当前位置:网站首页>Kotlin Foundation
Kotlin Foundation
2022-06-25 12:15:00 【User 9854323】
List of articles - One . Kotlin Basic knowledge of
- 1. HelloWorld:
- 2、 Common data types
- 3、 Type inference
- 4、 Value range
- 5、 function
- 6、 Character template
- 7、 String comparison
- 8、 Method parameters and null
- 9、when Conditional statements
- 9、 loop and Section
- 10、list And map
- 11、 Functional expression
- 12、 Default and named parameters
- 13、Stirng And Int Interturn
- 14、 exception handling
- 15、 Tail recursive optimization
- Two 、 object-oriented
- 3、 ... and 、 Higher order function ( Parameters / The return value is the function )(forEach,map,flatmap,fold,reduce,filter,takeWhite,let/run,also/apply,with,use)
- Four 、DSL( Domain specific languages )
- 5、 ... and 、 Closure
- 1. HelloWorld:
- 2、 Common data types
- 3、 Type inference
- 4、 Value range
- 5、 function
- 6、 Character template
- 7、 String comparison
- 8、 Method parameters and null
- 9、when Conditional statements
- 9、 loop and Section
- 10、list And map
- 11、 Functional expression
- 12、 Default and named parameters
- 13、Stirng And Int Interturn
- 14、 exception handling
- 15、 Tail recursive optimization
One . Kotlin Basic knowledge of
1. HelloWorld:
fun main(args: Array<String>){
System.out.println("hello world")
}2、 Common data types
3、 Type inference
4、 Value range
var aByte:Byte = Byte.MAX_VALUE
var bByte:Byte = Byte.MIN_VALUE5、 function
fun checkAge(age: Int): Boolean{
if(age > 18) return true else return false
}6、 Character template
fun diaryGeneraer(placeName: String){
var temple = """ It's sunny today , cloudless , Let's go to the ${placeName} play ,"""
println(temple)
}7、 String comparison
And Java It's different ,kotlin in “==” and equals() equally ,equals( , true) Ignore case
8、 Method parameters and null
fun test(){
heat(null) // Compile
heat1(null) // Compile but
}
// Parameters str It can be transmitted null
fun heat(str: String?): String{
return str + " heat "
}
// Parameters str You can't pass null
fun heat1(str: String): String{
return str + " heat "
}9、when Conditional statements
fun gradeStudent(score: Int){
when(score){
10 -> println(" Got full marks ")
8 -> println(" just so so ")
6 -> println(" Just passed ")
3 -> println(" No way. ")
else -> println("other")
}
}when Advanced conditional statements
fun diaryGenerator(placeName: String){
var diary = """ It's sunny today , We went to ${placeName} play ,
| The first thing that comes into view when you enter the gate is ${placeName}
|${strNum(placeName.length)} A large gold plated character """.trimMargin()
print(diary)
}
fun strNum(score: Int): String{
var result = when(score){
1 -> " One "
2 -> " Two "
3 -> " 3、 ... and "
4 -> " Four "
else -> " The place name is too long "
}
return result
}9、 loop and Section
fun main(): Unit{
var nums = 1 .. 100 // Closed interval [1, 100]
var result = 0;
for(num in nums){ // loop :in You can take out the numbers in the array
result = result + num
}
print(" The result is " + result)
print(" The result is ${result}")
}
Open range :
var nums = 1 until 100 // Closed interval [1, 100)
step:
var nums = 1 .. 100
for(num in nums step 2){
print("${num} ,")
}
reverse :
var nums = 1 .. 100
var nums1 = nums.reversed();
for(num in nums1 step 2){
print("${num} ,")
}10、list And map
- list No index
var lists = listOf<String>(" rice ", " egg ", " millet ", " Coix seed ")
for(str in lists){
print(str)
}- list belt index
var lists = listOf<String>(" rice ", " egg ", " millet ", " Coix seed ")
for((i, str) in lists.withIndex()){
print("" + i + " " + str)
print("$i $str")
}- Map
var map = HashMap<String, String>()
map["good"] = " good "
map["yes"] = " yes "
map["no"] = " No "
for(str in map){
println(str)
}
println(map.get("good"))
println(map["good"])11、 Functional expression
