当前位置:网站首页>[data mining] final review (sample questions + a few knowledge points)
[data mining] final review (sample questions + a few knowledge points)
2022-06-24 12:52:00 【Betula alnoides forest】
Catalog
- Chapter one The introduction
- Chapter two Data processing basis
- The third chapter Classification and regression
- Chapter four Clustering analysis
- 1、 Completion
- 2、 Judgment questions
- (1) One pass clustering algorithm can identify clusters from arbitrary shapes .( )
- (2)DBSCAN It is relatively noise resistant , And can recognize clusters of any shape and size .( )
- (3) In cluster analysis , The greater the similarity within the cluster , The greater the difference between clusters , The worse the clustering effect .( )
- 3、 Calculation questions
- 4、 Typical clustering methods
- 5、 Clustering algorithm evaluation
- The fifth chapter Correlation analysis
- Chapter six Outlier mining
Chapter one The introduction
1、 Completion
(1) From a technical point of view , Data mining is ( ). From the commercial level , Data mining is ( ).
answer : It's from a lot of 、 Not completely 、 Noisy 、 Vague 、 In random practical application data , Extraction is implicit in 、 What people don't know in advance 、 But potentially useful information .
A business information processing technology , Its main feature is to extract a large number of business data 、 transformation 、 Analysis and modeling processing , Extract key data to assist business decision-making .
(2) The information obtained from data mining has ( )、 Three characteristics of effectiveness and practicality .
answer : Previously unknown .
2、 The application of data mining in life scene


3、 Distinguish between data mining and query
Data mining and traditional data analysis methods ( Such as : Inquire about 、 report form 、 Online application analysis, etc ) There are essential differences . Data mining is to mine information and data without a clear premise Discover knowledge .
example :
Finding a person's name in a sentence is data mining , Finding people in the table is a query
Chapter two Data processing basis
1、 Completion
(1) The data is ( ), Attributes are divided into ( ).
answer : A collection of data objects and their attributes ; Nominal and ordinal attributes 、 Interval and ratio attributes .
2、 Calculation questions
(1) Calculate similarity measure
The scope given by the teacher :
Distance metric ( Manhattan 、 European style ):
Similarity coefficient ( Cosine similarity ):
The similarity of binary attributes ( Number of simple matching similarity relations d、s)
Jaccard coefficient :
Example 1:
answer :
Example 2:
answer :

(2) Calculation of statistical characteristics of data
Note the formula :
Arithmetic mean
Weighted arithmetic mean
trimmed mean : Discard high-end and low-end (p/2)% The data of , Then calculate the average .
Median
Four percentile
Number of columns in :(max+min)/2
The number of

answer :
3、 Q & A questions
(1) Why data preprocessing ? List three common pretreatment techniques ?
answer : The purpose of data preprocessing : Clean, provide 、 concise 、 Accurate data , Improve mining efficiency and accuracy .
Pretreatment technology : Data cleaning 、 Data integration 、 Data transformation 、 Data reduction 、 Data discretization .
① Data cleaning : The data is incomplete 、 Noisy 、 inconsistent ( Fill in missing values 、 Remove noise and identify discrete points 、 Correct inconsistent values in the data )
② Data integration ( polymerization ): Aggregate data , Data from two or more data sources , Stored in a consistent data storage device .
③ Data transformation : Transform data into a form suitable for mining .( smooth 、 Gather 、 Data generalization 、 Normalization 、 Data discretization )
④ Data reduction : Include sampling 、 feature selection .
4、 Noise data smoothing method
(1) Separate boxes :
First step : The data is divided into n Equal depth boxes
The second step : Use Average or boundary smooth
The deeper the box 、 The wider it is , The better the smoothing effect .
(2) clustering : Delete outliers
(3) Return to : Find the right function
5、 Data transformation
A、 Normalization
Normalization is to convert the original measurement value into a dimensionless value .( To scale , Map to a new value field )
(1) Minimum - Maximum normalization ( Turn into 【0,1】 Within the scope of )
(2)z-score Normalization ( Standardization of probability theory )
(3) Standardization of decimal scale ( Turn into ” A few tenths ×10 Of n Power “ The format of )
B、 Characteristic structure
A new feature set from the original feature ship .
C、 Data discretization
Replace the values of continuous attributes with classification value tags . It is divided into supervised and unsupervised discretization .
Unsupervised discrete method :(1) Equal width (2) Equal frequency (3) Based on cluster analysis .
Supervised discrete method :(1) Based on entropy : The top-down
6、 Data reduction
A、 Sampling
Number of compressed rows
There are three sampling methods . Put it back 、 No put back 、 layered (p36)
B、 feature selection
Number of compressed Columns
Ideal feature subset : Each valuable non target feature should be strongly related to the target feature , But not the uncorrelation or weak correlation between target features .
The third chapter Classification and regression
1、 Completion
(1) Methods for evaluating the accuracy of classification models include :( )、( ) And random subsampling .
answer : Keep the method 、k- Crossover verification .
2、 Judgment questions
(1) Regression prediction outputs continuous values ( )
answer :√
Classification prediction output : Discrete category values ( Predict a class ). Regression prediction outputs continuous values .
(2)KNN Classification methods need to be modeled in advance .( )
answer :×
KNN It is a passive learning method , No prior modeling . Basic steps :
1 Calculate distance . Given the test object , Calculate its distance from each object in the training set ;
2 Find a neighbor . Circle the nearest k Training object , As a close neighbor of the test object .
3 Make a classification . According to this k The main categories of neighbors , To classify test objects .
(3)AdaBoost The algorithm is a kind of algorithm that gathers multiple classifiers to improve the accuracy of classification .( )
answer :√
3、 Computer problems
The formula :
Information entropy :
Information gain :
Split information :
Information gain rate :
Gini coefficient :
Gini Coefficient gain :
(1) use ID3 Algorithm , Describe the decision tree building process



