当前位置:网站首页>Using pycaret for data mining: association rule mining
Using pycaret for data mining: association rule mining
2022-07-23 12:19:00 【-Send gods-】
Association rules Used to discover interesting relationships between variables in large databases . It aims to use some interesting methods to identify strong rules found in the database . By mining association rules, we can find the regularity between commodities in the large-scale transaction data of supermarkets or e-commerce , The most famous case is “ Beer and diapers ” The story of ,20 century 90 In American supermarkets in the S , Supermarket managers found an incomprehensible phenomenon when analyzing sales data : In certain circumstances ,“ beer ” And “ diapers ” Two seemingly unrelated items often appear in the same basket . For example, people find in the sales data of supermarkets , If customers buy bread and milk at the same time , They also buy butter . Such information can help enterprises make decisions about marketing activities .
Let's explain some basic theoretical knowledge about association rules , First we define :
 , among I Represents a collection of all items ,
, among I Represents a collection of all items ,  It means the first one 1, The first 2, The first ... A commodity .
It means the first one 1, The first 2, The first ... A commodity .
 , among D Represents all transactions in the database ( Order ) Record ,
, among D Represents all transactions in the database ( Order ) Record , Table is No 1, The first 2, The first ... Order records .
Table is No 1, The first 2, The first ... Order records .
Each stroke transaction stay D Have a unique transaction ID And it contains a collection of goods I Subset .
Association rules are searched frequently in the database if-then A combination of strongly related items of a pattern , This combination is called frequent itemsets . But it is not easy to find all frequent itemsets in the database , Because it involves traversing all data to find all possible itemset combinations from all possible itemsets . The collection of possible item sets is the collection of items I Of Power set , And the size is  , Of course, this means excluding empty sets that are not considered valid itemsets , But the size of the power set will vary with the items in the power set n The number increases exponentially by using the supported downward closure property ( Also known as anti monotonicity ), You can search effectively . This will ensure that frequent itemsets and all their subsets are also frequent , Therefore, infrequent itemsets will not be regarded as a subset of frequent itemsets . Take advantage of this feature , Some efficient algorithms ( for example ,Apriori and Eclat) You can find all frequent itemsets .
, Of course, this means excluding empty sets that are not considered valid itemsets , But the size of the power set will vary with the items in the power set n The number increases exponentially by using the supported downward closure property ( Also known as anti monotonicity ), You can search effectively . This will ensure that frequent itemsets and all their subsets are also frequent , Therefore, infrequent itemsets will not be regarded as a subset of frequent itemsets . Take advantage of this feature , Some efficient algorithms ( for example ,Apriori and Eclat) You can find all frequent itemsets .

The above item set :{a,b,c} The power set of is the set of all subsets ( Including empty sets ) The number of subsets is  , The number of frequent itemsets is
, The number of frequent itemsets is  ( Exclude empty sets ).
( Exclude empty sets ).
Association rules are defined as :
 , among
, among  , here X,Y All are I Subset , It can be understood that if the user buys 1 One or more products , Then I will also buy another 1 One or more products . here X,Y yes I Therefore, all of them contain 1 One or more products . This is the general definition of association rules , But in the actual application scenario, it is generally defined Between a subset of products and a single product Association rules of :
, here X,Y All are I Subset , It can be understood that if the user buys 1 One or more products , Then I will also buy another 1 One or more products . here X,Y yes I Therefore, all of them contain 1 One or more products . This is the general definition of association rules , But in the actual application scenario, it is generally defined Between a subset of products and a single product Association rules of :
 , among
, among  . This rule can be understood in this way : If the customer buys One or more goods , That will also buy another One goods . among
. This rule can be understood in this way : If the customer buys One or more goods , That will also buy another One goods . among  The meaning is “ If ... that ...”, That is... In English if... then.
The meaning is “ If ... that ...”, That is... In English if... then.
Here we use support( Support ) 、confidence( Degree of confidence )、lift( Promotion )、conviction( Error rate ) And other evaluation indicators to measure the strong correlation degree of frequent itemsets .
support ( Support ) Indicates the probability of two items appearing simultaneously in the data set :
support (X,Y)=
That is, the frequency of strongly correlated item combinations in a given data set , It's understandable , The proportion of orders that have purchased bread and milk at the same time in all orders .
confidence( Degree of confidence ) He expresses a conditional probability : It's understandable , Among all orders for bread, the proportion of orders that have purchased milk . We can use the formula of conditional probability to calculate the confidence :
It's understandable , Among all orders for bread, the proportion of orders that have purchased milk . We can use the formula of conditional probability to calculate the confidence :

