当前位置:网站首页>Prince language under insect date category
Prince language under insect date category
2022-06-23 04:18:00 【Hua Weiyun】
Fix it bug
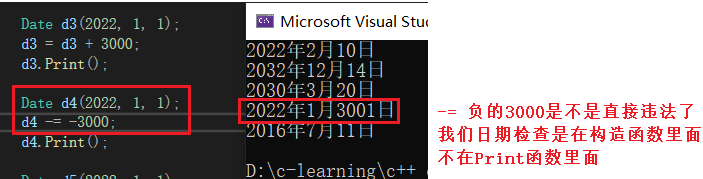
if -= If the date inside is negative
== Sometimes we need to consider that there are negative numbers in the date ==
== So we need to change the code , need += Code for , Direct appropriation ==
== Reuse is enough ==
// The date minus the number of days is assigned back at the same time Date& Date::operator-=(const int& day){ // It is also illegal to exceed the number of days per month // Reuse += that will do if (day < 0) { *this += -day; } else { // Say nothing more , Subtract the days first _day -= day; // If it's not legal, wait until it's legal while (_day <= 0) { // First reduce the number of months _month--; // First judge whether the month is zero , If yes, it will be years of operation if (_month <= 0) { _year--; _month = 12; } // Then ask him to add the correct number of days in the month _day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month); } } return *this;}
if += If the date inside is negative
== alike += If there is a negative number in it, it is handled the same way ==
== So we also put -= Bring the code of ==
== In the same way, it can be reused ==
// Date plus days are assigned back at the same time Date& Date::operator+=(const int& day){ // Negative multiplexed -= Of if (day < 0) { *this -= -day; } else { // We don't care , Let's add the sky directly _day += day; // Then judge whether it is legal while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)) { // First, subtract the number of days in the current month _day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month); // Next month ++ _month++; // If the month has passed, it will be a year ++ if (_month > 12) { _year++; _month = 1; } } } return *this;}
Comparison operator
Greater than >
==d1 > d2==
// Compare // Greater than d1 > d2 convert to d1.operator>(&d1,d2)bool Date::operator>(const Date& d){ if (_year > d._year) { return true; } else if (_year == d._year) { if (_month > d._month) { return true; } else if(_month == d._month) { if (_day > d._day) return true; } } // It's not the case above false return false;}
be equal to ==
==d1 == d2==
// be equal to bool Date::operator==(const Date& d){ return _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day;}
Greater than or equal to >=
==d1 >= d2==
// Greater than or equal to bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d){ return *this > d || *this == d;}
Less than <
==d1 < d2==
// Less than bool Date::operator<(const Date& d){ return !(*this >= d);}
Less than or equal to <=
==d1 <= d2==
// Less than or equal to bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d){ return !(*this > d);}
It's not equal to !=
==d1 != d2==
// It's not equal to bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d){ return !(*this == d);}
Life is real
We have to think about whether it is meaningful to subtract a date from a date
Is the date minus the date the difference in days , How do you operate this
// Date minus date // By counting If the years decrease Month minus month means you can't find the actual number of days int Date::operator-(const Date& d){ // First, let's assume that the previous big Date max = *this; // So the back is small Date min = d; // A symbol mark int flag = 1; // If you are wrong, exchange if (max < min) { max = d; min = *this; flag = -1; } // When min And max The same time is the time to stop counting int count = 0; while (min != max) { min++; count++; } // When you come out, you return the count with the mark return count * flag;}
Code
Date.h
Date.h#pragma once#include <iostream>#include <assert.h>using std::cout;using std::cin;using std::endl;class Date{public: Date(int year = 0, int month = 1, int day = 1); void Print(); // Like deconstruction , Copy structure , Assignment overloading can be done without writing , Because the default generation is enough , // image Stack You need to write these three // Date plus Minus days Then assign values to the past at the same time Date& operator+=(const int& day); Date& operator-=(const int& day); // Date plus Minus days No assignment is required Date operator+(const int& day); Date operator-(const int& day); // Date before, after, plus Date& operator++(); Date& operator++(int); // Date before date after date minus Date& operator--(); Date& operator--(int); // Compare bool operator>(const Date& d); bool operator<(const Date& d); bool operator>=(const Date& d); bool operator<=(const Date& d); bool operator==(const Date& d); bool operator!=(const Date& d); // Date minus date int operator-(const Date& d);private: int _year; int _month; int _day;};
Date.cpp
Date.cpp#include "Date.h"inline int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){ // The array stores the number of days of each month in a normal year The corresponding subscript is month The element inside is heaven static int dayArray[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 }; // Days of the month int day = dayArray[month]; // Leap year is 4 Once a year, once a century, or once every 400 years if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0) { // Leap year's 2 Month is 29 God day = 29; } return day;}// Constructors Date::Date(int year, int month, int day){ // Check the validity of the date if (year > 0 && month > 0 && month <13 && day > 0 && day <= GetMonthDay(year,month)) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } else { cout << endl; cout << " Illegal date " << endl; cout << year << " year " << month << " month " << day << " Japan " << endl; }}// Date printing void Date::Print(){ cout << _year << " year " << _month << " month " << _day << " Japan " << endl;}// Date plus days are assigned back at the same time Date& Date::operator+=(const int& day){ // Negative multiplexed -= Of if (day < 0) { *this -= -day; } else { // We don't care , Let's add the sky directly _day += day; // Then judge whether it is legal while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)) { // First, subtract the number of days in the current month _day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month); // Next month ++ _month++; // If the month has passed, it will be a year ++ if (_month > 12) { _year++; _month = 1; } } } return *this;}// Date plus days Don't give it back Date Date::operator+(const int& day){ // First create a temporary object Copy the previous copy to him first Date ret(*this); // Reuse += ret += day; return ret;}//++d Date before ++ Converted to d.operator++(&d)Date& Date::operator++(){ // Returns the value after the operation *this += 1; return *this;}//d++ Post date ++ Converted to d.operator++(&d,0)// there int It's just space , You don't need to give arguments , Play the role of function overloading Date& Date::operator++(int){ // After ++ Returns the value before the operation // So you need to save a temporary object first Date tmp(*this); *this += 1; return tmp;}// The date minus the number of days is assigned back at the same time Date& Date::operator-=(const int& day){ // It is also illegal to exceed the number of days per month // Reuse += that will do if (day < 0) { *this += -day; } else { // Say nothing more , Subtract the days first _day -= day; // If it's not legal, wait until it's legal while (_day <= 0) { // First reduce the number of months _month--; // First judge whether the month is zero , If yes, it will be years of operation if (_month <= 0) { _year--; _month = 12; } // Then ask him to add the correct number of days in the month _day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month); } } return *this;}// Date minus days Don't give it back Date Date::operator-(const int& day){ Date ret(*this); //-= Reuse of ret -= day; return ret;}// Pre subtraction Date& Date::operator--(){ *this -= 1; return *this;}// Post subtraction Date& Date::operator--(int){ Date tmp(*this); *this -= 1; return tmp;}// Compare // Greater than d1 > d2 convert to d1.operator>(&d1,d2)bool Date::operator>(const Date& d){ if (_year > d._year) { return true; } else if (_year == d._year) { if (_month > d._month) { return true; } else if(_month == d._month) { if (_day > d._day) return true; } } // It's not the case above false return false;}// be equal to bool Date::operator==(const Date& d){ return _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day;}// Greater than or equal to bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d){ return *this > d || *this == d;}// Less than bool Date::operator<(const Date& d){ return !(*this >= d);}// Less than or equal to bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d){ return !(*this > d);}// It's not equal to bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d){ return !(*this == d);}// Date minus date // By counting If the years decrease Month minus month means you can't find the actual number of days int Date::operator-(const Date& d){ // First, let's assume that the previous big Date max = *this; // So the back is small Date min = d; // A symbol mark int flag = 1; // If you are wrong, exchange if (max < min) { max = d; min = *this; flag = -1; } // When min And max The same time is the time to stop counting int count = 0; while (min != max) { min++; count++; } // When you come out, you return the count with the mark return count * flag;}
test.cpp
test.cpp#include "Date.h"void test1(){ // In front of ++ And post ++ It's all done ++, The difference is that the return value is different Date d(2022, 1, 1); d ++; // After ++ return ++ Previous value d.Print(); ++d; // In front of ++ return ++ Later value d.Print();}void test2(){ // In front of -- And post -- It's all done --, The difference is that the return value is different Date d(2022, 1, 1); d--; // After -- return -- Previous value d.Print(); --d; // In front of -- return -- Later value d.Print();}void test3(){ Date d1(2022, 1, 2); Date d2(2022, 1, 2); cout << (d1 != d2) << endl; d2 -= 1; cout << (d1 != d2) << endl;}void test4(){ Date d1(2024, 1, 2); Date d2(2022, 5, 7); cout << d1 - d2 << endl; cout << d2 - d1 << endl;}int main(){ test1(); test2(); test3(); test4(); Date d(2022,1,1); d += -40; d.Print(); Date d2(2022, 1, 1); d2 += 4000; d2.Print(); Date d3(2022, 1, 1); d3 = d3 + 3000; d3.Print(); Date d4(2022, 1, 1); d4 -= -3000; d4.Print(); Date d5(2022, 1, 1); d5 = d5-2000; d5.Print(); return 0;}
边栏推荐
- 顺序表查找
- Efficient remote office experience | community essay solicitation
- JD cloud distributed database stardb won the "stability practice pioneer" of China Academy of information technology
- 京东云分布式数据库StarDB荣获中国信通院 “稳定性实践先锋”
- QMainWindow
- redisTemplate和cacheManager操作redis有什么不同
- 直接插入排序
- A summary of PostgreSQL data types. All the people are here
- Pytorch---使用Pytorch的预训练模型实现四种天气分类问题
- 靜態查找錶和靜態查找錶
猜你喜欢

