当前位置:网站首页>虚拟文件系统
虚拟文件系统
2022-06-24 06:36:00 【51CTO】
找到了几年前的学习笔记;今天附上
虚拟文件系统(Virtual File System,简称VFS)是Linux内核的子系统之一,它为用户程序提供文件和文件系统操作的统一接口,屏蔽不同文件系统的差异和操作细节。借助VFS可以直接使用open()、read()、write()这样的系统调用操作文件,而无须考虑具体的文件系统和实际的存储介质。
VFS所隐含的思想主要是:引入一种普通文件模型,这个模型能够表示支持的所有的文件;VFS为底层提供了抽象即 1、提供了一个最小的通用模型,使得这个模型的功能时所有的文件系统的最小集。 2、提供一个尽量大的通用模型,使得这个模型包含所有文件系统功能的合集。
通用文件模型包含以下几个模块:
超级块对象 存放已安装文件系统的有关信息
索引节点对象 存放具体文件的一般信息
文件对象 存放打开文件与进程之间进行交互的有关信息。
目录项对象 存放目录项(也就是文件的特定名称)与对应文件进行连接的有关信息。

最近使用的目录项对象都存在所谓的目录项高速缓的磁盘高速缓存中,以加快从文件名到最后一个路径分量的索引节点的转换过程。
磁盘高速缓存属于软件机制;允许内核将原本存在磁盘上的某些信息保存在RAM中,以便能对这些数据进行快速访问;
VFS时应用程序和具体文件之间的一层,不过在某些情况下有些操作可以由VFS本身去执行,无需调用底层函数file_operation;比如close一个已经打开的文件时,bing
不需要涉及磁盘上的相应文件,只需要VFS释放对应的文件对象。
VFS 数据结构:
超级块对象:


