当前位置:网站首页>Stm32 w5500 implements TCP, DHCP and web server
Stm32 w5500 implements TCP, DHCP and web server
2022-06-23 21:14:00 【AnieaLanie】
1. W5500 Modbus
1.1 Modbus Protocol Brief
Modbus A protocol is a message structure , It is widely used to establish master-slave communication between intelligent devices . From master station to slave station Modbus The message contains the slave address 、“ command ”( for example “ Read register ” or “ Write register ”)、 Data and checksum (LRC or CRC).
because Modbus The protocol is just a message passing structure , It is independent of the underlying physical layer . It's traditionally used RS232、RS422 or RS485 Realization
Modbus The main reasons why it is more widely used than other communication protocols are :
- Published without copyright requirements
- Easy to deploy and maintain
- For suppliers , There are no restrictions on changing the local bit or byte
1.2 Modbus Of master/slave framework
Modbus It's a Lord / from (master/slave) Architecture protocol , A node is master node , The other nodes are slave node . every last slave Each node has a unique address . In serial and MB+ In the network , Only specified as master The node of the node can start a command . On the Ethernet , Any device can send a Modbus command , But there is usually only one master Node device startup instruction .
1.3 Modbus command
One Modbus The command includes the... Of the device to be executed Modbus Address . All devices will receive commands , But only the device with the corresponding address will run and respond to the command ( Address 0 With the exception of , Specify the address 0 The command of is a broadcast command , All devices that receive commands will run , But no response ). be-all Modbus The command contains the check code , To make sure that the incoming command is not broken . Basic Modbus A command can command a RTU ( Remote terminal unit ) Change a value of its register , Control or read a I/O port , And the command equipment will send the data in one or more registers .
1.4 Modbus request
The function code in the request tells the addressed slave what action to perform . The data bytes contain any additional information required by the slave station to perform this function . for example , Function code 03 The request reads the holding register from the host and responds to its contents . The data field must contain information that tells the slave which register to start with and how many registers to read . The error check field provides a way for the slave to verify the integrity of the message content .
1.5 Modbus Respond to
If the slave makes a normal response , Then the function code in the response is the echo of the function code in the request . The data bytes contain the data collected from the station , For example, register value or status . If an error occurs , Then modify the function code to indicate that the response is an error response , And the data bytes contain code that describes the error . The error check field allows the host to confirm that the message content is valid .
1.6 Modbus transmission mode
In standard Modbus When communicating on the network , The controller can be set to use one of two transmission modes :ASCII or RTU.
ASCII Pattern When the controller is set to use ASCII( American standard code for information exchange ) Patterns in Modbus When communicating on the network , Each octet in the message is treated as two ASCII Character sending . The main advantage of this mode is that it allows up to a second of time between characters without causing errors .
coding system Hexadecimal ASCII Printable characters 0 ... 9, A ... F Bits per byte 1 Starting bits 7 Data bits , The least significant bit is sent first 1 Bits are used for even / Odd parity - No bits for no parity 1 Stop bit if parity if no parity Error checking Longitudinal redundancy check (LRC), Then use 2 position
ASCII frame
stay ASCII In mode , The message is colon (:) character (ASCII 3A Hexadecimal ) Start , And return to the next line (CRLF) Yes (ASCII 0D and 0A Hexadecimal ) end . The allowed characters transmitted for all other fields are hexadecimal 0 ... 9、A ... F. Networked devices constantly monitor the network bus for colon characters . When you receive one , Each device will set the next field ( Address field ) decode , To determine if it is an addressable device . Characters in the message can be separated by up to one second . If there is a larger interval , Then the receiving device assumes that an error has occurred . A typical message frame is shown below .:
RTU Pattern When the controller is set to use RTU( Remote terminal unit ) Patterns in Modbus When communicating on the network , Each octet in the message contains two four digit hexadecimal characters . The main advantage of this mode is that at the same baud rate , Its greater character density is allowed than ASCII Better data throughput . Each message must be transmitted in a continuous stream .
coding system Eight bit binary 、 Hexadecimal 0 ... 9、A ... F Two hexadecimal characters contained in each octet field of the message Bits per byte 1 Start bit 8 Data bits , The least significant bit is sent first 1 Bits are used for even numbers / Odd parity - No parity position If parity is used 1 Stop bits - If there is no parity Error checking field by 2 position Cyclic redundancy check (CRC)
RTU frame stay RTU In mode , The message is at least 3.5 A silence interval of characters begins . This is most easily implemented as a multiple of the character time of the baud rate being used on the network ( Shown in the following figure as T1-T2-T3-T4). Then the first field transmitted is the device address . The allowed characters transmitted for all fields are hexadecimal 0 ... 9、A ... F. Networked devices continuously monitor the network bus , Included during silent intervals . When the first field is received ( Address field ) when , Each device decodes it , To determine if it is an addressable device . After the last transmitted character , At least 3.5 A similar interval of characters marks the end of the message . After this interval, you can start a new message . The entire message frame must be transmitted as a continuous stream . If more than... Occurs before the frame is completed 1.5 A silence interval of characters , The receiving device will refresh the incomplete message and assume that the next byte will be the address field of the new message . Similarly , If the start time of the new message is earlier than that of the previous message 3.5 Character time , The receiving device will regard it as a continuation of the previous message . This will set an error , Because in the end CRC The value in the field will not be valid for combined messages . A typical message frame is shown below .:
1.7 Message frame
Address field The address field of the message frame contains two characters (ASCII) Or octet (RTU). The address range allocated by each slave station equipment is 1 ... 247.
Function fields
The function code field tells the addressed slave what functions to perform . Modbus poll (Modbus Main Simulator ) The following functions are supported :
01 Read coil status 02 Read input status 03 Read holding register 04 Read input register 05 Write a single coil 06 Write to a single register 15 Write multiple coils 16 Write multiple registers
The data field contains the requested or sent data .
Error checking the contents of the field standard Modbus The network uses two error checking methods . The contents of the error check field depend on the method being used .
ASCII When ASCII When the mode is used for character framing , The error check field contains two ASCII character . The error check character is a vertical redundancy check performed on the message content (LRC) The result of the calculation , Start colon and end... Are not included CRLF character . LRC Character as CRLF The last field before the character is appended to the message .
BYTE LRC (BYTE *nData, WORD wLength)
{
BYTE nLRC = 0 ; // LRC char initialized
for (int i = 0; i < wLength; i++)
nLRC += *nData++;
return (BYTE)(-nLRC);
} // End: LRCRTU When RTU When the mode is used for character frames , The error check field contains a 16 A value , Implemented as two 8 Bit byte . The error check value is the result of the cyclic redundancy check calculation performed on the message content . CRC Field is attached to the message as the last field in the message . After completion , First, append the lower byte of the field , Then the high byte .CRC The upper byte is the last byte to be sent in the message .