lift( Promotion ), It can be used to compare expected Confidence And the actual Confidence, Means to contain X At the same time Y The possibility and unconditionally contain Y The probability ratio of , That is to say Y The possibility of its own emergence P(Y) On the basis of ,X The emergence of Y Of “ The rate of appearance ”P(Y|X) The degree of improvement :
 .
.
If lift = 1, Express X And Y Are independent of each other ,X Yes Y The probability of occurrence does not increase , The greater the value (lift >1) Express X Yes Y The greater the degree of improvement , It also means that the stronger the relevance .
conviction( Error rate ) , Its function is to measure the probability of wrong prediction of correlation rules , surface ⽰X appear ⽽Y Probability of not appearing .

Let's take a simple example to deepen our understanding of support,confidence,lift,conviction And other evaluation indicators : The... In the database is shown below 5 The transaction record contains 7 A commodity .
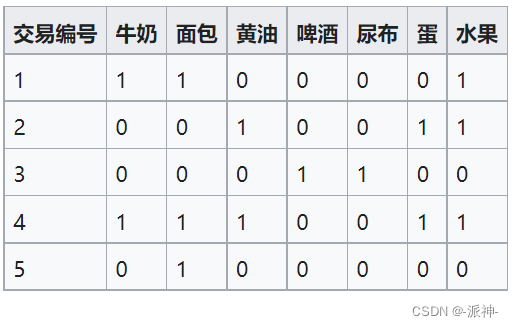
Let's figure it out { beer , diapers } Of support( Support ),
supp( beer , diapers )=1/5=0.2 , Of all the 5 In orders , Only one order has bought beer and diapers at the same time ( The first 3 Order per order ).
supp( milk , bread , butter )=1/5=0.2 , Of all the 5 In orders , Only one order has purchased milk at the same time , Bread and butter ( The first 4 Order per order ).
conf({ butter , bread } { milk })=P( milk | butter , bread )=P( milk ∩ butter ∩ bread )/P( butter ∩ bread )=1, Here, it means that among all the orders that have purchased butter and bread, multiple orders have also purchased milk , From the data sheet, we can find that only one order has purchased butter and bread ( The first 4 Order per order ) And I also bought milk in this order , therefore P( milk ∩ butter ∩ bread )/P( butter ∩ bread )=1/1=1.
{ milk })=P( milk | butter , bread )=P( milk ∩ butter ∩ bread )/P( butter ∩ bread )=1, Here, it means that among all the orders that have purchased butter and bread, multiple orders have also purchased milk , From the data sheet, we can find that only one order has purchased butter and bread ( The first 4 Order per order ) And I also bought milk in this order , therefore P( milk ∩ butter ∩ bread )/P( butter ∩ bread )=1/1=1.
conf( Fruits  egg )=P( egg | Fruits )=P( egg ∩ Fruits )/P( Fruits )=2/3=0.67 Here means there is 3 Fruit has been purchased on orders , Here 3 Among the orders for fruits, two orders have purchased eggs, so the probability is 2/3.
egg )=P( egg | Fruits )=P( egg ∩ Fruits )/P( Fruits )=2/3=0.67 Here means there is 3 Fruit has been purchased on orders , Here 3 Among the orders for fruits, two orders have purchased eggs, so the probability is 2/3.
lift({ milk , bread } { butter })=P( butter | milk , bread ) / P( butter )=0.5/0.4=1.25, here lift>1 Explain buying bread , Milk is helpful in buying butter , What needs to be explained here is : If lift (Y|X)= 1, Express X And Y Are independent of each other ,X Yes Y The probability of occurrence does not increase , The greater the value (lift >1) Express X Yes Y The greater the degree of improvement , It also means that the stronger the relevance .
{ butter })=P( butter | milk , bread ) / P( butter )=0.5/0.4=1.25, here lift>1 Explain buying bread , Milk is helpful in buying butter , What needs to be explained here is : If lift (Y|X)= 1, Express X And Y Are independent of each other ,X Yes Y The probability of occurrence does not increase , The greater the value (lift >1) Express X Yes Y The greater the degree of improvement , It also means that the stronger the relevance .
conv({ milk , bread } { butter })=
{ butter })=

