当前位置:网站首页>Common OJ questions of stack and queue
Common OJ questions of stack and queue
2022-07-24 13:24:00 【Chen San】
Stacks and queues

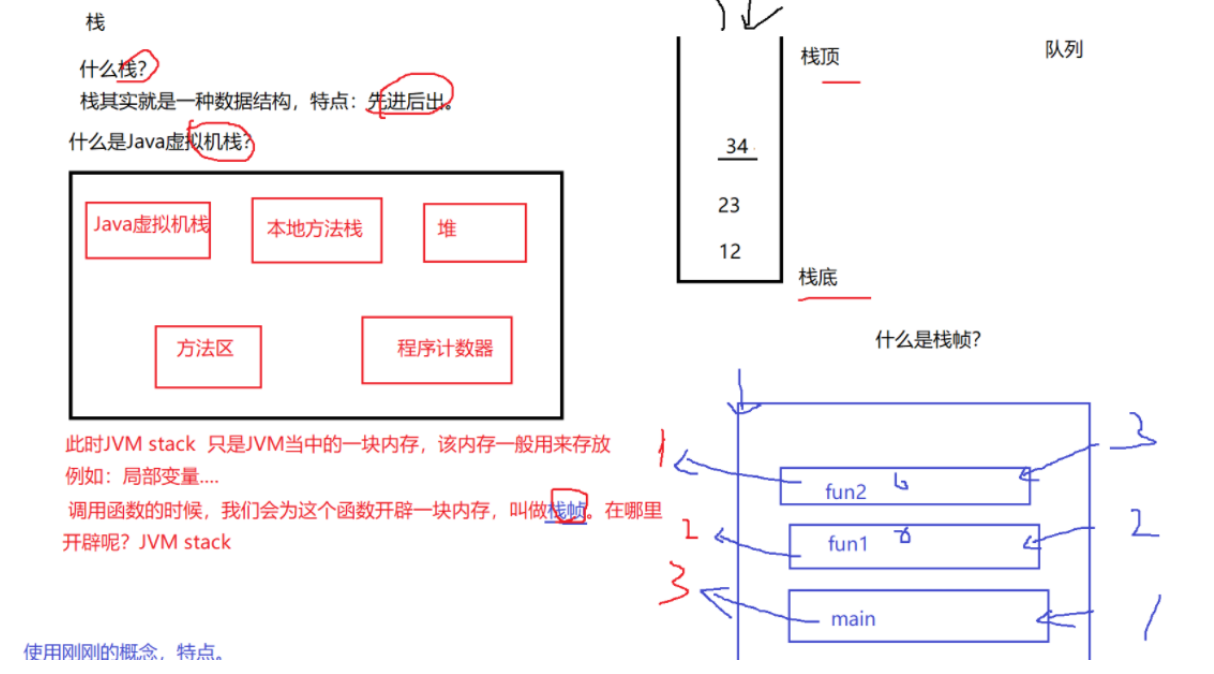
Stack is first in first out ( Delete and insert at the top of the stack ), So you can use it in some special places , Such as printing linked lists in reverse order .
For example, judge the order of stack data , Infix expression turn Postfix expression ( Suffix expression is also called inverse Polish expression )

Now it will be converted into a suffix expression , Use this expression to calculate . So how to convert it into a suffix expression You need a stack
Some methods in the stack , You can see api, More commonly used :peek,pop,push,isEmpty,search

public static void main(String[] args) {
MyStack stack = new MyStack();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.push(5);
stack.push(6);
System.out.println(stack.pop());// Pop up top element , And delete 6
System.out.println(stack.pop());// Pop up top element , And delete 5
System.out.println(stack.pop());// Pop up top element , And delete 4
System.out.println(stack.pop());// Pop up top element , And delete 3
System.out.println(stack.pop());// Pop up top element , And delete 2
System.out.println(stack.pop());// Pop up top element , And delete 1
System.out.println(stack.peek());// Get stack top element , But don't delete 5
System.out.println(stack.peek());// Get stack top element , But don't delete 5
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty());//false
System.out.println(stack.size());
}
The pop-up of the stack 、 Press out
Pressure into the stack 、 eject
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public boolean IsPopOrder(int [] pushA,int [] popA) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<pushA.length;i++){
stack.push(pushA[i]);
while(!stack.isEmpty() && j<popA.length && popA[j] == stack.peek()){
stack.pop();
j++;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
Inverse Polish evaluation
class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
String val = " ";
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0;i<tokens.length;i++){
val = tokens[i];
if(!isOperation(val)){
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(val));
}else{
int num2 = Integer.valueOf(stack.pop());
int num1 = Integer.valueOf(stack.pop());
switch(val){
case "+":
stack.push(num1+num2);
break;
case "-":
stack.push(num1-num2);
break;
case "*":
stack.push(num1*num2);
break;
case "/":
stack.push(num1/num2);
break;
}
}
}
return stack.pop();
}
public boolean isOperation(String x){
if(x.equals("+")||x.equals("-") || x.equals("*") || x.equals("/")){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
These are two problems solved by stack
Create stack objects , The default constructor actually provides a stack size of 10 Space
Realize some basic functions of stack
public class MyStack {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public MyStack() {
this.elem = new int[5];
}
public void push(int val) {
if(isFull()) {
// Capacity expansion
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
this.elem[this.usedSize] = val;
this.usedSize++;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}
public int pop() {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException(" The stack is empty. !");
}
int oldVal = this.elem[usedSize-1];
this.usedSize--;
return oldVal;
}
public int peek() {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException(" The stack is empty. !");
}
return this.elem[usedSize-1];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.usedSize == 0;
}
}