WORD CRC16 (const BYTE *nData, WORD wLength)
{
static const WORD wCRCTable[] = {
0X0000, 0XC0C1, 0XC181, 0X0140, 0XC301, 0X03C0, 0X0280, 0XC241,
0XC601, 0X06C0, 0X0780, 0XC741, 0X0500, 0XC5C1, 0XC481, 0X0440,
0XCC01, 0X0CC0, 0X0D80, 0XCD41, 0X0F00, 0XCFC1, 0XCE81, 0X0E40,
0X0A00, 0XCAC1, 0XCB81, 0X0B40, 0XC901, 0X09C0, 0X0880, 0XC841,
0XD801, 0X18C0, 0X1980, 0XD941, 0X1B00, 0XDBC1, 0XDA81, 0X1A40,
0X1E00, 0XDEC1, 0XDF81, 0X1F40, 0XDD01, 0X1DC0, 0X1C80, 0XDC41,
0X1400, 0XD4C1, 0XD581, 0X1540, 0XD701, 0X17C0, 0X1680, 0XD641,
0XD201, 0X12C0, 0X1380, 0XD341, 0X1100, 0XD1C1, 0XD081, 0X1040,
0XF001, 0X30C0, 0X3180, 0XF141, 0X3300, 0XF3C1, 0XF281, 0X3240,
0X3600, 0XF6C1, 0XF781, 0X3740, 0XF501, 0X35C0, 0X3480, 0XF441,
0X3C00, 0XFCC1, 0XFD81, 0X3D40, 0XFF01, 0X3FC0, 0X3E80, 0XFE41,
0XFA01, 0X3AC0, 0X3B80, 0XFB41, 0X3900, 0XF9C1, 0XF881, 0X3840,
0X2800, 0XE8C1, 0XE981, 0X2940, 0XEB01, 0X2BC0, 0X2A80, 0XEA41,
0XEE01, 0X2EC0, 0X2F80, 0XEF41, 0X2D00, 0XEDC1, 0XEC81, 0X2C40,
0XE401, 0X24C0, 0X2580, 0XE541, 0X2700, 0XE7C1, 0XE681, 0X2640,
0X2200, 0XE2C1, 0XE381, 0X2340, 0XE101, 0X21C0, 0X2080, 0XE041,
0XA001, 0X60C0, 0X6180, 0XA141, 0X6300, 0XA3C1, 0XA281, 0X6240,
0X6600, 0XA6C1, 0XA781, 0X6740, 0XA501, 0X65C0, 0X6480, 0XA441,
0X6C00, 0XACC1, 0XAD81, 0X6D40, 0XAF01, 0X6FC0, 0X6E80, 0XAE41,
0XAA01, 0X6AC0, 0X6B80, 0XAB41, 0X6900, 0XA9C1, 0XA881, 0X6840,
0X7800, 0XB8C1, 0XB981, 0X7940, 0XBB01, 0X7BC0, 0X7A80, 0XBA41,
0XBE01, 0X7EC0, 0X7F80, 0XBF41, 0X7D00, 0XBDC1, 0XBC81, 0X7C40,
0XB401, 0X74C0, 0X7580, 0XB541, 0X7700, 0XB7C1, 0XB681, 0X7640,
0X7200, 0XB2C1, 0XB381, 0X7340, 0XB101, 0X71C0, 0X7080, 0XB041,
0X5000, 0X90C1, 0X9181, 0X5140, 0X9301, 0X53C0, 0X5280, 0X9241,
0X9601, 0X56C0, 0X5780, 0X9741, 0X5500, 0X95C1, 0X9481, 0X5440,
0X9C01, 0X5CC0, 0X5D80, 0X9D41, 0X5F00, 0X9FC1, 0X9E81, 0X5E40,
0X5A00, 0X9AC1, 0X9B81, 0X5B40, 0X9901, 0X59C0, 0X5880, 0X9841,
0X8801, 0X48C0, 0X4980, 0X8941, 0X4B00, 0X8BC1, 0X8A81, 0X4A40,
0X4E00, 0X8EC1, 0X8F81, 0X4F40, 0X8D01, 0X4DC0, 0X4C80, 0X8C41,
0X4400, 0X84C1, 0X8581, 0X4540, 0X8701, 0X47C0, 0X4680, 0X8641,
0X8201, 0X42C0, 0X4380, 0X8341, 0X4100, 0X81C1, 0X8081, 0X4040 };
BYTE nTemp;
WORD wCRCWord = 0xFFFF;
while (wLength--)
{
nTemp = *nData++ ^ wCRCWord;
wCRCWord >>= 8;
wCRCWord ^= wCRCTable[nTemp];
}
return wCRCWord;
} // End: CRC161.8 experimental result
2. DHCP
2.1 DHCP brief introduction
DHCP( Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol ) Is a LAN network protocol . It refers to a period of time controlled by the server IP Address range , When the client logs in to the server, it can automatically get the server assigned IP Address and subnet mask .
2.2 DHCP function
- Guarantee any IP The address can only be set by one DHCP Used by the client .
- DHCP It should be possible to assign permanent IP Address .
- DHCP Should be available in the same way as in other ways IP Address host co-existence ( Such as manual configuration IP Address of the host ).
- DHCP The server should be directed to the existing BOOTP Clients provide services .
2.3 DHCP The way of distribution
DHCP There are three mechanisms for distribution IP Address :
- Automatic allocation method (Automatic Allocation),DHCP The server specifies a permanent IP Address , once DHCP The first successful client from DHCP Server side lease to IP After the address , You can use the address permanently .
- Dynamic distribution mode (Dynamic Allocation),DHCP The server specifies a time limited IP Address , When the time expires or the host explicitly gives up the address , This address can be used by other hosts .
- Job assignment method (Manual Allocation), Client's IP The address is specified by the network administrator ,DHCP The server will only specify IP Address to client host .
2.4 DHCP working principle
DHCP The agreement adopts UDP As a transport protocol , The host sends a request message to DHCP Server's 67 Port no. ,DHCP The server responds to the message sent to the host 68 Port no. . The detailed interaction process is as follows :
2.5 W5500+STM32F103 Realization DHCP Code
W5500 As DHCP client , Router as DHCP Server side , After connecting to the router , Routers are dynamically assigned to W5500IP Address .
stay DHCP During request , Include 4 There are two main stages : The discovery phase 、 Provision phase 、 Select phase and confirm phase .