//1、
fun add(x: Int, y: Int): Int{
return x + y
}
//2、 When the function body has only one sentence of code :,
fun add(x: Int, y:Int):Int = x + y
//3、 It can be written like this
var sum = {x:Int, y:Int -> x+y}
var i = sum(3, 5) // call
//4、
var sum1:(Int, Int) -> Int = {x,y -> x + y}12、 Default and named parameters
fun main(): Unit{
sum()
sum(1, 3)
sum(x = 3)
sum(y = 9) // Named parameters
}
// Default parameters
fun sum(x:Int = 2, y:Int = 5): Int{
return x + y
}13、Stirng And Int Interturn
fun main(): Unit{
var str = "123"
var int = 123;
var strInt = "123abc"
int = str.toInt();
str = int.toString();
int = strInt.toInt(); // The compiler will report an error java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "123abc"
}14、 exception handling
while (true) {
println(" Please enter a number ")
var str = readLine()
try {
var int = str!!.toInt()
}catch (e: Exception){
println(" eldest brother , To enter numbers ")
}
}15、 Tail recursive optimization
Two 、 object-oriented
1、 Inherit
open class Fathor{ // To be inherited requires open
var chactor: String = " introversion "
open fun action(){ // Need to be copied open
println(" Like to think ")
}
}
class Son: Fathor(){
override fun action() { // Replication requires override
println(" My son is very good ")
}
}2、 Interface
interface Iman {
fun say()
}
abstract class Human(var name:String){
abstract fun eat()
}
class Man(name: String) : Human(name), Iman {
override fun eat() {
println(" Take a big bite ")
}
override fun say() {
}
}3、 Agency and entrustment by
interface IWash {
abstract fun wash();
}
class BigHeadChild : IWash {
override fun wash() {
}
}
class SmallHeadFather : IWash by BigHeadChild(){
override fun wash() {
println(" I'm big daddy , My son helped me wash the dishes ")
BigHeadChild().wash()
}
}4、 Single case object
object BigHeadChild : IWash {
override fun wash() {
}
}
When called () Get rid of
class SmallHeadFather : IWash by BigHeadChild{
override fun wash() {
println(" I'm big daddy , My son helped me wash the dishes ")
BigHeadChild.wash()
}
}5、 enumeration and Seals
enumeration : Focus on data
fun main(): Unit{
println(Week. Monday )
println(Week. Monday .ordinal)
}
enum class Week{
Monday , Tuesday , Wednesday , Thursday , Friday , Saturday , Sunday ,
}Seals : Focus on type
fun main(): Unit{
var s1:Son = Son. Little donkey ()
var s2:Son = Son. Mule ()
}
sealed class Son{
fun sayHello(){
println(" Hello everyone ")
}
class Little donkey () : Son()
class Mule (): Son()
}3、 ... and 、 Higher order function ( Parameters / The return value is the function )(forEach,map,flatmap,fold,reduce,filter,takeWhite,let/run,also/apply,with,use)
//maxBy
printGirl(grilList.maxBy { it.height }) //Java You need to iterate through
//minby
printGirl(grilList.minBy { it.height })
//filter
println(grilList.filter {
(it.height > 123) and (it.height < 1234)
})
//map
var result = grilList.map { "${it.name} : ${it.height}" }
println(result)
//any Is there a
println(grilList.any{ it.height == 1253})
//count
println(grilList.count{ it.height <= 1253})
//find Find the first qualified
println(grilList.find{ it.height == 1253})
//groupBy Group according to different conditions
println(grilList.groupBy{ it.address})
println(grilList.groupBy{ it.address}.get(" Beijing "))
println(grilList.groupBy{ it.address}.get(" Beijing ")?.forEach { printGirl(it) })
//let
grilList.get(0)?.let { printGirl(it) }1、let The applicable scenario of the function
Reference resources :https://blog.csdn.net/u013064109/article/details/78786646 Scene one : The most common scenario is to use let Function processing needs to be directed at a null All objects are subject to space judgment . Scene two : Then it is necessary to specify that a variable can be used within a specific scope
