当前位置:网站首页>Basic knowledge of assembly language (2) -debug
Basic knowledge of assembly language (2) -debug
2022-06-25 01:14:00 【Day-3】
Basic knowledge of
Machine language is difficult to understand , And the length is long .
Assembly instruction is a writing format that is easy to memorize .
register : Simply put, yes CPU A device that can store data in .
Assembly language consists of three instructions :
(1) Assembly instruction : Mnemonics for machine codes , There is a corresponding machine code .( The core )
(2) Pseudo instruction : No corresponding machine code , By compiler , No corresponding machine code .
(3) Other symbols : Such as +、-、*、/ etc. , Recognized by compiler , No corresponding machine code .
Memory chips can be divided into two categories in terms of read-write properties :RAM( Ram ) and ROM( read-only memory ).
register
Different CPU, The number of registers 、 The structure is different .
General registers :AX、BX、CX、DX.
Physical address : Physical address = Segment address × \times ×+ offset
X Hexadecimal digits move one digit to the left , amount to × \times ×X
The segment address is stored in four segment registers CS、DS、SS、ES.
CS:IP Access address instruction .
jmp Instructions , modify CSip.
Debug
I installed a xp Virtual machine to achieve access debug Function of .
(1) use R Command view 、 change CPU The contents of the register .
We already know that AX BX CX DX CS IP These six registers , Now take a look at them .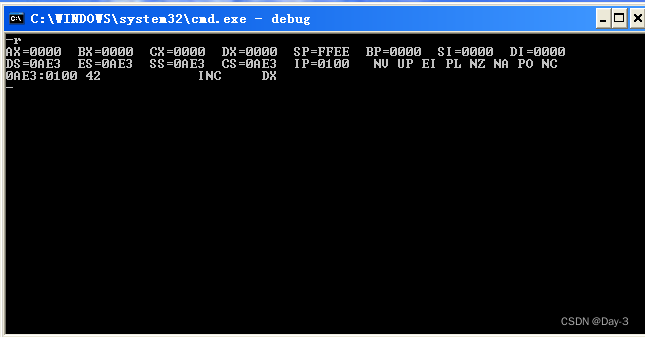
Modify the contents of the register .
In this figure ,CS:IP Point to )0AE3:0100, The machine code stored here is 40, The corresponding assembly instructions are INC AX;
have access to r Command to cs and ip Make changes .
(2) use debug Of d Command to view the contents of memory
If we want to know 10000H The content of , have access to “d Segment address : offset ” To view .
The data in the middle is the content stored in each address , On the left is the starting address of each line , On the right is the data in each memory unit that can be displayed ASCII code .
(3) use debug Of e Command to rewrite the contents of memory
-e Then add the address , Plus the number to be modified , Number customization 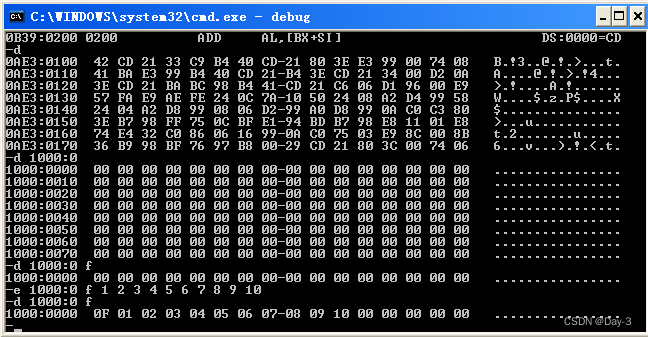
Or use -e You can also add addresses .
(4) use E Command to write machine code to memory , use U Command to view the meaning of machine code in memory , use T The command executes the machine code in memory .
-u Add address , Show assembly language ;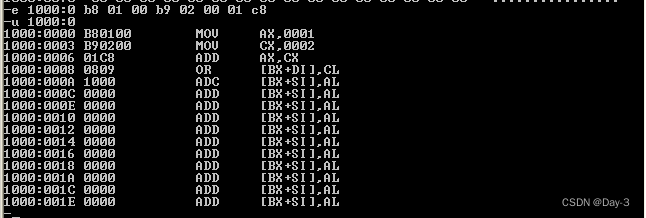
-t It can be done in one step .
边栏推荐
- Simulation questions and answers of the latest national fire facility operator (senior fire facility operator) in 2022
- Leetcode 1248. Statistics of "graceful subarray" (harm, suddenly found that it can only enumerate violently)
- 4 ans d'expérience de travail, 5 modes de communication Multi - thread ne peuvent pas être décrits, vous osez croire?
- Scala responsibility chain pattern
- Golang示例续期锁:Redis+Channel+sync.Mutex
- 2022年危险化学品经营单位安全管理人员考试试题及模拟考试
- Go语言运算符(第8课下)
- Preliminary understanding of qtoolbutton
- mysql查询时间戳转换成日期格式
- ImageView shows network pictures
猜你喜欢

QT (35) - operate excel qxlsx qaxobject

108 pages (40000 words) proposal for future apartment intelligent design platform project (version 2022)

汇编语言(2)基础知识-debug

Heavyweight: the domestic ide was released, developed by Alibaba, and is completely open source! (high performance + high customization)

Danish Technical University pioneered the application of quantum computing to power flow modeling of energy system

扎克伯格上手演示四款VR头显原型机,Meta透露元宇宙「家底」

2022 crane driver (limited to bridge crane) examination question bank simulated examination platform operation

Mobile security tool jar
最新QQ微信域名防红PHP程序源码+强制跳转打开

Bi SQL alias
随机推荐
Is it reliable to open an account on the flush with a mobile phone? Is there any hidden danger in this way
Bi-sql between
2022熔化焊接与热切割复训题库模拟考试平台操作
Scala trait construction mechanism
Scala trait exercise
移动安全工具-dex2jar
Danish Technical University pioneered the application of quantum computing to power flow modeling of energy system
Preliminary understanding of qtoolbutton
Scala IO read by character
腾讯云WeCity解决方案
Convolution and transpose convolution
[microservices sentinel] cluster link | microservices cluster environment construction
Première application de l'informatique quantique à la modélisation des flux de puissance dans les systèmes énergétiques à l'Université technique danoise
Simulation questions and answers of the latest national fire facility operator (senior fire facility operator) in 2022
汇编语言(4)函数传参
I brush the question I - copy the linked list with random pointer
ContentResolver,拿到手机短信内容
智能合约安全审计入门篇 —— delegatecall (2)
Introduction to bi-sql wildcards
QT (36) -rapidjson parsing nested JSON
