当前位置:网站首页>[JS] - [array application] - learning notes
[JS] - [array application] - learning notes
2022-06-24 23:17:00 【Interesting learning】
【js】-【 Array - application 】- Learning notes
Statement : This note is based on the Nuggets brochure , If you want to learn more details , Please move https://juejin.cn/book/6844733800300150797
1 Map The magic effect of
Sum of two numbers
Given nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9 So back [0, 1]
const twoSum = function(nums, target) {
# Here I use objects to simulate map The ability of
const diffs = {
}
// Cache array length
const len = nums.length
// Traversal array
for(let i=0;i<len;i++) {
// Judge the corresponding... Of the current value target Whether the difference exists ( Whether it has been traversed )
if(diffs[target-nums[i]]!==undefined) {
// If there is a corresponding difference , So the answer get!
return [diffs[target - nums[i]], i]
}
// If there is no corresponding difference , Then record the current value
diffs[nums[i]]=i
}
};
Map Realization ( Find out , In fact, the writing of objects is simpler )
const twoSum = function(nums, target) {
# Try Map
const map=new Map()
// Cache array length
const len = nums.length
// Traversal array
for(let i=0;i<len;i++) {
// Judge the corresponding... Of the current value target Whether the difference exists ( Whether it has been traversed )
if(map.get(target-nums[i])!==undefined) {
// If there is a corresponding difference , So the answer get!
return [map.get(target-nums[i]), i]
}
// If there is no corresponding difference , Then record the current value
map.set(nums[i],i)
}
};
2 Double finger needling
1. Merge two ordered arrays
Here are two arrays of ordered integers nums1 and nums2, Would you please nums2 Merge into nums1 in , send nums1 Make an ordered array
Input :
nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
Output :
[1,2,2,3,5,6]
Their thinking :
- Define two pointers , Points to the last bit of a valid array , Set up a k obtain num1 End index of
- Start traversing from back to front (i>0 perhaps j>0), Take the larger one from num1 The first k A place ( Save from back to front )
- If it is num1 Not finished traversing , No action required , if num2 Not finished traversing , That's by traversing it into num1 Just the front
const merge = function(nums1, m, nums2, n) {
// Initialize two pointers , Point to respectively num1 and num2 Last
let i = m - 1,
j = n - 1,
k = m + n - 1; # initialization nums1 Tail index k
// When both arrays are not traversed , The pointer moves synchronously
while(i >= 0 && j >= 0) {
# Take the larger value , Put it in num1 Last
if(nums1[i] >= nums2[j]) {
nums1[k] = nums1[i]
i--
k--
} else {
nums1[k] = nums2[j]
j--
k--
}
}
// nums2 What's left , Special treatment
while(j>=0) {
nums1[k] = nums2[j]
k--
j--
}
};
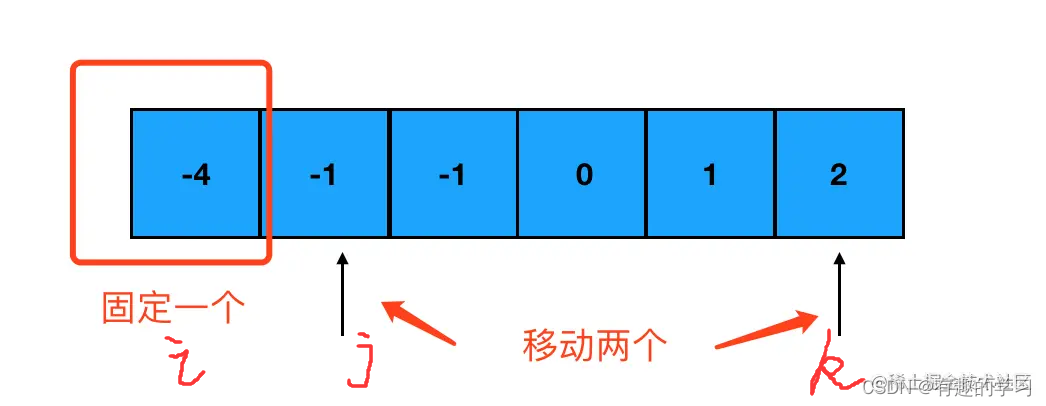
2. Summation of three numbers
describe :
Give you one containing n Array of integers nums, Judge nums Are there three elements in a,b,c , bring a + b + c = 0 ? Please find out all the triples that meet the conditions and do not repeat .
Given array nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4], The set of triples satisfying the requirement is : [ [-1, 0, 1], [-1, -1, 2] ]
Two finger needling is used in relation to summation 、 When compared to the array title of size class , The big premise is often : The array must Orderly . Otherwise, the double pointer will not help us narrow the positioning range . So the first step in this problem is to sort the array :
nums = nums.sort((a,b)=>{
return a-b
})
Ideas :
Two keys : Sort , Double pointer , duplicate removal
- Prioritize , The current is
i(i The range is 0-length-2), The left and right pointers are respectivelyj,k- Handle
iRepeated numbers , skip- The sum of three numbers is less than 0, The left pointer goes forward ( Handle the repetition of left pointer elements ); The sum of three numbers is greater than 0, The right pointer moves left *( Handle duplicate right pointer elements )*
- Get the target number combination , Push the result array , At the same time, the left and right pointers move ( It also deals with the repetition of left and right pointer elements )
Complete code
const threeSum = function(nums) {
// Used to store the result array
let res = []
!1. to nums Sort
nums = nums.sort((a,b)=>{
return a-b
})
// Cache array length
const len = nums.length
! 2. Note that it is sufficient for us to traverse to the penultimate number , Because the left and right pointers will traverse the next two numbers
for(let i=0;i<len-2;i++) {
// Left pointer j
let j=i+1
// Right pointer k
let k=len-1
! 3. If you encounter duplicate numbers , Then skip (“ Non repeating triples ”)
if(i>0&&nums[i]===nums[i-1]) {
continue
}
while(j<k) {
!4. The sum of three numbers is less than 0, The left pointer goes forward
if(nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[k]<0){
j++
!4.1 Handle the repetition of left pointer elements
while(j<k&&nums[j]===nums[j-1]) {
j++
}
} else if(nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[k]>0){
// The sum of three numbers is greater than 0, The right pointer goes back
k--
// Handle duplicate right pointer elements
while(j<k&&nums[k]===nums[k+1]) {
k--
}
} else {
// Get the target number combination , Push the result array
res.push([nums[i],nums[j],nums[k]])
// The left and right hands move forward together
j++
k--
// If left pointer element repeats , skip
while(j<k&&nums[j]===nums[j-1]) {
j++
}
// If the right pointer element repeats , skip
while(j<k&&nums[k]===nums[k+1]) {
k--
}
}
}
}
// Return result array
return res
};
My thinking : Whether to sort directly + duplicate removal Better ? Find out not to , Because if there are many elements 0 This situation , The weight is gone
边栏推荐
- 推送Markdown格式信息到釘釘機器人
- SQL -convert function
- Dynamic menu, auto align
- vulnhub DC: 2
- Sword finger offer 13 Range of motion of robot
- Laravel add helper file
- Laravel authentication module auth
- Laravel creates a service layer
- Attention, postgraduate candidates! They are the easiest scams to get caught during the preparation period?!
- Dig deep into MySQL - resolve the non clustered index of MyISAM storage engine
猜你喜欢
Paddledtx v1.0 has been released, and its security and flexibility have been comprehensively improved!

