendonly Turn it off or change the name
newly build redis****.conf
include /myRedis/redis.conf
pidfile /var/run/redis_6379.pid
port 6379
dbfilename dump6379.rdb
Start three services

perform slaveof host ip Port number

Commonly used 3 recruit
One master and two servants
- When you hang up from the service , Start again , It will not inherit the previous master-slave state , At this time, the service is master, It needs to be reset , And after resetting , The data of the main service will be copied
- When the main service hangs up , The state of the slave service does not change , When the main service is started again , It will automatically continue the previous master-slave status , The data will also be copied to the main service , Everything remains the same.
It's passed down from generation to generation
the previous Slave It could be the next slave Of Master,Slave Can also receive other slaves Connection and synchronization requests for , Then the slave As the next in the chain master, Can effectively reduce master The pressure of writing , Decentralization reduces risk .
- use slaveof
- Change direction in the middle : Will clear the previous data , Recreate the copy of the latest
- The risk is that once something slave Downtime , hinder slave No backup
- The mainframe is down , Slave or slave , Unable to write data

Going to
When one master After downtime , hinder slave Can be promoted to master, Behind it slave You don't have to make any changes .
use slaveof no one From slave to host .
Master slave replication principle
- After the server is linked to the primary server , Send a data synchronization message to the primary server
- The primary server receives a message , Pass the data through rdb Way to persist , take rdb File transfer to the slave server , From the server through rdb File read
- Whenever the primary server performs a write operation , Will notify the server to synchronize data
- The slave server only actively requests data synchronization during the first link , In other cases, the master server is responsible for data synchronization

Sentinel mode
brief introduction
The automatic version of anti guest oriented , Be able to monitor the failure of the host in the background , If it fails, it will automatically convert from the library to the main library according to the number of votes