struct super_block {
struct list_head s_list; /* Keep this first */
dev_t s_dev; /* search index; _not_ kdev_t */
unsigned char s_blocksize_bits;
unsigned long s_blocksize;
loff_t s_maxbytes; /* Max file size */
struct file_system_type *s_type;
const struct super_operations *s_op;
const struct dquot_operations *dq_op;
const struct quotactl_ops *s_qcop;
const struct export_operations *s_export_op;
unsigned long s_flags;
unsigned long s_magic;
struct dentry *s_root;
struct rw_semaphore s_umount;
struct mutex s_lock;
int s_count;
atomic_t s_active;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *s_security;
#endif
const struct xattr_handler **s_xattr;
struct list_head s_inodes; /* all inodes */
struct hlist_bl_head s_anon; /* anonymous dentries for (nfs) exporting */
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
struct list_head __percpu *s_files;
#else
struct list_head s_files;
#endif
struct list_head s_mounts; /* list of mounts; _not_ for fs use */
/* s_dentry_lru, s_nr_dentry_unused protected by dcache.c lru locks */
struct list_head s_dentry_lru; /* unused dentry lru */
int s_nr_dentry_unused; /* # of dentry on lru */
/* s_inode_lru_lock protects s_inode_lru and s_nr_inodes_unused */
spinlock_t s_inode_lru_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
struct list_head s_inode_lru; /* unused inode lru */
int s_nr_inodes_unused; /* # of inodes on lru */
struct block_device *s_bdev;
struct backing_dev_info *s_bdi;
struct mtd_info *s_mtd;
struct hlist_node s_instances;
struct quota_info s_dquot; /* Diskquota specific options */
struct sb_writers s_writers;
char s_id[32]; /* Informational name */
u8 s_uuid[16]; /* UUID */
void *s_fs_info; /* Filesystem private info */
unsigned int s_max_links;
fmode_t s_mode;
/* Granularity of c/m/atime in ns.
Cannot be worse than a second */
u32 s_time_gran;
/*
* The next field is for VFS *only*. No filesystems have any business
* even looking at it. You had been warned.
*/
struct mutex s_vfs_rename_mutex; /* Kludge */
/*
* Filesystem subtype. If non-empty the filesystem type field
* in /proc/mounts will be "type.subtype"
*/
char *s_subtype;
/*
* Saved mount options for lazy filesystems using
* generic_show_options()
*/
char __rcu *s_options;
const struct dentry_operations *s_d_op; /* default d_op for dentries */
/*
* Saved pool identifier for cleancache (-1 means none)
*/
int cleancache_poolid;
struct shrinker s_shrink; /* per-sb shrinker handle */
/* Number of inodes with nlink == 0 but still referenced */
atomic_long_t s_remove_count;
/* Being remounted read-only */
int s_readonly_remount;
};
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
View Code
所有的超级快对象都以双向循环链表形式连接在一起。链表中的第一个元素用super_blocks表示,sb_lock自旋锁保护链表免受多处理器的同时访问。
命名空间:
安装普通文件系统:
mount 系统调用:
sys_mount函数分析如下;
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(mount, char __user *, dev_name, char __user *, dir_name,
char __user *, type, unsigned long, flags, void __user *, data)
{
int ret;
char *kernel_type;
char *kernel_dir;
char *kernel_dev;
unsigned long data_page;
ret = copy_mount_string(type, &kernel_type);
if (ret < 0)
goto out_type;
kernel_dir = getname(dir_name);
if (IS_ERR(kernel_dir)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(kernel_dir);
goto out_dir;
}
ret = copy_mount_string(dev_name, &kernel_dev);
if (ret < 0)
goto out_dev;
ret = copy_mount_options(data, &data_page);
if (ret < 0)
goto out_data;
ret = do_mount(kernel_dev, kernel_dir, kernel_type, flags,
(void *) data_page);
free_page(data_page);
out_data:
kfree(kernel_dev);
out_dev:
putname(kernel_dir);
out_dir:
kfree(kernel_type);
out_type:
return ret;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
从上述code中可以看出:1、将用户态参数copy到内核态;2、调用do_mount()函数;
为什么存在copy用户参数到内核地址? 原因和为什么有copy_from_user()等函数存在一样的原因。
因为: copy_from_user 函数的目的是从用户空间拷贝数据到内核空间,失败返回没有 被拷贝的字节数,成功返回 0.这个函数含盖了许多关于内核方面的知识,比如内核关于异常出错 的处理.从用户空间拷贝 数据到内核中时必须非常小心,如果用户空间的数据地址是个非法的地址、
超出用户空间的范围,或者 那些地址还没有被映射到,都可能对内核产生很大的影响,如 oops,或者被造 成系统安全的影响.所以 copy_from_user 函数的功能就不只是从用户空间拷贝数据那样简单了,它还要 做一些指针检查以及处理这些 问题的方法
转债自http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-23769728-id-3189280.html
最近貌似有人问为什么要用copy_from_user这类函数的问题,难道内核不能使用用户态的指针吗?那人自己做了个实验,不用copy_from_user,而是直接在内核里使用用户态指针,程序运行得好好的,啥事也没有。那么内核干嘛还要提供这么些函数呢?
我看网上有人说用户态指针在内核里没有意义了,如同内核指针在用户态一样没有意义了。这话其实不对,以x86来说,页目录表是放在CR3中的,这个寄存器 没有什么内核态用户态之分,换句话说一个用户态进程通过系统调用进入内核态,task_struct结构中的cr3都是不变的,
没有页目录表变化的情况发 生。所以内核态使用用户进程传递过来的指针是有意义的,而且在用户态下内核的指针也是有意义的,只不过因为权限不够,用户进程使用内核指针就有异常发生。
回到上面的话题,既然内核可以使用用户进程传递过来的指针,那干吗不使用memcpy呢?绝大多数情况下使用memcpy取代 copy_from_user都是OK的,事实上在没有MMU的体系上,copy_from_user就是memcpy。但是为什么有MMU就不一样了 呢,使用copy_from_user除了那个access_ok检查之外,
它的实现前半部分就是memcpy,后边多了个两个section。这话要得 从内核提供的缺页异常说起,而且copy_from_user就是用来对付用户态的指针所指向的虚拟地址没有映射到实际物理内存这种情况,这个现象在用户 空间不是什么大事,缺页异常会自动提交物理内存,之后发生异常的指令正常运行,
彷佛啥事也没发生。但是这事放到内核里就不一样了,内核需要显式地去修正这 个异常,背后的思想是:内核对于没有提交物理地址的虚拟地址空间的访问不能象用户进程那样若无其事,内核得表明下态度--别想干坏事,老子盯着你呢。就这 么个意思。所以copy_from_user和memcpy的区别就是多了两个section,
这样对于缺页的异常,copy_from_user可以修 正,但是memcpy不行。
用户空间传过来的指针是在虚拟地址空间上的,它指向的虚拟地址空间很可能还没有真正映射到实际的物理页面上。但这又能怎样呢?缺页导致的异常会透明的被内核予以修复(为缺页的地址空间提交新的物理页面),访问到缺页的指令会继续运行仿佛什么都没有发生一样。但这只是用户空间缺页异常的行为,
在内核空间这样却因一场必须被显示的修复,这是由内核提供的缺页异常处理函数的设计模式决定的,其背后的思想后:在内核态中,如果程序试图访问一个尚未提交物理页面的用户空间地址,内核必须对此保持警惕而不能像用户空间那样毫无察觉。
如果内核访问一个尚未被提交物理页面的空间,将产生缺页异常,内核会调用do_page_fault,因为异常发生在内核空间,do_page_fault将调用search_exception_tables在“ __ex_table”中查找异常指令的修复指令,在__arch_copy_from_user函数中经常使用USER宏,这个宏中了定义了“__ex_table”section。
linux/include/asm-arm/assembler.h
#define USER(x...) \
9999: x; \
.section __ex_table,"a"; \
.align 3; \
.long 9999b,9001f; \
.previous
该定义中有如下数据;
.long 9999b,9001f;
其中9999b对应标号9999处的指令,9001f是9001处的指令,是9999b处指令的修复指令。这样,当标号9999处发生缺页异常时,系统将调用do_page_fault提交物理页面,然后跳到9001继续执行。
如果在驱动程序中不使用copy_from_user而用memcpy来代替,对于上述的情形会产生什么结果呢?当标号9999出发生缺页异常时,系统在“__ex_table”section总将找不到修复地址,因为memcpy没有像copy_from_user那样定义一个“__ex_table”section,此时do_page_fault将通过no_context函数产生Oops。
极有可能会看到类似如下信息:
Unable to handle kernel NULL pointer dereference at virtual address 00000fe0
所有为了确保设备驱动程序的安全,应该使用copy_from_user函数而不是memcpy。
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
/*
* Flags is a 32-bit value that allows up to 31 non-fs dependent flags to
* be given to the mount() call (ie: read-only, no-dev, no-suid etc).
*
* data is a (void *) that can point to any structure up to
* PAGE_SIZE-1 bytes, which can contain arbitrary fs-dependent
* information (or be NULL).
*
* Pre-0.97 versions of mount() didn't have a flags word.
* When the flags word was introduced its top half was required
* to have the magic value 0xC0ED, and this remained so until 2.4.0-test9.
* Therefore, if this magic number is present, it carries no information
* and must be discarded.
*/
/* 以下几个函数将用户态参数拷贝至内核态,包括:
** 1. kernel_type:挂载文件系统类型,如ext3
** 2. kernel_dir: 挂载点路径
** 3. dev_name: 设备名称
** 4. data_pages: 选项信息
*/
/* 参数:
** dev_name : 挂载设备名称
** dir_name : 挂载点名称
** type_page: 保存挂载的文件系统类型,如"ext3"
** flags : 挂载标志
** data_page: 大部分情况下为NULL
*/
long do_mount(char *dev_name, char *dir_name, char *type_page,
unsigned long flags, void *data_page)
{
struct path path;
int retval = 0;
int mnt_flags = 0;
/* Discard magic */
if ((flags & MS_MGC_MSK) == MS_MGC_VAL)
flags &= ~MS_MGC_MSK;
/* Basic sanity checks */
if (!dir_name || !*dir_name || !memchr(dir_name, 0, PAGE_SIZE))
return -EINVAL;
if (data_page)
((char *)data_page)[PAGE_SIZE - 1] = 0;
/* ... and get the mountpoint */
/* 调用kern_path(),根据挂载点名称查找其dentry等信息
** 参数:@dir_name : 挂载点路径
** :@LOOKUP_FOLLOW: 查找标志,遇到链接继续查找
** :@path : 查找结果保存与此结构中
*/
retval = kern_path(dir_name, LOOKUP_FOLLOW, &path);
if (retval)
return retval;
retval = security_sb_mount(dev_name, &path,
type_page, flags, data_page);
if (retval)
goto dput_out;
/* Default to relatime unless overriden */
if (!(flags & MS_NOATIME))
mnt_flags |= MNT_RELATIME;
/* Separate the per-mountpoint flags */
if (flags & MS_NOSUID)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NOSUID;
if (flags & MS_NODEV)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NODEV;
if (flags & MS_NOEXEC)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NOEXEC;
