Let's take a general look at MySQL Of SQL layer An architectural process of layer :
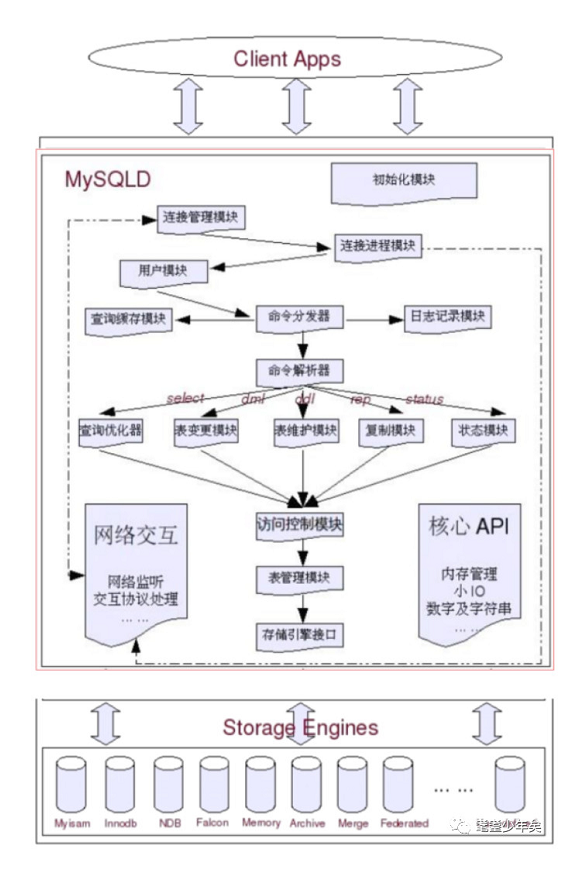
Give a brief description of some key modules :
1. Initial module : Some initial parameters , For example, at the beginning myinit The configuration file ( Under the root directory of the installation ) Some of the parameters in .
2. Connection management module : Start listening , Listen for connection requests
3. Connect the process module : It can be understood as thread pool
4. User module : Verify user , Tokens and permissions
5. Command dispenser : Handle different types of requests
6. Query cache module : Do cache processing , To make inquiries cache, You can think of it as one Map, The query statement is key, The result value is value
7. Logging module
8. Command parser (parser): For different types of sql Statement to process distribution ,select: Query optimizer ,dml: Table change module ,ddl: Table maintenance module ,rep: Copy module ( Master slave copy ),status: Status module .
9. Access control :
10. Table management module :
11. Storage engine interface : and Storage Engines Dealing with
Come straight to Storage Engines, The most talked about is the engine , Such as :
Myisam、Innodb、Faicon、Memory、Archive Wait, engine
And what we usually use is Innodb and Myisam These two kinds of , The most direct difference between these two indexes , From the data table file generated by the corresponding engine , Contrast . such as : use Innodb The engine generates tables A, use Myisam Index generation table B.
Now you can go from Mysql The installation directory /data/ Database name , Under this directory, you can see 5 File :
A.frm : Table definition file
A.ibd : Data and indexes are stored in this file
B.frm : Table definition file
B.myd : Data files
B.myi : Index file
obviously , The difference between the two from the file experience is ,Myisam It is to store data and index separately in two different files .( What is the difference in its essence ? What's the rush )
Let's see , What is the standard to measure an index ?
Namely ,IO Gradual complexity , The adult translation is : When there is more and more data , Whether the index is still efficient , That is, the query is still so fast .
To some extent, the efficiency of an index depends on its index structure .
Hash Indexes :
Make changes to the index field Hash Calculation , Fall into different slots , One obvious drawback is , Unable to do range query , for example select * from data where id >1
Fulltext Indexes :
Full text search index , For example, the value of the field is :abcdefghijk, It will generate another column abcde* , Fuzzy full-text search for prefixes .
R-Tree Indexes :
The cited scenarios are mainly Spatial index , for instance , The American group booked movie tickets , You can choose 3km Cinemas within the scope , The result was found .
B-Tree Indexes :
This index is what I want to focus on , because Innodb and Myisam It's using B+ Tree Indexes , and B+ Tree It's from B-Tree It's evolved from .
that B-Tree What is it like ? Pictured :
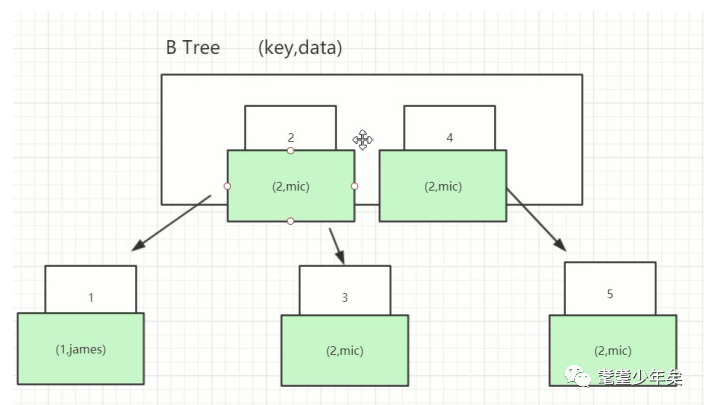
There is an index on each node ( The number above ,id Value ), The data corresponding to the index ( Blue below :id, name)
and B+Tree:

The white numbers above are indexed key, and data Put it all down .( Live in this structure , If you want to know how it is based on key Find the corresponding... From top to bottom data Of , I offer a very interesting web Tools , Go play and think about it .https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/Algorithms.html)
although Innodb and Myisam Are all used B+Tree Indexes , But they are different , Pictured :


As I said before ,Myisam Engine mode , The index and data are stored separately in two files , A file is responsible for inserting data 、 Update, etc. , The other is responsible for maintaining the index . Pictured , White in the index key For the value of the index , The light green below is data: Address of corresponding data . If there are multiple indexes , Just a few of these patterns , Pictured , With name Index , Is the same .
and Innodb: Pictured :


As mentioned above ,Innodb Data and index are put in the same file , The coexistence of index and data is : Pictured , The one in white is key, Even index , When the corresponding... Is found from top to bottom key after ,key The following is the whole corresponding data , Instead of thinking Myisam That will store the address corresponding to the data .
So here comes the question ,Innodb Multiple indexes , What kind of existence is it , Or as shown on the right side of the above figure , Add fields name Index : It will build a secondary index tree , The same structure , white key The index stores name The value corresponding to the field , And the blue square data Stored in the main index tree key.
for instance , When id and name As an index , perform select * from table where name = ‘james’ ,
The first step is to find in the sub index key by james Of data by 1,1 Is the primary index key.
Step 2: go to the main index to find key To be right 1 The data of .(select * from table where id= 1)
One more sentence , This way of indexing is called “ Clustered index ”, Understood as a key and data Are bound together .
and Myisam The way of indexing is called “ Nonclustered indexes ”.
about B+Tree This index , Let's talk about it uuid And self increase id.
Uuid yes 32 Bit , Beyond all doubt , Relative to self increasing id,uuid The storage space is large . and uuid When indexing , It requires more complex operations , Finalize the index key Where to insert .
And self increase id, It fits every time you add 1 The rules of , And the rules have been set , It doesn't have to do too many calculations , Expand horizontally directly from left to right ( Insert ), This makes a difference in performance , Pictured (B+Tree The height of the tree is fixed , by 4 layer ):


Even so ,uuid There is still a market for some projects :
Self increasing id Although there are many advantages , However, self growth is rarely used in large-scale projects id Of , Why is that ? because uuid It almost guarantees the consistency of different tables in different databases id only , You can split and merge data , And self growth id Only one table in a database can be guaranteed id only , Database consolidation will fail due to primary key conflicts , It's a hard injury .
And some bloggers say : Distributed architecture , This means that you need to maintain the uniqueness of the primary key of a table in multiple instances . At this time, the common single table increases automatically ID The primary key is not appropriate , Because of multiple mysql The instance will encounter the problem of global uniqueness of the primary key
Let's talk about some small problems of composite index
Composite indexes are sequential , It's called the leftmost principle . What does that mean . for instance :
name、age、weight this 3 Fields form a combined index ,name In the first 1 position , So the query statement where There has to be name=”value” This condition , Otherwise, this index will not work , This is called The principle of left .
Then I quote an example from the Internet :

The benefits of indexing are :
1. Improve retrieval efficiency
2. Reduce sorting costs , The fields corresponding to the index will have an automatic sorting function , The default is ascending asc.
Every coin has two sides, Its disadvantage is
1. Update index IO The amount .
That is to say , When inserting a piece of data , In addition to inserting the data itself , Also insert the node corresponding to the index information of the data , If the corresponding table has multiple indexes , Insert index information nodes corresponding to multiple data . And these are stored on the hard disk as file types .
2. The amount of calculation caused by adjusting the index ,
How to understand this , for instance , image B-tree Indexes , Before inserting the index , All have to be calculated , How much space does the index require , Where to insert .
3. Occupied storage space .
It turns out that the index is both good and bad , When to index , When is it not necessary to ?
fit :
1. More frequent fields as query criteria should be indexed
Not suitable for :
1. The uniqueness of the field value is too poor for A separate Do the index
2. Fields that are updated very frequently are not
3. Will not appear in where The fields in the sentence are not suitable for .