Implementation steps
One servant and two masters
Self defined /myRedis New under the directory sentinel.conf file
Deploy sentinels , Fill in the content
sentinel monitor mymaster 127.0.0.1 6379 1
among mymaster Server name for the monitored object , 1 For at least how many sentinels agree to move the number .
Activate the sentry
/usr/local/bin
redis For pressure measurement, you can use your own re dis-benchmark Tools
perform redis-sentinel /myredis/sentinel.conf
When the host goes down , A new host is generated from the election of the slave computer
( Probably 10 You can see the sentry window log in seconds , Switched to a new host )
Which is elected as the host from the opportunity ? According to priority :slave-priority
After the original host is restarted, it will become a slave .
Replication delay
Because all the writing operations are first in Master On the operation , Then sync update to Slave On , So from Master Synchronize to Slave The machine has a certain delay , When the system is busy , The delay problem will be more serious ,Slave The increase in the number of machines will make the problem more serious .
Fault recovery
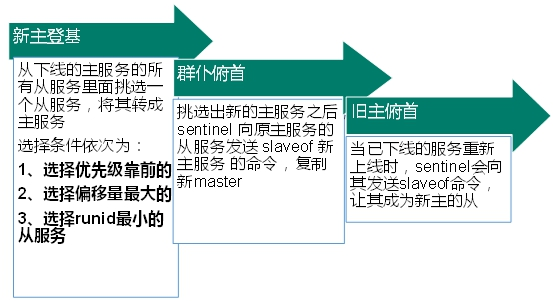
The priority is redis.conf The default :slave-priority 100, The lower the value, the higher the priority
Offset refers to the most complete data of the original host
Every redis After the instance is started, it will generate one randomly 40 Bit runid
java Set up
private static JedisSentinelPool jedisSentinelPool=null;
public static Jedis getJedisFromSentinel(){
if(jedisSentinelPool==null){
Set<String> sentinelSet=new HashSet<>();
sentinelSet.add("192.168.11.103:26379");
JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig =new JedisPoolConfig();
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxTotal(10); // Maximum number of connections available
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(5); // Maximum number of idle connections
jedisPoolConfig.setMinIdle(5); // Minimum number of idle connections
jedisPoolConfig.setBlockWhenExhausted(true); // Whether the connection is exhausted and wait
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(2000); // Waiting time
jedisPoolConfig.setTestOnBorrow(true); // Test the connection ping pong
jedisSentinelPool=new JedisSentinelPool("mymaster",sentinelSet,jedisPoolConfig);
return jedisSentinelPool.getResource();
}else{
return jedisSentinelPool.getResource();
}
}
Redis6 colony
problem
Not enough capacity ,redis How to expand ?
Concurrent write operations , redis How to apportion ?
in addition , A master-slave mode , Pass on mode , Host down , Lead to ip The address has changed , The corresponding host address needs to be modified for configuration in the application 、 Port and other information .
Previously, it was solved by proxy host , however redis3.0 The solution . That is, decentralized cluster configuration .
brief introduction
Redis The cluster has realized to Redis Horizontal expansion of , Start now N individual redis node , The entire database is distributed and stored here N A node in the , Each node stores the total data 1/N.
Redis Clusters are partitioned (partition) To provide a certain degree of usability (availability): Even if some nodes in the cluster fail or fail to communicate , The cluster can also continue to process command requests .
To configure
Configure basic information
Turn on daemonize yes
Pid File name
Designated port
Log File name
Dump.rdb name
Appendonly Turn it off or change the name
redis cluster Configuration modification
cluster-enabled yes Open cluster mode
cluster-config-file nodes-6379.conf Set the node profile name
cluster-node-timeout 15000 Set the node loss time , Beyond that time ( millisecond ), The cluster automatically switches between master and slave .
include /home/bigdata/redis.conf
port 6379
pidfile "/var/run/redis_6379.pid"
dbfilename "dump6379.rdb"
dir "/home/bigdata/redis_cluster"
logfile "/home/bigdata/redis_cluster/redis_err_6379.log"
cluster-enabled yes
cluster-config-file nodes-6379.conf
cluster-node-timeout 15000
Start all services
Combine six nodes into a cluster
Before combination , Please make sure that all redis After the instance is started ,nodes-xxxx.conf All files are generated normally .
- Fit cd /opt/redis-6.2.1/src
- edis-cli --cluster create --cluster-replicas 1 192.168.150.111:6379 192.168.150.111:6380 192.168.150.111:6381 192.168.150.111:6389 192.168.150.111:6390 192.168.150.111:6391
Use cluster policy to connect , The setting data will be automatically switched to the corresponding write host
adopt cluster nodes Command to view cluster information
Node allocation
A cluster must have at least three master nodes .
Options --cluster-replicas 1 Indicates that we want to create a slave node for each master node in the cluster .
The allocation principle tries to ensure that each master database runs on different servers IP Address , Each slave library and master library are not in one IP Address .
slots
[OK] All nodes agree about slots configuration.
>>> Check for open slots…
>>> Check slots coverage…
[OK] All 16384 slots covered.
One Redis The cluster contains 16384 Slots (hash slot), Every key in the database belongs here 16384 One of the slots ,
The cluster uses the formula CRC16(key) % 16384 To calculate the key key Which slot does it belong to , among CRC16(key) Statements are used to evaluate keys key Of CRC16 The checksum .
Each node in the cluster is responsible for processing a portion of the slots . for instance , If a cluster can have a master node , among :
node A Responsible for handling 0 No. to 5460 Slot number .
node B Responsible for handling 5461 No. to 10922 Slot number .
node C Responsible for handling 10923 No. to 16383 Slot number .
Enter values in the cluster
stay redis-cli Every time you enter 、 Query key values ,redis The accountant worked out the key Slot that should be sent , If it is not the slot of the server corresponding to the client ,redis Will report a mistake , And inform those who should go redis Instance address and port .
redis-cli The client provides –c Parameter to implement automatic redirection .
Such as redis-cli -c –p 6379 After logging in , Re entry 、 Query key value pairs can be redirected automatically .
Not in one slot Key values under , Can't use mget,mset Wait for multi key operation .

Can pass {} To define the concept of a group , So that key in {} Key value pairs with the same content in a slot In the middle

Query the values in the cluster
CLUSTER GETKEYSINSLOT return count individual slot Key in groove .

