当前位置:网站首页>Explain the imaging principle of various optical instruments in detail
Explain the imaging principle of various optical instruments in detail
2022-06-27 09:43:00 【Xiaobai learns vision】
Click on the above “ Xiaobai studies vision ”, Optional plus " Star standard " or “ Roof placement ”
Heavy dry goods , First time delivery Geometric optics is the basis of optical design , To do a good job in optical design, we must understand the imaging principle of some optical instruments , Today, photoelectric information has sorted out some information about the imaging principles of various optical instruments for you , There is something ZEMAX Learning video , Don't miss it !

Optical imaging
Using refraction 、 The information of the object is reproduced by means of reflection . Imaging is one of the key problems in geometric optics .
Real image and virtual image 、 Physical and virtual objects
1, Both objects and images are composed of a series of points , Object points and image points correspond to each other .
2, Material object 、 The meaning of the real image is that there is light actually coming from or passing through this point , And virtual objects 、 The virtual image is just an illusion caused by the linear propagation of light , There is actually no light passing through this point .
3, Objects and images have relativity , Virtual reality can also be transformed .
Equal path surface and strict imaging
The basic requirement of ideal imaging is to meet the invariance of concentric beams , And from the correspondence between the whole thing and the image , We must also meet the similarity between objects and images .
The positions of each point in space should correspond to each other one by one , At the same time, the colors of each pair of object image points should correspond one by one .
It is required that the imaging optical system does not produce distortion , No aberration 、 Color difference, etc .
Ideal optical system is a necessary condition for strict imaging .
Projector
The structure of the projector

Key parameters of the projector
brightness : Ordinary household 2000-3000 ANSI Lumen ( Details of radiation Optics )
Standard resolution ( Real resolution or physical resolution )
Contrast : Between the brightest white and darkest black in the light and dark areas Measurement of different brightness levels ( The human eye is generally close to 2000:1)
Projection ratio : Projection distance D / Screen width W.( In the same distance , The larger the projected picture ) Calculate projection and screen size 、 The best relationship between distances .
The projection ratio is generally at 1.5-1.9 Between , Less than 1 It is generally called short focus lens , Less than 0.6 It is called ultrashort focus . Projection screens are usually marked by diagonal inches , It needs to be converted according to the length width ratio .

Screen selection for projection
Glass bead curtain , The surface is coated with optical crystal glass balls . The feature is that the picture has a distinct sense of focus and vitality , High gain 、 Small Perspective . And the biggest feature is “ Light reversibility ”, That is, the reflected light enters The direction of the light beam is returned , This is also a reason for the high gain , Have a certain effect on light “ collect ” effect .
White plastic curtain , Direct use of coarse white fabric , No surface treatment . The feature is that the performance of the projector , The original performance , Without embellishment , Low gain 、 The perspective is very big 、 Natural color .

camera
The simplest structure of a camera — Box camera

characteristic : No reflector , Direct framing .
shortcoming : Early focus is slow , Modern digital anti camera ( Micro single ) Focusing speed can reach 0.06 Within seconds (sony a6000)!
Double lens reflex camera ( “ Double reverse ” Twin-Lens Reflex-TLR)

characteristic : Two shots , The upper lens is responsible for shooting and focusing through a fixed reflector , Linked with the following lens ; The following lens is responsible for transmitting the image to the film .
shortcoming : It's bigger , The operation is inconvenient , When changing lenses Both need to be replaced together .

Single lens reflex camera

characteristic :(1) Pentaprism 、(2) reflector panel . almost A perfect solution “ What you see is what you get ” The problem of .
shortcoming :(1) The movable reflector increases the size of the camera ;(2) Vibration of reflector opening 、 Mechanical switching time, etc Affect the performance of the camera .

The samsara from single reflex to no reflex

The size and angle of view of the camera

Focal length and field angle of camera lens

The focal length of the camera lens and the size of the image
The longer the focus , Like the bigger ( The smaller the proportion of images that can be collected on a fixed size film , Corresponding to the reduction of field angle )

