当前位置:网站首页>Several abnormal scenarios of things system
Several abnormal scenarios of things system
2022-06-22 23:49:00 【Kunlunbase Kunlun database】
background
The author recently reviewed multi version concurrency control (MVCC), Here is a brief summary of the relevant contents , Let's start with the isolation level .
Why talk about isolation , What is the scene ?
First , As a transaction system , If... Per unit time , Only one transaction is running , There is no isolation .
But actually , Real transaction system for actual production , In a unit time, multiple transactions are reading and writing resources at the same time .
Then there must be a concurrent read / write problem for the same resource , If you don't control it, you will make mistakes .
Therefore, the scenario discussed here is the data processing scenario in the multi transaction concurrent environment .
What problems can isolation solve ? Why should isolation be graded ?
What kind of transaction system is reasonable , Correct , Or it can accurately abstract the logic of the real world ? Satisfy ACID characteristic . Satisfy C To be realized I, Therefore, the purpose of isolation is to meet C.
However, it is necessary to answer why isolation should be graded , We must never be satisfied C The abnormal scene of must be disassembled for analysis .
Several abnormal scenarios of transaction system
1、Lost Update Update missing
What is update loss ? Two concurrent transactions T1、T2, Write to the same resource without any lock .T1 The result of the change is T2 Transaction tampering , This is the missing update . The point is that there is no means of isolation , Pure concurrency . This scenario , Can not appear in any reasonable application system , It is a fundamental major error .
2、Dirty Read Dirty reading
Definition of dirty reading , Is to read dirty data . First of all, let's clarify what dirty data is .
In a transaction system , Dirty data refers to uncommitted data , Intermediate state data . Then read the data that the transaction did not commit , Is to read dirty data , It's called dirty reading . You can use the following diagram to show :

This is from the Internet
There are two things T1 T2 At the same time ,T1 To change the a Value , When not submitted ,T2 It reads a By T1 Changed value . If at this time ,T1 Rolled back , that T2 Read the a Value , Is a value that is not considered to exist , Or read the intermediate state of the transaction , This is dirty reading .
We can simply use the method of locking to understand that : All transactions here are on access to critical resources , Only the read lock is added . It means , Other transactions can read uncommitted data at any time ( Because read locks are compatible ), But you cannot write data that has been modified ( Because read lock and write lock are incompatible ). So in the dirty reading scenario , The general default is that , The problem of missing updates has been solved .
3、Un-repeatable Read / Read skew Non repeatability / Reading partial order
Unrepeatable refers to the scene , Business T1 The data read is due to other transactions T2 After modification and submission , When T1 When reading again , There are different results . Let's first look at , The difference between unrepeatable and dirty reading is that : It can't be read repeatedly , All the results read , Are submitted data , The dirty data is invisible . You can use the following figure to show :

This is from the Internet
Through the above figure, we can simply understand , To achieve the difference between non repeatability and dirty reading , Is in T2 When a transaction prepares to write data , The read lock is upgraded to write lock , bring T1 Can't read T2 The data value before the transaction is committed , But when T2 After all the locks have been released ,T1 When reading data again , It is already a modified version .
4、Phantom Read Fantasy reading
Unreal reading refers to ,T1 Different points in time during the execution of a transaction , The result sets obtained with the same predicate conditions are different , This is limited to extra data , Not the data . What we need to make clear here is , The difference between unreal reading and unrepeatable reading mentioned above is : Under the unreal reading scene , There is no problem that can not be repeated , That is, the value of the same primary key is the same in two queries , There are only some more records ( Why not lack data ?). You can use the following diagram to show :

This is from the Internet
We can simply understand it as , Business T1 On the resources to be operated , Read only data is locked , Write lock the data to be modified , And they are all released after the transaction is committed . Therefore, other transactions cannot modify the same resource , So in the scenario of unreal reading , Non repeatability does not happen . however T1 But the newly generated data row cannot be locked , Therefore, the difference between unreal reading and unrepeatable degree is reflected here, that is, the result set of the same predicate is different , Generally, the result set of the last time is a superset of the result set of the previous time .
summary
Disassemble from the above analysis , And understand these abnormal scenarios from the perspective of locking , You can find one Progressive relationship : When the last problem is solved , Another new problem has been discovered . That's why , The concept of different isolation levels with progressive relationships defined according to these exception scenarios .
In the next chapter < Isolation level of the transaction system > In the analysis of , We can still find , Each isolation level , Solve a level problem . Coming soon ~
KunlunDB The project is open source
【GitHub:】
https://github.com/zettadb
【Gitee:】
https://gitee.com/zettadb
END
边栏推荐
- 剑指 Offer 11. 旋转数组的最小数字
- Programmers' choice of taking private jobs and part-time jobs
- xml转义字符对照表
- IPV4的未来替代品!一文读懂IPV6的优势特点和地址类型
- 13. Roman numeral to integer
- Various schemes for lazy loading of pictures
- 在一条DML语句中插入/更新/删除/获取几百万行数据,你会特别注意什么?
- Learning the interpretable representation of quantum entanglement, the depth generation model can be directly applied to other physical systems
- KunlunDB 查询优化(一)
- [STM32 skill] use the hardware I2C of STM32 Hal library to drive rx8025t real-time clock chip
猜你喜欢