First W5500 The client sends DHCP DISCOVER news (IP Address rental application ), The message was broadcast , In all networks DHCP The server will receive this message . And then , Network DHCP The server responds with one DHCPOFFER news (IP Address rental offers ), At this time, the client does not have a network address , therefore DHCP OFFER It is also sent by broadcast . after , Send... To the server DHCP REQUEST news . stay DHCP REQUEST The message will contain the... Requested by the client IP Address . Last ,DHCP The server will echo DHCP ACK To notify the client that the IP Address , This confirmation contains the assigned IP Address and a stable term lease for that address ( The default is 8 God ), And update at the same time DHCP database .
Main code :
while(1)
{
DHCP_run();
}
uint8_t DHCP_run(void)
{
uint8_t type;
uint8_t ret;
if(dhcp_state == STATE_DHCP_STOP) return DHCP_STOPPED;
if(getSn_SR(SOCK_DHCP) != SOCK_UDP)
socket(SOCK_DHCP, Sn_MR_UDP, DHCP_CLIENT_PORT, 0x00);
ret = DHCP_RUNNING;
type = parseDHCPMSG();
switch ( dhcp_state )
{
case STATE_DHCP_READY :
DHCP_allocated_ip[0] = 0;
DHCP_allocated_ip[1] = 0;
DHCP_allocated_ip[2] = 0;
DHCP_allocated_ip[3] = 0;
send_DHCP_DISCOVER();
dhcp_time = 0;
dhcp_state = STATE_DHCP_DISCOVER;
break;
case STATE_DHCP_DISCOVER :
if (type == DHCP_OFFER)
{
#ifdef _DHCP_DEBUG_
printf("> Receive DHCP_OFFER\r\n");
#endif
DHCP_allocated_ip[0] = pDHCPMSG->yiaddr[0];
DHCP_allocated_ip[1] = pDHCPMSG->yiaddr[1];
DHCP_allocated_ip[2] = pDHCPMSG->yiaddr[2];
DHCP_allocated_ip[3] = pDHCPMSG->yiaddr[3];
send_DHCP_REQUEST();
dhcp_time = 0;
dhcp_state = STATE_DHCP_REQUEST;
}
else
ret = check_DHCP_timeout();
break;
case STATE_DHCP_REQUEST :
if (type == DHCP_ACK)
{
#ifdef _DHCP_DEBUG_
printf("> Receive DHCP_ACK\r\n");
#endif
if (check_DHCP_leasedIP())
{
printf("ip:%d.%d.%d.%d\r\n",DHCP_allocated_ip[0],DHCP_allocated_ip[1],DHCP_allocated_ip[2],DHCP_allocated_ip[3]);
printf("sn:%d.%d.%d.%d\r\n",DHCP_allocated_sn[0],DHCP_allocated_sn[1],DHCP_allocated_sn[2],DHCP_allocated_sn[3]);
printf("gw:%d.%d.%d.%d\r\n",DHCP_allocated_gw[0],DHCP_allocated_gw[1],DHCP_allocated_gw[2],DHCP_allocated_gw[3]);
dhcp_ip_assign();
reset_DHCP_timeout();
hcp_state = STATE_DHCP_LEASED;
}
else
{
reset_DHCP_timeout();
dhcp_ip_conflict();
dhcp_state = STATE_DHCP_READY;
}
}
else if (type == DHCP_NAK)
{
#ifdef _DHCP_DEBUG_
printf("> Receive DHCP_NACK\r\n");
#endif
reset_DHCP_timeout();
dhcp_state = STATE_DHCP_DISCOVER;
}
else
ret = check_DHCP_timeout();
break;
case STATE_DHCP_LEASED :
ret = DHCP_IP_LEASED;
if ((dhcp_lease_time != DEFAULT_LEASETIME) && ((dhcp_lease_time/2) < dhcp_time))
{
#ifdef _DHCP_DEBUG_
printf("> Maintains the IP address \r\n");
#endif
type = 0;
OLD_allocated_ip[0] = DHCP_allocated_ip[0];
OLD_allocated_ip[1] = DHCP_allocated_ip[1];
OLD_allocated_ip[2] = DHCP_allocated_ip[2];
OLD_allocated_ip[3] = DHCP_allocated_ip[3];
DHCP_XID++;
send_DHCP_REQUEST();
reset_DHCP_timeout();
dhcp_state = STATE_DHCP_REREQUEST;
}
break;
case STATE_DHCP_REREQUEST :
ret = DHCP_IP_LEASED;
if (type == DHCP_ACK)
{
dhcp_retry_count = 0;
if (OLD_allocated_ip[0] != DHCP_allocated_ip[0] ||
OLD_allocated_ip[1] != DHCP_allocated_ip[1] ||
OLD_allocated_ip[2] != DHCP_allocated_ip[2] ||
OLD_allocated_ip[3] != DHCP_allocated_ip[3])
{
ret = DHCP_IP_CHANGED;
dhcp_ip_update();
#ifdef _DHCP_DEBUG_
printf(">IP changed.\r\n");
#endif
}
#ifdef _DHCP_DEBUG_
else printf(">IP is continued.\r\n");
#endif
reset_DHCP_timeout();
dhcp_state = STATE_DHCP_LEASED;
}
else if (type == DHCP_NAK)
{
#ifdef _DHCP_DEBUG_
printf("> Receive DHCP_NACK, Failed to maintain ip\r\n");
#endif
reset_DHCP_timeout();
dhcp_state = STATE_DHCP_DISCOVER;
}
else ret = check_DHCP_timeout();
break;
default :
break;
}
return ret;
}2.6 Code run results
Connect this computer to the router , This machine IP The address is as follows :
take W5500+STM32 Connect the router , from STM32 Serial port output view W5500 Of IP The address is as follows :
This machine ping W5500 result :
Successful connection .
