当前位置:网站首页>R tree of search tree
R tree of search tree
2022-06-23 03:33:00 【Short section senior】
The background
Geospatial data involves a variety of massive and complex data , Finding an appropriate index is very important for the processing of spatial data .
Conventional B Tree index pin to character 、 Designed for the main keyword of one-dimensional attribute data such as numbers , It is not applicable to multi-dimensional geospatial data .
stay GIS and CAD Driven by the demand of the system for spatial index , In order to meet the rapid retrieval and analysis of two-dimensional and multi-dimensional spatial data , Guttman On 1984 It was proposed that R Tree index structure .
Definition
R A tree is a multi-level balanced tree , It is B The extension of tree in multidimensional space . It uses the concept of spatial segmentation , It's not the original data , It's the smallest bounding rectangle of the data (MBR ), It is a tree data structure used for spatial data storage .
principle
In order to achieve R Tree structure , The minimum bounding rectangle is used to frame an area surrounded by each data ( In the figure, it is represented by a solid line rectangle ), Several minimum bounding rectangles are obtained , Such as R8,R9,R10,R11 etc. .
among R8,R9,R10 The three rectangles are closest , Use a larger rectangle R3( In the figure, it is represented by a dotted rectangle ) Frame three rectangles .
Through constant iteration , Frame all rectangles with larger rectangles .
Store all large and small rectangles in R In the tree .
nature
The number of subnodes that each node can have has upper and lower limits . All nodes except the root node contain m to M A record index ( entry ). Usually ,m=M/2.
For records on non leaf nodes ,R The data structure of the non leaf node of the tree is :(I, child-pointer).child-pointer It's a pointer to a child's node ,I It's a rectangle covering all child nodes .
For records on leaf nodes , The data saved by the leaf node is in the form of :(I, tuple-identifier). among ,tuple-identifier Represents a record stored in the database .I It's a n The rectangles of dimensional space , And you can just frame all the records in this leaf node n Points in dimensional space .
R Tree derivation
R+ Trees : The main difference is that R+ The spatial regions corresponding to sibling nodes in the tree do not overlap .
advantage : Reduce the number of invalid queries , It greatly improves the efficiency of spatial index
shortcoming : Because the operation should ensure that there is no overlap in the spatial area, the insertion rate is reduced 、 Efficiency of deleting spatial objects
R* Trees :1990 The best dynamic proposed in R Varieties of trees .
advantage : The insertion of nodes 、 The splitting algorithm is improved , use “ Force reinsertion ” Method to optimize the structure of the tree
shortcoming : Still can not effectively reduce the degree of spatial overlap , In the amount of data 、 Especially when the dimension increases .
Existing problems
R The tree mainly considers the area of the circumscribed rectangle , There are many parameters that affect the retrieval performance .
The area covered by the directory rectangle should be minimized .
The overlap of rectangles between different paths should be minimized .
Reduce the number of paths to be traversed
Storage space utilization should be optimized .
Welcome to join me for wechat exchange and discussion ( Please note csdn Add )
边栏推荐
- [advanced Android] entrusted by kotlin
- How to store easydss version 3.0 video files in other free disks?
- [quick view] Analysis on the development status and future development trend of the global and Chinese diamond cultivation industry in 2021 [figure]
- Free upgrade of 2-core 2GB for old generation 1-core 2GB machines below standard S5 and SA2
- Summary of some precautions and problems in the use of tars framework (mengxinxiang)
- Establishment of JMeter distributed pressure measurement environment
- 【二分】leetcode1011. Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days
- Bi skills - authority control
- Wwdc21 - App store server API practice summary
- CFs of cifs/smb protocol is mounted on win10/2019. Error 1272 is reported. The security policy prevents unauthenticated guest access
猜你喜欢

Gakataka student end to bundle Version (made by likewendy)
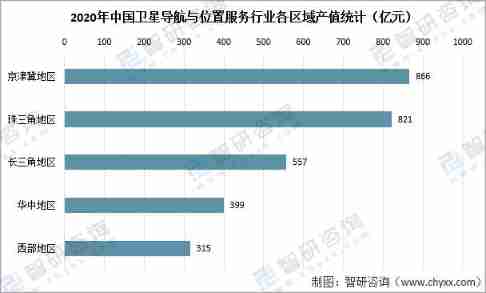
Analysis on the development of China's satellite navigation industry chain in 2021: satellite navigation is fully integrated into production and life, and the satellite navigation industry is also boo

【二分】leetcode1011. Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days
One of the touchdesigner uses - Download and install

Svn local computer storage configuration
![Analysis of the number of urban residents covered by basic medical insurance, their treatment and medical treatment in other places in China in 2021 [figure]](/img/81/4d3cb059f700dd9243645e64023be7.jpg)
Analysis of the number of urban residents covered by basic medical insurance, their treatment and medical treatment in other places in China in 2021 [figure]

【贪心】leetcode991. Broken Calculator

Analysis on the development of China's graphene industry chain in 2021: with the support of energy conservation and environmental protection policies, the scale of graphene industry will continue to e

Encryption related to returnee of national market supervision public service platform

Jmeter- (V) simulated user concurrent login for interface test
随机推荐
How to batch generate ean14 barcode through TXT file
"Tianzhou II" successfully docked! Three minutes to understand the shocking black technology on "Tianzhou II"! Headlines
How to make distribution box label
【二分】leetcode1011. Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days
Implementation process of the new electronic amplification function of easycvr video fusion cloud platform
Brief introduction to arm architecture
Analysis on the development of China's graphene industry chain in 2021: with the support of energy conservation and environmental protection policies, the scale of graphene industry will continue to e
Flink practice tutorial: advanced 7- basic operation and maintenance
6 values in JS are 'false'
JS how to delete an item specified in an array
On the way home from the Spring Festival transportation, traffic visualization will escort you
PHP composer yii2 installation
Record an edusrc vulnerability mining
Analysis of China's integrated circuit industry chain in 2021: huge downstream market demand [figure]
An implementation of universal interface caching Middleware
DDoS attack under Kali
How to generate code-11 barcode in batch through TXT file
How to get started with apiccloud app and multi terminal development of applet based on zero Foundation
How to print multiple barcode labels on one sheet of paper
Analysis of the number of urban residents covered by basic medical insurance, their treatment and medical treatment in other places in China in 2021 [figure]