当前位置:网站首页>Reading notes: you only look once:unified, real time object detection
Reading notes: you only look once:unified, real time object detection
2022-07-24 19:17:00 【to be__】
One 、Abstract
Consider target detection as a regression problem , Use a single network to predict directly from a picture bounding box And class probability ,YOLO There will be more positioning errors, but very fast .
Two 、Introduction
At present, detection systems use classifiers to perform detection , In order to detect the target , These systems use classifiers for targets and use various positions and sizes on a test image to evaluate . similar DPM The system uses the sliding window method , That is, the classifier moves a certain spatial location on the whole image on average .
At present, it is more similar to R-CNN The method uses the region candidate method , First, generate a potential bounding box, Then run a classifier in these candidate boxes , In the post-processing process , Refine bounding box, Remove duplicate tests , These complex pipelines are very slow and difficult to optimize , Because each individual part must be trained separately .
We redefine target detection as a single regression problem, which is obtained directly from image pixels bounding box Coordinates and class probabilities .
A single convolutional neural network is used to predict multiple bounding box And these boxes Class probability of ,YOLO Train on the whole image and directly optimize the detection representation .
Unlike sliding windows and candidate region based techniques ,YOLO Look at a whole image during training and similarity measurement , Explicitly encode the whole information , Category information and representation .YOLO Learn a more generalized representation of the goal .
YOLO It still lags behind the advanced detection system in accuracy .
3、 ... and 、Unified Detection
Divide the input image into S*S A grid , If the center of the object falls in a grid , Then this grid is responsible for predicting and detecting the object .
Each grid predicts B individual bounding box And the confidence scores of these lattices , These confidence scores reflect the confidence of the grid containing the goal and the accuracy of the goal .
Every bbox Include 5 Predicted values :x,y,w,h,c (x,y,w,h Are normalized )
Each grid predicts C A conditional probability ,![]() The premise of these probabilities is that the grid has a target , Each grid predicts only one set (C individual ) Class probability , And B The value of has nothing to do with . The image output is 7*7*30 Size ,30 Contains two bbox Of x,y,w,h,c, The rest 20 Dimension outputs a set of class probabilities (C namely 20 individual ).
The premise of these probabilities is that the grid has a target , Each grid predicts only one set (C individual ) Class probability , And B The value of has nothing to do with . The image output is 7*7*30 Size ,30 Contains two bbox Of x,y,w,h,c, The rest 20 Dimension outputs a set of class probabilities (C namely 20 individual ).
At testing time , Put the grid ![]() With each bbox Confidence prediction
With each bbox Confidence prediction ![]() Multiply , That is, the confidence score of the exact class of each lattice . Those points Numbers indicate bbox The probability that the target belongs to each category and bbox Match the quality of the target .
Multiply , That is, the confidence score of the exact class of each lattice . Those points Numbers indicate bbox The probability that the target belongs to each category and bbox Match the quality of the target .
Degree of confidence :confidence=![]() Pr(Object) If there is a goal, it is 1, If there is no goal, it is 0
Pr(Object) If there is a goal, it is 1, If there is no goal, it is 0
Each grid predicts B individual bbox, as well as bbox Of confidence score and confidence
( Degree of confidence :bbox The probability of containing goals ![]() ,bbox The accuracy of
,bbox The accuracy of ![]() , Confidence is the value of multiplying the two )
, Confidence is the value of multiplying the two )
( One grid cell Can predict B individual bbox,B individual bbox Separate from this object Of groud truth seek IOU value , Output IOU The biggest one bbox)
Four 、 Loss function

Every bbox It is necessary to calculate the positioning error ( Item 1 and 2 ) And confidence error ( The third one ), Contains the probability of the grid prediction class of the target ( Item 5 ), It does not include the confidence error of object prediction ( Item four )
The first and second terms of the loss function are each bbox Coordinate prediction of , The third item contains goals bbox Of confidence forecast , The fourth item contains no goals bbox Of confidence forecast , The fifth item is category prediction for each grid
After an image is output , Is divided into S*S A grid ( This paper is about 7) Each grid predicts B( This paper is about 2) individual bbox Then the whole image is divided into 7*7=49 A grid Whole image generation 7*7*2=98 individual bbox , Each grid predicts (5*B+C) It's worth , One image predicts S*S*(5*B+C) It's worth
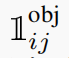 i It means the first one i A grid ,j It means the first one i The th of the grid j individual bbox
i It means the first one i A grid ,j It means the first one i The th of the grid j individual bbox
 i It means the first one i A grid
i It means the first one i A grid
 For those with goals box The punishment ( Great contribution , Then the power is great , by 5)
For those with goals box The punishment ( Great contribution , Then the power is great , by 5)![]() For those without goals bbox The punishment ( Small contribution , Then the weight is small , by 0.5)
For those without goals bbox The punishment ( Small contribution , Then the weight is small , by 0.5)
ask :
Every grid cell Medium bbox How to predict ?
How the object selection box is finally generated ?
How to determine a cell Does it include object,Pr(Object)=1?
边栏推荐
- Installation and use of lsky Pro lancong drawing bed: a drawing bed program for online uploading and managing pictures
- How does PostgreSQL decide PG's backup strategy
- 杭电多校第一场第三题 Backpack(异或dp+bitset)
- Analysis of dropout principle in deep learning
- Sequences, time series and prediction in tessorflow quizs on coursera (II)
- Environment preparation of Nacos configuration center
- MySQL (data types and integrity constraints)
- Excel practice notes 1
- FPGA 20个例程篇:9.DDR3内存颗粒初始化写入并通过RS232读取(下)
- OpenGL learning (II) opengl rendering pipeline
猜你喜欢

Easily learn pytoch transfer learning to realize surface defect inspection

asp. Net coree file upload and download example

matplotlib

Convolutional Neural Networks in TensorFlow quizs on Coursera

深度学习中Dropout原理解析

Reading notes of XXL job source code

FPGA 20 routines: 9. DDR3 memory particle initialization write and read through RS232 (Part 2)

FPGA 20个例程篇:9.DDR3内存颗粒初始化写入并通过RS232读取(下)
![[laser principle and application -6]:q switching element and Q drive circuit board](/img/30/e199b73fb9b0ad335f26f2378cfc45.png)
[laser principle and application -6]:q switching element and Q drive circuit board
OpenGL learning (II) opengl rendering pipeline
随机推荐
多线程与并发编程常见问题(未完待续)
Summary of articles in 2020
Converter
[in depth study of 4g/5g/6g topic -39]: urllc-10 - in depth interpretation of 3GPP urllc related protocols, specifications and technical principles -3- how to distinguish urllc services? Detailed expl
Meshlab&PCL ISS关键点
MySQL hidden version number
Hidden Markov model HMM
Principle and application of database
2020-2021 new technology lecture course
Sequences, time series and prediction in tessorflow quizs on coursera (I)
Calendar common methods
Interceptors and filters
Zooinspector Download
MySQL index principle and query optimization "suggestions collection"
High speed ASIC packaging trends: integration, SKU and 25g+
PCIe link initialization & Training
Why is gradient the fastest changing direction of function
Configmanager of unity framework [JSON configuration file reading and writing]
Nacos introduction and console service installation
About core files