当前位置:网站首页>September 3, 2020: naked writing algorithm: loop matrix traversal.
September 3, 2020: naked writing algorithm: loop matrix traversal.
2020-11-06 21:50:00 【Daily problem of Fuda big frame constructor】
Fogo's answer 2020-09-03:
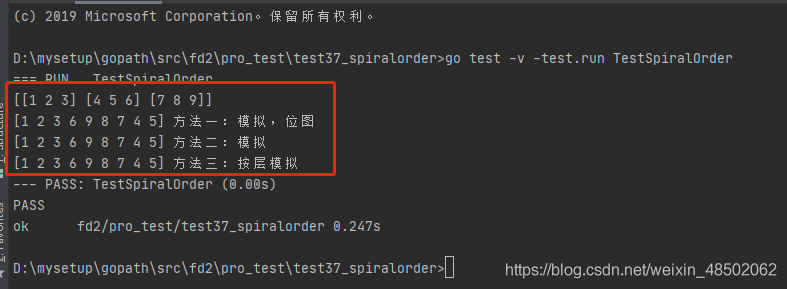
Method 1 : simulation , Bitmap mode .
Follow Method 2 equally , The difference is auxiliary matrix visited Save space with bitmaps .
Method 2 : simulation .
You can simulate the path of a spiral matrix . The initial position is the upper left corner of the matrix , The initial direction is to the right , When a path goes out of bounds or enters a previously visited location , Turn clockwise , Go to the next direction .
To determine whether a path enters a previously visited location, an auxiliary matrix of the same size as the input matrix is required visited, Each of these elements indicates whether the location has been accessed . When an element is accessed , take visited Set the element at the corresponding position in the to be accessed .
How to judge whether the path is over ? Because every element in the matrix is accessed once , So the length of the path is the number of elements in the matrix , When the length of the path reaches the number of elements in the matrix, it is a complete path , Return the path .
Complexity analysis
Time complexity :O(mn), among m and n The number of rows and columns of the input matrix . Every element in the matrix is accessed once .
Spatial complexity :O(mn). You need to create a size of m×n Matrix visited Record whether each location has been visited .
Method 3 : Layer by layer simulation
You can think of a matrix as layers , First output the outermost element , Second, output the sub outer elements , Until the innermost element is output .
Define the order of a matrix k The distance from the layer to the nearest boundary is k All the vertices of . for example , The outermost elements of the matrix in the figure below are all the first 1 layer , The sub outer elements are the first 2 layer , The rest of the elements are the first 3 layer .
Complexity analysis
Time complexity :O(mn), among m and n The number of rows and columns of the input matrix . Every element in the matrix is accessed once .
Spatial complexity :O(1). In addition to the output array , Space complexity is a constant .
The code to use golang To write , as follows :
package test37_spiralorder
import (
"fmt"
"testing"
)
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/spiral-matrix/solution/luo-xuan-ju-zhen-by-leetcode-solution/
//go test -v -test.run TestSpiralOrder
func TestSpiralOrder(t *testing.T) {
const N = 3
matrix := make([][]int, N)
for i := 0; i < N; i++ {
matrix[i] = make([]int, N)
for j := 0; j < N; j++ {
matrix[i][j] = i*N + j + 1
}
}
fmt.Println(matrix)
ret := spiralOrder1(matrix)
fmt.Println(ret, " Method 1 : simulation , Bitmap ")
ret = spiralOrder2(matrix)
fmt.Println(ret, " Method 2 : simulation ")
ret = spiralOrder3(matrix)
fmt.Println(ret, " Method 3 : Layer by layer simulation ")
}
// Method 1 : simulation , Bitmap
func spiralOrder1(matrix [][]int) []int {
if len(matrix) == 0 || len(matrix[0]) == 0 {
return []int{}
}
rows, columns := len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
visited := make([]byte, (rows*columns+7)/8)
var (
total = rows * columns
order = make([]int, total)
row, column = 0, 0
directions = [][]int{[]int{0, 1}, []int{1, 0}, []int{0, -1}, []int{-1, 0}}
directionIndex = 0
)
for i := 0; i < total; i++ {
order[i] = matrix[row][column]
SetBitMapValue(visited, row*columns+column, true)
nextRow, nextColumn := row+directions[directionIndex][0], column+directions[directionIndex][1]
if nextRow < 0 ||
nextRow >= rows ||
nextColumn < 0 ||
nextColumn >= columns ||
GetBitMapValue(visited, nextRow*columns+nextColumn) {
directionIndex = (directionIndex + 1) % 4
}
row += directions[directionIndex][0]
column += directions[directionIndex][1]
}
return order
}
// Method 2 : simulation
func spiralOrder2(matrix [][]int) []int {
if len(matrix) == 0 || len(matrix[0]) == 0 {
return []int{}
}
rows, columns := len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
visited := make([][]bool, rows)
for i := 0; i < rows; i++ {
visited[i] = make([]bool, columns)
}
var (
total = rows * columns
order = make([]int, total)
row, column = 0, 0
directions = [][]int{[]int{0, 1}, []int{1, 0}, []int{0, -1}, []int{-1, 0}}
directionIndex = 0
)
for i := 0; i < total; i++ {
order[i] = matrix[row][column]
visited[row][column] = true
nextRow, nextColumn := row+directions[directionIndex][0], column+directions[directionIndex][1]
if nextRow < 0 || nextRow >= rows || nextColumn < 0 || nextColumn >= columns || visited[nextRow][nextColumn] {
directionIndex = (directionIndex + 1) % 4
}
row += directions[directionIndex][0]
column += directions[directionIndex][1]
}
return order
}
// Method 3 : Layer by layer simulation
func spiralOrder3(matrix [][]int) []int {
if len(matrix) == 0 || len(matrix[0]) == 0 {
return []int{}
}
var (
rows, columns = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
order = make([]int, rows*columns)
index = 0
left, right, top, bottom = 0, columns - 1, 0, rows - 1
)
for left <= right && top <= bottom {
for column := left; column <= right; column++ {
order[index] = matrix[top][column]
index++
}
for row := top + 1; row <= bottom; row++ {
order[index] = matrix[row][right]
index++
}
if left < right && top < bottom {
for column := right - 1; column > left; column-- {
order[index] = matrix[bottom][column]
index++
}
for row := bottom; row > top; row-- {
order[index] = matrix[row][left]
index++
}
}
left++
right--
top++
bottom--
}
return order
}
// Get bitmap No index The value of the element
func GetBitMapValue(data []byte, index int) bool {
return data[index/8]&(1<<(index%8)) != 0
}
// Set bitmap No index The value of the element
func SetBitMapValue(data []byte, index int, v bool) {
if v {
data[index/8] |= 1 << (index % 8)
} else {
data[index/8] &= ^(1 << (index % 8))
}
} knock go test -v -test.run TestSpiralOrder command , give the result as follows :
版权声明
本文为[Daily problem of Fuda big frame constructor]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- 2020-08-24:什么是小文件?很多小文件会有什么问题?很多小文件怎么解决?(大数据)
- 消防器材RFID固定资产管理系统
- 实用工具类函数(持续更新)
- 2020-08-18:介绍下MR过程?
- How much disk space does a new empty file take?
- ES6 learning notes (4): easy to understand the new grammar of ES6
- An article will take you to understand CSS3 fillet knowledge
- To teach you to easily understand the basic usage of Vue codemirror: mainly to achieve code editing, verification prompt, code formatting
- C calls SendMessage to refresh the taskbar icon (the icon does not disappear at the end of forcing)
- Vue communication and cross component listening state Vue communication
猜你喜欢

