当前位置:网站首页>[redis] cluster and common errors
[redis] cluster and common errors
2022-06-22 21:10:00 【fate _ zore】
Redis6 colony
problem
Not enough capacity ,redis How to expand ?
Concurrent write operations , redis How to apportion ?
in addition , A master-slave mode , Pass on mode , Host down , Lead to ip The address has changed , The corresponding host address needs to be modified for configuration in the application 、 Port and other information .
Previously, it was solved by proxy host , however redis3.0 The solution . That is, decentralized cluster configuration .
brief introduction
Redis The cluster has realized to Redis Horizontal expansion of , Start now N individual redis node , The entire database is distributed and stored here N A node in the , Each node stores the total data 1/N.
Redis Clusters are partitioned (partition) To provide a certain degree of usability (availability): Even if some nodes in the cluster fail or fail to communicate , The cluster can also continue to process command requests .
To configure
Configure basic information
Turn on daemonize yes
Pid File name
Designated port
Log File name
Dump.rdb name
Appendonly Turn it off or change the name
redis cluster Configuration modification
cluster-enabled yes Open cluster mode
cluster-config-file nodes-6379.conf Set the node profile name
cluster-node-timeout 15000 Set the node loss time , Beyond that time ( millisecond ), The cluster automatically switches between master and slave .
include /home/bigdata/redis.conf
port 6379
pidfile "/var/run/redis_6379.pid"
dbfilename "dump6379.rdb"
dir "/home/bigdata/redis_cluster"
logfile "/home/bigdata/redis_cluster/redis_err_6379.log"
cluster-enabled yes
cluster-config-file nodes-6379.conf
cluster-node-timeout 15000
Start all services
Combine six nodes into a cluster
Before combination , Please make sure that all redis After the instance is started ,nodes-xxxx.conf All files are generated normally .
- Fit cd /opt/redis-6.2.1/src
- edis-cli --cluster create --cluster-replicas 1 192.168.150.111:6379 192.168.150.111:6380 192.168.150.111:6381 192.168.150.111:6389 192.168.150.111:6390 192.168.150.111:6391
Use cluster policy to connect , The setting data will be automatically switched to the corresponding write host
adopt cluster nodes Command to view cluster information
Node allocation
A cluster must have at least three master nodes .
Options --cluster-replicas 1 Indicates that we want to create a slave node for each master node in the cluster .
The allocation principle tries to ensure that each master database runs on different servers IP Address , Each slave library and master library are not in one IP Address .
slots
[OK] All nodes agree about slots configuration.
>>> Check for open slots…
>>> Check slots coverage…
[OK] All 16384 slots covered.
One Redis The cluster contains 16384 Slots (hash slot), Every key in the database belongs here 16384 One of the slots ,
The cluster uses the formula CRC16(key) % 16384 To calculate the key key Which slot does it belong to , among CRC16(key) Statements are used to evaluate keys key Of CRC16 The checksum .
Each node in the cluster is responsible for processing a portion of the slots . for instance , If a cluster can have a master node , among :
node A Responsible for handling 0 No. to 5460 Slot number .
node B Responsible for handling 5461 No. to 10922 Slot number .
node C Responsible for handling 10923 No. to 16383 Slot number .
Enter values in the cluster
stay redis-cli Every time you enter 、 Query key values ,redis The accountant worked out the key Slot that should be sent , If it is not the slot of the server corresponding to the client ,redis Will report a mistake , And inform those who should go redis Instance address and port .
redis-cli The client provides –c Parameter to implement automatic redirection .
Such as redis-cli -c –p 6379 After logging in , Re entry 、 Query key value pairs can be redirected automatically .
Not in one slot Key values under , Can't use mget,mset Wait for multi key operation .

Can pass {} To define the concept of a group , So that key in {} Key value pairs with the same content in a slot In the middle

Query the values in the cluster
CLUSTER GETKEYSINSLOT return count individual slot Key in groove .