Bracket matching problem
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
int k = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<s.length();i++){
String s1 = s.charAt(i)+"";
if(s1.equals("(") ||s1.equals("{") ||s1.equals("[")){
stack.push(s1);
k++;
}else{
switch(s1){
case ")":
if(!stack.isEmpty() && "(".equals(stack.peek())){
stack.pop();
}else{
return false;
}
break;
case "}":
if(!stack.isEmpty() && "{".equals(stack.peek())){
stack.pop();
}else{
return false;
}
break;
case "]":
if(!stack.isEmpty() && "[".equals(stack.peek())){
stack.pop();
}else{
return false;
}
break;
}
}
}
if(k != 0){
return stack.isEmpty();
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
Implement the minimum stack
// BOGO explained the last part of the section in the stack
class MinStack {
private Stack<Integer> stack;
private Stack<Integer> minStack;
public MinStack() {
stack = new Stack<>();
minStack = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int val) {
stack.push(val);
if(!minStack.isEmpty()){
int cur = minStack.peek();
if(val <= cur){
minStack.push(val);
}
}else{
minStack.push(val);
}
}
public void pop() {
int popVal = stack.pop();
if(!minStack.isEmpty()){
int top = minStack.peek();
if(top == popVal){
minStack.pop();
}
}
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}

LinkedList The bottom layer is a two-way linked list

public static void main1(String[] args) {
//LinkedList Realized Queue and Deque, The parent class reference points to the subclass object , Achieved upward transformation , But the way
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); // Normal queue : Head to head , At the end of the team
Deque<Integer> queue2 = new LinkedList<>();// deque : The head and tail of the team can go in and out
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
Here again, the upward transformation : The methods used by the first two references must be included in the methods of the parent class , So there are few methods , And the third kind does not adopt upward transformation , More ways . But we usually use the words of upward transformation , It doesn't need that method , Enough for us , And can clearly point out that we just want to use Queue This class .
Queues can also be implemented in the structure of arrays and linked lists , It is better to use the structure of linked list , Because if you use the structure of an array , Out of the queue on the array header
Data , It will be less efficient



public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueue queue = new MyQueue();
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
System.out.println(queue.peek());//1
System.out.println(queue.poll());//1
System.out.println(queue.poll());//2
System.out.println(queue.poll());//3
System.out.println(queue.poll());//
}
public static void main2(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(2);
System.out.println(queue.peek());//1
System.out.println(queue.poll());//1
}
public static void main3(String[] args) {
Deque<Integer> queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
queue2.offerLast(1);// By default, those who join the team at the end of the team
queue2.offerFirst(2);
//2 1
System.out.println(queue2.peekFirst());//2
System.out.println(queue2.peekLast());//1
}

The picture above says : Two way linked list can realize ordinary queue 、 deque 、 Double linked list .
Next, a single linked list is used to implement the queue ( A two-way linked list can also )
But if you join the team in the single linked list The time complexity is O(1) But the time complexity of leaving the team is O(N) So you add a tail pointer

class Node{
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public class MyQueue {
public Node head;
public Node last;
public void offer(int val){
Node node = new Node(val);
if(head == null){
head = node;
last = node;
}else{
last.next = node;
last = last.next;
}
}
/** * Out of the team */
public int poll(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException(" The queue is empty , Unable to get out of the queue ");
}
int oldVal = this.head.val;
this.head = head.next;
return oldVal;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return head == null;
}
public int peek(){
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException(" The queue is empty , Unable to get out of the queue ");
}
return head.val;
}
}
Circular queue



