当前位置:网站首页>Paging query and join Association query optimization
Paging query and join Association query optimization
2022-06-26 18:04:00 【Time is light, you are safe】
One 、 Paging query optimization
The existing table is as follows :
CREATE TABLE `employees` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(24) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT ' full name ',
`age` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT ' Age ',
`position` varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT ' Position ',
`hire_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT ' On entry between ',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `idx_name_age_position` (`name`,`age`,`position`) USING BTREE
)
1.1 scene
This table currently has 10 Ten thousand data , When it comes to paging , Maybe most of my friends will use the following SQL Realization :
select * from employees limit 100000,10;
But this most conventional way of writing has its drawbacks .
If there's not a lot of data , There's no big problem ;
But if the amount of data is millions or even tens of millions , If you still query in this way , And the query data is relatively backward ( Turned to dozens or even hundreds of pages ), The more you turn back, the slower it will be .
Why is this so ?
It seems that only a few pieces of data have been checked , however Actually this one SQL Read first 100010 Bar record , And then before I leave 100000 Bar record , Then read back 10 Data you want . Therefore, you need to query the data behind a large table , Execution efficiency is very low .
1.2 Optimization techniques
This paging optimization , You need to look at specific scenarios , Not all apply , Let's introduce it in detail
1.2.1 Paged query sorted by auto increasing and continuous primary key
Prerequisite : The query is based on the primary key , And the primary key is self increasing and continuous
SQL The following forms can be optimized :
select * from employees where id > 100000 limit 10;
After the optimization , have access to explain Look at the next two SQL Results of execution .
We can see that if you use limit, The query did not take the index , from rows It can be seen that it is equivalent to a full table scan ( Table data share 102834 That's ok , Scanned 102872 That's ok )

Optimized SQL, The primary key index is used , And the number of lines scanned is greatly reduced , Used B+ Tree Index tree of , So the efficiency will be much higher .
shortcoming
The limitations of this optimization are obvious , The primary key is required to be self incremented and continuous , This kind of situation is very rare .
Because in most cases, there will be data deletion , If you delete a piece of data in the middle ,SQL The query has no problem before this record , But if the data is larger than this one , The result set is problematic .
You can simulate this scenario :
First delete a piece of data , Do two more SQL sentence , View results :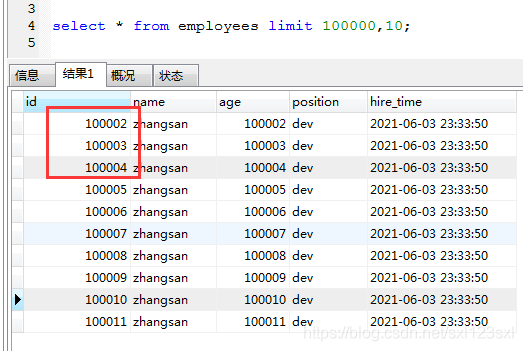

You can see two SQL The result set is not the same
therefore , If the primary key is not continuous , The optimization method described above cannot be used . In addition, if the original SQL yes order by Non primary key fields , Rewriting according to the above method will lead to two SQL The results are inconsistent .
So this rewriting is The following two conditions are met :
The primary key is self increasing and continuous
The result is sorted by primary key
1.2.2 Paging queries sorted by non primary key fields
There are the following SQL:
select * from employees ORDER BY name limit 90000,5;
Use Explain View analysis :
Here is also a full table scan , And sorting also uses file sorting :filesort
Come here , There may be a small partner who will have questions , This table clearly has idx_name_age_position Indexes , Now we use name Field , Is consistent with the leftmost prefix principle , Why didn't you go through the index , It also uses file sorting ? How to optimize ?
The specific reasons have been introduced in the article before : Scan the entire index and find no index The line of ( You may have to traverse multiple index trees ) The cost of is higher than the cost of scanning the full table , therefore MySQL The optimizer discards indexes .
In fact, if this kind of statement needs to use an index , You can use the overlay index , Specify the fields to be checked . Then we can use this idea : Make the fields as few as possible when sorting , Specify the fields to be queried after sorting .
So you can let sorting and paging find the primary key first , Then find the corresponding record according to the primary key ,SQL Rewrite as follows :
select * from employees e
inner join (select id from employees order by name limit 90000,5) ed on e.id = ed.id;