The focal length of the lens determines the field of view , That is, how much the camera can capture “ wide ” The picture of . If the intersection of light The point is close to the sensor .
This makes the subject's image smaller , Otherwise, it will be larger . therefore , A short focal length produces a wide field of view —— This is called a short focal length lens “ Wide Angle ” The reason for the camera .
And vice versa : A long focal length produces a narrow field of view , This kind of lens is called “ long-focus ” The lens .
Focal length and vertical spacing of camera lens
Short focal length , Large longitudinal spacing , Long focal length , The longitudinal spacing is small .
The field of view and image of the lens
The focal length of the standard lens is the picture of the imaging surface of the camera The diagonal length of the frame shall prevail , When the focal length of the lens approaches a certain The length of the frame diagonal of the camera like imaging surface is called It is the standard focal length lens of this kind of camera , Abbreviation: standard Lens or header .
The angle of view of a standard focal length lens is about 50° , The focal length Usually it is 45-55mm, The perspective relationship of the picture is similar The perspective relationship felt by the human eye , The shooting effect Quite plain . Is the most basic photographic lens .
The shutter of the camera — Diaphragm
The definition of an aperture : The aperture of a beam of light when forming an image of a lens 、 A transparency that limits the extent to which the imaging point deviates from the optical axis Mirror frame 、 Frame or specially set perforated barrier .
Aperture is a necessary requirement for approximate imaging of spherical optical system . Aperture stop (aperture diaphragm): The aperture that determines the passage of the object point on the axis through the beam aperture of the optical device group is called An aperture or effective aperture .
Something confined by an aperture 、 The opening angles of the imaging beams on the image side are respectively called in Perforation diameter angle and exit diameter angle . Aperture diaphragm is the requirement of paraxial condition of object point on axis .
Incident pupil (pupil) And exit pupil : The conjugation of aperture apertures on the object and image sides .

Aperture apertures and pupil are conjugated to a specific compound 、 As far as point is concerned , Different conjugate points can have different aperture apertures and pupil .
Main light : matter 、 Like in a conjugate beam , Light conjugate with the light passing through the center of the incident pupil and the exit pupil .
Field aperture (field diaphragm): Determine whether the main light of the off-axis object point can pass through the aperture of the optical device group . The angle between the main ray and the optical axis that can just pass through the optical device group on the object side and the image side is called the incident field angle and the outgoing field angle . The field aperture is an off-axis object point Requirements for paraxial conditions .
Incident window (window) And the exit window : The conjugation of the field of view aperture on the object side and the image side .
Vignetting : When the object point gradually moves away from the optical axis , The amount of light involved in imaging gradually decreases , Causes the image to fade out , It's called vignetting . When the incident window is on the object plane , Vignetting will not occur .

The aperture of the camera



Depth of field and depth of focus of the camera
The effect of depth of field : prospects 、 The background is all virtualized



The factors that affect the depth of field

The relationship between depth of field and aperture

Summary of factors affecting depth of field

Lens parameters

Aberrations

Aberrations — Spherical aberration
The large aperture light emitted by the object point on the axis does not focus on one point .

Aberrations — Coma aberration
The wide beam from an off-axis object point no longer intersects at one point , Form bright spots like comets , Called coma .

Aberrations — Astigmatism
A wide beam of light from an off-axis object point , The convergence points of horizontal and vertical rays are on different planes , And the two convergence points evolve into two mutually perpendicular lines , Called astigmatism .
Clear circle is the place for negative film The best position .

Aberrations — Image field bending

Aberrations — distortion
For all points on the object plane , The lateral magnification varies with the distance from the optical axis , Make the figure on the image plane out of proportion to the original . With the ball 、 Coma and astigmatism are different , Distortion does not destroy the concentricity of the beam , Thus, the definition of the image is not affected .

Aberrations — chromatic aberration
Refractive index varies with color ( wavelength ) And change , Cause white light to image , The positions and sizes of images formed by different colors of light are different , Called chromatic aberration . Divided into axial ( Location ) chromatic aberration 、 The transverse ( Magnification ) chromatic aberration .

Magnifying glass and eyepiece
A magnifying glass is an eyepiece , The function is to form a magnified virtual image , Easy for eyes to observe .
characteristic : The object is inside the focal plane of the object , The image distance is about the apparent distance .
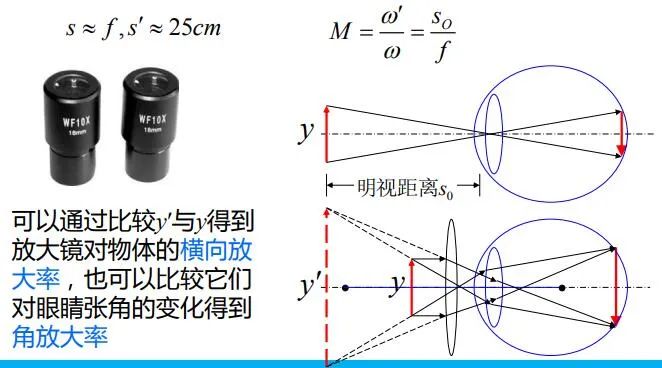

Eyepieces are used in optical instruments , The function is similar to that of a magnifying glass , It is a virtual image that can be directly observed by the eye near the bright sight distance . It is usually used in combination with an objective lens , Observe the real image formed by the objective lens . One of the key points of eyepiece design is to eliminate visual color difference .

Microscope
Optical instruments with high magnification , The utility model is composed of an objective lens group and an eyepiece group .