Fault recovery
If the master node goes offline , Whether the slave node can be automatically promoted to the master node ? Be careful :15**** Second timeout Meeting
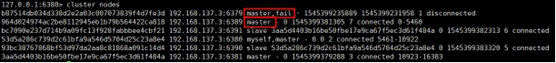
After the primary node is restored , What about the master-slave relationship ? When the master node comes back, it becomes a slave .
If all the master and slave nodes in a certain slot are down ,redis Whether the service can continue ?
If the master and slave of a certain slot hang up , and cluster-require-full-coverage by yes , that , The whole cluster is down
If the master and slave of a certain slot hang up , and cluster-require-full-coverage by no , that , None of the slot data is available , Can't store .
redis.conf Parameters in cluster-require-full-coverage
Clustered jedis
Even if the host is not connected , The cluster automatically switches host storage . Host write , Read from machine .
Decentralized master-slave cluster . No matter which host the data is written from , Data can be read on other hosts .
public class JedisClusterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<HostAndPort>set =new HashSet<HostAndPort>();
set.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.31.211",6379));
JedisCluster jedisCluster=new JedisCluster(set);
jedisCluster.set("k1", "v1");
System.out.println(jedisCluster.get("k1"));
}
}
Pros and
advantage
- Realize capacity expansion
- Apportionment pressure
- No central configuration is relatively simple
Inferiority
- Multi key operation is not supported
- Multibond Redis Transactions are not supported .lua Scripts are not supported
- Due to the late emergence of the cluster scheme , Many companies have adopted other clustering schemes , The proxy or client partition scheme wants to migrate to redis cluster, Overall migration is required rather than gradual transition , High complexity .
Redis6 Apply problem solving
Cache penetration

key The corresponding data does not exist in the data source , Every time for this key The request for could not be fetched from the cache , Requests are pushed to the data source , That could crush the data source . For example, use a non-existent user id Get user information , No matter cache or database , If hackers exploit this vulnerability, they may crush the database .
Solution
There must be no data that cannot be cached or queried , Because the cache is written passively on Miss , And for the sake of fault tolerance , If no data can be found from the storage tier, it will not be written to the cache , This will cause the non-existent data to be queried by the storage layer every time it is requested , It loses the meaning of caching .
- ** Cache null values :** If the data returned by a query is empty ( Whether the data doesn't exist or not ), We still put this empty result (null) Cache , Setting the expiration time for empty results can be very short , Up to five minutes
- ** Set up an accessible list ( White list ):** Use bitmaps Type defines a list of accessible , list id As bitmaps The offset , Every visit and bitmap Inside id Compare , If you visit id be not in bitmaps Inside , To intercept , Access not allowed
- Use of Blum filter :( The bloon filter (Bloom Filter) yes 1970 Proposed by bron in . It's actually a very long binary vector ( Bitmap ) And a series of random mapping functions ( hash function ). The bloom filter can be used to retrieve whether an element is in a collection . Its advantage is that the space efficiency and query time are far more than the general algorithm , The disadvantage is that it has certain error recognition rate and deletion difficulty .) Hash all possible data to a large enough bitmaps in , A certain nonexistent data will be This bitmaps Intercept , Thus, the query pressure on the underlying storage system is avoided .
- Real-time monitoring : If I found Redis It's starting to drop , Need to check access objects and data , Cooperate with operation and maintenance personnel , You can set up a blacklist to restrict services
Cache breakdown
key The corresponding data exists , But in redis Medium overdue , At this time, if a large number of concurrent requests come , These requests usually find that the cache is expired from the back end DB Load data and reset to cache , At this time, a large number of concurrent requests may instantly put the back end DB Overwhelmed .
Solution
key It may be accessed at some point in time with super high concurrency , It's a very “ hotspot ” The data of . This is the time , A question needs to be considered : The cache is “ breakdown ” The problem of .
Preset hot data : stay redis Before the summit visit , Put some hot data into redis Inside , Increase the hot data key Duration
** Real time adjustments :** What data is hot on the spot , Real time adjustments key The expiration time of
Using locks :
- When the cache fails ( Judge that the value is empty ), Not immediately load db.
- First, use some operations of the cache tool with the return value of the successful operation ( such as Redis Of SETNX)(1) Go to set One mutex key
- When the operation returns success , Proceed again load db The operation of , And reset the cache , Finally delete mutex key;
- When the operation returns failure , Prove that there are threads in load db, The current thread sleeps for a period of time and then retries the whole get Caching method .