The native API of the future trend of the front end: web components

Unity performance optimization

Why is the LS command stuck when there are too many files?

迅为iMX6开发板-设备树内核-menuconfig的使用

Common mathematical basic formulas of recursive and backtracking algorithms

git远程库回退指定版本

Zero basis to build a web search engine of its own

jenkins安装部署过程简记

With this artifact, quickly say goodbye to spam messages

The essence of transaction and the principle of deadlock
随机推荐
How much disk space does a file of 1 byte actually occupy
ORA-02292: 违反完整约束条件 (MIDBJDEV2.SYS_C0020757) - 已找到子记录
Windows 10 蓝牙管理页面'添加蓝牙或其他设备'选项点击无响应的解决方案
The method of realizing high SLO on large scale kubernetes cluster
Metersphere developer's Manual
Using an example to understand the underlying processing mechanism of JS function
With this artifact, quickly say goodbye to spam messages
An article will take you to understand CSS alignment
磁存储芯片STT-MRAM的特点
list转换map(根据key来拆分list,相同key的value为一个list)
An article taught you to use HTML5 SVG tags
Zero basis to build a web search engine of its own
Contract trading system development | construction of smart contract trading platform
jenkins安装部署过程简记
Message queue - Analysis
Interviewer: how about shardingsphere
非易失性MRAM存储器应用于各级高速缓存
CloudQuery V1.2.0 版本发布
Unexpected element.. required element
git远程库回退指定版本