3. W5500 TCP
3.1 Local establishment TCP The server
Turn off the local network , Use TCP Test tool establishment TCP The server
3.2 Use W5500, Set static IP, establish TCP client
Connect W5500 On this machine , Run the program , start-up TCP The server , see W5500 Data sent by the client
int main(void)
{
System_Initialization(); //STM32 System initialization function ( initialization STM32 Clock and peripherals )
Load_Net_Parameters(); // Load network parameters
W5500_Hardware_Reset(); // Hardware reset W5500
W5500_Initialization(); //W5500 Initial cargo configuration
while (1)
{
W5500_Socket_Set();//W5500 Port initialization configuration
if(W5500_Interrupt)// Handle W5500 interrupt
{
W5500_Interrupt_Process();//W5500 Interrupt handler framework
}
if((S0_Data & S_RECEIVE) == S_RECEIVE)// If Socket0 Data received
{
S0_Data&=~S_RECEIVE;
Process_Socket_Data(0);//W5500 Receive and send the received data
}
else if(W5500_Send_Delay_Counter >= 500)// Send the string regularly
{
if(S0_State == (S_INIT|S_CONN))
{
S0_Data&=~S_TRANSMITOK;
memcpy(Tx_Buffer, "\r\nWelcome To NiRenElec!\r\n", 23);
Write_SOCK_Data_Buffer(0, Tx_Buffer, 23);// Appoint Socket(0~7) Send data processing , port 0 send out 23 Bytes of data
}
W5500_Send_Delay_Counter=0;
}
}
}3.3 experimental result
4. The embedded Web The server
4.1 wiring part
Connect W5500 And routers ,PC Also connected to the router , Easy access to web pages .
4.2 Code section
Use socket encapsulation TCP agreement , The matter is based on TCP Of Socket signal communication
#include "socket.h"
#include "config.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "w5500.h"
#include "ult.h"
static uint16 local_port;
extern uint16 sent_ptr;
/**
@brief This Socket function initialize the channel in perticular mode, and set the port and wait for W5200 done it.
@return 1 for sucess else 0.
*/
uint8 socket(SOCKET s, uint8 protocol, uint16 port, uint8 flag)
{
uint8 ret;
if (
((protocol&0x0F) == Sn_MR_TCP) ||
((protocol&0x0F) == Sn_MR_UDP) ||
((protocol&0x0F) == Sn_MR_IPRAW) ||
((protocol&0x0F) == Sn_MR_MACRAW) ||
((protocol&0x0F) == Sn_MR_PPPOE)
)
{
close(s);
IINCHIP_WRITE(Sn_MR(s) ,protocol | flag);
if (port != 0) {
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_PORT0(s) ,(uint8)((port & 0xff00) >> 8));
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_PORT1(s) ,(uint8)(port & 0x00ff));
} else {
local_port++; // if don't set the source port, set local_port number.
IINCHIP_WRITE(Sn_PORT0(s) ,(uint8)((local_port & 0xff00) >> 8));
IINCHIP_WRITE(Sn_PORT1(s) ,(uint8)(local_port & 0x00ff));
}
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_CR(s) ,Sn_CR_OPEN); // run sockinit Sn_CR
/* wait to process the command... */
while( IINCHIP_READ(Sn_CR(s)) )
;
/* ------- */
ret = 1;
}
else
{
ret = 0;
}
return ret;
}
/**
@brief This function close the socket and parameter is "s" which represent the socket number
*/
void close(SOCKET s)
{
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_CR(s) ,Sn_CR_CLOSE);
/* wait to process the command... */
while( IINCHIP_READ(Sn_CR(s) ) )
;
/* ------- */
/* all clear */
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_IR(s) , 0xFF);
}
/**
@brief This function established the connection for the channel in passive (server) mode. This function waits for the request from the peer.
@return 1 for success else 0.
*/
uint8 listen(SOCKET s)
{
uint8 ret;
if (IINCHIP_READ( Sn_SR(s) ) == SOCK_INIT)
{
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_CR(s) ,Sn_CR_LISTEN);
/* wait to process the command... */
while( IINCHIP_READ(Sn_CR(s) ) )
;
/* ------- */
ret = 1;
}
else
{
ret = 0;
}
return ret;
}
/**
@brief This function established the connection for the channel in Active (client) mode.
This function waits for the untill the connection is established.
@return 1 for success else 0.
*/
uint8 connect(SOCKET s, uint8 * addr, uint16 port)
{
uint8 ret;
if
(
((addr[0] == 0xFF) && (addr[1] == 0xFF) && (addr[2] == 0xFF) && (addr[3] == 0xFF)) ||
((addr[0] == 0x00) && (addr[1] == 0x00) && (addr[2] == 0x00) && (addr[3] == 0x00)) ||
(port == 0x00)
)
{
ret = 0;
}
else
{
ret = 1;
// set destination IP
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_DIPR0(s), addr[0]);
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_DIPR1(s), addr[1]);
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_DIPR2(s), addr[2]);
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_DIPR3(s), addr[3]);
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_DPORT0(s), (uint8)((port & 0xff00) >> 8));
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_DPORT1(s), (uint8)(port & 0x00ff));
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_CR(s) ,Sn_CR_CONNECT);
/* wait for completion */
while ( IINCHIP_READ(Sn_CR(s) ) ) ;
while ( IINCHIP_READ(Sn_SR(s)) != SOCK_SYNSENT )
{
if(IINCHIP_READ(Sn_SR(s)) == SOCK_ESTABLISHED)
{
break;
}
if (getSn_IR(s) & Sn_IR_TIMEOUT)
{
IINCHIP_WRITE(Sn_IR(s), (Sn_IR_TIMEOUT)); // clear TIMEOUT Interrupt
ret = 0;
break;
}
}
}
return ret;
}
/**
@brief This function used for disconnect the socket and parameter is "s" which represent the socket number
@return 1 for success else 0.
*/
void disconnect(SOCKET s)
{
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_CR(s) ,Sn_CR_DISCON);
/* wait to process the command... */
while( IINCHIP_READ(Sn_CR(s) ) )
;
/* ------- */
}
/**
@brief This function used to send the data in TCP mode
@return 1 for success else 0.
*/
uint16 send(SOCKET s, const uint8 * buf, uint16 len)
{
uint8 status=0;
uint16 ret=0;
uint16 freesize=0;
if (len > getIINCHIP_TxMAX(s)) ret = getIINCHIP_TxMAX(s); // check size not to exceed MAX size.
else ret = len;
// if freebuf is available, start.
do
{
freesize = getSn_TX_FSR(s);
status = IINCHIP_READ(Sn_SR(s));
if ((status != SOCK_ESTABLISHED) && (status != SOCK_CLOSE_WAIT))
{
ret = 0;
break;
}
} while (freesize < ret);
// copy data
send_data_processing(s, (uint8 *)buf, ret);
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_CR(s) ,Sn_CR_SEND);
/* wait to process the command... */
while( IINCHIP_READ(Sn_CR(s) ) );
while ( (IINCHIP_READ(Sn_IR(s) ) & Sn_IR_SEND_OK) != Sn_IR_SEND_OK )
{
status = IINCHIP_READ(Sn_SR(s));
if ((status != SOCK_ESTABLISHED) && (status != SOCK_CLOSE_WAIT) )
{
printf("SEND_OK Problem!!\r\n");
close(s);
return 0;
}
}
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_IR(s) , Sn_IR_SEND_OK);
#ifdef __DEF_IINCHIP_INT__
putISR(s, getISR(s) & (~Sn_IR_SEND_OK));
#else
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_IR(s) , Sn_IR_SEND_OK);
#endif
return ret;
}
/**
@brief This function is an application I/F function which is used to receive the data in TCP mode.