Cache avalanche
key The corresponding data exists , But in redis Medium overdue , At this time, if a large number of concurrent requests come , These requests usually find that the cache is expired from the back end DB Load data and reset to cache , At this time, a large number of concurrent requests may instantly put the back end DB Overwhelmed .
The difference between cache avalanche and cache breakdown is that there are many key cache , The former is a certain key Normal visit

Solution
The avalanche effect of cache failure has a terrible impact on the underlying system !
- ** Building a multi-level cache architecture :**nginx cache + redis cache + Other caches (ehcache etc. )
- Use locks or queues : Lock or queue to ensure that there will not be a large number of threads to read and write the database at one time , So as to avoid a large number of concurrent requests falling on the underlying storage system in case of failure . Not for high concurrency
- ** Set expiration flag to update cache :** Record whether the cache data is out of date ( Set the lead amount ), If it expires, it will trigger another thread to update the actual situation in the background key The cache of .
- Decentralized cache expiration time : For example, we can add a random value to the original failure time , such as 1-5 Minutes at random , In this way, the repetition rate of each cache expiration time will be reduced , It's hard to trigger a collective failure .
Distributed lock
With the needs of business development , After the original single machine deployment system is evolved into a distributed cluster system , Due to multithreading in distributed system 、 Multi process and distributed on different machines , This will invalidate the concurrent control lock policy in the case of the original stand-alone deployment , pure Java API It doesn't provide the ability of distributed locks . In order to solve this problem, we need a kind of cross JVM To control the access of shared resources , This is the problem of distributed lock !
The mainstream implementation of distributed lock :
Implementation of distributed lock based on Database
Cache based (Redis etc. )
be based on Zookeeper
Every distributed lock solution has its own advantages and disadvantages :
performance :redis The highest
reliability :zookeeper The highest
here , We are based on redis Implement distributed locks .
redis Implement distributed locks
redis: command
set sku:1:info “OK” NX PX 10000
EX second : Set the expiration time of the key to second second . SET key value EX second The effect is equivalent to SETEX key second value .
PX millisecond : Set the expiration time of the key to millisecond millisecond . SET key value PX millisecond The effect is equivalent to PSETEX key millisecond value .
NX : Only if the bond doesn't exist , To set the key . SET key value NX The effect is equivalent to SETNX key value .
XX : Only if the bond already exists , To set the key .

Multiple clients acquire locks at the same time (setnx)
To be successful , Execute business logic { from db get data , Put into cache }, Execute complete release lock (del)
Other clients wait to try again
java Code
@GetMapping("testLock")
public void testLock(){
//1 Get the lock ,setne
Boolean lock = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent("lock", "111");
//2 Lock acquired successfully 、 Inquire about num Value
if(lock){
Object value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("num");
//2.1 Judge num It's empty return
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(value)){
return;
}
//2.2 If it's worth something, it turns into int
int num = Integer.parseInt(value+"");
//2.3 hold redis Of num Add 1
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("num", ++num);
//2.4 Release the lock ,del
redisTemplate.delete("lock");
}else{
//3 Lock acquisition failed 、 every other 0.1 Second to get
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
testLock();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
problem :setnx Just got the lock , Exception in business logic , Causes the lock to fail to release
solve : Set expiration time , Automatic release lock .
Optimize the lock expiration time
There are two ways to set the expiration time :
The first thing to think about is through expire Set expiration time ( Lacking atomicity : If in setnx and expire There is an exception between , The lock doesn't release either )
stay set Specify the expiration time when ( recommend )

Residual problems
scene : If the execution time of business logic is 7s. The execution process is as follows
\1. index1 Business logic is not finished ,3 Seconds later, the lock is released automatically .
\2. index2 Get lock , Execute business logic ,3 Seconds later, the lock is released automatically .
\3. index3 Get lock , Execute business logic
\4. index1 Business logic execution complete , Start calling del Release the lock , What's released is index3 Lock of , Lead to index3 Our business only performs 1s I'll be released by someone else .
In the end, it's the case of no lock .
solve :setnx When you get the lock , Set a specified unique value ( for example :uuid); Get this value before releasing , Judge if it's your own lock
Optimize it UUID Error proofing


