当前位置:网站首页>二叉树基础oj练习-
二叉树基础oj练习-
2022-07-23 05:44:00 【潜水少年请求出战】
二叉树
按照规则,二叉树的遍历有:前序/中序/后序的递归结构遍历:
前序遍历(Preorder Traversal 亦称先序遍历)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之前。
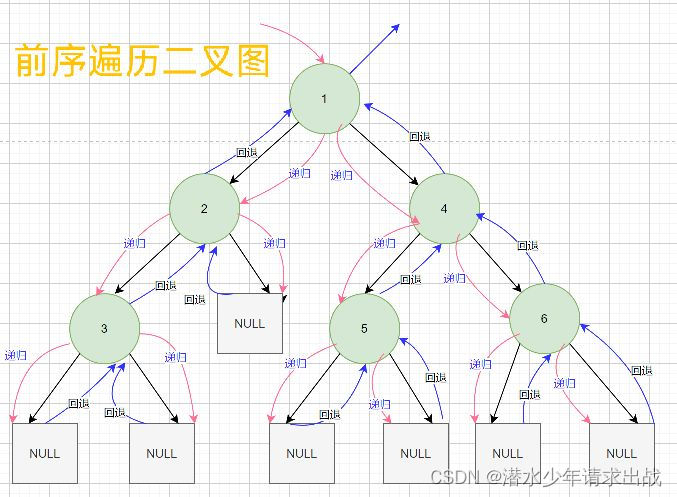
先序、中序与后序遍历大同小异
前序遍历结果:1 2 3 4 5 6
中序遍历结果:3 2 1 5 4 6
后序遍历结果:3 1 5 6 4 1中序遍历(Inorder Traversal)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之中(间)。
后序遍历(Postorder Traversal)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之后。
题目链接
1.链接: 单值二叉树
2.链接: 相同的树
3.链接: 对称二叉树
4.链接: 二叉树的前序遍历
5.链接: 二叉树的中序遍历
6.链接: 二叉树的后序遍历
解题思路:
1.遍历二叉树,并且每一个节点值都和根节点的值进行比对,如果不等于根节点的值,则不是单值树。
2.遍历二叉树,并且一个树节点的值与另一个书的结点值进行比对,如果不等于根节点的值,则不是相同的树。
3.先分成两个树后,遍历二叉树,并且一个树节点的值与另一个书的结点值进行比对,如果不等于根节点的值,则不是相同的树,即不是对称树。
代码:
1.单值树
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
bool BTd(struct TreeNode* root, int x)
{
if(root==NULL)
return true;
if(root->val != x)
return false;
return BTd(root->left, x) && BTd(root->right, x);
}
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return true;
int a = root->val;
return BTd(root, a);
}
2.相同的树
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q)
{
if(p==NULL && q==NULL)
return true;
if(p==NULL || q==NULL)
return false;
if(p->val != q->val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left, q->left) && isSameTree(p->right, q->right);
}
3.对称树
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q)
{
if(p==NULL && q==NULL)
return true;
if(p==NULL || q==NULL)
return false;
if(p->val != q->val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left, q->right) && isSameTree(p->right, q->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return true;
struct TreeNode* p=root->left;
struct TreeNode* q=root->right;
return isSameTree(p, q);
}
4. 二叉树的前序遍历
提醒:数组的下标我们要传地址,这样可以保证递归的时候用的是都一个i,(例如;根的左右结点,左结点用完后i自增后,不会影响右边结点的i。)
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
/** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */
int BTSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
return 1+BTSize(root->left)+BTSize(root->right);
}
void preorder(struct TreeNode* root, int* a, int* pi)
{
if(root==NULL)
return;
a[(*pi)++]=root->val;
preorder(root->left, a, pi);
preorder(root->right, a, pi);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize = BTSize(root);
int* a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize * 4);
if(a==NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
int i=0;
preorder(root, a, &i);
return a;
}
5二叉树的中序遍历
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
/** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */
int BTSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
return 1+BTSize(root->left)+BTSize(root->right);
}
void inorder(struct TreeNode* root, int* a, int* pi)
{
if(root==NULL)
return;
inorder(root->left, a, pi);
a[(*pi)++]=root->val;
inorder(root->right, a, pi);
}
int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize=BTSize(root);
int* a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize * 4);
if(a==NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
int i=0;
inorder(root, a, &i);
return a;
}
6. 二叉树的后序遍历
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
/** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */
int BTSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return root==NULL?0:1+BTSize(root->left)+BTSize(root->right);
}
void postorder(struct TreeNode* root, int* a, int* pi)
{
if(root==NULL)
return;
postorder(root->left, a, pi);
postorder(root->right, a, pi);
a[(*pi)++]=root->val;
}
int* postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize=BTSize(root);
int* a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize * 4);
if(a==NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail");
}
int i=0;
postorder(root, a, &i);
return a;
}
感想友友们的观看。
边栏推荐
- Interpretation of the paper: DNA enhancer sequence recognition transformer structure based on Bert and two-dimensional convolutional neural network
- LVGL8.1版本笔记
- 高等代数100道题及答案解析
- 【AUTOSAR CanDrive 2.了解通信Hoh、CanId与PduID的Mapping关系】
- 3.2daydayup举一反三:三天打鱼两天晒网式学习
- 快速排序的按区间的三个版本及优化--友友们不一定了解
- 博客搭建二:NexT主题相关设置beta
- Prometheus
- [AUTOSAR candrive 1. learn the function and structure of candrive]
- 【AUTOSAR DCM 1.模块简介(DSL,DSD,DSP)】
猜你喜欢

ARM架构与编程7--异常与中断(基于百问网ARM架构与编程教程视频)

ARM架构与编程2--ARM架构(基于百问网ARM架构与编程教程视频)
Blog Building III: comment system selection

利用or-tools来求解带容量限制的路径规划问题(CVRP)

高等代数100道题及答案解析

Interpretation of the paper: DNA enhancer sequence recognition transformer structure based on Bert and two-dimensional convolutional neural network

快速排序的按区间的三个版本及优化--友友们不一定了解

Data analysis of time series (I): main components

ARM架构与编程3--按键控制LED(基于百问网ARM架构与编程教程视频)
![[AUTOSAR CP general 1. how to read AUTOSAR official documents]](/img/3a/8521278a4bd21bb269603a52f07b0e.png)
[AUTOSAR CP general 1. how to read AUTOSAR official documents]
随机推荐
ARM架构与编程3--按键控制LED(基于百问网ARM架构与编程教程视频)
Review of basic principles of steel structure
高分子物理名词解释
二叉树的实现-c
Data mining scenario - false invoice
Using or tools to solve the path planning problem with capacity constraints (CVRP)
Data analysis (II)
线性规划之Google OR-Tools 简介与实战
1、经济学十大原理
[AUTOSAR CP general 1. how to read AUTOSAR official documents]
鋼結構基本原理複習
Data analysis of time series (III): decomposition of classical time series
求矩阵的鞍点及其对应的下标。
高电压技术复习资料
How to establish data analysis thinking
堆的实现与堆排序实现
Integrate all lvgl controls into one project (lvgl6.0 version)
Baidu Shen Shuo: focus on the scene, deeply cultivate the industry, and bring practical results to enterprise Digitalization
高电压技术-名词解释题
大小写字母转换
