当前位置:网站首页>Server hardware and RAID configuration practice
Server hardware and RAID configuration practice
2022-07-24 06:28:00 【Aka · Brooklyn Fairy】
Catalog
One ,RAID Disk array Introduction
One ,RAID Disk array Introduction
yes Redundant Array of lndependent Disks Abbreviation , Chinese abbreviation is independent redundant disk array .
Combine several independent physical hard disks in different ways to form a silver disk group ( Logical hard disk , So as to provide higher storage performance than a single hard disk and provide data backup technology
The different ways to make up a disk array are called RAID Level (RAID Levels)
frequently-used RAID Level
RAID0 RAID1 RAID5 RAID6 RAID1+0 etc.
RAID 0( Striped storage )
RAID 0 Divide data continuously in bits or bytes , Read in parallel / Write on multiple disks , Therefore, it has high data transmission rate , But it has no data redundancy .
RAID 0 Just simply improve performance , There is no guarantee for improving the reliability of data , And the failure of one of the disks will affect all the data
RAID 0 It can't be used in the situation with high data security requirements
 N The fast hard disks are combined in parallel into a new logical disk
N The fast hard disks are combined in parallel into a new logical disk
explain :RAID 0 It is to connect more than two hard disks in parallel , towards RAID 0 When storing data , It will be distributed and stored in all disks under it . Reading and writing are done from multiple disks , So reading and writing speed is very fast , But there is no redundancy , One hard disk is broken , Whole RAID 0 Your data will be lost .
RAID 1( Mirrored storage )
Realize data redundancy through disk data mirroring , Generate backup data on a pair of independent disks
When raw data is busy , Data can be read directly from the mirror copy , therefore RAID 1 Can improve read performance
RAID 1 It's the highest cost per unit in a disk array , But it provides high data security and availability . When a disk fails , The system can automatically switch to read and write on the mirror disk , And there's no need to reorganize failed data
 N An even number of fast hard disks form an image ,N/2 Capacity
N An even number of fast hard disks form an image ,N/2 Capacity
explain :RAID 1 Must be a paired disk combination , At least 2 A disk , A disk is the most normal use , Another disk as a backup , When the disk in normal use is busy or damaged , You can switch to the backup disk for reading and writing . Data written to RAID 1 It takes a long time , Because you need to write data to two disks , The reading speed does not change , But it can improve performance , Effective reading ( One is broken , You can go to another one to read ).
RAID 5
N(N>=3) Fast disks form an array , A data generation n-1 A strip , As well as 1 Validation data , common N The sub data is N Cycle on the disk
N Read and write at the same time , High reading performance , Due to the problem of effective mechanism , Write performance is relatively low
(N-1)/N Disk utilization , High reliability , Allow blocks 1 Block plate , Does not affect all data

explain :RAID 5 Minimum need 3 It's made up of two disks , Two disks are the storage of data , A disk is the verification data , Data reading and writing of data storage disk RAID 1( Distributed storage ) It's the same , But there is a verification mechanism , So the writing speed is relatively RAID 0 A little worse , The reading speed is very high . Any disk data is lost or damaged , Will not lead to the loss of the entire data , Because the disk with verification mechanism will calculate the damaged disk content data through other undamaged disks .
RAID 6
N (N>=4) The plates form a whole column ,(N-2)/N Disk utilization
And RAID 5 comparison ,RAID 6 Added a second independent surprise Even check information is fast
Two independent wonders Even systems use different algorithms , Even if the two disks fail at the same time, the use of image data will not
relative RAID 5 There are bigger ones “ Write loss ”, Therefore, the write performance is poor

RAID 1+0
N ( even numbers ,N>=4) After two mirrored disks , In combination into one RAID 0
N /2 Disk utilization
N/2 The fast disk is written at the same time ,N The disks are read, written and accessed at the same time
High performance , High reliability

explain :RAID 1+0 array , First two hard disks RAID 1, Then two more RAID 1 Make it RAID 0, It is equivalent to having backup function and improving reading speed . Write to 4 Block disk for writing , Writing is slow , Read read from multiple disks , It's very efficient . And there is a backup mechanism .
each RAID Zone between levels
| RAID Level | Hard disk space | Disk utilization | The ability to protect | Write performance |
| RAID 0 | N | N | nothing | The hard disk N times |
| RAID 1 | N( even numbers ) | N/2 | nothing | Write two pairs of storage devices , Prepare for each other |
| RAID 5 | N>3 | (N-1)N | Yes | Need to write calculation validity |
| RAID 6 | N>4 | (N-2)N | Yes | Double counting test is required |
| RAID 10 | N>=( even numbers ) | N/2 | nothing | N/2 All disks are written simultaneously |
Two , Disk array practice
RAID 0
Verify that... Is installed 
Commands and formatting
/dev/md0: finger raid0 -n2: It refers to the need for two hard disks ,-l0: Refers to the type of raid0
/dev/sd[f-g]1: It refers to the area that needs several disks to do raid0