=(1-0.4)/(1-0.5)=0.6/0.5=1.2
This shows that the probability of containing milk and bread but not butter increases 20%.
Apriori Algorithm
Apriori from R. Agrawal and R. Srikant stay 1994 Given in , For frequent itemset mining and association rule learning . It identifies individual items that frequently appear in the database and extends them to an increasing set of items , As long as these item sets appear frequently enough . The name of the algorithm is Apriori, Because it uses a priori knowledge of frequent itemset attributes .

Apriori The algorithm uses “ Bottom up ” Methods , Among them, frequent subsets expand one term at a time ( be called Candidate generation Steps for ), And test candidate groups for data . When no further successful extensions are found , Algorithm was terminated .Apriori Use Breadth first search and Hash tree Structure to effectively calculate candidate item sets . It generates candidate length item sets from long item sets . Then it prunes candidates with uncommon sub patterns . According to the downward closure theorem , Candidate sets contain all frequent length itemsets . after , It scans the database to identify frequent itemsets in candidates .
Below is a sample of a cancer data set , The letters represent a specific mutation combination , We need to search for frequent itemsets in these combinations :

First calculate the of each letter support ( Support ), Then set a minimum threshold :3 To trim the project set :

Because the support of all letters is greater than or equal to 3, So no pruning . Frequent itemsets are {a}、{b}、{c} and {d}, Next we are {a}、{b}、{c} and {d} Calculate two tuples based on ( Any combination of two letters ) support :
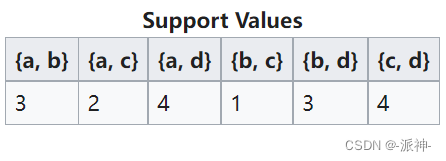
Now let's set the minimum support threshold of binary to 4, So after pruning, only {a, d} and {c, d} Will be kept . And then we have {a, d} and {c, d} Calculate triples based on ( Any combination of three letters ) support :