if (flags & MS_NOATIME)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NOATIME;
if (flags & MS_NODIRATIME)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NODIRATIME;
if (flags & MS_STRICTATIME)
mnt_flags &= ~(MNT_RELATIME | MNT_NOATIME);
if (flags & MS_RDONLY)
mnt_flags |= MNT_READONLY;
flags &= ~(MS_NOSUID | MS_NOEXEC | MS_NODEV | MS_ACTIVE | MS_BORN |
MS_NOATIME | MS_NODIRATIME | MS_RELATIME| MS_KERNMOUNT |
MS_STRICTATIME);
if (flags & MS_REMOUNT)
/*修改已经存在的文件系统参数,即改变超级块对象s_flags
字段的安装标志*/
retval = do_remount(&path, flags & ~MS_REMOUNT, mnt_flags,
data_page);
else if (flags & MS_BIND) /**要求在系统目录树的另一个安装点上的文件或者目录能够可见**/
retval = do_loopback(&path, dev_name, flags & MS_REC);
else if (flags & (MS_SHARED | MS_PRIVATE | MS_SLAVE | MS_UNBINDABLE))
retval = do_change_type(&path, flags);
else if (flags & MS_MOVE)
retval = do_move_mount(&path, dev_name);/*改变已安装文件的安装点*/
else /*handles normal mount operations. This is the default situation, so no special flags are required*/
retval = do_new_mount(&path, type_page, flags, mnt_flags,
dev_name, data_page); /*安装普通文件系统*/
dput_out:
path_put(&path);
return retval;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
对于 :kern_path(dir_name, LOOKUP_FOLLOW, &path);
其中: /* 调用kern_path(),根据挂载点名称查找其dentry等信息
** 参数:@dir_name : 挂载点路径
** :@LOOKUP_FOLLOW: 查找标志,遇到链接继续查找
** :@path : 查找结果保存与此结构中
*/
根据挂载点的路径名在内核中查找其内存目录项结构(struct dentry),保存在path中;
对于do_new_mount(.......)分析;
/*
* create a new mount for userspace and request it to be added into the
* namespace's tree
*/
static int do_new_mount(struct path *path, const char *fstype, int flags,
int mnt_flags, const char *name, void *data)
{
struct file_system_type *type;
struct user_namespace *user_ns = current->nsproxy->mnt_ns->user_ns;
struct vfsmount *mnt;
int err;
if (!ns_capable(current_user_ns(), CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
if (!fstype)
return -EINVAL;
type = get_fs_type(fstype);
if (!type)
return -ENODEV;
if (user_ns != &init_user_ns) {
/* Only in special cases allow devices from mounts
* created outside the initial user namespace.
*/
if (!(type->fs_flags & FS_USERNS_DEV_MOUNT)) {
flags |= MS_NODEV;
mnt_flags |= MNT_NODEV | MNT_LOCK_NODEV;
}
if (type->fs_flags & FS_USERNS_VISIBLE) {
if (!fs_fully_visible(type, &mnt_flags)) {
put_filesystem(type);
return -EPERM;
}
}
}
/* 在内核建立vfsmount对象和superblock对象 */
mnt = vfs_kern_mount(type, flags, name, data);
if (!IS_ERR(mnt) && (type->fs_flags & FS_HAS_SUBTYPE) &&
!mnt->mnt_sb->s_subtype)
mnt = fs_set_subtype(mnt, fstype);
put_filesystem(type);
if (IS_ERR(mnt))
return PTR_ERR(mnt);
err = do_add_mount(real_mount(mnt), path, mnt_flags);
if (err)
mntput(mnt);
return err;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
vfs_kern_mount:
/*vfs_kern_mount主要完成三件事:
1. alloc_vfsmnt创造一个新的struct mount结构
2. 在mount_fs函数里调用特定文件系统的mount回调函数构造一个root dentry,包含特定文件系统的super block信息
3. 用第二步得到的结果完成对struct mount的构造,返回vfsmnt结构。
par name:表示/dev/sda设备名称
*/
struct vfsmount *
vfs_kern_mount(struct file_system_type *type, int flags, const char *name, void *data)
{
struct mount *mnt;
struct dentry *root;
if (!type)
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
// alloc一个新的struct mount结构,并初始化里面一部分(如链表指针、mnt_devname等成员内容
mnt = alloc_vfsmnt(name);
if (!mnt)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
if (flags & MS_KERNMOUNT)
mnt->mnt.mnt_flags = MNT_INTERNAL;
/* 调用具体文件系统的mount回调函数type->mount,继续挂载操作 ;比如ext2_fs_type->ext2_mount
ext4_fs_type->ext4_mount */
/*
ext2_fs_type->ext2_mount----->
ext4_fs_type->ext4_mount ---->
其最后调用的是 mount_bdev 以及其对应的ext2/ext4_fill_super 回调
*/
root = mount_fs(type, flags, name, data);
if (IS_ERR(root)) {
mnt_free_id(mnt);
free_vfsmnt(mnt);
return ERR_CAST(root);
}
// 完成mnt结构的最后赋值,并返回vfsmount结构
mnt->mnt.mnt_root = root;//mount关联根dentry (使用vfsmount关联)
mnt->mnt.mnt_sb = root->d_sb;//mount关联超级块
mnt->mnt_mountpoint = mnt->mnt.mnt_root;// mount关联挂载点
mnt->mnt_parent = mnt;//父挂载指向自己 (临时指向 后面会设置
lock_mount_hash();
list_add_tail(&mnt->mnt_instance, &root->d_sb->s_mounts);
unlock_mount_hash();
return &mnt->mnt;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
mount_bdev主要逻辑是
1.根据要挂载的块设备文件名查找到对应的块设备描述符(内核后面操作块设备都是使用块设备描述符);
2.首先在文件系统类型的fs_supers链表查找是否已经读取过指定的vfs超级块,会对比每个超级块的s_bdev块设备描述符,没有创建一个vfs超级块;
3.新创建的vfs超级块,需要调用具体文件系统的fill_super方法来读取填充超级块。
/*blkdev_get_by_path根据设备名得到block_device结构
sget得到已经存在或者新分配的super_block结构
如果是已经存在的sb,就释放第一步得到的bdev结构
如果是新的sb,就调用文件系统个别实现的fill_super函数继续处理新的sb,并创建根inode, dentry
返回得到的s_root
*/
struct dentry *mount_bdev(struct file_system_type *fs_type,
int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data,
int (*fill_super)(struct super_block *, void *, int))
{
struct block_device *bdev;
struct super_block *s;
fmode_t mode = FMODE_READ | FMODE_EXCL;
int error = 0;
if (!(flags & MS_RDONLY))
mode |= FMODE_WRITE;
// 通过dev_name设备名(如/dev/sda1)得到对应的block_device结构
// 首先是一个路径查找的过程,调用kern_path()得到struct path
// 然后以path.dentry->d_inode为参数调用bd_acquire得到block_device结构
// 对于路径查找和块设备的问题以后再叙述
bdev = blkdev_get_by_path(dev_name, mode, fs_type);
if (IS_ERR(bdev))
return ERR_CAST(bdev);
if (current_user_ns() != &init_user_ns) {
/*
* For userns mounts, disallow mounting if bdev is open for
* writing
*/
if (!atomic_dec_unless_positive(&bdev->bd_inode->i_writecount)) {
error = -EBUSY;
goto error_bdev;
}
if (bdev->bd_contains != bdev &&
!atomic_dec_unless_positive(&bdev->bd_contains->bd_inode->i_writecount)) {
atomic_inc(&bdev->bd_inode->i_writecount);
error = -EBUSY;
goto error_bdev;
}
}
/*
* once the super is inserted into the list by sget, s_umount
* will protect the lockfs code from trying to start a snapshot
* while we are mounting
*/
mutex_lock(&bdev->bd_fsfreeze_mutex);
if (bdev->bd_fsfreeze_count > 0) {
mutex_unlock(&bdev->bd_fsfreeze_mutex);
error = -EBUSY;
goto error_inc;
}
/*/ sget现在现存fs_type->fs_supers链表中查找已经存在的对应的超级块实例(因为一个设备可能已经被挂载过了),
fs_supers是file_system_type的成员,它指向一个特定文件系统下的所有超级块实例的链表表头。比较的过程就
是遍历fs_supers链表,用每一个super_block->s_bdev和sget的bdev参数做比较,比较他们是不是同一个设备,
test_bdev_super就是为了比较bdev而传入的函数参数。 如果没能找到已经存在的超级块实例,
那就只能创建一个新的了。此时set_bdev_super函数就是用来把bdev参数设置到新创建的super_block的s_bdev域中。
然后设置一下s_type和s_id(s_id这里先初始化为文件系统名,之后如果发现是磁盘设备再改为磁盘设备名),
并把这个新的sb加入到全局super_blocks链表,以及此file_system_type的fs_supers链表中。
到此就得到了一个已知的或新的super_block实例,后面的工作都是为了填充这个super_block的内容,
并把它加入到各种链表中。
*/
s = sget(fs_type, test_bdev_super, set_bdev_super, flags | MS_NOSEC,
bdev);//----> s->s_bdev = bdev;
mutex_unlock(&bdev->bd_fsfreeze_mutex);
if (IS_ERR(s))
goto error_s;
// 这个if是判断得到的sb是一个已经存在的还是一个新的sb,已经存在的sb的s_root已经被初始化了,新的sb的s_root还是空
if (s->s_root) {
/* 被mount文件系统的根目录项已经存在 切实只读*/
if ((flags ^ s->s_flags) & MS_RDONLY) {
deactivate_locked_super(s);
error = -EBUSY;
goto error_inc;
}
/*
* s_umount nests inside bd_mutex during
* __invalidate_device(). blkdev_put() acquires
* bd_mutex and can't be called under s_umount. Drop
* s_umount temporarily. This is safe as we're
* holding an active reference.
这几个锁 暂时还没有理清楚 需要详细看并发的原因*/
up_write(&s->s_umount);
// 这里对应前面的blkdev_get_by_path 防止blkdev的引用计数由于getbypath 后一直在增长
blkdev_put(bdev, mode);
down_write(&s->s_umount);
} else {
char b[BDEVNAME_SIZE];
s->s_mode = mode;
strlcpy(s->s_id, bdevname(bdev, b), sizeof(s->s_id));
sb_set_blocksize(s, block_size(bdev));
/*/ 设置了sb的mode, id, blocksize后,就到了fill_super的时候了。fill_super是一个函数参数,
它由具体文件系统自己实现,如xfs就实现了xfs_fs_fill_super ----或者ext4_fill_super*/
error = fill_super(s, data, flags & MS_SILENT ? 1 : 0);
if (error) {
deactivate_locked_super(s);
goto error;
}
s->s_flags |= MS_ACTIVE;
bdev->bd_super = s;
}
/* 正常返回被mount文件系统根目录项 */
return dget(s->s_root);
error_s:
error = PTR_ERR(s);
error_inc:
if (current_user_ns() != &init_user_ns) {
atomic_inc(&bdev->bd_inode->i_writecount);
if (bdev->bd_contains != bdev)
atomic_inc(&bdev->bd_contains->bd_inode->i_writecount);
}
error_bdev:
blkdev_put(bdev, mode);
error:
return ERR_PTR(error);
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
- 104.
- 105.
- 106.
- 107.
- 108.
- 109.
- 110.
- 111.
- 112.
- 113.
- 114.
- 115.
- 116.
- 117.
- 118.
- 119.
- 120.
- 121.