(2) Given a weather data set , Seek information gain , Information gain rate ,Gini Coefficient gain .

(1) step :
Calculation The entropy of a data set E(S)
Calculation basis temperature The division of The entropy of a subset E(Si)
Calculation E temperature(S)= (|Si|/|S|) *E(Si) The sum of
Calculation Information gain Gain(S,temperature)=E(S)-E temperature(S)


(3)KNN Book examples


4、 Q & A questions
(1) Write the Bayes formula , Please give the steps of naive Bayesian method .
answer : The formula :P(A|B) = P(B|A)*P(A) / P(B)
step :
( The official answer is as follows , I know every word by looking at it , I can't understand it when I put it together ...)
- First, according to the given sample with unknown class label , Calculate the posterior probabilities of the class labels .
- According to the Bayes formula , The calculation of the posterior probability is transformed into the probability product of the conditional probability of each attribute of the sample and the prior probability , These two can be easily calculated from the given conditions .
- Among all kinds of calculation results, the one with the greatest probability , Classify the sample into this category .
( Simplified edition )
- First calculate Probability of each classification ;
- Then calculate the prediction data The probability of each feature in each classification dimension ;
- Calculate according to the classification dimension : Classification probability * Probability of each characteristic ;
- elect step 3 The biggest result in It's what you want ;
(2) Naive Bayes “ simple ” What does that mean? ? Briefly introduce the main idea of naive Bayes .

Chapter four Clustering analysis
1、 Completion
(1) Clustering algorithms are divided into partition methods 、 Hierarchical approach 、 Density based approach 、 Graph based approach 、 A model-based approach , among k-means Belong to ( ) Method ,DBSCAN Belong to ( ) Method .
answer : Divide ; Based on density .
2、 Judgment questions
(1) One pass clustering algorithm can identify clusters from arbitrary shapes .( )
answer :×
The one pass algorithm is to divide the data into hyperspheres of almost the same size , It can not be used to find non convex clusters .
(2)DBSCAN It is relatively noise resistant , And can recognize clusters of any shape and size .( )
answer :√
DBSCAN The algorithm is density based
(3) In cluster analysis , The greater the similarity within the cluster , The greater the difference between clusters , The worse the clustering effect .( )
answer :×
A good clustering method produces high-quality clusters : High intra cluster similarity , Low inter cluster similarity .
3、 Calculation questions
(1)k-means Algorithm
Algorithm :

subject :

answer :
4、 Typical clustering methods
(1) Division method :k-means、 One trip algorithm
(2) Hierarchical approach : condensation ( Bottom up )、 Split hierarchical clustering method ( The top-down )、CURE、BIRCH
(3) Density based approach :DBSCAN
(4) Graph based clustering algorithm :Chameleon、SNN
(5) A model-based approach
K-means Deficiency
(1) The number of clusters is given in advance
(2) The selection of initial values is highly dependent , Algorithms often fall into local optima
(3) The algorithm needs to constantly adjust the sample classification
(4) Sensitive to noise and outliers
(5) Non convex clusters cannot be found , Or clusters of different sizes or densities
(6) Data sets that can only be used for numeric attributes
Hierarchical clustering algorithm
The top-down 、 From the bottom up .
Three improved Agglomerative hierarchical clustering ( Bottom up ) Method : BIRCH、ROCK、CURE.
Density based clustering algorithm DBSCAN
According to the density of the points , There are three types of points :
(1) emphasis : A point inside a dense area
(2) Boundary point : Points on the edge of dense areas
(3) Noise or background points : Points in sparse regions
Direct density up to :p stay q Of Eps In the neighborhood
Density can reach : Yes Eps Connections within the range , Pay attention to directivity !
Density is connected :p and q from O About Eps and MinPts Density can be reached
DBSCAN Textbook examples :
Algorithm :
subject :