Because in the end, we only have a triple , So the next round of quads is empty , So the algorithm will stop . The last frequent itemset retained is :{a}、{b}、{c} 、{d}、{a, d} 、 {c, d}、{a,c,d}.
utilize pycaret To realize data association rule mining
PyCaret yes Python Open source in 、 Low code machine learning library , It can automatically execute machine learning workflow . It is an end-to-end machine learning and model management tool , It can double your work efficiency . Compared with other open source machine learning libraries ,PyCaret Is a low code machine learning framework , It can be used to replace hundreds of lines of code you wrote before with just a few lines of code . This makes the development process exponentially fast and efficient .PyCaret It is essentially a combination of several machine learning libraries and frameworks Python Wrappers , for example scikit-learn、XGBoost、LightGBM、CatBoost、spaCy、Optuna、Hyperopt、Ray wait . Today we will take a look at a simple example of association rule mining pycaret How powerful !
pycaret To realize association rule mining, there are generally the following steps :
- Getting Data: from PyCaret The repository imports simulation data , Or you can read external real data
- Setting up Environment: stay PyCaret Set the algorithm environment in and prepare to start implementing association rule mining
- Create Model: Create the algorithm model of association rule mining
- Plot Model: Use various plots to analyze model performance
data
We will use from UCI Data sets A small sample of , Called online retail dataset . This is a transaction data set , It includes 2010 year 1 month 12 solstice 2011 year 9 month 12 Transactions between the two days . The following is a brief description of the meaning of data fields :
- InvoiceNo: Invoice number , One 6 Unique integer of bits . If this code is written in letters “c” start , It means cancel .
- StockCode: Commodity code , One 5 An integer , Each product has a unique code .
- Description: Description of the product .
- Quantity: The quantity of each commodity per transaction .
- InvoiceDate: Invoice date and time , The date and time when each transaction was generated .
- UnitPrice: Unit price of goods , The price of goods in pounds .
- CustomerID: Customer number , Each customer is uniquely assigned 5 An integer .
- Country: Country name , The name of each customer's country .
1.Getting Data
because pycaret This retail data set has been built in , So you can use pycaret Provided get_data Method to get the data :
from pycaret.datasets import get_data
data = get_data('france')
print(' Unique invoice quantity :',data.InvoiceNo.nunique())
print(' Number of unique products :',data.Description.nunique()) 
We found that the only invoice quantity in the dataset is 461, The only quantity of goods is 1565.
2.Setting up Environment
Here we will use setup() function , Its function is to initialize PyCaret Environment in , And convert the data set into Apriori Acceptable shape of Algorithm . setup() Three mandatory parameters are required :pandas Of dataframe、transaction_id, It means transaction id The name of the column ( In this case, the publication number ), Will be used to perspective the matrix ; item_id Is the name of the column used to create the rule ( In this case, it is Description). Usually , This will be the variable of interest . You can also pass optional parameters ignore_items To ignore item_id Some values in .
from pycaret.arules import *
exp=setup(data=data,transaction_id='InvoiceNo',item_id = 'Description')