ext2_fill_super分析如下:


static int ext2_fill_super(struct super_block *sb, void *data, int silent)
{
struct buffer_head * bh;//缓冲区头 记录读取的磁盘超级块
struct ext2_sb_info * sbi; //内存的ext2 超级块信息
struct ext2_super_block * es;//磁盘上的 超级块信息
struct inode *root;
unsigned long block;
unsigned long sb_block = get_sb_block(&data);
unsigned long logic_sb_block;
unsigned long offset = 0;
unsigned long def_mount_opts;
long ret = -EINVAL;
int blocksize = BLOCK_SIZE;
int db_count;
int i, j;
__le32 features;
int err;
err = -ENOMEM;
sbi = kzalloc(sizeof(*sbi), GFP_KERNEL); //分配 内存的ext2 超级块信息结构
if (!sbi)
goto failed;
sbi->s_blockgroup_lock =
kzalloc(sizeof(struct blockgroup_lock), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!sbi->s_blockgroup_lock) {
kfree(sbi);
goto failed;
}
sb->s_fs_info = sbi; //vfs的超级块 的s_fs_info指向内存的ext2 超级块信息结构
sbi->s_sb_block = sb_block;
spin_lock_init(&sbi->s_lock);
/*
* See what the current blocksize for the device is, and
* use that as the blocksize. Otherwise (or if the blocksize
* is smaller than the default) use the default.
* This is important for devices that have a hardware
* sectorsize that is larger than the default.
*/
blocksize = sb_min_blocksize(sb, BLOCK_SIZE);
if (!blocksize) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR, "error: unable to set blocksize");
goto failed_sbi;
}
/*
* If the superblock doesn't start on a hardware sector boundary,
* calculate the offset.
*/
if (blocksize != BLOCK_SIZE) {
logic_sb_block = (sb_block*BLOCK_SIZE) / blocksize;
offset = (sb_block*BLOCK_SIZE) % blocksize;
} else {
logic_sb_block = sb_block;
}
if (!(bh = sb_bread(sb, logic_sb_block))) { // 读取磁盘上的超级块到内存的 使用buffer_head关联内存缓冲区和磁盘扇区
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR, "error: unable to read superblock");
goto failed_sbi;
}
/*
* Note: s_es must be initialized as soon as possible because
* some ext2 macro-instructions depend on its value
*/
es = (struct ext2_super_block *) (((char *)bh->b_data) + offset);//转换为struct ext2_super_block 结构
sbi->s_es = es; // 内存的ext2 超级块信息结构的 s_es指向真正的ext2磁盘超级块信息结构
sb->s_magic = le16_to_cpu(es->s_magic);//获得文件系统魔数 ext2为0xEF53
if (sb->s_magic != EXT2_SUPER_MAGIC) //验证 魔数是否正确
goto cantfind_ext2;
/* Set defaults before we parse the mount options */
def_mount_opts = le32_to_cpu(es->s_default_mount_opts);
if (def_mount_opts & EXT2_DEFM_DEBUG)
set_opt(sbi->s_mount_opt, DEBUG);
if (def_mount_opts & EXT2_DEFM_BSDGROUPS)
set_opt(sbi->s_mount_opt, GRPID);
if (def_mount_opts & EXT2_DEFM_UID16)
set_opt(sbi->s_mount_opt, NO_UID32);
#ifdef CONFIG_EXT2_FS_XATTR
if (def_mount_opts & EXT2_DEFM_XATTR_USER)
set_opt(sbi->s_mount_opt, XATTR_USER);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_EXT2_FS_POSIX_ACL
if (def_mount_opts & EXT2_DEFM_ACL)
set_opt(sbi->s_mount_opt, POSIX_ACL);
#endif
if (le16_to_cpu(sbi->s_es->s_errors) == EXT2_ERRORS_PANIC)
set_opt(sbi->s_mount_opt, ERRORS_PANIC);
else if (le16_to_cpu(sbi->s_es->s_errors) == EXT2_ERRORS_CONTINUE)
set_opt(sbi->s_mount_opt, ERRORS_CONT);
else
set_opt(sbi->s_mount_opt, ERRORS_RO);
sbi->s_resuid = make_kuid(&init_user_ns, le16_to_cpu(es->s_def_resuid));
sbi->s_resgid = make_kgid(&init_user_ns, le16_to_cpu(es->s_def_resgid));
set_opt(sbi->s_mount_opt, RESERVATION);
if (!parse_options((char *) data, sb))
goto failed_mount;
sb->s_flags = (sb->s_flags & ~MS_POSIXACL) |
((EXT2_SB(sb)->s_mount_opt & EXT2_MOUNT_POSIX_ACL) ?
MS_POSIXACL : 0);
sb->s_iflags |= SB_I_CGROUPWB;
if (le32_to_cpu(es->s_rev_level) == EXT2_GOOD_OLD_REV &&
(EXT2_HAS_COMPAT_FEATURE(sb, ~0U) ||
EXT2_HAS_RO_COMPAT_FEATURE(sb, ~0U) ||
EXT2_HAS_INCOMPAT_FEATURE(sb, ~0U)))
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_WARNING,
"warning: feature flags set on rev 0 fs, "
"running e2fsck is recommended");
/*
* Check feature flags regardless of the revision level, since we
* previously didn't change the revision level when setting the flags,
* so there is a chance incompat flags are set on a rev 0 filesystem.
*/
features = EXT2_HAS_INCOMPAT_FEATURE(sb, ~EXT2_FEATURE_INCOMPAT_SUPP);
if (features) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR, "error: couldn't mount because of "
"unsupported optional features (%x)",
le32_to_cpu(features));
goto failed_mount;
}
if (!(sb->s_flags & MS_RDONLY) &&
(features = EXT2_HAS_RO_COMPAT_FEATURE(sb, ~EXT2_FEATURE_RO_COMPAT_SUPP))){
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR, "error: couldn't mount RDWR because of "
"unsupported optional features (%x)",
le32_to_cpu(features));
goto failed_mount;
}
//获得磁盘读取的块大小
blocksize = BLOCK_SIZE << le32_to_cpu(sbi->s_es->s_log_block_size);
if (sbi->s_mount_opt & EXT2_MOUNT_DAX) {
if (blocksize != PAGE_SIZE) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR,
"error: unsupported blocksize for dax");
goto failed_mount;
}
if (!sb->s_bdev->bd_disk->fops->direct_access) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR,
"error: device does not support dax");
goto failed_mount;
}
}
/* If the blocksize doesn't match, re-read the thing.. */
if (sb->s_blocksize != blocksize) {
brelse(bh);
if (!sb_set_blocksize(sb, blocksize)) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR,
"error: bad blocksize %d", blocksize);
goto failed_sbi;
}
logic_sb_block = (sb_block*BLOCK_SIZE) / blocksize;
offset = (sb_block*BLOCK_SIZE) % blocksize;
bh = sb_bread(sb, logic_sb_block);//重新 读取超级块
if(!bh) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR, "error: couldn't read"
"superblock on 2nd try");
goto failed_sbi;
}
es = (struct ext2_super_block *) (((char *)bh->b_data) + offset);
sbi->s_es = es;
if (es->s_magic != cpu_to_le16(EXT2_SUPER_MAGIC)) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR, "error: magic mismatch");
goto failed_mount;
}
}
sb->s_maxbytes = ext2_max_size(sb->s_blocksize_bits);//设置最大文件大小
sb->s_max_links = EXT2_LINK_MAX;
//读取或设置 inode大小和第一个inode号
if (le32_to_cpu(es->s_rev_level) == EXT2_GOOD_OLD_REV) {
sbi->s_inode_size = EXT2_GOOD_OLD_INODE_SIZE;
sbi->s_first_ino = EXT2_GOOD_OLD_FIRST_INO;
} else {
sbi->s_inode_size = le16_to_cpu(es->s_inode_size);
sbi->s_first_ino = le32_to_cpu(es->s_first_ino);
if ((sbi->s_inode_size < EXT2_GOOD_OLD_INODE_SIZE) ||
!is_power_of_2(sbi->s_inode_size) ||
(sbi->s_inode_size > blocksize)) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR,
"error: unsupported inode size: %d",
sbi->s_inode_size);
goto failed_mount;
}
}
sbi->s_frag_size = EXT2_MIN_FRAG_SIZE <<
le32_to_cpu(es->s_log_frag_size);
if (sbi->s_frag_size == 0)
goto cantfind_ext2;
sbi->s_frags_per_block = sb->s_blocksize / sbi->s_frag_size;
sbi->s_blocks_per_group = le32_to_cpu(es->s_blocks_per_group); //赋值每个块组 块个数
sbi->s_frags_per_group = le32_to_cpu(es->s_frags_per_group);
sbi->s_inodes_per_group = le32_to_cpu(es->s_inodes_per_group); //赋值每个块组 inode个数
if (EXT2_INODE_SIZE(sb) == 0)
goto cantfind_ext2;
sbi->s_inodes_per_block = sb->s_blocksize / EXT2_INODE_SIZE(sb);//赋值每个块 inode个数
if (sbi->s_inodes_per_block == 0 || sbi->s_inodes_per_group == 0)
goto cantfind_ext2;
sbi->s_itb_per_group = sbi->s_inodes_per_group /
sbi->s_inodes_per_block;
sbi->s_desc_per_block = sb->s_blocksize /
sizeof (struct ext2_group_desc);//赋值每个块 块组描述符个数
sbi->s_sbh = bh;//赋值读取的超级块缓冲区
sbi->s_mount_state = le16_to_cpu(es->s_state);//赋值挂载状态
sbi->s_addr_per_block_bits =
ilog2 (EXT2_ADDR_PER_BLOCK(sb));
sbi->s_desc_per_block_bits =
ilog2 (EXT2_DESC_PER_BLOCK(sb));
if (sb->s_magic != EXT2_SUPER_MAGIC)
goto cantfind_ext2;
if (sb->s_blocksize != bh->b_size) {
if (!silent)
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR, "error: unsupported blocksize");
goto failed_mount;
}
if (sb->s_blocksize != sbi->s_frag_size) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR,
"error: fragsize %lu != blocksize %lu"
"(not supported yet)",
sbi->s_frag_size, sb->s_blocksize);
goto failed_mount;
}
if (sbi->s_blocks_per_group > sb->s_blocksize * 8) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR,
"error: #blocks per group too big: %lu",
sbi->s_blocks_per_group);
goto failed_mount;
}
if (sbi->s_frags_per_group > sb->s_blocksize * 8) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR,
"error: #fragments per group too big: %lu",
sbi->s_frags_per_group);
goto failed_mount;
}
if (sbi->s_inodes_per_group > sb->s_blocksize * 8) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR,
"error: #inodes per group too big: %lu",
sbi->s_inodes_per_group);
goto failed_mount;
}
if (EXT2_BLOCKS_PER_GROUP(sb) == 0)
goto cantfind_ext2;
//计算块组描述符 个数
sbi->s_groups_count = ((le32_to_cpu(es->s_blocks_count) -
le32_to_cpu(es->s_first_data_block) - 1)
/ EXT2_BLOCKS_PER_GROUP(sb)) + 1;
db_count = (sbi->s_groups_count + EXT2_DESC_PER_BLOCK(sb) - 1) /
EXT2_DESC_PER_BLOCK(sb);
sbi->s_group_desc = kmalloc (db_count * sizeof (struct buffer_head *), GFP_KERNEL);//分配块组描述符 bh数组
if (sbi->s_group_desc == NULL) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR, "error: not enough memory");
goto failed_mount;
}
bgl_lock_init(sbi->s_blockgroup_lock);
sbi->s_debts = kcalloc(sbi->s_groups_count, sizeof(*sbi->s_debts), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!sbi->s_debts) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR, "error: not enough memory");
goto failed_mount_group_desc;
}
for (i = 0; i < db_count; i++) {//读取块组描述符
block = descriptor_loc(sb, logic_sb_block, i);
sbi->s_group_desc[i] = sb_bread(sb, block);
if (!sbi->s_group_desc[i]) { //读取的 块组描述符缓冲区保存 到sbi->s_group_desc[i]
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
brelse (sbi->s_group_desc[j]);
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR,
"error: unable to read group descriptors");
goto failed_mount_group_desc;
}
}
if (!ext2_check_descriptors (sb)) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR, "group descriptors corrupted");
goto failed_mount2;
}
sbi->s_gdb_count = db_count;
get_random_bytes(&sbi->s_next_generation, sizeof(u32));
spin_lock_init(&sbi->s_next_gen_lock);
/* per fileystem reservation list head & lock */
spin_lock_init(&sbi->s_rsv_window_lock);
sbi->s_rsv_window_root = RB_ROOT;
/*
* Add a single, static dummy reservation to the start of the
* reservation window list --- it gives us a placeholder for
* append-at-start-of-list which makes the allocation logic
* _much_ simpler.
*/
sbi->s_rsv_window_head.rsv_start = EXT2_RESERVE_WINDOW_NOT_ALLOCATED;
sbi->s_rsv_window_head.rsv_end = EXT2_RESERVE_WINDOW_NOT_ALLOCATED;
sbi->s_rsv_window_head.rsv_alloc_hit = 0;
sbi->s_rsv_window_head.rsv_goal_size = 0;
ext2_rsv_window_add(sb, &sbi->s_rsv_window_head);
err = percpu_counter_init(&sbi->s_freeblocks_counter,
ext2_count_free_blocks(sb), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!err) {
err = percpu_counter_init(&sbi->s_freeinodes_counter,
ext2_count_free_inodes(sb), GFP_KERNEL);
}
if (!err) {
err = percpu_counter_init(&sbi->s_dirs_counter,
ext2_count_dirs(sb), GFP_KERNEL);
}
if (err) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR, "error: insufficient memory");
goto failed_mount3;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_EXT2_FS_XATTR
sbi->s_mb_cache = ext2_xattr_create_cache();
if (!sbi->s_mb_cache) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR, "Failed to create an mb_cache");
goto failed_mount3;
}
#endif
/*
* set up enough so that it can read an inode
*/
sb->s_op = &ext2_sops;//赋值超级块操作
sb->s_export_op = &ext2_export_ops;
sb->s_xattr = ext2_xattr_handlers;
#ifdef CONFIG_QUOTA
sb->dq_op = &dquot_operations;
sb->s_qcop = &dquot_quotactl_ops;
sb->s_quota_types = QTYPE_MASK_USR | QTYPE_MASK_GRP;
#endif
root = ext2_iget(sb, EXT2_ROOT_INO);//读取根inode (ext2 根根inode号为2)
if (IS_ERR(root)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(root);
goto failed_mount3;
}
if (!S_ISDIR(root->i_mode) || !root->i_blocks || !root->i_size) {
iput(root);
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR, "error: corrupt root inode, run e2fsck");
goto failed_mount3;
}
sb->s_root = d_make_root(root); //创建根dentry 并建立根inode和根dentry关系
if (!sb->s_root) {
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR, "error: get root inode failed");
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto failed_mount3;
}
if (EXT2_HAS_COMPAT_FEATURE(sb, EXT3_FEATURE_COMPAT_HAS_JOURNAL))
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_WARNING,
"warning: mounting ext3 filesystem as ext2");
if (ext2_setup_super (sb, es, sb->s_flags & MS_RDONLY))
sb->s_flags |= MS_RDONLY;
ext2_write_super(sb);//同步超级块信息到磁盘 如挂载时间等
return 0;
cantfind_ext2:
if (!silent)
ext2_msg(sb, KERN_ERR,
"error: can't find an ext2 filesystem on dev %s.",
sb->s_id);
goto failed_mount;
failed_mount3:
if (sbi->s_mb_cache)
ext2_xattr_destroy_cache(sbi->s_mb_cache);
percpu_counter_destroy(&sbi->s_freeblocks_counter);
percpu_counter_destroy(&sbi->s_freeinodes_counter);
percpu_counter_destroy(&sbi->s_dirs_counter);
failed_mount2:
for (i = 0; i < db_count; i++)
brelse(sbi->s_group_desc[i]);
failed_mount_group_desc:
kfree(sbi->s_group_desc);
kfree(sbi->s_debts);
failed_mount:
brelse(bh);
failed_sbi:
sb->s_fs_info = NULL;
kfree(sbi->s_blockgroup_lock);
kfree(sbi);
failed:
return ret;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
- 104.
- 105.
- 106.
- 107.
- 108.
- 109.
- 110.
- 111.
- 112.
- 113.
- 114.
- 115.
- 116.
- 117.
- 118.
- 119.
- 120.
- 121.
- 122.
- 123.
- 124.
- 125.
- 126.
- 127.
- 128.
- 129.
- 130.
- 131.
- 132.
- 133.
- 134.
- 135.
- 136.
- 137.
- 138.
- 139.
- 140.
- 141.
- 142.
- 143.
- 144.
- 145.
- 146.
- 147.
- 148.
- 149.
- 150.
- 151.
- 152.
- 153.
- 154.
- 155.
- 156.
- 157.
- 158.
- 159.
- 160.
- 161.
- 162.
- 163.
- 164.
- 165.
- 166.
- 167.
- 168.
- 169.
- 170.
- 171.
- 172.
- 173.
- 174.
- 175.
- 176.
- 177.
- 178.
- 179.
- 180.
- 181.
- 182.
- 183.
- 184.
- 185.
- 186.
- 187.
- 188.
- 189.
- 190.
- 191.
- 192.
- 193.
- 194.
- 195.
- 196.
- 197.
- 198.
- 199.
- 200.
- 201.
- 202.
- 203.
- 204.
- 205.
- 206.
- 207.
- 208.
- 209.
- 210.
- 211.
- 212.
- 213.
- 214.
- 215.
- 216.
- 217.
- 218.
- 219.
- 220.
- 221.
- 222.
- 223.
- 224.
- 225.
- 226.
- 227.
- 228.
- 229.
- 230.
- 231.
- 232.
- 233.
- 234.
- 235.
- 236.
- 237.
- 238.
- 239.
- 240.
- 241.
- 242.
- 243.
- 244.
- 245.
- 246.
- 247.
- 248.
- 249.
- 250.
- 251.
- 252.
- 253.
- 254.
- 255.
- 256.
- 257.
- 258.
- 259.
- 260.
- 261.
- 262.
- 263.
- 264.
- 265.
- 266.
- 267.
- 268.
- 269.
- 270.
- 271.
- 272.
- 273.
- 274.
- 275.
- 276.
- 277.
- 278.
- 279.
- 280.
- 281.
- 282.
- 283.
- 284.
- 285.
- 286.
- 287.
- 288.
- 289.
- 290.
- 291.
- 292.
- 293.
- 294.
- 295.
- 296.
- 297.
- 298.
- 299.
- 300.
- 301.
- 302.
- 303.
- 304.
- 305.
- 306.
- 307.
- 308.
- 309.
- 310.
- 311.
- 312.
- 313.
- 314.
- 315.
- 316.
- 317.
- 318.
- 319.
- 320.
- 321.
- 322.
- 323.
- 324.
- 325.
- 326.
- 327.
- 328.
- 329.
- 330.
- 331.
- 332.
- 333.
- 334.
- 335.
- 336.
- 337.
- 338.
- 339.
- 340.
- 341.
- 342.
- 343.
- 344.
- 345.
- 346.
- 347.
- 348.
- 349.
- 350.
- 351.
- 352.
- 353.
- 354.
- 355.
- 356.
- 357.
- 358.
- 359.
- 360.
- 361.
- 362.
- 363.
- 364.
- 365.
- 366.
- 367.
- 368.
- 369.
- 370.
- 371.
- 372.
- 373.
- 374.
- 375.
- 376.
- 377.
- 378.
- 379.
- 380.
- 381.
- 382.
- 383.
- 384.
- 385.
- 386.
- 387.
- 388.
- 389.
- 390.
- 391.
- 392.
- 393.
- 394.
- 395.
- 396.
- 397.
- 398.
- 399.
- 400.
View Code
可以看到ext2_fill_super主要工作为:
- 1.读取磁盘上的超级块;
- 2.填充并关联vfs超级块;
- 3.读取块组描述符;
- 4.读取磁盘根inode并建立vfs 根inode;
- 5.创建根dentry关联到根inode。
准备好了挂载点之后,接下来子mount实例关联挂载点以及添加子mount实例到全局的文件系统挂载树中。
do_add_mount 函数分析
其主要内容为:
将mount实例与挂载点联系起来(会将mount实例加入到mount 哈希表,父文件系统的vfsmount和真正的挂载点的dentry组成的二元组为索引,路径名查找时便于查找),
以及mount实例与文件系统的跟dentry联系起来(路径名查找的时候便于沿着跟dentry来访问这个文件系统的所有文件)