Don't use let, Not elegant enough
mVideoPlayer?.setVideoView(activity.course_video_view)
mVideoPlayer?.setControllerView(activity.course_video_controller_view)
mVideoPlayer?.setCurtainView(activity.course_video_curtain_view
)
Use let
mVideoPlayer?.let {
it.setVideoView(activity.course_video_view)
it.setControllerView(activity.course_video_controller_view)
it.setCurtainView(activity.course_video_curtain_view)
}2、with Applicable scenarios of function
When calling multiple methods of the same class , Class name repetition can be omitted , Call the method of the class directly , Often used for Android in RecyclerView in onBinderViewHolder in , data model Properties of map to UI On :
Not used with front :
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(ViewHolder holder, int position) {
ArticleSnippet item = getItem(position);
holder.tvNewsTitle.setText(StringUtils.trimToEmpty(item.titleEn));
holder.tvNewsSummary.setText(StringUtils.trimToEmpty(item.summary));
String gradeInfo = " difficulty :" + item.gradeInfo;
String wordCount = " Number of words :" + item.length;
String reviewNum = " Journal entry :" + item.numReviews;
String extraInfo = gradeInfo + " | " + wordCount + " | " + reviewNum;
holder.tvExtraInfo.setText(extraInfo);
...
}
Use with after : $ Instead of item
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: ViewHolder, position: Int){
val item = getItem(position)?: return
with(item){
holder.tvNewsTitle.text = StringUtils.trimToEmpty(titleEn)
holder.tvNewsSummary.text = StringUtils.trimToEmpty(summary)
holder.tvExtraInf.text = " difficulty :$gradeInfo | Number of words :$length | Journal entry : $numReviews"
...
}
}3、run Applicable scenarios of function
Apply to let,with Function any scenario . because run The function is let,with A combination of two functions , To be precise, it makes up for let The function must use... In the body of the function it Parameter substitution object , stay run Functions can look like with Functions can also be omitted , Directly access the public properties and methods of the instance , On the other hand, it makes up for with Function input object null problem , stay run Functions can look like let Function to do the same empty processing .
run Before using the function :
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: ViewHolder, position: Int){
val item = getItem(position)?: return
with(item){
holder.tvNewsTitle.text = StringUtils.trimToEmpty(titleEn)
holder.tvNewsSummary.text = StringUtils.trimToEmpty(summary)
holder.tvExtraInf = " difficulty :$gradeInfo | Number of words :$length | Journal entry : $numReviews"
...
}
}Use run after :
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: ViewHolder, position: Int){
getItem(position)?.run{
holder.tvNewsTitle.text = StringUtils.trimToEmpty(titleEn)
holder.tvNewsSummary.text = StringUtils.trimToEmpty(summary)
holder.tvExtraInf = " difficulty :$gradeInfo | Number of words :$length | Journal entry : $numReviews"
...
}
}4、apply Applicable scenario
Overall function and run The function is very similar to , The only difference is that the value it returns is the object itself , and run A function is a closure that returns , Returns the value of the last line . It is based on this difference that its applicable scenarios are slightly different from run The function is a little different . apply It is generally used when an object instance is initialized , You need to assign values to the properties in the object . Or dynamic inflate a XML Of View You need to give View Binding data also uses , This kind of situation is very common . Especially in our development, there will be some data model towards View model In the process of transformation instantiation, we need to use .