It continues to wait for data as much as the application wants to receive.
@return received data size for success else -1.
*/
uint16 recv(SOCKET s, uint8 * buf, uint16 len)
{
uint16 ret=0;
if ( len > 0 )
{
recv_data_processing(s, buf, len);
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_CR(s) ,Sn_CR_RECV);
/* wait to process the command... */
while( IINCHIP_READ(Sn_CR(s) ));
/* ------- */
ret = len;
}
return ret;
}
/**
@brief This function is an application I/F function which is used to send the data for other then TCP mode.
Unlike TCP transmission, The peer's destination address and the port is needed.
@return This function return send data size for success else -1.
*/
uint16 sendto(SOCKET s, const uint8 * buf, uint16 len, uint8 * addr, uint16 port)
{
uint16 ret=0;
if (len > getIINCHIP_TxMAX(s)) ret = getIINCHIP_TxMAX(s); // check size not to exceed MAX size.
else ret = len;
if( ((addr[0] == 0x00) && (addr[1] == 0x00) && (addr[2] == 0x00) && (addr[3] == 0x00)) || ((port == 0x00)) )//||(ret == 0) )
{
/* added return value */
ret = 0;
}
else
{
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_DIPR0(s), addr[0]);
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_DIPR1(s), addr[1]);
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_DIPR2(s), addr[2]);
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_DIPR3(s), addr[3]);
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_DPORT0(s),(uint8)((port & 0xff00) >> 8));
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_DPORT1(s),(uint8)(port & 0x00ff));
// copy data
send_data_processing(s, (uint8 *)buf, ret);
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_CR(s) ,Sn_CR_SEND);
/* wait to process the command... */
while( IINCHIP_READ( Sn_CR(s) ) )
;
/* ------- */
while( (IINCHIP_READ( Sn_IR(s) ) & Sn_IR_SEND_OK) != Sn_IR_SEND_OK )
{
if (IINCHIP_READ( Sn_IR(s) ) & Sn_IR_TIMEOUT)
{
/* clear interrupt */
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_IR(s) , (Sn_IR_SEND_OK | Sn_IR_TIMEOUT)); /* clear SEND_OK & TIMEOUT */
return 0;
}
}
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_IR(s) , Sn_IR_SEND_OK);
}
return ret;
}
/**
@brief This function is an application I/F function which is used to receive the data in other then
TCP mode. This function is used to receive UDP, IP_RAW and MAC_RAW mode, and handle the header as well.
@return This function return received data size for success else -1.
*/
uint16 recvfrom(SOCKET s, uint8 * buf, uint16 len, uint8 * addr, uint16 *port)
{
uint8 head[8];
uint16 data_len=0;
uint16 ptr=0;
uint32 addrbsb =0;
if ( len > 0 )
{
ptr = IINCHIP_READ(Sn_RX_RD0(s) );
ptr = ((ptr & 0x00ff) << 8) + IINCHIP_READ(Sn_RX_RD1(s));
addrbsb = (uint32)(ptr<<8) + (s<<5) + 0x18;
switch (IINCHIP_READ(Sn_MR(s) ) & 0x07)
{
case Sn_MR_UDP :
wiz_read_buf(addrbsb, head, 0x08);
ptr += 8;
// read peer's IP address, port number.
addr[0] = head[0];
addr[1] = head[1];
addr[2] = head[2];
addr[3] = head[3];
*port = head[4];
*port = (*port << 8) + head[5];
data_len = head[6];
data_len = (data_len << 8) + head[7];
addrbsb = (uint32)(ptr<<8) + (s<<5) + 0x18;
wiz_read_buf(addrbsb, buf, data_len);
ptr += data_len;
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_RX_RD0(s), (uint8)((ptr & 0xff00) >> 8));
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_RX_RD1(s), (uint8)(ptr & 0x00ff));
break;
case Sn_MR_IPRAW :
wiz_read_buf(addrbsb, head, 0x06);
ptr += 6;
addr[0] = head[0];
addr[1] = head[1];
addr[2] = head[2];
addr[3] = head[3];
data_len = head[4];
data_len = (data_len << 8) + head[5];
addrbsb = (uint32)(ptr<<8) + (s<<5) + 0x18;
wiz_read_buf(addrbsb, buf, data_len);
ptr += data_len;
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_RX_RD0(s), (uint8)((ptr & 0xff00) >> 8));
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_RX_RD1(s), (uint8)(ptr & 0x00ff));
break;
case Sn_MR_MACRAW :
wiz_read_buf(addrbsb, head, 0x02);
ptr+=2;
data_len = head[0];
data_len = (data_len<<8) + head[1] - 2;
if(data_len > 1514)
{
printf("data_len over 1514\r\n");
while(1);
}
addrbsb = (uint32)(ptr<<8) + (s<<5) + 0x18;
wiz_read_buf(addrbsb, buf, data_len);
ptr += data_len;
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_RX_RD0(s), (uint8)((ptr & 0xff00) >> 8));
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_RX_RD1(s), (uint8)(ptr & 0x00ff));
break;
default :
break;
}
IINCHIP_WRITE( Sn_CR(s) ,Sn_CR_RECV);
/* wait to process the command... */
while( IINCHIP_READ( Sn_CR(s)) ) ;
/* ------- */
}
return data_len;
}
#ifdef __MACRAW__
void macraw_open(void)
{
uint8 sock_num;
uint16 dummyPort = 0;
uint8 mFlag = 0;
sock_num = 0;
close(sock_num); // Close the 0-th socket
socket(sock_num, Sn_MR_MACRAW, dummyPort,mFlag); // OPen the 0-th socket with MACRAW mode
}
uint16 macraw_send( const uint8 * buf, uint16 len )
{
uint16 ret=0;
uint8 sock_num;
sock_num =0;
if (len > getIINCHIP_TxMAX(sock_num)) ret = getIINCHIP_TxMAX(sock_num); // check size not to exceed MAX size.