/*
* add a mount into a namespace's mount tree
*/
static int do_add_mount(struct mount *newmnt, struct path *path, int mnt_flags)
{
struct mountpoint *mp;
struct mount *parent;
int err;
mnt_flags &= ~MNT_INTERNAL_FLAGS;
mp = lock_mount(path);
if (IS_ERR(mp))
return PTR_ERR(mp);
parent = real_mount(path->mnt);//获得父挂载点的挂载实例
err = -EINVAL;
if (unlikely(!check_mnt(parent))) {
/* that's acceptable only for automounts done in private ns */
if (!(mnt_flags & MNT_SHRINKABLE))
goto unlock;
/* ... and for those we'd better have mountpoint still alive */
if (!parent->mnt_ns)
goto unlock;
}
/* Refuse the same filesystem on the same mount point */
err = -EBUSY;
if (path->mnt->mnt_sb == newmnt->mnt.mnt_sb &&
path->mnt->mnt_root == path->dentry)
goto unlock;
err = -EINVAL;
if (d_is_symlink(newmnt->mnt.mnt_root))
goto unlock;
newmnt->mnt.mnt_flags = mnt_flags;
err = graft_tree(newmnt, parent, mp);
unlock:
unlock_mount(mp);
return err;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
View Code
lookup_mnt(path); //lookup_mnt takes a reference to the found vfsmount. 分析如下