对抗训练理论分析:自适应步长快速对抗训练

推送Markdown格式信息到钉钉机器人

【js】-【链表-应用】-学习笔记

宁德时代定增450亿:高瓴认购30亿 曾毓群仍控制23%股权

The large-scale market of graduate dormitory! Here comes the enviable graduate dormitory!

JD 618 conference tablet ranking list announced that the new dark horse brand staff will compete for the top three, learning from Huawei, the leader of domestic products
Tech Talk 活动回顾|云原生 DevOps 的 Kubernetes 技巧

2022 safety officer-a certificate examination questions and answers

Simulated 100 questions and online simulated examination of high voltage electrician examination in 2022
随机推荐
idea创建模块提示已存在
Dig deep into MySQL - resolve the difference between clustered and non clustered indexes
A big factory interview must ask: how to solve the problem of TCP reliable transmission? 8 pictures for you to learn in detail
Case analysis: using "measurement" to improve enterprise R & D efficiency | ones talk
记录一下MySql update会锁定哪些范围的数据
Epics record reference 4 -- fields for all input records and fields for all output records
The large-scale market of graduate dormitory! Here comes the enviable graduate dormitory!
Simulated 100 questions and online simulated examination of high voltage electrician examination in 2022
Building Survey [2]
【js】-【数组、栈、队列、链表基础】-笔记
Laravel pagoda security configuration
Canvas to add watermark to pictures
去处电脑桌面小箭头
07_ Springboot for restful style
03_SpingBoot 核心配置文件
golang convert map to json string
【js】-【字符串-应用】- 学习笔记
Financial management [2]
Building Survey [1]
Epics record reference 3 -- fields common to all records