Light path and principle of microscope

Parameters and identification of microscope eyepiece
Eyepiece category : Huygens eyepiece (H)、 Ramsden eyepiece (R), KELNER eyepiece (K), etc.
Magnification ,5×,10×,……
Visual field diameter (mm)Φ20,……
10×/18, Indicates magnification 10 times , field 18mm
Parameters and identification of microscopic objective lens

Chromatic ring and numerical aperture of microscope objective

The telescope
Used to observe distant objects , Enlarge the angle of the object to the eye , It is equivalent to forming a reduced real image in the near , Then observe through the eyepiece .
Structure diagram of Hubble Space Telescope

Kepler The telescope

Galileo The telescope

Newton A reflecting telescope

Binoculars


eyes
The visual system

Visual response to color

Characteristics of the human visual system

The above is about the imaging principles of various optical instruments !
The good news !
Xiaobai learns visual knowledge about the planet
Open to the outside world

download 1:OpenCV-Contrib Chinese version of extension module
stay 「 Xiaobai studies vision 」 Official account back office reply : Extension module Chinese course , You can download the first copy of the whole network OpenCV Extension module tutorial Chinese version , Cover expansion module installation 、SFM Algorithm 、 Stereo vision 、 Target tracking 、 Biological vision 、 Super resolution processing and other more than 20 chapters .
download 2:Python Visual combat project 52 speak
stay 「 Xiaobai studies vision 」 Official account back office reply :Python Visual combat project , You can download, including image segmentation 、 Mask detection 、 Lane line detection 、 Vehicle count 、 Add Eyeliner 、 License plate recognition 、 Character recognition 、 Emotional tests 、 Text content extraction 、 Face recognition, etc 31 A visual combat project , Help fast school computer vision .
download 3:OpenCV Actual project 20 speak
stay 「 Xiaobai studies vision 」 Official account back office reply :OpenCV Actual project 20 speak , You can download the 20 Based on OpenCV Realization 20 A real project , Realization OpenCV Learn advanced .
Communication group
Welcome to join the official account reader group to communicate with your colleagues , There are SLAM、 3 d visual 、 sensor 、 Autopilot 、 Computational photography 、 testing 、 Division 、 distinguish 、 Medical imaging 、GAN、 Wechat groups such as algorithm competition ( It will be subdivided gradually in the future ), Please scan the following micro signal clustering , remarks :” nickname + School / company + Research direction “, for example :” Zhang San + Shanghai Jiaotong University + Vision SLAM“. Please note... According to the format , Otherwise, it will not pass . After successful addition, they will be invited to relevant wechat groups according to the research direction . Please do not send ads in the group , Or you'll be invited out , Thanks for your understanding ~边栏推荐
- 巴基斯坦安全部队开展反恐行动 打死7名恐怖分子
- Take you to play with the camera module
- 基于STM32设计的蓝牙健康管理设备
- SVN版本控制器的安装及使用方法
- 你睡觉时大脑真在自动学习!首个人体实验证据来了:加速1-4倍重放,深度睡眠阶段效果最好...
- Introduction to websocket protocol
- 小白也能看懂的网络基础 03 | OSI 模型是如何工作的(经典强推)
- Demand visual Engineer
- 12 necessary tools for network engineers
- std::memory_ order_ seq_ CST memory order
猜你喜欢

1098 Insertion or Heap Sort(堆排序解释)(PAT甲级)

视频文件太大?使用FFmpeg来无损压缩它

This application failed to start because it could not find or load the QT platform plugin

Installation and use of SVN version controller

邮件系统(基于SMTP协议和POP3协议-C语言实现)

Es update values based on Index Names and index fields
Scientists develop two new methods to provide stronger security protection for intelligent devices

新旧两个界面对比

Semi-supervised Learning入门学习——Π-Model、Temporal Ensembling、Mean Teacher简介

SVN版本控制器的安装及使用方法
随机推荐
Google browser chropath plug-in
强化学习中好奇心机制
有关二叉树的一些练习题
隐私计算FATE-离线预测
Brief introduction to SSL encryption process
leetcode:522. 最长特殊序列 II【贪心 + 子序列判断】
Installation and usage of source insight tool
谷歌浏览器 chropath插件
R语言使用caret包的preProcess函数进行数据预处理:对所有的数据列进行center中心化(每个数据列减去平均值)、设置method参数为center
Source insight 工具安装及使用方法
ucore lab5
ucore lab4
ucore lab3
[system design] proximity service
[vivid understanding] the meanings of various evaluation indicators commonly used in deep learning TP, FP, TN, FN, IOU and accuracy
详细记录YOLACT实例分割ncnn实现
Use CAS to complete concurrent operations with atomic variables
更改pip镜像源
借助原子变量,使用CAS完成并发操作
Reading and writing Apache poi