else ret = len;
send_data_processing(sock_num, (uint8 *)buf, len);
//W5500 SEND COMMAND
IINCHIP_WRITE(Sn_CR(sock_num),Sn_CR_SEND);
while( IINCHIP_READ(Sn_CR(sock_num)) );
while ( (IINCHIP_READ(Sn_IR(sock_num)) & Sn_IR_SEND_OK) != Sn_IR_SEND_OK );
IINCHIP_WRITE(Sn_IR(sock_num), Sn_IR_SEND_OK);
return ret;
}
uint16 macraw_recv( uint8 * buf, uint16 len )
{
uint8 sock_num;
uint16 data_len=0;
uint16 dummyPort = 0;
uint16 ptr = 0;
uint8 mFlag = 0;
sock_num = 0;
if ( len > 0 )
{
data_len = 0;
ptr = IINCHIP_READ(Sn_RX_RD0(sock_num));
ptr = (uint16)((ptr & 0x00ff) << 8) + IINCHIP_READ( Sn_RX_RD1(sock_num) );
//-- read_data(s, (uint8 *)ptr, data, len); // read data
data_len = IINCHIP_READ_RXBUF(0, ptr);
ptr++;
data_len = ((data_len<<8) + IINCHIP_READ_RXBUF(0, ptr)) - 2;
ptr++;
if(data_len > 1514)
{
printf("data_len over 1514\r\n");
printf("\r\nptr: %X, data_len: %X", ptr, data_len);
//while(1);
/** recommand : close and open **/
close(sock_num); // Close the 0-th socket
socket(sock_num, Sn_MR_MACRAW, dummyPort,mFlag); // OPen the 0-th socket with MACRAW mode
return 0;
}
IINCHIP_READ_RXBUF_BURST(sock_num, ptr, data_len, (uint8*)(buf));
ptr += data_len;
IINCHIP_WRITE(Sn_RX_RD0(sock_num),(uint8)((ptr & 0xff00) >> 8));
IINCHIP_WRITE(Sn_RX_RD1(sock_num),(uint8)(ptr & 0x00ff));
IINCHIP_WRITE(Sn_CR(sock_num), Sn_CR_RECV);
while( IINCHIP_READ(Sn_CR(sock_num)) ) ;
}
return data_len;
}
#endif
Use SPI2 Connect W5500 and STM32
#include "stm32f10x.h"
#include "config.h"
#include "socket.h"
#include "w5500.h"
#include "ult.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void WIZ_SPI_Init(void)
{
SPI_InitTypeDef SPI_InitStructure;
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
RCC_APB1PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB1Periph_SPI2, ENABLE);
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd( RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOB |RCC_APB2Periph_AFIO , ENABLE);
// Port B output
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_12;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_Out_PP;
GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStructure);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOB, GPIO_Pin_12);
/* Configure SPIy pins: SCK, MISO and MOSI */
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_13| GPIO_Pin_14| GPIO_Pin_15;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_PP;
GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStructure);
/* SPI Config -------------------------------------------------------------*/
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_Direction = SPI_Direction_2Lines_FullDuplex;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_Mode = SPI_Mode_Master;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_DataSize = SPI_DataSize_8b;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CPOL = SPI_CPOL_Low;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CPHA = SPI_CPHA_1Edge;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_NSS = SPI_NSS_Soft;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_BaudRatePrescaler = SPI_BaudRatePrescaler_4;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_FirstBit = SPI_FirstBit_MSB;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CRCPolynomial = 7;
SPI_Init(SPI2, &SPI_InitStructure);
SPI_Cmd(SPI2, ENABLE);
}
// Connected to Data Flash
void WIZ_CS(uint8_t val)
{
if (val == LOW)
{
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOB, WIZ_SCS);
}
else if (val == HIGH)
{
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOB, WIZ_SCS);
}
}
uint8_t SPI2_SendByte(uint8_t byte)
{
while (SPI_I2S_GetFlagStatus(SPI2, SPI_I2S_FLAG_TXE) == RESET);
SPI_I2S_SendData(SPI2, byte);
while (SPI_I2S_GetFlagStatus(SPI2, SPI_I2S_FLAG_RXNE) == RESET);
return SPI_I2S_ReceiveData(SPI2);
}Web HTTP part , take html The content is written into the code , In coordination http The status code of the protocol implements the web page
#ifndef __WEBPAGE_H
#define __WEBPAGE_H
#define INDEX_HTML "<!DOCTYPE html>"\
"<html>"\
"<head>"\
"<title>Ç峿µÄÍøÒ³ÅäÖÃ</title>"\
"<meta http-equiv='Content-Type' content='text/html; charset=GB2312'/>"\
"<style type='text/css'>"\
"body {text-align:left; background-color:#c0deed;font-family:Verdana;}"\
"#main {margin-right:auto;margin-left:auto;margin-top:30px;}"\
"label{display:inline-block;width:150px;}"\
"#main h3{color:#66b3ff; text-decoration:underline;}"\
"</style>"\
"<script>"\
"function $(id) { return document.getElementById(id); };"\
"function settingsCallback(o) {"\
"if ($('txtVer')) $('txtVer').value = o.ver;"\
"if ($('txtMac')) $('txtMac').value = o.mac;"\
"if ($('txtIp')) $('txtIp').value = o.ip;"\
"if ($('txtSub')) $('txtSub').value = o.sub;"\
"if ($('txtGw')) $('txtGw').value = o.gw;"\
\
"if ($('txtCode')) $('txtCode').value = o.Code;"\
"if ($('txtDTMB_Freq')) $('txtDTMB_Freq').value = o.DTMB_Freq;"\
"if ($('txtFM_Freq')) $('txtFM_Freq').value = o.FM_Freq;"\
"if ($('txtSx_Freq')) $('txtSx_Freq').value = o.Sx_Freq;"\
\
"};"\
"</script>"\
"</head>"\
"<body>"\
"<div id='main'>"\
"<div style='background:snow; display:block;padding:10px 20px;'>"\