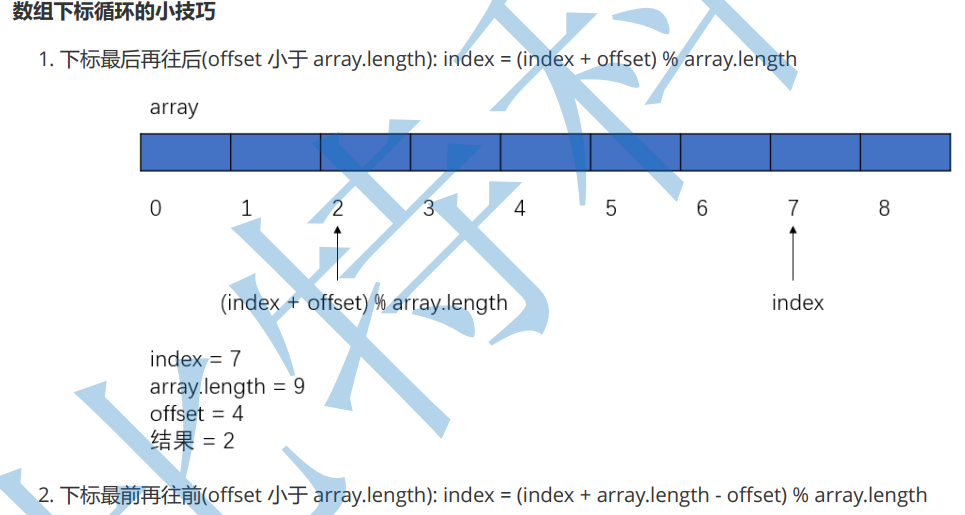
Design loop queue
class MyCircularQueue {
public int front;
public int rear;
public int[] elem;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
this.elem = new int[k+1]; // Here is the third , Waste a space , But you have to create another space , Otherwise not satisfied oj
}
/** * The team * @param value * @return */
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
elem[rear] = value;
rear = (rear+1) % elem.length; // Every time you join the team ,rear Both ++, But when you are length-1s when , If you add more, it will become a subscript 0 了 , here
// Using this formula
return true;
}
/** * Out of the team * @param * @return */
public boolean deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()){
return false;
}
// It's the same every time you leave the team , When you front Come out length-1 When , You should have ++, At this point, you need to draw the subscript 0, But at this time front++ become length
// So we still have to use this formula
front = (front+1) % elem.length;
return true;
}
/** * Get the team leader element * @return */
public int Front() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return elem[front];
}
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
int index = -1;
// Returns the element at the end of the team ( A way to waste a space ), Your last element should be rear-1 The location of , But when you are rear = 0, You should be length-1 The value of the subscript , Also to judge
if(rear == 0 ){
index = elem.length-1;
}else{
index = rear-1;
}
return elem[index];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
public boolean isFull() {
//rear Is your next front , It's a waste of space , Then there must be a space empty , and front and rear It is caught in the middle that is slow , It is suggested to refer to the figure of the third kind above
if((rear+1) %elem.length == front){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
Use two queues to implement a stack
Use two queues to implement a stack
class MyStack {
// This question also uses two queues , Now put the data into the queue that is not empty ( If all are empty , First specify a ) When the element comes out , Put the elements out of the stack that are not empty into the empty stack , But only size-1 individual , The last one makes us get out of the stack , So we don't put it in the second stack , But directly out . Then, the output element of the stack is realized ,peek Words , Same thing , You can also put them all in the second stack , Then return the last data put
// Using two queues to implement the stack
private Queue<Integer> qu1;
private Queue<Integer> qu2;
public MyStack() {
qu1 = new LinkedList<>();
qu2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
if(!qu1.isEmpty()){
qu1.offer(x);
}else if(!qu2.isEmpty()){
qu2.offer(x);
}else{
qu1.offer(x);
}
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(!qu1.isEmpty()){
int size = qu1.size();
int val = -1;
for(int i = 0;i<size-1;i++){
val = qu1.poll();
qu2.offer(val);
}
return qu1.poll();
}
if(!qu2.isEmpty()){
int size = qu2.size();
int val = -1;
for(int i = 0;i<size-1;i++){
val = qu2.poll();
qu1.offer(val);
}
return qu2.poll();
}
return -1;
}
public int top() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(!qu1.isEmpty()){
int size = qu1.size();
int val = -1;
for(int i = 0;i<size;i++){
val = qu1.poll();
qu2.offer(val);
}
return val;
}
if(!qu2.isEmpty()){
int size = qu2.size();
int val = -1;
for(int i = 0;i<size;i++){
val = qu2.poll();
qu1.offer(val);
}
return val;
}
return -1;
}
public boolean empty() {
return qu1.isEmpty() && qu2.isEmpty();
}
}
Using stack to realize queue
class MyQueue {
// The basic idea is to put all the data on the stack 1, First, judge the stack 2 Empty not empty , If it's empty, don't let it go , In fact, at first I didn't understand why I had to judge the stack 2 Empty not empty , Later, a debugging found , If you don't have this condition , Stack 2 It was originally an element , If you continue to put it in if you are not empty , The element at the top of your stack is the following element , The previous elements haven't come out yet , So you have to make sure that the elements in front of you are finished before you can continue to put the elements behind
Stack<Integer> stack1 ;
Stack<Integer> stack2 ;
public MyQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<>();
stack2 = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
int val = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(val);
}
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(stack2.isEmpty()){
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
int val = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(val);
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty();
}
}
The entry and exit elements of the stack are push、pop
The entry and exit elements of the queue are offer、poll The screenshot above has
deque
deque (deque) It refers to a queue that allows both ends to queue in and out ,deque yes “double ended queue” For short .
That means that elements can go out of the team and join the team , You can also get out of the team and join the team from the end of the team
}
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(stack2.isEmpty()){
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
int val = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(val);
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty();
}
}
------
== The entry and exit elements of the stack are push、pop==
== The entry and exit elements of the queue are offer、poll The screenshot above has ==
## deque
deque (deque) It refers to a queue that allows both ends to queue in and out ,deque yes “double ended queue” For short .
That means that elements can go out of the team and join the team , You can also get out of the team and join the team from the end of the team
边栏推荐
- [datasheet] interpretation of cs5480 data book of metering chip
- Repair the problem of adding device groups and editing exceptions on easycvr platform
- Introduction of embedded network interface scheme and summary of driver debugging methods
- I realize large top stack with C I
- About the concept of thread (1)
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 261 F // 树状数组
- 现代数据架构选型:Data Fabric、Data Mesh
- How can the easycvr platform access special devices without authentication?
- DDD based on ABP -- Entity creation and update
- hdparm
猜你喜欢