Fault recovery
If the master node goes offline , Whether the slave node can be automatically promoted to the master node ? Be careful :15**** Second timeout Meeting
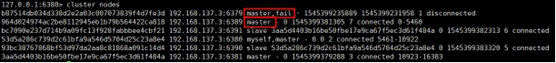
After the primary node is restored , What about the master-slave relationship ? When the master node comes back, it becomes a slave .
If all the master and slave nodes in a certain slot are down ,redis Whether the service can continue ?
If the master and slave of a certain slot hang up , and cluster-require-full-coverage by yes , that , The whole cluster is down
If the master and slave of a certain slot hang up , and cluster-require-full-coverage by no , that , None of the slot data is available , Can't store .
redis.conf Parameters in cluster-require-full-coverage
Clustered jedis
Even if the host is not connected , The cluster automatically switches host storage . Host write , Read from machine .
Decentralized master-slave cluster . No matter which host the data is written from , Data can be read on other hosts .
public class JedisClusterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<HostAndPort>set =new HashSet<HostAndPort>();
set.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.31.211",6379));
JedisCluster jedisCluster=new JedisCluster(set);
jedisCluster.set("k1", "v1");
System.out.println(jedisCluster.get("k1"));
}
}
Pros and
advantage
- Realize capacity expansion
- Apportionment pressure
- No central configuration is relatively simple
Inferiority
- Multi key operation is not supported
- Multibond Redis Transactions are not supported .lua Scripts are not supported
- Due to the late emergence of the cluster scheme , Many companies have adopted other clustering schemes , The proxy or client partition scheme wants to migrate to redis cluster, Overall migration is required rather than gradual transition , High complexity .
Redis6 Apply problem solving
Cache penetration

key The corresponding data does not exist in the data source , Every time for this key The request for could not be fetched from the cache , Requests are pushed to the data source , That could crush the data source . For example, use a non-existent user id Get user information , No matter cache or database , If hackers exploit this vulnerability, they may crush the database .
Solution
There must be no data that cannot be cached or queried , Because the cache is written passively on Miss , And for the sake of fault tolerance , If no data can be found from the storage tier, it will not be written to the cache , This will cause the non-existent data to be queried by the storage layer every time it is requested , It loses the meaning of caching .
- ** Cache null values :** If the data returned by a query is empty ( Whether the data doesn't exist or not ), We still put this empty result (null) Cache , Setting the expiration time for empty results can be very short , Up to five minutes
- ** Set up an accessible list ( White list ):** Use bitmaps Type defines a list of accessible , list id As bitmaps The offset , Every visit and bitmap Inside id Compare , If you visit id be not in bitmaps Inside , To intercept , Access not allowed
- Use of Blum filter :( The bloon filter (Bloom Filter) yes 1970 Proposed by bron in . It's actually a very long binary vector ( Bitmap ) And a series of random mapping functions ( hash function ). The bloom filter can be used to retrieve whether an element is in a collection . Its advantage is that the space efficiency and query time are far more than the general algorithm , The disadvantage is that it has certain error recognition rate and deletion difficulty .) Hash all possible data to a large enough bitmaps in , A certain nonexistent data will be This bitmaps Intercept , Thus, the query pressure on the underlying storage system is avoided .
- Real-time monitoring : If I found Redis It's starting to drop , Need to check access objects and data , Cooperate with operation and maintenance personnel , You can set up a blacklist to restrict services
Cache breakdown
key The corresponding data exists , But in redis Medium overdue , At this time, if a large number of concurrent requests come , These requests usually find that the cache is expired from the back end DB Load data and reset to cache , At this time, a large number of concurrent requests may instantly put the back end DB Overwhelmed .
Solution
key It may be accessed at some point in time with super high concurrency , It's a very “ hotspot ” The data of . This is the time , A question needs to be considered : The cache is “ breakdown ” The problem of .
Preset hot data : stay redis Before the summit visit , Put some hot data into redis Inside , Increase the hot data key Duration
** Real time adjustments :** What data is hot on the spot , Real time adjustments key The expiration time of
Using locks :
- When the cache fails ( Judge that the value is empty ), Not immediately load db.
- First, use some operations of the cache tool with the return value of the successful operation ( such as Redis Of SETNX)(1) Go to set One mutex key
- When the operation returns success , Proceed again load db The operation of , And reset the cache , Finally delete mutex key;
- When the operation returns failure , Prove that there are threads in load db, The current thread sleeps for a period of time and then retries the whole get Caching method .