Successful execution setup() after , It prints an information grid containing a small amount of important information :
- Transactions : The number of unique transactions in the dataset . under these circumstances , Unique InvoiceNo The number of .
- Items : The number of unique items in the dataset .
- Ignore Items : Items to be ignored in rule mining . A lot of times , The combination of frequent itemsets is meaningless , So you may want to ignore them . for example : Many transaction datasets will contain freight , Many other goods may be strongly related to freight , So in order to ignore this meaningless frequent itemset, we can setup() Use in ignore_items Parameter ignored . Later we will run setup() once , Later we will ignore some specific meaningless items .
It's calculated here Transactions and Items The quantity of is the same as the result of our previous statistics .
3.Create a Model
Creating an association rule model is simple , create_model() No mandatory parameters are required . It has 4 Optional parameters , As shown below :
- metric: Set evaluation indicators : 'confidence','support', 'lift', 'leverage', 'conviction', The default value is ‘confidence’
- threshold: The minimum threshold of the evaluation index , The default setting is 0.5.
- min_support:0 To 1 The floating point number between , The minimum support for the returned item set is 0.05
- round: The decimal indicator in the score in the evaluation result will be rounded
Next, we will create an association rule model using default parameters , Eventually, all frequent itemsets will be mined {  }:
}:
model1 = create_model()
print(' Number of frequent itemsets :',len(model1))
model1.head()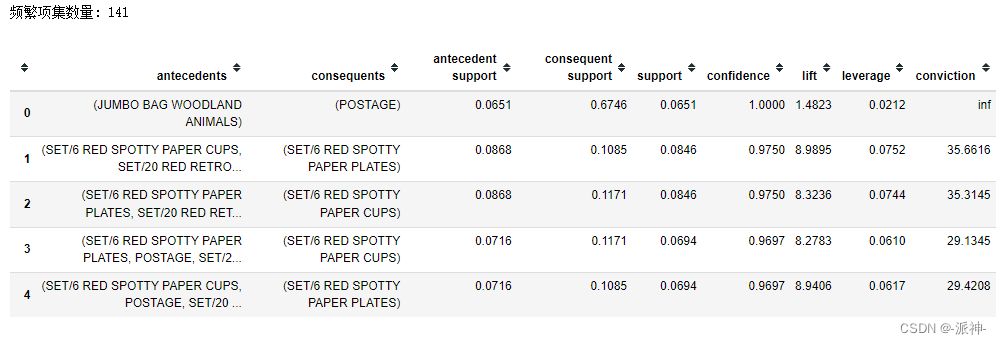 Here the association rule model mining out 141 Frequent itemsets {
Here the association rule model mining out 141 Frequent itemsets {  }, And calculate 'confidence','support', 'lift', 'leverage', 'conviction' And so on .
}, And calculate 'confidence','support', 'lift', 'leverage', 'conviction' And so on .
4.Setup with ignore_items
We find that in the results of the above frequent itemsets antecedents and consequents There are many POSTAGE, and POSTAGE Means freight , So most frequent itemsets combined with freight are meaningless , So we have to get rid of POSTAGE. And now we're going to go to the setup() Method used in Ignore Items Parameters to exclude POSTAGE.
exp=setup(data=data,
transaction_id='InvoiceNo',
item_id = 'Description',
ignore_items = ['POSTAGE'])
model2 = create_model()
print(' Number of frequent itemsets :',len(model2))
model2.head() 
After elimination POSTAGE Association rule model mining out 45 Frequent itemsets .
5.Plot Model
Next, we use two-dimensional and three-dimensional visualization methods to show the distribution of evaluation scores of each group of frequent itemsets in plane and space :
plot_model(model2) 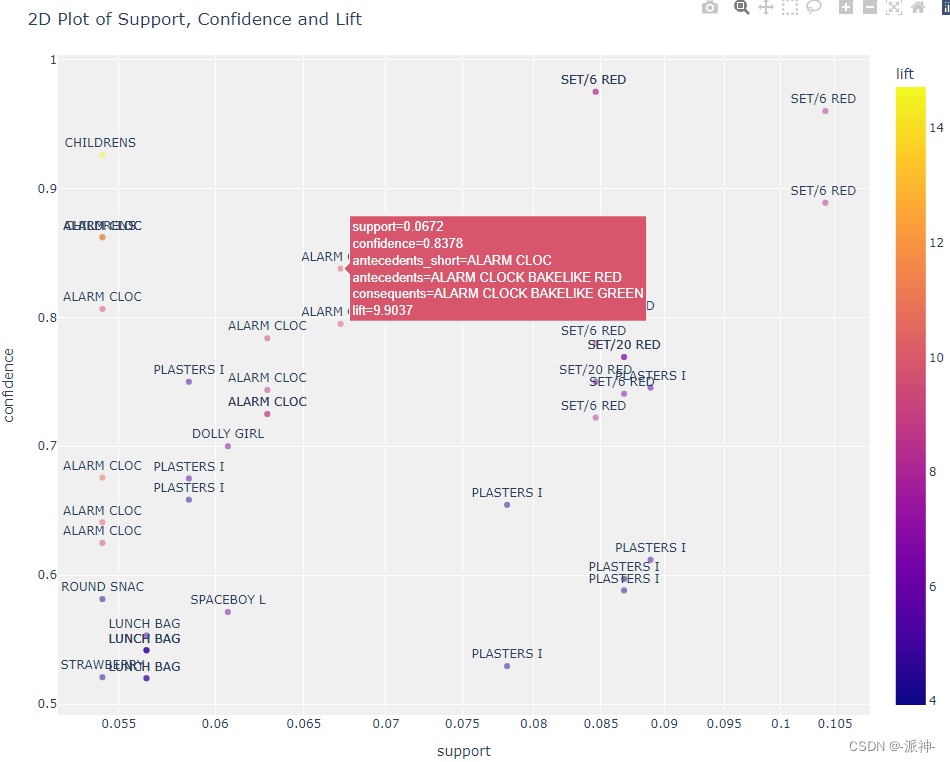
plot_model(model2, plot = '3d') 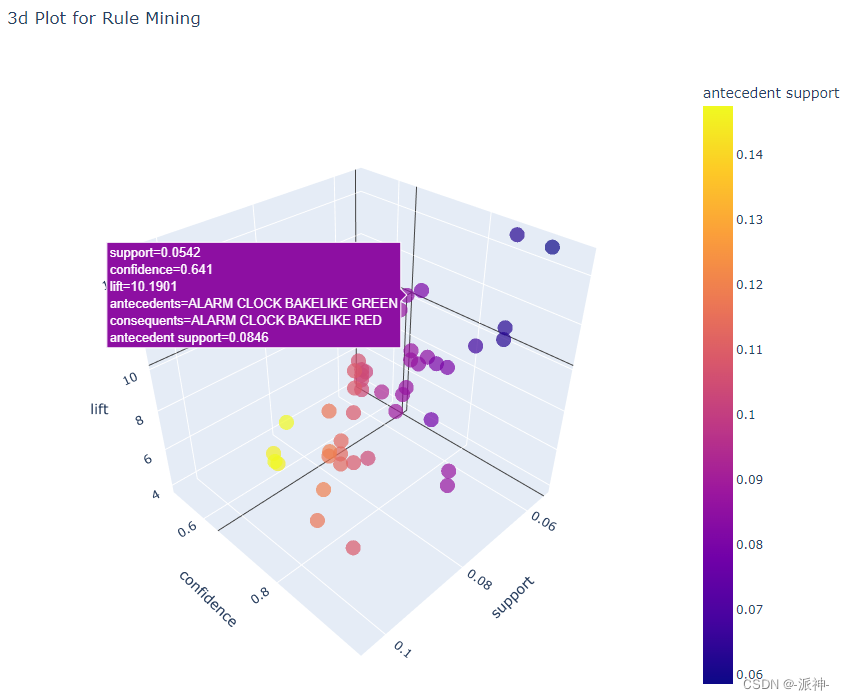
Reference material
边栏推荐
- Using Google or tools to solve logical problems: Zebra problem
- Matplotlib Usage Summary
- Ninja file syntax learning
- 论文解读:《利用注意力机制提高DNA的N6-甲基腺嘌呤位点的鉴定》
- Gartner research: how is China's digital development compared with the world level? Can high-performance computing dominate?
- All kinds of ice! Use paddegan of the propeller to realize makeup migration
- ARM架构与编程3--按键控制LED(基于百问网ARM架构与编程教程视频)
- ARM架构与编程1--LED闪烁(基于百问网ARM架构与编程教程视频)
- 深度卷积生成对抗网络
- Interpretation of the paper: attention based multi label neural network for comprehensive prediction and interpretation of 12 widely existing RNA modifications
猜你喜欢
时间序列的数据分析(三):经典时间序列分解