Copy of array and array address value

登临科技联合创始人王平:创新+自研“双核”驱动,GPU+赋能AI落地生根|量子位·视点分享回顾...

如何生成预期数据?埃默里大学等最新《深度学习可控数据生成》综述,52页pdf涵盖346篇文献全面阐述可控生成技术体系

2022.07.21

28. Rainwater connection

Representation and basic application of regular expressions

30. Rearrange the linked list

27. Longest increasing subsequence
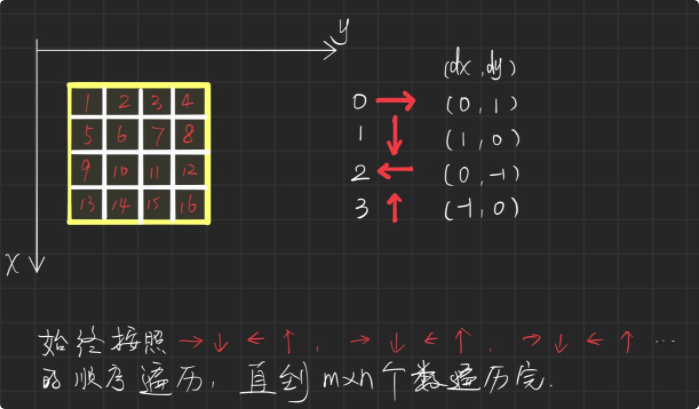
23. Spiral matrix

Outdoor billboards cannot be hung up if you want! Guangzhou urban management department strengthens the safety management of outdoor advertising
随机推荐
Pointer advanced part (1)
How can flinksql run in perjob mode on yarn? I submit tasks on SqlClient
【论文阅读】TEMPORAL ENSEMBLING FOR SEMI-SUPERVISED LEARNING
Analysis of device restart jamming -reboot jamming
【论文阅读】Mean teachers are better role models
Search engine based on boost library
汉字风格迁移篇---用于汉字多字体生成的多样性正则化StarGAN
Finclip's "applet export app" function has been updated again by the company
Handler learning
Research on data governance quality assurance
Is there any potential safety hazard for Xiaobai to open an account with Guotai Junan?
On node embedding
CMake基本语法(一)
Notes on Linear Algebra -- lesson 25 -- projection of vectors on axes
Arduino框架下ESP32 EEPROM库函数实现对各数据类型保存示例
Redis (13) -- on master-slave replication of redis
Queue (stack)
Activity start (launchactivity/startactivity)_ (1)_ WMS of flow chart
Copy of array and array address value
Experience on how to improve the anti-interference of TTL (UART) communication