Graph based clustering algorithm Chameleon
Absolute connectivity EC (EC The bigger it is , The higher the relevance , It is better to merge )
Relative connectivity RI (RI The bigger it is , The connection between the two classes is almost the same as the connection within the two classes , Better connection )

Absolute tightness S
Relative tightness RC

5、 Clustering algorithm evaluation
(1) Internal quality evaluation criteria
The internal quality evaluation standard calculates the average similarity within the cluster 、 Average similarity between clusters 、 The overall similarity is used to evaluate the clustering effect .
for example :
CH indicators :

CH The bigger it is ( namely traceB increase ,traceW Reduce ), The greater the difference in the mean value of each cluster , The better the clustering effect is .
traceW min = 0, The points in a class coincide , The effect is good .
(2) External quality evaluation criteria
The external quality evaluation standard is based on an existing manual classification data set ( You already know the category of each object ) To evaluate .
The fifth chapter Correlation analysis
1、 Completion
(1) Association rule mining algorithm can be divided into two steps :①( ),②( ).
answer :① Generate frequent itemsets : Find all itemsets that satisfy the minimum support threshold , Frequent itemsets .
② Generate rules : Extract rules larger than the confidence threshold from the set of frequent items found in the previous step , That is, strong rules .
2、 Judgment questions
(1) If itemset X It's a frequent itemset , be X A subset of must be a frequent itemset ( )
answer :√
(2) The itemsets with higher support must have higher confidence ( )
answer :×
3、 Calculation questions
Aprior Algorithm :

(1) The known shopping basket data is shown in the table on the lower right , Please complete the following tasks

answer :( Later, during the inspection, it was found that ,2- Itemset is missing { bread , egg }:1,{ beer , egg }:1,{ diapers , egg }:1, But it has little effect on the final result .)
(2)
support({ bread }->{ diapers })= 3/5
confidence({ bread }->{ diapers })= 3/4 <80%
So it is not a strong association rule .
4、 Application scenarios of correlation analysis
(1) Mining store sales data , Find the connection between commodities , Help stores to promote sales and put shelves .
(2) Mining medical diagnostic data , The association between certain symptoms and certain diseases can be found , Diagnose diseases for doctors
(3) Web Mining : Reveal interesting connections between different web pages .
5、 The concept of association analysis
(1) Itemsets : A contain k An itemset of data items is called k- Itemsets .
(2) Frequent itemsets : If the support of an itemset Greater than or equal to Some threshold , Is called frequent itemset .
(3) Support count : The number of occurrences of an itemset , That is, the number of transactions in the entire transaction data set .
(4) Association rules : Form like X->Y The implication of
(5) Support :
(6) Degree of confidence :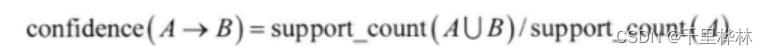
(7) Strong association rules : Association rules that are greater than the minimum support threshold and the minimum confidence threshold .
6、Apriori Algorithm
Apriori nature : Any subset of a frequent itemset should also be a frequent itemset .
inference : If a itemset is infrequent , Then its superset is also infrequent .
The algorithm contains Join and prune Two steps .
7、 correlation analysis
(1) Promotion (lift). Its value is greater than 1, There is a positive correlation between the two ; Less than 1, negative correlation ; be equal to 1, There's no correlation .
(2) Interest factor
(3) The correlation coefficient
(4) Cosine measure
8、 Count of itemsets
1、 Given k The item , Altogether 2k-1 Itemsets .
2、 frequent k Itemset has 2k-2 Individual call candidate association rules ( remove L->ᴓ and ᴓ->L)
Chapter six Outlier mining
1、 Judgment questions
(1) If an object does not strongly belong to any cluster , Then the object is an outlier based on clustering ( ).
answer :√
2、 Calculation questions
(1) Given a two-dimensional dataset , The coordinates of the points are as follows , take k=3, utilize k-means Algorithm for finding points p14 and p16 The outlier factor of OF1, Which point is more likely to be an outlier ?