Not used apply The code for the function looks like this :
mSheetDialogView = View.inflate(activity, R.layout.layout_sheet_inner, null)
mSheetDialogView.course_comment_tv_label.paint.isFakeBoldText = true
mSheetDialogView.course_comment_tv_confirm.paint.isFakeBoldText = true
mSheetDialogView.course_comment_seek_bar.max = 10
mSheetDialogView.course_comment_seek_bar.progress = 0Use apply The code after the function is like this :
mSheetDialogView = View.inflate(activity, R.layout.layout_sheet_inner, null).apply{
course_comment_tv_label.paint.isFakeBoldText = true
course_comment_tv_score.paint.isFakeBoldText = true
course_comment_seek_bar.max = 10
course_comment_seek_bar.progress = 0
}Multiple levels of judgment :
if (mSectionMetaData == null || mSectionMetaData.questionnaire == null || mSectionMetaData.section == null) {
return;}
if (mSectionMetaData.questionnaire.userProject != null) {
renderAnalysis();
return;}
if (mSectionMetaData.section != null) {
fetchQuestionData();
return;}apply After optimization :
mSectionMetaData?.apply{
//mSectionMetaData Operate when not empty mSectionMetaData
}?.questionnaire?.apply{
//questionnaire Operate when not empty questionnaire
}?.section?.apply{
//section Operate when not empty section
}?.sectionArticle?.apply{
//sectionArticle Operate when not empty sectionArticle
}Four 、DSL( Domain specific languages )
There is only one parameter , And use infix Modified function
// book
class Book{
//infix Infix expressions for custom operators . Ben didn't on, Customize a , No class name is required . Method to call
// Pass in any type of , Return to one Boolean Parameters of type
infix fun on(any: Any): Boolean{
return true
}
}
// Table
class Desk
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
if(Book() on Desk()){
println(" The book is on the desk ")
}
}5、 ... and 、 Closure
边栏推荐
- Database Series: MySQL index optimization summary (comprehensive version)
- 20. MVVM command binding of WPF
- SDN系统方法 | 9. 接入网
- Share 7 immortal wallpaper websites, let the new wallpaper give you a little joy, and don't fall into the repetition year after year.
- How to use SPSS to do grey correlation analysis? Quick grasp of hand-to-hand Teaching
- What should I do to dynamically add a column and button to the gird of VFP?
- VFP calls the command line image processing program, and adding watermark is also available
- Uncover gaussdb (for redis): comprehensive comparison of CODIS
- 一套自动化无纸办公系统(OA+审批流)源码:带数据字典
- 现在网上炒股开户身份证信息安全吗?
猜你喜欢