Cache avalanche
key The corresponding data exists , But in redis Medium overdue , At this time, if a large number of concurrent requests come , These requests usually find that the cache is expired from the back end DB Load data and reset to cache , At this time, a large number of concurrent requests may instantly put the back end DB Overwhelmed .
The difference between cache avalanche and cache breakdown is that there are many key cache , The former is a certain key Normal visit

Solution
The avalanche effect of cache failure has a terrible impact on the underlying system !
- ** Building a multi-level cache architecture :**nginx cache + redis cache + Other caches (ehcache etc. )
- Use locks or queues : Lock or queue to ensure that there will not be a large number of threads to read and write the database at one time , So as to avoid a large number of concurrent requests falling on the underlying storage system in case of failure . Not for high concurrency
- ** Set expiration flag to update cache :** Record whether the cache data is out of date ( Set the lead amount ), If it expires, it will trigger another thread to update the actual situation in the background key The cache of .
- Decentralized cache expiration time : For example, we can add a random value to the original failure time , such as 1-5 Minutes at random , In this way, the repetition rate of each cache expiration time will be reduced , It's hard to trigger a collective failure .
Distributed lock
With the needs of business development , After the original single machine deployment system is evolved into a distributed cluster system , Due to multithreading in distributed system 、 Multi process and distributed on different machines , This will invalidate the concurrent control lock policy in the case of the original stand-alone deployment , pure Java API It doesn't provide the ability of distributed locks . In order to solve this problem, we need a kind of cross JVM To control the access of shared resources , This is the problem of distributed lock !
The mainstream implementation of distributed lock :
Implementation of distributed lock based on Database
Cache based (Redis etc. )
be based on Zookeeper
Every distributed lock solution has its own advantages and disadvantages :
performance :redis The highest
reliability :zookeeper The highest
here , We are based on redis Implement distributed locks .
redis Implement distributed locks
redis: command
set sku:1:info “OK” NX PX 10000
EX second : Set the expiration time of the key to second second . SET key value EX second The effect is equivalent to SETEX key second value .
PX millisecond : Set the expiration time of the key to millisecond millisecond . SET key value PX millisecond The effect is equivalent to PSETEX key millisecond value .
NX : Only if the bond doesn't exist , To set the key . SET key value NX The effect is equivalent to SETNX key value .
XX : Only if the bond already exists , To set the key .

Multiple clients acquire locks at the same time (setnx)
To be successful , Execute business logic { from db get data , Put into cache }, Execute complete release lock (del)
Other clients wait to try again
java Code
@GetMapping("testLock")
public void testLock(){
//1 Get the lock ,setne
Boolean lock = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent("lock", "111");
//2 Lock acquired successfully 、 Inquire about num Value
if(lock){
Object value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("num");
//2.1 Judge num It's empty return
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(value)){
return;
}
//2.2 If it's worth something, it turns into int
int num = Integer.parseInt(value+"");
//2.3 hold redis Of num Add 1
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("num", ++num);
//2.4 Release the lock ,del
redisTemplate.delete("lock");
}else{
//3 Lock acquisition failed 、 every other 0.1 Second to get
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
testLock();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
problem :setnx Just got the lock , Exception in business logic , Causes the lock to fail to release
solve : Set expiration time , Automatic release lock .
Optimize the lock expiration time
There are two ways to set the expiration time :
The first thing to think about is through expire Set expiration time ( Lacking atomicity : If in setnx and expire There is an exception between , The lock doesn't release either )
stay set Specify the expiration time when ( recommend )