Then we can use explain To analyze the performance :
From the results we can see , Used the set index , And the sort also uses the index sort .
On the face of it , The final SQL I checked twice , I checked it once , Finally, I put ID Check the table again , Will the performance be low ??
The answer is no . First and foremost SQL:select id from employees order by name limit 90000,5 Make full use of the overlay index and still use the index sorting , This article SQL The search results actually represent the final data set ID It has come out and is in good order , Finally, the query performance of the external layer is also very high , Most of the time , Our paging data is 10 Article or 20 strip , The primary key association performance of these data back tables is very high .
Two 、JOIN Association query optimization
The existing table is as follows :
t1 Table has 10000 Data
CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`a` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`b` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `idx_a` (`a`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=10201 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
t2 Yes 100 Number of pieces
CREATE TABLE `t2` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`a` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`b` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `idx_a` (`a`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=101 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
2.1 MySQL Two common algorithms for table Association
Nested-Loop Join Algorithm
Block Nested-Loop Join Algorithm
Let's introduce these two algorithms in detail
2.1.1 Nested loop connection Nested-Loop Join(NLJ) Algorithm
As follows SQL:
select*from t1 inner join t2 on t1.a= t2.a;

Use explain Check the query , We can see that it is queried first t2 surface , Then query the t1 surface ( My previous blog has written id Big first ,id Do the same from top to bottom ).
So why did you check first t2 Watch ? If you put t1 and t2 Change places , Which table will you check first ?
We can see that the result is the same . All are priority queries t2 surface .
Actually ,MySQL Have your own algorithm when choosing , For table associations , An associated field has an index ,mysql The nested loop connection will be selected at the bottom Nested-Loop Join(NLJ) Algorithm ( The bottom layer of this algorithm is not Cartesian product ).
Nested loop connection Nested-Loop Join(NLJ) Algorithm : Loop from the first table one row at a time ( be called The driver table (ps: That is to say t2 surface )) Read lines in , Get the associated field in this row of data , According to the associated fields in another table ( Driven surface ) Take out the line that meets the conditions , Then take out the result set of the two tables .
Summarized below :
We can see this information from the above implementation plan :
①、 The drive table is t2, The driven table is t1. The first thing to execute is the drive table ( The results of the implementation plan id If the same, execute from top to bottom sql); The optimizer usually preferentially selects small tables as the driving tables . So use inner join when , The top table is not necessarily the driving table .
②、 Used NLJ Algorithm . commonly join In the sentence , If Implementation plan Extra There is no Using join buffer Indicates the used join count Law is NLJ
above sql The general process is as follows :
- From the table t2 Read a row of data in the ;
- From 1 Step data , Take out the associated fields a, To table t1 Search for ;
- Take out the watch t1 The line that satisfies the condition in , Follow t2 Merge the results obtained in , Return to the client as a result ;
- Repeat the above 3 Step .
The whole process will read t2 All data of table ( scanning 100 That's ok ), Then traverse the fields in each row of data a Value , according to t2 In the table a Value index scan t1 surface Corresponding lines in ( scanning 100 Time t1 Index of tables ps: Scanning the index is very fast , Time is almost negligible ,1 One scan can be considered as only scanning in the end t1 One row of complete data in the table , That's all t1 The watch was also scanned 100 That's ok ). So the whole process scans 200 That's ok .
explain : Result scan 100+100=200 Why .
Because first scan t2 All data of table , That is to say 100 Scans .
Each time from t2 A record is scanned out of the table , And t1 Table de comparison , Because it is indexed , The index scan time is ignored here , Think from t1 One scan in the table can obtain the available data t2 The data corresponding to the table .
therefore , in other words , from t1 Scan the table once ,t2 Scan the table once , You can get a result set .t2 Total 100 Row data , So the total number of scans 200 Time ( Two tables each 100 Time ).
If the associated field of the driven table has no index , Use NLJ The performance of the algorithm will be low ( Here's a detailed explanation ),mysql Will choose Block Nested-Loop Join Algorithm
2.1.2 Block based nested loop connections Block Nested-Loop Join(BNL) Algorithm
As follows SQL:
select*from t1 inner join t2 on t1.b= t2.b;
This time, the non indexed field association is used 
Extra in Of Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop) This indicates that the association query uses BNL Algorithm .
Block based nested loop connections Block Nested-Loop Join(BNL) Algorithm : hold The driver table (ps: A driver table is a small table , As can be seen from the execution plan : The driver table here is still t2) Data read into join_buffer (ps: You can use this as a memory , That is to say mysql new A small connection cache area ) in , Then scan Was the driver table , hold Was the driver table Take out each line and follow join_buffer Compare the data in .
above sql The general process is as follows :
- hold t2 Put all the data into join_buffer in
- Keep watch t1 Take out every line in the , Follow join_buffer Compare the data in ( The comparison is done in memory . After comparing a piece of data, the memory will be released , Not all data is always stored in memory , So there is no risk of high memory .)
- Return to satisfaction join Conditional data
The whole process is on the table t1 and t2 We did a full scan , therefore The total number of rows scanned is 10000( surface t1 Total data of ) + 100( surface t2 Total data of ) = 10100, also join_buffer The data in the is out of order , So watch t1 Each line in , Do it all 100 Second judgment , therefore The number of judgements in memory is 100 * 10000= 100 Ten thousand times .
The associated field of the driven table has no index. Why do you choose to use BNL Algorithm without using Nested-Loop Join Well ?
If the associated field is not indexed sql Use Nested-Loop Join, Then the number of scanning lines is 100 * 10000 = 100 Ten thousand times , This is ScanDisk .
Obviously , use BNL The number of disk scans is much less , Compared to disk scanning ,BNL Memory computing will be much faster .
therefore MySQL For an associated query with no index for the associated field of the driven table , Generally used BNL Algorithm . If there is an index, generally choose NLJ Algorithm , Yes In the case of indexing NLJ Algorithm ratio BNL The algorithm has higher performance
2.2 For Association sql The optimization of the
① The associated fields are , Give Way mysql do join Try to choose NLJ Algorithm
② Small tables drive large tables , Write multi table join sql If Be clear about Which table is a small table that can be used straight_join Fixed connection drive mode , Omit mysql The optimizer's own time .
straight_join:straight_join Same function join similar , But let the left watch drive the right watch , It can change the execution order of the table optimizer for the associated table query .
MySQL The internal query engine will probably optimize SQL, But sometimes the optimization may not be accurate .
For example, the above query ,MySQL Execute after optimization t2 surface , This is the general case , The optimizer can properly optimize , Let the small table execute first . But sometimes it is not necessary to optimize the query for small tables first .
therefore , If in some cases , It is clear which of the connected tables is a small table , You can use straight_join Grammar to make connections , Specify which table to execute first .
Aforementioned SQL It can be rewritten as :
select * from t2 straight_join t1 on t2.a = t1.a;
So you don't have to MySQL Internal optimization ( Determine which table has a large amount of data , Which data volume is small ), Clearly tell the optimizer which is the driving table , Let the optimizer choose as little as possible
We need to pay attention to : Aforementioned t2 It's a small table. , The premise is that the two tables have no conditions . The real small table driving large table does not mean that a table with a small total data volume is the driving table , It is The amount of data that really participates in the association Size determines which is the driver table .
straight_join Only applicable to inner join, It doesn't apply to left join,right join.( because left join,right join The execution order of the table has been specified on behalf of )
Let the optimizer judge as much as possible , Because most of the time mysql The optimizer is smarter than people . Use straight_join Be careful , because In some cases, the artificially specified execution order is not necessarily more reliable than the optimization engine .
More optimization , You can go to in and exsits、count(*) Query optimization see .
边栏推荐
- MySQL add column failed because there was data before, not null by default
- MySql 导出数据库中的全部表索引
- How to open a stock account? Is it safe to open an account online now?
- tag动态规划-刷题预备知识-2. 0-1背包理论基础和二维数组解法模板
- 背包问题求方案数
- 深入理解MySQL锁与事务隔离级别
- The difference between round and truncate in SQL (round or truncate)
- Get and set settings in 26class
- ZCMU--1367: Data Structure
- 你好,现在网上股票开户买股票安全吗?
猜你喜欢