answer :

3、 Q & A questions
(1) What are outliers ? May I ask whether the outliers detected by the outlier mining algorithm must correspond to the actual abnormal behavior ? If it is , Please give an explanation ; If not , Please give a counterexample .
answer : Outliers are data sets Data that deviates from most of the data , It makes people doubt the deviation of these data Not by random factors produce , It is Arising from different mechanisms .
In a general way , Outliers may correspond to actual abnormal behavior . The mechanism of outliers is uncertain , Outlier mining algorithm detected “ outliers ” Whether it corresponds to actual abnormal behavior , It is not explained by outlier mining algorithm 、 Interpreted , Only by Domain experts to explain .
Outliers may be measurements 、 Input error or system operation error , It may also be determined by the inherent characteristics of the data , Or caused by the abnormal behavior of the object .
for example : The age of one is -999, It may be because the program handles the default data 、 Set the default value . The salary of a company's top management is significantly higher than that of ordinary employees, which may become outlier data , But reasonable data . The cost of a home phone is charged by 200 From less than yuan to thousands of yuan , It may be caused by theft or other special reasons . The obvious high consumption of a credit card may be due to the theft of the card .
4、 Causes of outliers
(1) measurement 、 Input error or system operation error
(2) Determined by the intrinsic characteristics of data
(3) Caused by the abnormal behavior of the object
5、 Outlier mining needs to deal with 3 A question

6、 Statistical based methods
Identify data inconsistent with the model as outliers . If the probability distribution model of an object with respect to data has a low probability value , It is considered as an outlier .
The probability distribution model estimates the distribution parameters specified by the user , Created from data .
Quality control diagram


7、 Distance based approach
(1) spot x The outlier factor of :OF1 The bigger it is , spot x The more outlying .

Textbook examples : Calculation OF1


8、 Method based on relative density
(1) Local neighborhood density :
(2) Relative density : Outliers are detected by comparing the density of an object with the average density of objects in its neighborhood .

Textbook examples : Calculation OF3


9、 Clustering based methods
Detection methods for outliers of dynamic and static data :
10、 Evaluation of outlier mining methods
Mixed matrix :
Two indicators of the accuracy of outlier mining methods :
(1) Detection rate
(2) The rate of false positives 
That's all .
END
边栏推荐
- Kubernetes practical skill: entering container netns
- Codereview tool chain for micro medicine
- Istio FAQ: istio init crash
- Who said that "programmers are useless without computers? The big brother around me disagrees! It's true
- 使用 Abp.Zero 搭建第三方登录模块(一):原理篇
- Reading notes of returning to hometown
- On the value foam of digital copyright works from the controversial nature of "Meng Hua Lu"
- go Cobra命令行工具入门
- 99% of the students can't write good code because of this problem!
- 一文讲透植物内生菌研究怎么做 | 微生物专题
猜你喜欢

MySQL 外键影响

手把手教你用AirtestIDE无线连接手机!

Babbitt | metauniverse daily must read: 618 scores have been announced. How much contribution has the digital collection made behind this satisfactory answer

Getting started with the go Cobra command line tool

WPF从零到1教程详解,适合新手上路

使用 Abp.Zero 搭建第三方登录模块(一):原理篇

MySQL foreign key impact

【2022国赛模拟】摆(bigben)——行列式、杜教筛

【数据挖掘】期末复习(样卷题目+少量知识点)

A hero's note stirred up a thousand waves across 10 countries, and the first-line big factories sent people here- Gwei 2022 Singapore
随机推荐
简述聚类分析
IIS WCF 808 port service access exception
Common special characters in JS and TS
Codereview tool chain for micro medicine
Continuous testing | making testing more free: practicing automated execution of use cases in coding
[programming navigation] the practical code summarized by foreign great God, learned in 30 seconds!
A scheme for crawlers to collect public opinion data
生成 4维 的 气压温度的 nc文件,之后进行代码读取(提供代码)
Kubernetes log viewer - kubetail
Tencent security monthly report - zero trust development trend forum, digital Expo Technology Award, Mercedes Benz security research results
The pod is evicted due to insufficient disk space of tke node
A hero's note stirred up a thousand waves across 10 countries, and the first-line big factories sent people here- Gwei 2022 Singapore
Automatic reconstruction of pod after modifying resource object
pipeline groovy
Getting started with the lvgl Library - colors and images
[5 minutes to play lighthouse] create an immersive markdown writing environment
SMS SMS
手把手教你用AirtestIDE无线连接手机!
WPF from zero to 1 tutorial details, suitable for novices on the road
Attack Science: ARP attack