Residual problems
scene : If the execution time of business logic is 7s. The execution process is as follows
\1. index1 Business logic is not finished ,3 Seconds later, the lock is released automatically .
\2. index2 Get lock , Execute business logic ,3 Seconds later, the lock is released automatically .
\3. index3 Get lock , Execute business logic
\4. index1 Business logic execution complete , Start calling del Release the lock , What's released is index3 Lock of , Lead to index3 Our business only performs 1s I'll be released by someone else .
In the end, it's the case of no lock .
solve :setnx When you get the lock , Set a specified unique value ( for example :uuid); Get this value before releasing , Judge if it's your own lock
Optimize it UUID Error proofing


problem : Deletion operation lacks atomicity .
Optimize it LUA Scripts guarantee atomicity of deletion
@GetMapping("testLockLua")
public void testLockLua() {
//1 Make a statement uuid , Will be as a value Put in our key In the corresponding value
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
//2 Define a lock :lua Scripts can use the same lock , To delete !
String skuId = "25"; // visit skuId by 25 No 100008348542
String locKey = "lock:" + skuId; // What's locked is the data of each commodity
// 3 Get the lock
Boolean lock = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(locKey, uuid, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// The first one is : lock Don't write any code between the expiration time .
// redisTemplate.expire("lock",10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);// Set expiration time
// If true
if (lock) {
// The business logic of execution begins
// Get the num data
Object value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("num");
// If it's empty, return to
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(value)) {
return;
}
// Not empty If something goes wrong here ! that delete The deletion failed ! That is to say, the lock always exists !
int num = Integer.parseInt(value + "");
// send num Every time +1 Put into cache
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("num", String.valueOf(++num));
/* Use lua Script to lock */
// Definition lua Script
String script = "if redis.call('get', KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then return redis.call('del', KEYS[1]) else return 0 end";
// Use redis perform lua perform
DefaultRedisScript<Long> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>();
redisScript.setScriptText(script);
// Set the return value type by Long
// Because when you delete judgment , Back to 0, Encapsulate it as a data type . If it's not encapsulated, it will return by default String type ,
// So return the string and 0 There will be mistakes .
redisScript.setResultType(Long.class);
// The first is if script Script , The second thing that needs to be judged key, The third is key The corresponding value .
redisTemplate.execute(redisScript, Arrays.asList(locKey), uuid);
} else {
// Other threads wait
try {
// sleep
Thread.sleep(1000);
// When I wake up , Calling method .
testLockLua();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Numpy learning notes (6) -- sum() function
[the penultimate node in the linked list]
百家讲坛 黄帝内经(第一部)
R 语言USArrests 数据集可视化
NBA playoff match chart
软件测试——测试用例设计&测试分类详解
【奇葩需求之记录对象不同的日志】
苹果CoreFoundation源代码
53页智慧校园智能化系统设计方案(附下载)
[observation] innovation in the software industry has entered a "new cycle". How can we make a new start in the changing situation?
Fluent system architecture
Pytorch's model saving, loading and continuing training
[redis]配置文件
【876. 链表的中间结点】
华为云发布拉美互联网战略
【观察】软件行业创新进入“新周期”,如何在变局中开新局?
MySql给某列字段添加(追加)前缀后缀
【142. 环形链表 II】
Code to Image Converter | 代码生成漂亮图片工具
pytorch的模型保存加载和继续训练
![[138. copy linked list with random pointer]](/img/87/b2f1d224cfc627b4311208ccb9e274.png)





![[142. circular linked list II]](/img/c1/f3a0b863286e9eeda0ae4021420912.png)