"<h3 align='center'>²é¿´ÍøÂç²ÎÊý</h3>"\
"<form id='frmSetting' method='POST' action='config.cgi'>"\
"<p><label for='txtIp'>¹Ì¼þ°æ±¾ºÅ:</label><input type='text' id='txtVer' name='ver' size='16' disabled='disabled' /></p>"\
"<p><label for='txtIp'>MACµØÖ·:</label><input type='text' id='txtMac' name='mac' size='16' disabled='disabled' /></p>"\
"<p><label for='txtIp'>IPµØÖ·:</label><input type='text' id='txtIp' name='ip' size='16' disabled='disabled'/></p>"\
"<p><label for='txtSub'>×ÓÍøÑÚÂë:</label><input type='text' id='txtSub' name='sub' size='16' disabled='disabled'/></p>"\
"<p><label for='txtGw'>ĬÈÏÍø¹Ø:</label><input type='text' id='txtGw' name='gw' size='16' disabled='disabled'/></p>"\
\
"<p><label for='txtCode'>ÐÐÕþ±àÂë:</label><input type='text' id='txtCode' name='Code' size='16' disabled='disabled'/></p>"\
"<p><label for='txtDTMB_Freq'>DTMBƵÂÊ:</label><input type='text' id='txtDTMB_Freq' name='DTMB_Freq' size='16' disabled='disabled' /></p>"\
"<p><label for='txtFM_Freq'>µ÷ƵƵÂÊ:</label><input type='text' id='txtFM_Freq' name='FM_Freq' size='16' disabled='disabled'/></p>"\
"<p><label for='txtSx_Freq'>ÎÞÏßƵÂÊ:</label><input type='text' id='txtSx_Freq' name='Sx_Freq' size='16' disabled='disabled' /></p>"\
"<p style='color:DarkBlue'><label for='txtPassword'>µÇ¼ÃÜÂë6λ:</label><input type='password' id='txtPassword' name='Password' size='16' enabled='enabled'/></p>"\
"<input type='submit' value=' µÇ ¼ ' /></p>"\
\
"</form>"\
"</div>"\
"</div>"\
"<div style='margin:5px 5px;'>"\
"©Copyright 2017 by Ç峿"\
"</div>"\
"<script type='text/javascript' src='w5500.js'></script>"\
"</body>"\
"</html>"
#endif/* HTML Doc. for ERROR */ #define ERROR_HTML_PAGE "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: text/html\r\nContent-Length: 78\r\n\r\n<HTML>\r\n<BODY>\r\nSorry, the page you requested was not found.\r\n</BODY>\r\n</HTML>\r\n\0" //static char ERROR_HTML_PAGE[] = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: text/html\r\nContent-Length: 78\r\n\r\n<HTML>\r\n<BODY>\r\nSorry, the page you requested was not found.\r\n</BODY>\r\n</HTML>\r\n\0"; #define ERROR_REQUEST_PAGE "HTTP/1.1 400 OK\r\nContent-Type: text/html\r\nContent-Length: 50\r\n\r\n<HTML>\r\n<BODY>\r\nInvalid request.\r\n</BODY>\r\n</HTML>\r\n\0" //static char ERROR_REQUEST_PAGE[] = "HTTP/1.1 400 OK\r\nContent-Type: text/html\r\nContent-Length: 50\r\n\r\n<HTML>\r\n<BODY>\r\nInvalid request.\r\n</BODY>\r\n</HTML>\r\n\0"; #define RETURN_CGI_PAGE "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: text/html\r\nContent-Length: 59\r\n\r\n<html><head><title>iWeb - Configuration</title></head><BODY>CGI command was executed.</BODY></HTML>\0" /* Response header for HTML*/ #define RES_HTMLHEAD_OK "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: text/html\r\nContent-Length: " //static PROGMEM char RES_HTMLHEAD_OK[] = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: text/html\r\nContent-Length: "; /* Response head for TEXT */ #define RES_TEXTHEAD_OK "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: text/plain\r\nContent-Length: " /* Response head for GIF */ #define RES_GIFHEAD_OK "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: image/gif\r\nContent-Length: " /* Response head for JPEG */ #define RES_JPEGHEAD_OK "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: image/jpeg\r\nContent-Length: " /* Response head for FLASH */ #define RES_FLASHHEAD_OK "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: application/x-shockwave-flash\r\nContent-Length: " //static PROGMEM char RES_FLASHHEAD_OK[] = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: application/x-shockwave-flash\r\nContent-Length: "; /* Response head for MPEG */ #define RES_MPEGHEAD_OK "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: video/mpeg\r\nContent-Length: " /* Response head for PDF */ #define RES_PDFHEAD_OK "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: application/pdf\r\nContent-Length: " //digital I/O out put control result response #define DOUT_RES_1 "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: text/plain\r\nContent-Length: 1\r\n\r\n1" #define DOUT_RES_0 "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: text/plain\r\nContent-Length: 1\r\n\r\n0"
4.3 experimental result
5. Reference resources
[1] Get dynamic from the router IP Address
[2] DHCP
[3] STM32 transplant FreeModbus Detailed process
边栏推荐
- Is it safe for flush to open an account online? Is the Commission high
- Fortress deployment server setup operation guide for novices
- How PMO uses two dimensions for performance appraisal
- What if there are too few jetpack compose theme colors? Design your own color system
- How to deal with product pictures? How to select mapping software?
- QPS fails to go up due to frequency limitation of public network CLB bandwidth
- [development skills] how to add "live broadcast" status display bar on easynvr platform
- JS delete object attribute
- Excel text function
- Steps for formulating the project PMO strategic plan
猜你喜欢

I am 30 years old, no longer young, and have nothing

How to view the role of PMO in agile organizations?