problem : Deletion operation lacks atomicity .
Optimize it LUA Scripts guarantee atomicity of deletion
@GetMapping("testLockLua")
public void testLockLua() {
//1 Make a statement uuid , Will be as a value Put in our key In the corresponding value
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
//2 Define a lock :lua Scripts can use the same lock , To delete !
String skuId = "25"; // visit skuId by 25 No 100008348542
String locKey = "lock:" + skuId; // What's locked is the data of each commodity
// 3 Get the lock
Boolean lock = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(locKey, uuid, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// The first one is : lock Don't write any code between the expiration time .
// redisTemplate.expire("lock",10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);// Set expiration time
// If true
if (lock) {
// The business logic of execution begins
// Get the num data
Object value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("num");
// If it's empty, return to
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(value)) {
return;
}
// Not empty If something goes wrong here ! that delete The deletion failed ! That is to say, the lock always exists !
int num = Integer.parseInt(value + "");
// send num Every time +1 Put into cache
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("num", String.valueOf(++num));
/* Use lua Script to lock */
// Definition lua Script
String script = "if redis.call('get', KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then return redis.call('del', KEYS[1]) else return 0 end";
// Use redis perform lua perform
DefaultRedisScript<Long> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>();
redisScript.setScriptText(script);
// Set the return value type by Long
// Because when you delete judgment , Back to 0, Encapsulate it as a data type . If it's not encapsulated, it will return by default String type ,
// So return the string and 0 There will be mistakes .
redisScript.setResultType(Long.class);
// The first is if script Script , The second thing that needs to be judged key, The third is key The corresponding value .
redisTemplate.execute(redisScript, Arrays.asList(locKey), uuid);
} else {
// Other threads wait
try {
// sleep
Thread.sleep(1000);
// When I wake up , Calling method .
testLockLua();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

Redis6 new function
ACL
brief introduction
Redis ACL yes Access Control List( Access control list ) Abbreviation , This function allows some connections to be restricted according to the commands that can be executed and the keys that can be accessed .
stay Redis 5 Before the release ,Redis The security rule is only password control And through rename To adjust high-risk orders, such as flushdb , KEYS* , shutdown etc. .Redis 6 Provide ACL More fine-grained permission control for users :
- Access rights : User name and password
- Orders that can be executed
- It can be operated KEY
command
- Use
acl listThe command displays a list of user permissions

Use acl cat command
View add permission instruction category

Add the parameter type name to view the specific commands under the type
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-ESLqIrqI-1655813763243)(https://pic.imgdb.cn/item/62b1b3960947543129cde382.png)]
Use
acl whoamiCommand to view the current user[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-QoEW2Uur-1655813763244)(https://pic.imgdb.cn/item/62b1b3b10947543129ce094c.png)]
Use
aclsetuserCommand to create and edit users ACLThe rules : Some rules are only used to activate or delete flags , Or to users ACL A single word that performs a given change . Other rules are character prefixes , They are the same as the command or category name 、 Key mode, etc .
ACL The rules type Parameters explain Start and disable users on Activate a user account off Disable a user account . Be careful , The verified connection is still working . If the default user is marked off, The new connection will start without authentication , And ask users to use AUTH Option send AUTH or HELLO, To authenticate in some way . Add and delete permissions + Add an instruction to the list of instructions that the user can call - Removes an instruction from the user executable instruction list [email protected] Add all instructions to be called by the user in this category , Valid categories are @admin、@set、@sortedset… etc. , By calling ACL CAT Command to view the complete list . Special categories @all All commands , Include commands that currently exist in the server , And commands that will be loaded through the module in the future . [email protected] Removes a category from a user callable instruction allcommands [email protected] Another name for nocommand [email protected] Another name for Addition or deletion of operable keys ~ Add a mode that can be used as a user operable key . for example ~* Allow all keys
Create new user default permissions by command
![[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-vjCpzbE3-1655813763245)(https://pic.imgdb.cn/item/62b1b4210947543129cec73e.png)]](/img/2e/6314d410c9fe5a423c8d87443a8f41.png)
In the example above , I didn't specify any rules at all . If the user doesn't exist , This will use just created To create a user . If the user already exists , Then the above command will not perform any operation .
Set user name 、 password 、ACL jurisdiction 、 And enabled users
acl setuser user2 on >password ~cached:* +get
Switching users , Verify permissions