Twitter与Shopify合作 将商家产品引入Twitter购物当中

Insert sort directly

Compilation, installation and global configuration section description of haproxy

x64dbg 基本使用技巧

直接插入排序

mysql常用指令

京东云分布式数据库StarDB荣获中国信通院 “稳定性实践先锋”

Full analysis of embedded software testing tool tpt18 update
软件项目管理 8.4.软件项目质量计划

MySQL common instructions
随机推荐
虫子 日期类 上 太子语言
Is LinkedList a one-way linked list or a two-way linked list?
直接插入排序
How can I realize video call and interactive live broadcast in a small program?
redisTemplate和cacheManager操作redis有什么不同
虫子 日期类 下 太子语言
会话和守护进程
mysql能不能在linux中使用
JD cloud distributed database stardb won the "stability practice pioneer" of China Academy of information technology
How to print array contents
AI 视频云 VS 窄带高清,谁是视频时代的宠儿
Pytorch---Pytorch进行自定义Dataset
仿360桌面悬浮球插件
城链科技董事长肖金伟:践行数据经济系国家战略,引领数字时代新消费发展!
Black horse PostgreSQL, why is it black in the end
SVG+JS智能家居监控网格布局
支持在 Kubernetes 运行,添加多种连接器,SeaTunnel 2.1.2 版本正式发布!
【LeetCode】23. 合并K个升序链表
[tcapulusdb knowledge base] [list table] example code of batch deleting data at specified location in the list
【LeetCode】翻转链表II