/*
lock_mount传递的path 之前不是挂载点:
调用链为:
lock_mount
->mnt = lookup_mnt(path) //没有子mount 返回NULL
->mp = get_mountpoint(dentry) //分配mountpoint 加入mountpoint hash表(dentry计算hash),设置dentry为挂载点
->return mp //返回找到的挂载点实例
2)lock_mount传递的path 之前是挂载点:我们现在执行 mount -t ext2 /dev/sda4 /mnt
之前 /mnt的挂载情况
mount /dev/sda1 /mnt (1)
mount /dev/sda2 /mnt (2)
mount /dev/sda3 /mnt (3)
调用链为:
lock_mount
->mnt = lookup_mnt(path) //返回(1)的mount实例
->path->mnt = mnt //下一次查找的 path->mnt赋值(1)的mount实例
->dentry = path->dentry = dget(mnt->mnt_root) // //下一次查找path->dentry 赋值(1)的根dentry
->mnt = lookup_mnt(path) //返回(2)的mount实例
->path->mnt = mnt //下一次查找的 path->mnt赋值(2)的mount实例
->dentry = path->dentry = dget(mnt->mnt_root) // //下一次查找path->dentry 赋值(2)的根dentry
->mnt = lookup_mnt(path) //返回(3)的mount实例
->path->mnt = mnt //下一次查找的 path->mnt赋值(3)的mount实例
->dentry = path->dentry = dget(mnt->mnt_root) // //下一次查找path->dentry 赋值(3)的根dentry
-> mnt = lookup_mnt(path) //没有子mount 返回NULL
->mp = get_mountpoint(dentry) //分配mountpoint 加入mountpoint hash表(dentry计算hash),设置dentry为挂载点((3)的根dentry作为挂载点)
->return mp //返回找到的挂载点实例(也就是最后一次挂载(3) 文件系统的根dentry)
*/
static struct mountpoint *lock_mount(struct path *path)
{
struct vfsmount *mnt;
struct dentry *dentry = path->dentry;
retry:
mutex_lock(&dentry->d_inode->i_mutex);
if (unlikely(cant_mount(dentry))) {
mutex_unlock(&dentry->d_inode->i_mutex);
return ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
}
namespace_lock();
mnt = lookup_mnt(path); //lookup_mnt takes a reference to the found vfsmount.
if (likely(!mnt)) {
struct mountpoint *mp = get_mountpoint(dentry);
if (IS_ERR(mp)) {
namespace_unlock();
mutex_unlock(&dentry->d_inode->i_mutex);
return mp;
}
return mp;
}
namespace_unlock();
mutex_unlock(&path->dentry->d_inode->i_mutex);
path_put(path);
path->mnt = mnt;
dentry = path->dentry = dget(mnt->mnt_root);
goto retry;
}
/*
* lookup_mnt - Return the first child mount mounted at path
*
* "First" means first mounted chronologically. If you create the
* following mounts:
*
* mount /dev/sda1 /mnt
* mount /dev/sda2 /mnt
* mount /dev/sda3 /mnt
*
* Then lookup_mnt() on the base /mnt dentry in the root mount will
* return successively the root dentry and vfsmount of /dev/sda1, then
* /dev/sda2, then /dev/sda3, then NULL.
*
* lookup_mnt takes a reference to the found vfsmount.
*/
struct vfsmount *lookup_mnt(struct path *path)
{
struct mount *child_mnt;
struct vfsmount *m;
unsigned seq;
rcu_read_lock();
do {
seq = read_seqbegin(&mount_lock);
child_mnt = __lookup_mnt(path->mnt, path->dentry);
m = child_mnt ? &child_mnt->mnt : NULL;
} while (!legitimize_mnt(m, seq));
rcu_read_unlock();
return m;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
- 104.
- 105.
- 106.
- 107.
- 108.
- 109.
- 110.
- 111.
- 112.
- 113.
View Code