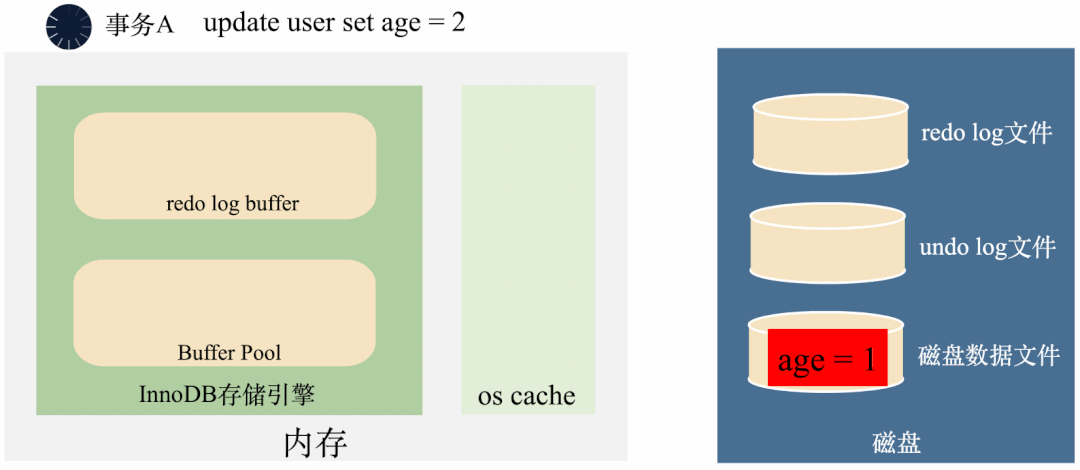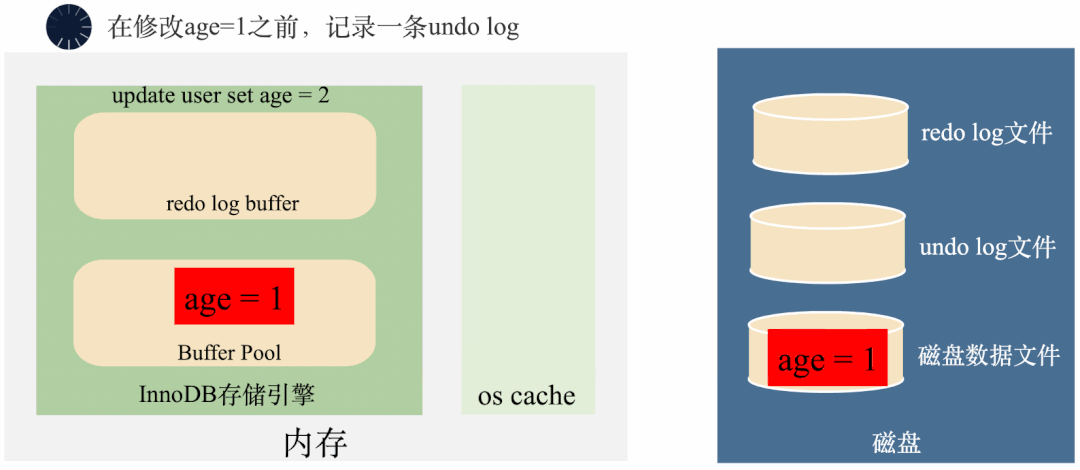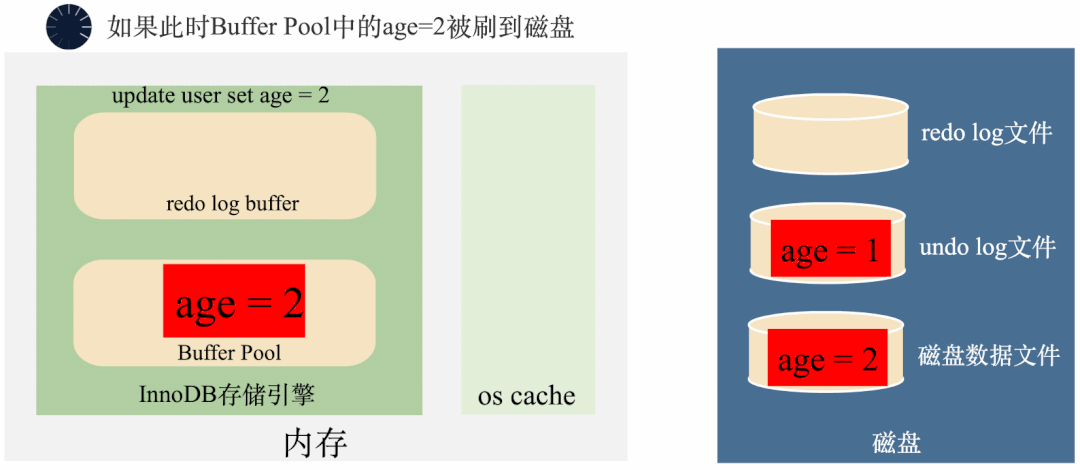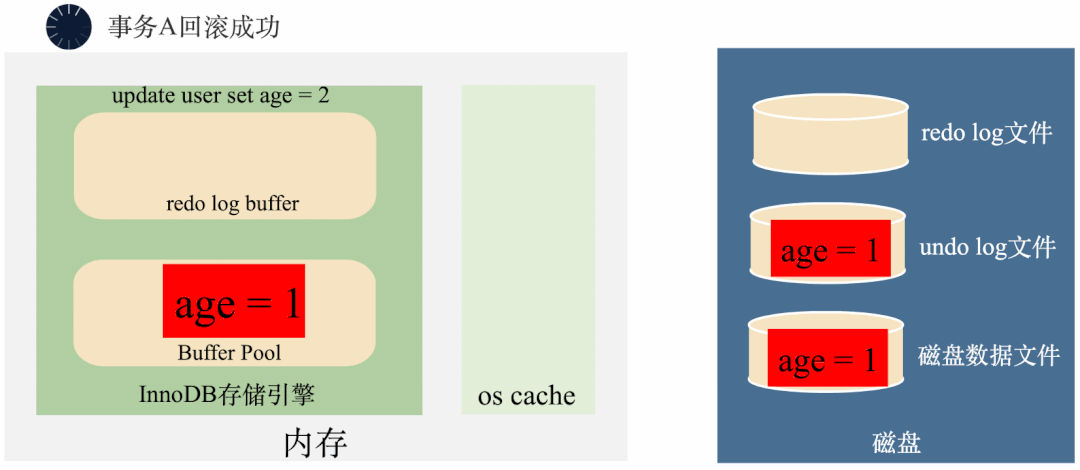
3000 frame animation illustrating why MySQL needs binlog, redo log and undo log

Four aspects of PMO Department value assessment

How PMO uses two dimensions for performance appraisal

JS advanced programming version 4: generator learning

How to gradually improve PMO's own ability and management level
Application of JDBC in performance test

Applet development framework recommendation

What are the main dimensions of PMO performance appraisal?
随机推荐
From different angles, you can learn about the implementation of sliding list in fluent
3000 frame animation illustrating why MySQL needs binlog, redo log and undo log
Yukeng MySQL service installation error
JS advanced programming version 4: generator learning
Global and Chinese markets for e-cigarettes and tobacco vapors 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Talk about leap seconds
What are the main dimensions of PMO performance appraisal?
JS naming conventions
Command line add user set password never expires add remote group add administrator group
How is the picture mosaic clear? What is mosaic for?
Which is better for securities companies? I don't understand. Is it safe to open an account online?
How to build a cloud game platform on the server? How to select a cloud game server?
How does the fortress machine connect to the server? Novice must know operation steps
Implementation of flashback query for PostgreSQL database compatible with Oracle Database
JS namespace
Sharelist supports simultaneous mounting of Google drive/onedrive multiple network disks
How to handle the prompt that DNS is incorrect when adding resolution to Tencent cloud?
How to build Tencent cloud game server? Differences between cloud game platforms and ordinary games
What is the role of computer auto audit audio? What content failed to pass the audit?
[tutorial] Tencent lightweight cloud builds an online customer service chat system