DCC888 :SSA (static single assignment form)
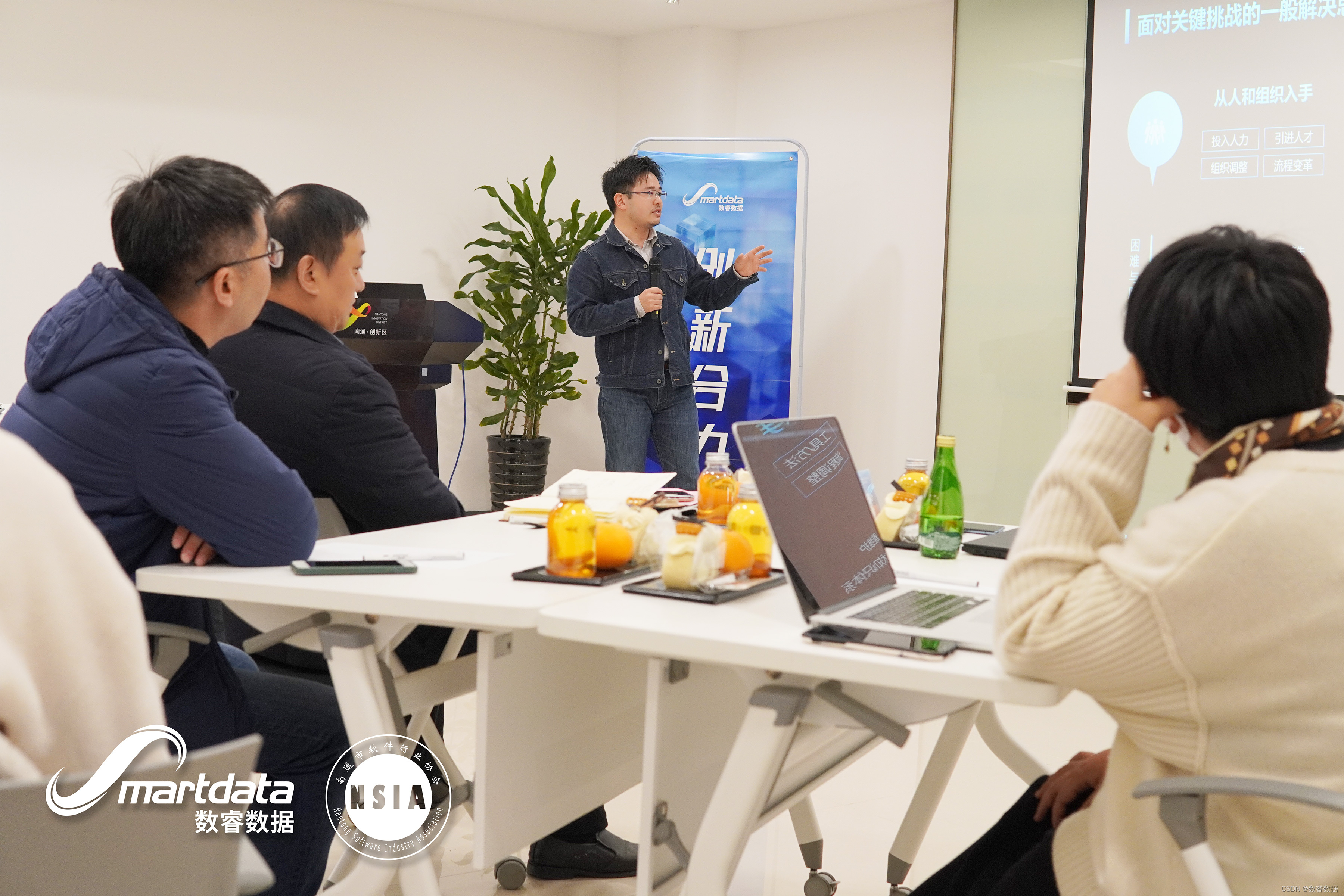

Digital data was invited to participate in Nantong enterprise digital transformation Seminar

10 Super VIM plug-ins, I can't put them down

JSBridge

【首发】Redis系列2:数据持久化提高可用性
![[kubernetes series] overview of kubernetes](/img/c2/b42f7a0db236558cc466a508d3d579.png)
[kubernetes series] overview of kubernetes
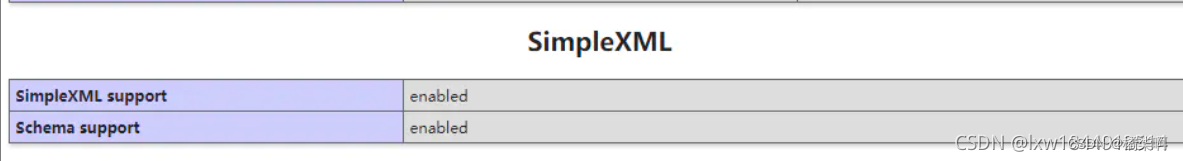
Php7.3 error undefined function simplexml_ load_ string()
Tp5.1 upload excel file and read its contents
![[go] getting started with go modules](/img/0a/58c50bb624c91b88a88aea280aa650.jpg)
[go] getting started with go modules

DCC888 :SSA (static single assignment form)
随机推荐
LeetCode_ Backtracking_ Dynamic programming_ Medium_ 131. split palindrome string
【GO】Go Modules入門
Array and string offset access syntax with curly braces is no longer support
After passing the hcip exam, I still failed to change my career. What do professional network workers value most
【ARM】讯为rk3568开发板lvds屏设置横屏显示
Flutter outsourcing, undertaking flutter project
Redistemplate encountered problems with \x00
13. Roman numeral to integer
周国华 读书随记
Webrtc series - 4connection sorting of network transmission
Stop using system Currenttimemillis() takes too long to count. It's too low. Stopwatch is easy to use!
【GO】Go数组和切片(动态数组)
弱电转职业网工难不难?华为售前工程师分享亲身经历
OJ每日一练——整理命名
What does password security mean? What are the password security standard clauses in the ISO 2.0 policy?
为什么大家很少使用外键了?
c# sqlsugar,hisql,freesql orm框架全方位性能测试对比 sqlserver 性能测试
OJ每日一练——单词的长度
tp5.1解决跨域
[go] go array and slice (dynamic array)