/*
* @source_mnt : mount tree to be attached
* @nd : place the mount tree @source_mnt is attached
* @parent_nd : if non-null, detach the source_mnt from its parent and
* store the parent mount and mountpoint dentry.
* (done when source_mnt is moved)
*
* NOTE: in the table below explains the semantics when a source mount
* of a given type is attached to a destination mount of a given type.
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
* | BIND MOUNT OPERATION |
* |**************************************************************************
* | source-->| shared | private | slave | unbindable |
* | dest | | | | |
* | | | | | | |
* | v | | | | |
* |**************************************************************************
* | shared | shared (++) | shared (+) | shared(+++)| invalid |
* | | | | | |
* |non-shared| shared (+) | private | slave (*) | invalid |
* ***************************************************************************
* A bind operation clones the source mount and mounts the clone on the
* destination mount.
*
* (++) the cloned mount is propagated to all the mounts in the propagation
* tree of the destination mount and the cloned mount is added to
* the peer group of the source mount.
* (+) the cloned mount is created under the destination mount and is marked
* as shared. The cloned mount is added to the peer group of the source
* mount.
* (+++) the mount is propagated to all the mounts in the propagation tree
* of the destination mount and the cloned mount is made slave
* of the same master as that of the source mount. The cloned mount
* is marked as 'shared and slave'.
* (*) the cloned mount is made a slave of the same master as that of the
* source mount.
*
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
* | MOVE MOUNT OPERATION |
* |**************************************************************************
* | source-->| shared | private | slave | unbindable |
* | dest | | | | |
* | | | | | | |
* | v | | | | |
* |**************************************************************************
* | shared | shared (+) | shared (+) | shared(+++) | invalid |
* | | | | | |
* |non-shared| shared (+*) | private | slave (*) | unbindable |
* ***************************************************************************
*
* (+) the mount is moved to the destination. And is then propagated to
* all the mounts in the propagation tree of the destination mount.
* (+*) the mount is moved to the destination.
* (+++) the mount is moved to the destination and is then propagated to
* all the mounts belonging to the destination mount's propagation tree.
* the mount is marked as 'shared and slave'.
* (*) the mount continues to be a slave at the new location.
*
* if the source mount is a tree, the operations explained above is
* applied to each mount in the tree.
* Must be called without spinlocks held, since this function can sleep
* in allocations.
*/
static int attach_recursive_mnt(struct mount *source_mnt,
struct mount *dest_mnt,
struct mountpoint *dest_mp,
struct path *parent_path)
{
HLIST_HEAD(tree_list);
struct mnt_namespace *ns = dest_mnt->mnt_ns;
struct mountpoint *smp;
struct mount *child, *p;
struct hlist_node *n;
int err;
/* Preallocate a mountpoint in case the new mounts need
* to be tucked under other mounts.
*/
smp = get_mountpoint(source_mnt->mnt.mnt_root);
if (IS_ERR(smp))
return PTR_ERR(smp);
/* Is there space to add these mounts to the mount namespace? */
if (!parent_path) {
err = count_mounts(ns, source_mnt);
if (err)
goto out;
}
if (IS_MNT_SHARED(dest_mnt)) {
err = invent_group_ids(source_mnt, true);
if (err)
goto out;
err = propagate_mnt(dest_mnt, dest_mp, source_mnt, &tree_list);
lock_mount_hash();
if (err)
goto out_cleanup_ids;
for (p = source_mnt; p; p = next_mnt(p, source_mnt))
set_mnt_shared(p);
} else {
lock_mount_hash();
}
if (parent_path) {
detach_mnt(source_mnt, parent_path);
attach_mnt(source_mnt, dest_mnt, dest_mp);
touch_mnt_namespace(source_mnt->mnt_ns);
} else {
/**
child_mnt->mnt_mountpoint = mp->m_dentry; //关联子mount到挂载点的dentry
child_mnt->mnt_parent = mnt; //子mount->mnt_parent指向父mount
child_mnt->mnt_mp = mp; //子mount->mnt_mp指向挂载点
hlist_add_head(&child_mnt->mnt_mp_list, &mp->m_list); //mount添加到挂载点链表*/
mnt_set_mountpoint(dest_mnt, dest_mp, source_mnt);
commit_tree(source_mnt);//提交挂载树
/*/----->/*__attach_mnt(mnt, parent)
-> hlist_add_head_rcu(&mnt->mnt_hash,
¦ m_hash(&parent->mnt, mnt->mnt_mountpoint)); //添加到mount hash表 ,通过父挂载点的vfsmount和挂载点的dentry作为索引(如上面示例中的<(3)的vfsmount , (3)的根dentry>)
list_add_tail(&mnt->mnt_child, &parent->mnt_mounts); //添加到父mount链表
*/
}
hlist_for_each_entry_safe(child, n, &tree_list, mnt_hash) {
struct mount *q;
hlist_del_init(&child->mnt_hash);
q = __lookup_mnt(&child->mnt_parent->mnt,
child->mnt_mountpoint);
if (q)
mnt_change_mountpoint(child, smp, q);
commit_tree(child);
}
put_mountpoint(smp);
unlock_mount_hash();
return 0;
out_cleanup_ids:
while (!hlist_empty(&tree_list)) {
child = hlist_entry(tree_list.first, struct mount, mnt_hash);
child->mnt_parent->mnt_ns->pending_mounts = 0;
umount_tree(child, UMOUNT_SYNC);
}
unlock_mount_hash();
cleanup_group_ids(source_mnt, NULL);
out:
ns->pending_mounts = 0;
read_seqlock_excl(&mount_lock);
put_mountpoint(smp);
read_sequnlock_excl(&mount_lock);
return err;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
- 84.
- 85.
- 86.
- 87.
- 88.
- 89.
- 90.
- 91.
- 92.
- 93.
- 94.
- 95.
- 96.
- 97.
- 98.
- 99.
- 100.
- 101.
- 102.
- 103.
- 104.
- 105.
- 106.
- 107.
- 108.
- 109.
- 110.
- 111.
- 112.
- 113.
- 114.
- 115.
- 116.
- 117.
- 118.
- 119.
- 120.
- 121.
- 122.
- 123.
- 124.
- 125.
- 126.
- 127.
- 128.
- 129.
- 130.
- 131.
- 132.
- 133.
- 134.
- 135.
- 136.
- 137.
- 138.
- 139.
- 140.
- 141.
- 142.
- 143.
- 144.
- 145.
- 146.
- 147.
- 148.
- 149.
- 150.
- 151.
- 152.
View Code
do_add_mount 之后vfs对象数据结构之间关系图ps:/mnt之前不是挂载点情况
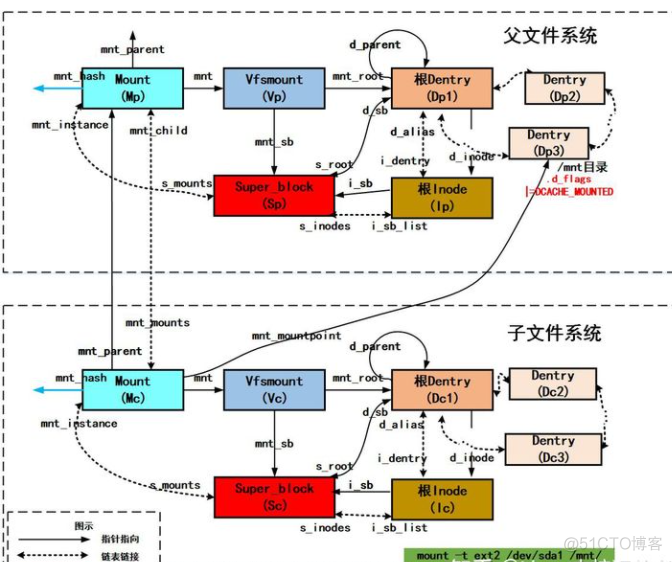
图中/dev/sda1中的子文件系统挂载到父文件系统的/mnt目录下。当挂载的时候会创建mount、super_block、跟inode、跟dentry四大数据结构并建立相互关系,将子文件系统的mount加入到(Vp, Dp3)二元组为索引的mount哈希表中,通过设置mnt的目录项(Dp3)的DCACHE_MOUNTED来将其标记为挂载点,并与父文件系统建立亲缘关系挂载就完成了。
当需要访问子文件系统中的某个文件时,就会通过路径名各个分量解析到mnt目录,发现其为挂载点,就会通过(Vp, Dp3)二元组在mount哈希表中找到子文件系统的mount实例(Mc),然后就会从子文件系统的跟dentry(Dc1)开始往下继续查找,最终访问到子文件系统上的文件
多文件系统单挂载点关系图解