Eigen multi version library installation

In depth interpretation of Google or tools' complex scheduling program

Development and deployment of steel defect detection using paddlex yolov3 of propeller

论文解读:《开发一种基于多层深度学习的预测模型来鉴定DNA N4-甲基胞嘧啶修饰》

Using or tools to solve the path planning problem (TSP)

深度卷积生成对抗网络

数据挖掘场景-发票虚开

ARM架构与编程7--异常与中断(基于百问网ARM架构与编程教程视频)

时间序列的数据分析(二):数据趋势的计算
随机推荐
笔记 | 百度飞浆AI达人创造营:深度学习模型训练和关键参数调优详解
Chaoslibrary · UE4 pit opening notes
Practical convolution correlation trick
“東數西算”下數據中心的液冷GPU服務器如何發展?
知识图谱、图数据平台、图技术如何助力零售业飞速发展
论文解读:《提高N7-甲基鸟苷(m7G)位点预测性能的迭代特征表示方法》
strand
利用or-tools来求解路径规划问题(VRP)
All kinds of ice! Use paddegan of the propeller to realize makeup migration
Eigen multi version library installation
How to develop the liquid cooled GPU server in the data center under the "east to West calculation"?
Using Google or tools to solve logical problems: Zebra problem
常用數學知識匯總
论文解读:《Deep-4mcw2v: 基于序列的预测器用于识别大肠桿菌中的 N4- 甲基胞嘧啶(4mC)位点》
数据分析(一)
Nt68661 screen parameter upgrade-rk3128-start up and upgrade screen parameters yourself
BST tree
The data set needed to generate yolov3 from the existing voc207 data set, and the places that need to be modified to officially start the debugging program
利用or-tools来求解带容量限制的路径规划问题(CVRP)
Eigen多版本库安装