Real software developers will use this method to predict the future
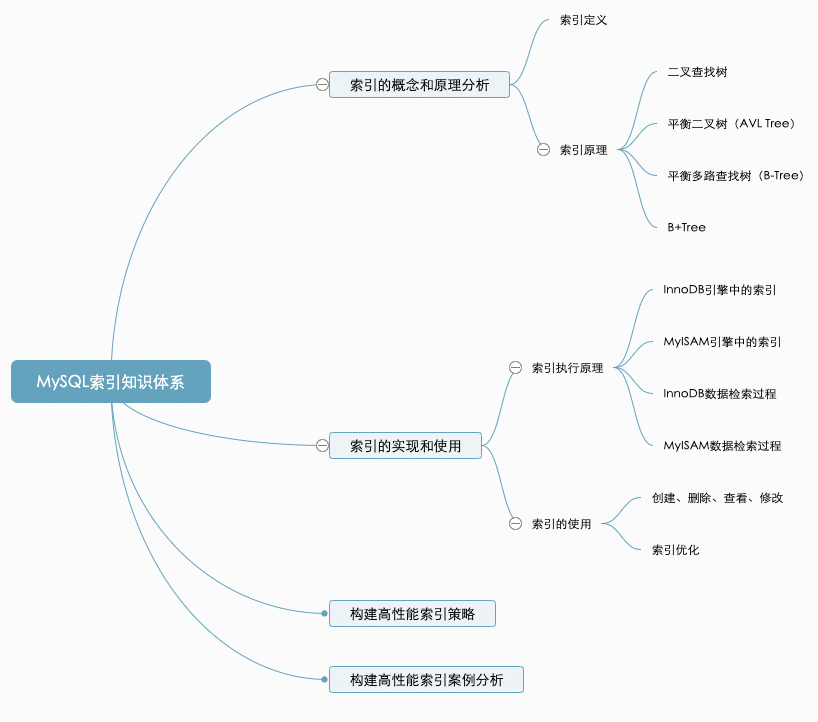
数据库系列:MySQL索引优化总结(综合版)

SQL server saves binary fields to disk file
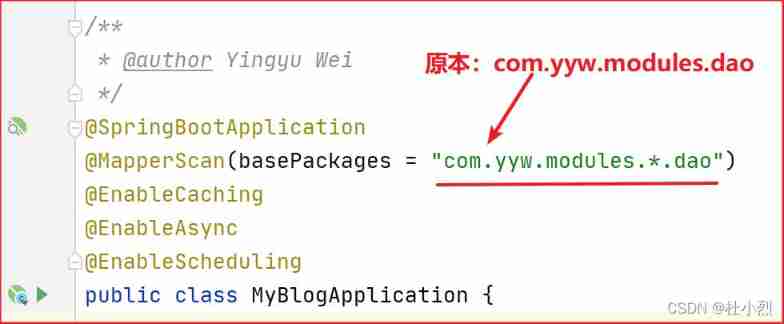
The service layer reports an error. The XXX method invalid bound statement (not found) cannot be found

ROS notes (06) - definition and use of topic messages

Pd1.4 to hdmi2.0 adapter cable disassembly.
![[论]Learning Dynamic and Hierarchical Traffic Spatiotemporal Features with Transformer](/img/58/d68112a3d019de66150e2f5102f436.png)
[论]Learning Dynamic and Hierarchical Traffic Spatiotemporal Features with Transformer

黑马畅购商城---2.分布式文件存储FastDFS

黑马畅购商城---3.商品管理

Explain factor analysis in simple terms, with case teaching (full)
随机推荐
Mpai data science platform random forest classification \ explanation of regression parameter adjustment
A set of automated paperless office system (oa+ approval process) source code: with data dictionary
VFP develops a official account to receive coupons, and users will jump to various target pages after registration, and a set of standard processes will be sent to you
How terrible is it not to use error handling in VFP?
How to use SPSS to do grey correlation analysis? Quick grasp of hand-to-hand Teaching
Why can't you Ping the website but you can access it?
R语言使用nnet包的multinom函数构建无序多分类logistic回归模型、使用epiDisplay包的lrtest函数执行多个模型似然比检验对比两个模型的性能是否有差异
Use PHP script to view the opened extensions
JS to realize the calculation of discrete aggregation points
.Net Core 中使用工厂模式
Sword finger offer II 091 Painting house: application of state machine DP
Understanding and construction of devsecops and Devops
How to use ARIMA model for prediction?
R language uses GLM function to build Poisson logarithmic linear regression model, processes three-dimensional contingency table data to build saturation model, and poisgof function of epidisplay pack
机器学习自学成才的十条戒律
R language uses the multinom function of NNET package to build an unordered multi classification logistic regression model, and uses the lrtest function of epidisplay package to perform multiple model
R语言使用scale函数对神经网络的输入数据进行最小最大缩放、把数据缩放到0到1之间、并划分数据集为训练集和测试集
R语言dplyr包summarise_at函数计算dataframe数据中多个数据列(通过向量指定)的计数个数、均值和中位数、在每个函数内部指定na.rm参数、通过list指定函数列表
【OceanBase】OceanBase简介及其与MySQL的比较
R language uses the multinom function of NNET package to build an unordered multi classification logistic regression model, and uses the summary function to obtain the summary statistical information