图中先将块设备/dev/sda1中的子文件系统1挂载到/mnt目录,然后再将块设备/dev/sdb1中的子文件系统2挂载到/mnt目录上。
当子文件系统1挂载的时候,会创建mount、super_block、跟inode、跟dentry四大数据结构(分别对应与Mc1、Sc1、Dc1、Ic1)并建立相互关系,将子文件系统的Mc1加入到(Vp, Dp3)二元组为索引的mount哈希表中,通过设置/mnt的目录项的DCACHE_MOUNTED来将其标记为挂载点,并与父文件系统建立亲缘关系挂载就完成了。
当子文件系统2挂载的时候,会创建mount、super_block、跟inode、跟dentry四大数据结构(分别对应与Mc2、Sc2、Dc4、Ic2)并建立相互关系,这个时候会发现/mnt目录是挂载点,则会将子文件系统1的根目录(Dc1)作为文件系统2的挂载点,将子文件系统的Mc2加入到(Vc1, Dc1)二元组为索引的mount哈希表中,通过设置Dc1的DCACHE_MOUNTED来将其标记为挂载点,并与父文件系统建立亲缘关系挂载就完成了。
此时,子文件系统1已经被子文件系统2隐藏起来了,当路径名查找到/mnt目录时,发现其为挂载点,则通过(Vp, Dp3)二元组为索引在mount哈希表中找到Mc1,会转向文件系统1的跟目录(Dc1)开始往下继续查找,发现Dc1也是挂载点,则(通过Vc1, Dc1)二元组为索引在mount哈希表中找到Mc2, 会转向文件系统1的跟目录(Dc4)开始往下继续查找,于是就访问到了文件系统2中的文件。除非,文件系统2被卸载,文件系统1的跟dentry(Dc1)不再是挂载点,这个时候文件系统1中的文件才能再次被访问到。

父子挂载点的挂载关系
假设在/mnt上挂载着一个文件系统,根据上面条件我们以/dev/sda1挂载到/mnt/a上为例,来解释一下/mnt/a上这个挂载实例和/mnt的挂载实例的关系,如下图所示:

父文件系统代表/mnt上的文件系统,子文件系统代表/mnt/a上的文件系统(带颜色的地方为重点要注意的地方)。父子文件系统通过mnt_parent, mount_child, mnt_mounts等成员来联系在一起,每个挂载实例的mnt_sb都指向这个挂载实例所属文件系统的super_block。每个挂载实例的mnt_root都指向这个文件系统的根dentry。
根dentry就是一个文件系统的路径的起始,也就是"/"。比如一个路径名/mnt/a/dir/file。在/mnt/a这个文件系统下看这个文件是/dir/file,这个起始的"/"代表/mnt/a下挂载的文件系统的根,也就是如上图红色所示的dentry,它是这一文件系统的起始dentry。当发现到了一个文件系统的根后,如果想继续探寻完整路径应该根据/mnt/a的挂载实例向上找到其父文件系统,也就是/mnt下挂载的文件系统。/dev/sda1挂载在了/mnt/a上,这里的/mnt/a代表/mnt下文件系统的一个子dentry,如图绿色部分所示。注意红色和绿色是两个文件系统下的两个不同的dentry,虽然不是很恰当的说它们从全局来看是一个路径名。那么从/mnt所在的文件系统看/mnt/a就是/a。最后再往上就到了rootfs文件系统,也就是最上层的根"/"。所以我们之前说过,表示一个文件的路径需要<mount, dentry>二元组来共同确定。
子文件系统的mnt_mountpoint就指向了父文件系统的一个dentry,这个dentry也就是子文件系统的真正挂载点。可以说子文件系统在挂载后会新创建一个dentry,并在此构建这个文件系统下的路径结构。
宗上所述,/mnt/a上这个新挂载的文件系统创建了一个新的mount, super_block, 根inode和根dentry。在看懂了一个简单的父子文件系统挂载关系后,我们来看下多个文件系统挂载到同一路径名下时又是什么样子
单文件系统多挂载点的挂载关系

一个文件系统对应一个super_block,所以同一个文件系统当然只有一个super_block。但是因为挂载了两次,所有每一次挂载对应一个挂载实例struct mount,也就是有两个mount实例。此外同一个文件系统只有一个根,也就是两个挂载实例公用一个根dentry。但是因为挂载在两个不同的路经下,所以每个挂载实例的mnt_mountpoint指向不同的dentry。由于/mnt/a和/mnt/x都属于同一文件系统的下的两个子目录,所以两个子mount才指向同一个父mount
重要规律
1)文件系统被挂载后都会有以下几大vfs对象被创建:
super_block
mount
根inode
根dentry
注:其中mount为纯软件构造的对象(内嵌vfsmount对象),其他对象视文件系统类型,可能涉及到磁盘操作。
super_block 超级块实例,描述一个文件系统的信息,有的需要磁盘读取在内存中填充来构建(如磁盘文件系统),有的直接内存中填充来构建。
mount 挂载实例,描述一个文件系统的一次挂载,主要关联一个文件系统到挂载点,为路径名查找做重要准备工作。
根inode 每个文件系统都会有根inode,有的需要磁盘读取在内存中填充来构建(如磁盘文件系统,根inode号已知),有的直接内存中填充来构建。
根dentry 每个文件系统都会有根dentry,根据根inode来构建,路径名查找时会步进到文件系统的根dentry来访问这个文件系统的文件。
2)一个目录可以被多个文件系统挂载。第一次挂载是直接挂载这个目录上,新挂载的文件系统实际上是挂载在上一个文件系统的根dentry上。
3)一个目录被多个文件系统挂载时,新挂载导致之前的挂载被隐藏。
4)一个目录被文件系统挂载时,原来目录中包含的其他子目录或文件被隐藏。
5)每次挂载都会有一个mount实例描述本次挂载。
6)一个快设备上的文件系统可以被挂载到多个目录,有多个mount实例,但是只会有一个super_block、根dentry 和根inode。
7)mount实例用于关联挂载点dentry和文件系统,起到路径名查找时“路由”的作用。
8)挂载一个文件系统必须保证所要挂载的文件系统类型已经被注册。
9)挂载时会查询文件系统类型的fs_type->fs_supers链表,检查是否已经有super_block被加入链表,如果没有才会分配并读磁盘超级块填充。
10)对象层次:一个fs_type->fs_supers链表可以挂接属于同一个文件系统的被挂载的超级块,超级块链表可以挂接属于同一个超级块的mount实例 fs_type -> super_block -> mount 从高到低的包含层次。
http代理服务器(3-4-7层代理)-网络事件库公共组件、内核kernel驱动 摄像头驱动 tcpip网络协议栈、netfilter、bridge 好像看过!!!! 但行好事 莫问前程 --身高体重180的胖子
边栏推荐
- Configure PHP development environment in MAC environment: apache+php+mysql
- Free and easy-to-use screen recording and video cutting tool sharing
- Tencent launched the "reassuring agricultural product plan" to support 100 landmark agricultural product brands!
- Reasons for automatic allocation failure of crawler agent IP
- Word cannot copy and paste processing method
- Cloud native high availability and Disaster Recovery Series (I): pod break up scheduling
- What is the domain name query network and how it should be used
- Go current limiting component package rate source code analysis
- leetcode:剑指 Offer 26:判断t1中是否含有t2的全部拓扑结构
- Tencent security apkpecker launched dex-vmp automatic shelling service
猜你喜欢

【JUC系列】Executor框架之CompletionFuture
程序员使用个性壁纸

解读AI机器人产业发展的顶层设计

puzzle(019.1)Hook、Gear

leetcode:85. 最大矩形

基于三维GIS系统的智慧水库管理应用
Leetcode: Sword finger offer 26: judge whether T1 contains all topologies of T2

Record -- about the problem of garbled code when JSP foreground passes parameters to the background
leetcode:84. The largest rectangle in the histogram
![跳跃游戏II[贪心练习]](/img/e4/f59bb1f5137495ea357462100e2b38.png)
跳跃游戏II[贪心练习]
随机推荐
Programmers use personalized Wallpapers
SAP hum unbinds Hu from delivery order
What I regret most when I learn programming!
WordPress pill applet build applet from zero to one [applet registration configuration]
Interpreting the new features of Appstore: Customizing product pages and a/b test tools
Nature Neuroscience: challenges and future directions of functional brain tissue characterization
The new version of Tencent Youtu ncnn is suitable for domestic CPUs, and the maximum speed is increased by 70 times
Wordpress5.8 is coming, and the updated website is faster!
程序员使用个性壁纸
Koa source code analysis
Use of SAP QM inspection points
Web automated testing (1): further discussion on UI development history and UI and function automated testing
Go current limiting component package rate source code analysis
Papamelon 11 number of calculation permutation [combinatorics]
In the half year, there were 2.14 million paying users, a year-on-year increase of 62.5%, and New Oriental online launched its private domain
How does go limit the flow of services?
Produce kubeconfig with permission control
Come on, it's not easy for big factories to do projects!
What are the audio formats? Can the audio format be converted
If you want to learn programming well, don't recite the code!