MySQL add column failed because there was data before, not null by default

MySQL的MVCC机制详解

transforms.RandomCrop()的输入只能是PIL image 不能是tensor

Plt How to keep show() not closed

wechat_ Solve the problem of page Jump and parameter transfer by navigator in wechat applet

MySQL exports all table indexes in the database

Solve the problem that each letter occupies a space in pycharm

next(iter(dataloader))的一点点体会

Leetcode - 226. Retourner l'arbre binaire (bfs)

行锁分析和死锁
随机推荐
vutils.make_grid()与黑白图像有关的一个小体会
How about opening an account at Guojin securities? Is it safe?
MYSQL的下载与配置 mysql远程操控
[unity] use C in unity to execute external files, such as Exe or bat
pycharm的plt.show()如何保持不关闭
padding百分比操作
【uniapp】uniapp手机端使用uni.navigateBack失效问题解决
JS common regular expressions
请指教同花顺开户选选择哪家券商比较好?现在在线开户安全么?
LeetCode——226. 翻轉二叉樹(BFS)
(必须掌握的多线程知识点)认识线程,创建线程,使用Thread的常见方法及属性,以及线程的状态和状态转移的意义
RSA encryption and decryption details
接水面试题
[code Capriccio - dynamic planning] t583. Deleting two strings
[QNX] Command
The king of Internet of things protocol: mqtt
QPushButton 样式使用示例(以及按钮setmenu添加下拉菜单的方法)
[buuctf.reverse] 126-130
Class inheritance of 25class
MySql 导出数据库中的全部表索引