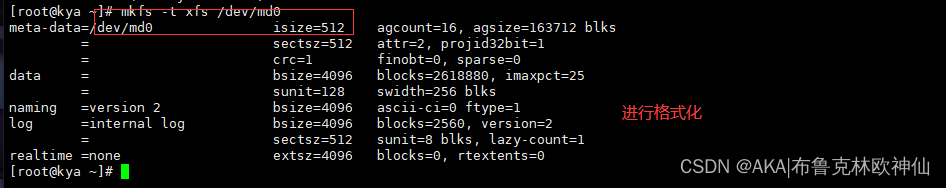
Mount
![]()
RAID 0 Show details

RAID 1
Naming and formatting
/dev/md1: finger raid1 -n2: It refers to the need for two hard disks ,-l1: Refers to the type of raid1
/dev/sd[f-g]2: It refers to the area that needs several disks to do raid1

format

Mount
![]()
RAID 1 Show details

Input lsblk see

RAID 5
Name and format

format

Mount

see raid5, Information

test : Remove a copy etc The next disk , See if it will have an impact ,

cat /proc/mdstat
raid 10
establish RAID

see



summary
RAID It has the advantage of fast reading and writing , Different at the same time RAID Level , Select according to data storage and access requirements RAUD, Generally speaking , A single server is very important , Not much disk , Use RAID1 It's very suitable , The main database of the database or storage server is RAID10, From the library is RAID5 perhaps RAID0,WEB The server , Without a lot of data , Use RAID5/RAID0, There are multiple monitors / In the case of application server , Use RAID5 perhaps RAID0 All can .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

一批面试题及答案_20180403最新整理

【218】CS架构和BS架构以及数据放在服务端和客户端的利与弊?

Homework in the second week

简单三步快速实现内网穿透

Simple but easy to use: using keras 2 to realize multi-dimensional time series prediction based on LSTM

