当前位置:网站首页>Adapter mode
Adapter mode
2022-06-26 13:11:00 【baboon_ chen】
Reference resources :
Adapter pattern (Adapter Pattern ) Detailed explanation (biancheng.net)
design-patterns-cpp/adapter at master · JakubVojvoda/design-patterns-cpp · GitHub
adapter design pattern ( Wrapper mode ) (refactoringguru.cn)
One 、 What is adapter mode ?
Put the incompatible interface , Through adaptation and modification to achieve unity , Convenient for users .
Adapter patterns are divided into two types: class structure and object structure , The former is implemented by multiple inheritance , High coupling degree , The latter uses a combination , Low coupling .
For example, scenes in life , The power adapter , Notebook adapter , Card reader, etc .

Two 、 Advantages and disadvantages , Applicable scenario
advantage
- The client can call the target interface transparently through the adapter .
- Reuse existing classes , Programmers do not need to modify the original code and reuse the existing adapter class .
- Decouple the target class from the adapter class , It solves the problem that the interface between the target class and the adapter class is inconsistent .
- In many business scenarios, it conforms to the opening and closing principle .
shortcoming
- The adapter writing process needs to be fully considered in the context of business scenarios , It may increase the complexity of the system .
- Increase the difficulty of code reading , Reduce code readability , Using too many adapters can clutter system code .
Applicable scenario
- Previously developed systems have classes that meet the functional requirements of new systems , But its interface is not the same as that of the new system .
- Use third party supplied components , But the component interface definition is different from the interface definition required by itself .
3、 ... and 、 Example
Adapter pattern (Adapter) Include the following main characters :
- The goal is (Target) Interface : The interface expected by the current system business , It can be an abstract class or interface .
- Adapter (Adaptee) class : Existing component interfaces .
- Adapter (Adapter) class : converter , By inheriting or referencing an adapter's object , Convert the adapter interface to the target interface , Let the customer access the adapter in the format of the target interface .
1、 Class structural type
/*
* C++ Design Patterns: Adapter (Class scope)
* Author: Jakub Vojvoda [github.com/JakubVojvoda]
* 2016
*
* Source code is licensed under MIT License
* (for more details see LICENSE)
*
*/
#include <iostream>
/*
* Target
* Define the interface type required by the user
*/
class Target
{
public:
virtual ~Target() {}
virtual void request() = 0;
// ...
};
/*
* Adaptee
* Adapter , Provide existing interfaces
*/
class Adaptee
{
public:
~Adaptee() {}
void specificRequest()
{
std::cout << "specific request" << std::endl;
}
// ...
};
/*
* Adapter
* Adapter , Reuse existing interfaces , Class structs are implemented through multiple continuations
*/
class Adapter : public Target, private Adaptee
{
public:
virtual void request()
{
specificRequest();
}
// ...
};
int main()
{
Target *t = new Adapter();
t->request();
delete t;
return 0;
}
2、 Object structured
/*
* C++ Design Patterns: Adapter (Object scope)
* Author: Jakub Vojvoda [github.com/JakubVojvoda]
* 2016
*
* Source code is licensed under MIT License
* (for more details see LICENSE)
*
*/
#include <iostream>
/*
* Target
* defines specific interface that Client uses
*/
class Target
{
public:
virtual ~Target() {}
virtual void request() = 0;
// ...
};
/*
* Adaptee
* defines an existing interface that needs adapting and thanks
* to Adapter it will get calls that client makes on the Target
*
*/
class Adaptee
{
public:
void specificRequest()
{
std::cout << "specific request" << std::endl;
}
// ...
};
/*
* Adapter
* By combination , Reuse existing interfaces
*/
class Adapter : public Target
{
public:
Adapter() : adaptee() {}
~Adapter()
{
delete adaptee;
}
void request()
{
adaptee->specificRequest();
// ...
}
// ...
private:
Adaptee *adaptee;
// ...
};
int main()
{
Target *t = new Adapter();
t->request();
delete t;
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- HDU1724[辛普森公式求积分]Ellipse
- Processing polyhedron change
- Accumulation of interview questions
- System tasks (display / print class) in Verilog - $display, $write, $strobe, $monitor
- 利用scrapy爬取句子迷网站优美句子存储到本地(喜欢摘抄的人有福了!)
- 软件测试测试常见分类有哪些?
- Electron official docs series: Development
- Lightflow completed the compatibility certification with "daocloud Enterprise Cloud native application cloud platform"
- Enjoy element mode (flyweight)
- Explain C language 10 in detail (C language series)
猜你喜欢
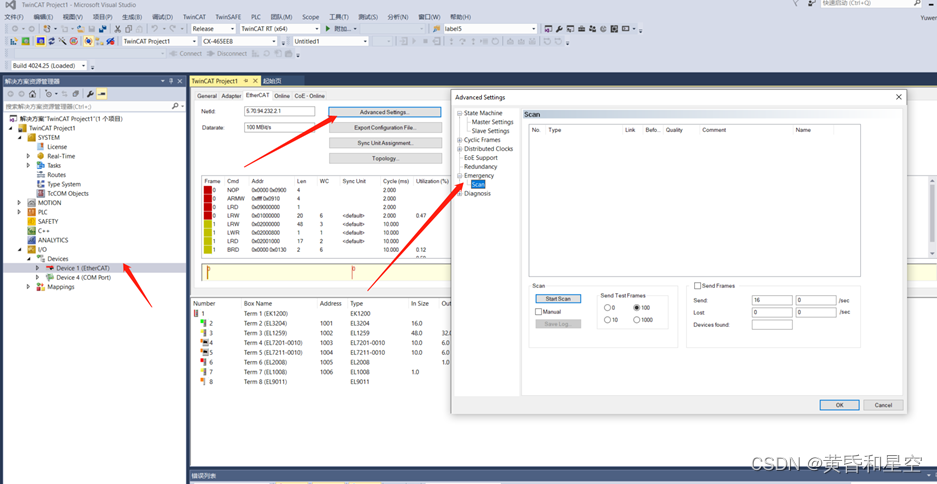
Biff TwinCAT can quickly detect the physical connection and EtherCAT network through emergency scan

别乱用 FULL_CASE 和 PARALLEL_CASE

Beifu PLC passes MC_ Readparameter read configuration parameters of NC axis

Design of four kinds of linear phase FIR filters -- complete set of Matlab source code

桥接模式(Bridge)

倍福EtherCAT Xml描述文件更新和下载

Learning Processing Zoog

Processing 多面体变化

OPLG: 新一代云原生可观测最佳实践
How does easygbs solve the abnormal use of intercom function?
随机推荐
sql 将数据表b字段值赋值到数据表a中某一列
H - Sumsets POJ 2229
C# const详解:C#常量的定义和使用
倍福TwinCAT3 NCI在NC轴界面中的基本配置和测试
OPLG: 新一代云原生可观测最佳实践
Solution of Splunk iowait alarm
Use the script to crawl the beautiful sentences of the sentence fan website and store them locally (blessed are those who like to excerpt!)
HDU1724[辛普森公式求积分]Ellipse
Dark horse notes - Common APIs
机器学习笔记 - 时间序列的季节性
Basic principle and application routine of Beifu PLC rotary cutting
C - Common Subsequence
Guacamole installation
Photoshop 2022 23.4.1增加了哪些功能?有知道的吗
倍福EtherCAT Xml描述文件更新和下载
Electron official docs series: Testing And Debugging
code force Party Lemonade
单例的常用创建和使用方式
适配器模式(Adapter)
mariadb学习笔记