IO Multithreading
brief introduction
IO Multithreading actually means Client interaction part Of The Internet IO Interactive processing module Multithreading , Instead of Execute command multithreading .Redis6 Executing commands is still single threaded .
principle
Redis 6 Join multithreading , But follow Memcached Such from IO There are some differences in the implementation mode of processing to data access multithreading .Redis The multithreading part is only used to process network data reading and writing and protocol parsing , Executing commands is still single threaded . The reason for this design is that we don't want to be complicated by multithreading , Need to control key、lua、 Business ,LPUSH/LPOP And so on . The overall design is as follows :
![[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-wSg43Msc-1655813763247)(https://pic.imgdb.cn/item/62b1b4cd0947543129cfdc38.png)]](/img/56/8c65216db900555b394d1d44295c5f.png)
in addition , Multithreading IO It is also not enabled by default , You need to configure... In the configuration file
io-threads-do-reads yes
io-threads 4
Support Cluster
Before the old version Redis If you want to build a cluster, you need to install it separately ruby Environmental Science ,Redis 5 take redis-trib.rb Integrated into redis-cli . Another official redis-benchmark Tools start to support cluster The model , Through the way of multithreading, the pressure test is carried out for multiple pieces .
other
Redis6 New features include :
1、RESP3 new Redis Communication protocol : Optimize the communication between server and client
2、Client side caching Client cache : be based on RESP3 The client cache function of the protocol . In order to further improve the cache performance , The data that the client often accesses cache To client . Reduce TCP Network interaction .
3、Proxy Cluster agent mode :Proxy function , Give Way Cluster It has the same access method as single instance , Reduce your use cluster Threshold . However, it should be noted that the agent does not change Cluster The functional limitations of , Commands that are not supported will not be supported , For example, cross slot More Key operation .
4、Modules API
Redis 6 Middle module API Great development progress , because Redis Labs To develop complex functions , Use it from the beginning Redis modular .Redis Can become a framework , utilize Modules To build different systems , Instead of writing from scratch and then BSD The license .Redis At the beginning, it was an open platform for writing various systems .
边栏推荐
- The access succeeds but an exception is thrown: could not find acceptable representation
- [redis] cluster and common errors
- Win10 installation net3.5. docx
- 【OR36 链表的回文结构】
- Moke 5. Service discovery -nacos
- 2022年起重机械指挥考试模拟100题及模拟考试
- R语言midwest数据集可视化
- R 语言 UniversalBank.csv“ 数据分析
- 评估指标及代码实现(NDCG)
- MySql给某列字段添加(追加)前缀后缀
猜你喜欢

2022年起重机械指挥考试模拟100题及模拟考试

The road to systematic construction of geek planet business monitoring and alarm system

【链表中倒数第k个结点】
![[redis]Redis6的主从复制](/img/47/3be33a0d7435bd75cdd6e7b4ea51d4.png)
[redis]Redis6的主从复制

2022危险化学品经营单位主要负责人上岗证题库及模拟考试
![[redis]redis persistence](/img/83/9af9272bd485028062067ee2d7a158.png)
[redis]redis persistence
![[the penultimate node in the linked list]](/img/b2/be3b0611981dd0248b3526e8958386.png)
[the penultimate node in the linked list]

R 语言 UniversalBank.csv“ 数据分析
![[cm11 linked list splitting]](/img/66/6ac3f78db20ec7f177b88c88028dde.png)
[cm11 linked list splitting]
Flutter System Architecture(Flutter系统架构图)
随机推荐
Code to Image Converter | 代码生成漂亮图片工具
Objective-C不同数据类型占用字节大小
2022团体程序设计天梯赛L1
[the penultimate node in the linked list]
慕课6、实现负载均衡-Ribbon
R 语言 UniversalBank.csv“ 数据分析
Feign FAQ summary
71-对2010年阿里一道Oracle DBA面试题目的分析
Apple Objective-C source code
The real king of cache
Correspondence between int and char in C language
Scheduling with Testing
已解决:一個錶中可以有多個自增列嗎
Golang learning notes - structure
[redis]发布与订阅
Visualization of R language penguins dataset
[redis] publish and subscribe
R language usarrests dataset visualization
云服务器中安装mysql(2022版)
启牛送的券商账户是安全的吗?启牛提供的券商账户是真的?