异地远程连接在家里的群晖NAS【无公网IP,免费内网穿透】

Polkadot | interprets how liberty plan, which subverts traditional social media, will be launched in Poka
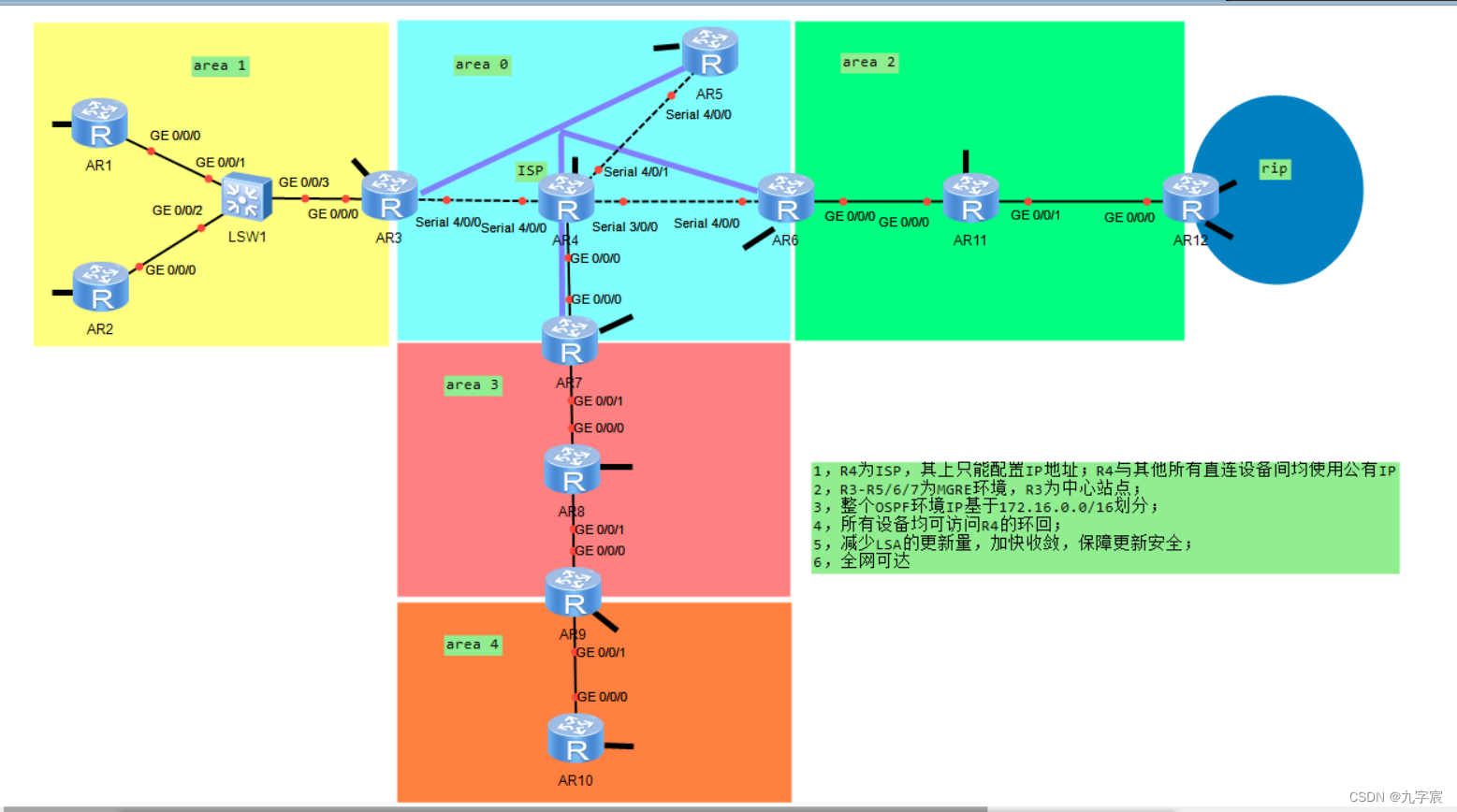
IP课(OSPF)综合实验
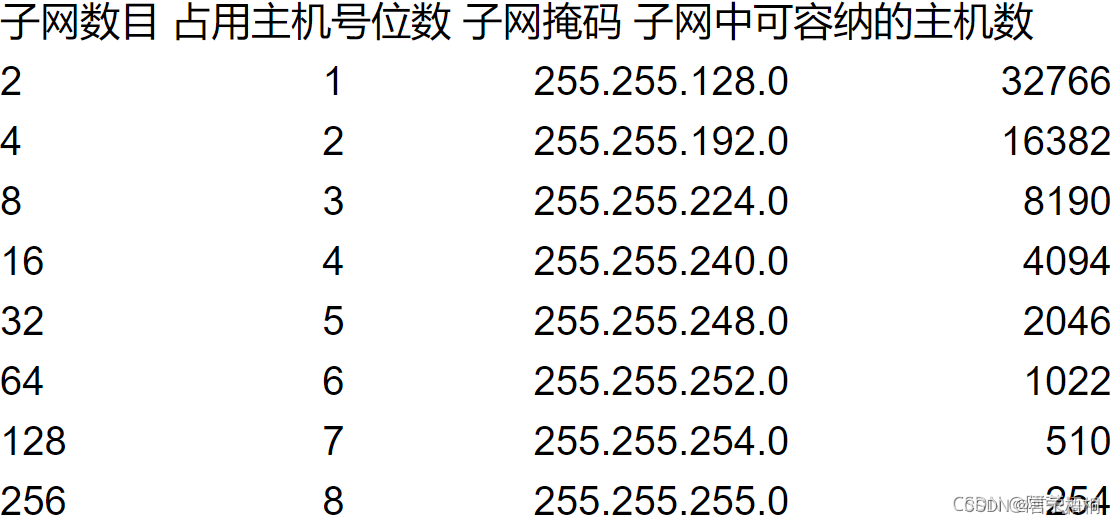
Ia class summary (1)
![Public access intranet IIS website server [no public IP required]](/img/e5/45d7c59ed30bbf901f793f25e229e2.png)
Public access intranet IIS website server [no public IP required]
随机推荐
[222] memory overflow and location
【301】怪诞行为学-可预测的非理性
Simple but easy to use: using keras 2 to realize multi-dimensional time series prediction based on LSTM
Summary of common working methods (7S, SWOT analysis, PDCA cycle, smart principle, 6w2h, time management, WBS, 28 principles)
将内网映射到公网【无需公网IP】
LuckyFrameWeb测试平台(一款支持接口自动化、WEB UI自动化、APP自动化,并且支持分布式测试的全纬度免费开源测试平台)
Jenkins自动化无人值守运行(上/下)
Flink state use
IP lesson summary (3)
IP课笔记(5)
Pycharm set code template
How to build a website full of ritual sense and publish it on the public website 1-2
Use intranet penetration to realize public network access to the Intranet
IP notes (12)
公网访问内网IIS网站服务器【无需公网IP】
Getting started with Lunix commands - user and file permissions (Chmod details)
Website B video is embedded in the web page, and relevant controls are hidden
Ia class summary (2)
利用内网穿透,实现公网访问内网
Flink function (1): rich function