当前位置:网站首页>Illustration tcp/ip - Chapter 3 and 4 notes
Illustration tcp/ip - Chapter 3 and 4 notes
2022-06-25 20:59:00 【Leap soil and tea】
3. The data link
3.1 The role of the data link
The data link layer protocol specifies the specifications for transmission between devices interconnected through information communication media . The responsibility of the physical layer :0,1 Wait for the computer binary -> Voltage level , The flash out of light and the strength of electric waves .
- TCP/IP For in the OSI The data link layer of the reference model and the following parts are not defined , because TCP/IP On the premise that the functions of these two layers are transparent
- Data link is a protocol that allows Internet computers to communicate with each other , Also means of communication .
- Involving nouns :VLAN(Virtual Local Area Network Virtual LAN ),WLAN(Wireless Local Area Network Unlimited lan ),PPP(Point to Point Protocol Point to point protocol ),FDDI(Fiber Distributed Data Interface Fiber distributed data interface ),ATM(Asynchronous Transfer Mode Asynchronous transmission mode ).
- Segments of the data link : A divided network . for example , The two network cables connected by the repeater are one network at the network layer , But on the data link layer 2 Segments , One network cable, one segment .
3.2 Data link technology
3.2.1 MAC Address
MAC Address : Used to identify interconnected nodes in a data link .
- Ethernet or FDDI Medium MAC And wireless LAN And Bluetooth, etc MAC Are different specifications ;
- Burn in ROM in , The only one in the world ;
- The length is 48 The bit
- The first 1 position : Unicast address 0 / Multicast address 1;
- The first 2 position : Global address 0 / Local address 1;
- 3-24 position : Vendor identification number (Organizationally Unique Identifier, OUI),IEEE Management ensures that the manufacturer does not repeat ;
- 25-48 position : Product identification number , It shall be managed by the manufacturer without repetition .
- That is, no matter what kind of data link network ( Ethernet ,FDDI、ATM、 wireless LAN、 Bluetooth, etc ), Not at all Have the same MAC Address
3.2.2 Shared media network
- A network in which multiple devices share a communication medium .
- Shared media , Basically, half duplex communication is adopted , Each station checks the data MAC Whether to point to yourself , If not, discard , Like radio , But there is only one copy of the data .
- There are two media access control methods in a shared media network :
- The way of contention (Contention, also called Carrier Sense Multiple Access,CSMA, Carrier monitor multiple access ): Fight for the right to obtain data transmission . First come first served basis , Conflict prone .
- CSMA/CD(Collision Detection) The way : Each station checks for conflicts in advance , Release the channel as soon as possible in case of conflict .
- If the channel has no data , Then send ;
- In case of conflict ( By monitoring whether the voltage exceeds the specified value , Over is conflict ), Give up sending data , Release channel ;
- After giving up , Wait randomly for a period of time and try again
- Token passing method (Token Ring): Data can only be sent after obtaining a token ; No conflict , Each station has the opportunity to obtain a token through an equal cycle .
- Network congestion does not affect performance , But the speed is slow when the network is not congested ;
- The way of contention (Contention, also called Carrier Sense Multiple Access,CSMA, Carrier monitor multiple access ): Fight for the right to obtain data transmission . First come first served basis , Conflict prone .
3.2.3 Non media sharing network
- Do not share media , Each station is directly connected to the switch , The switch is responsible for forwarding data frames , Full duplex communication , A one-to-one connection is formed between the computer and the switch port .
- advantage : Using switch and twisted pair ( Transceiver line ) Full duplex is possible ( Each transceiver has its own dedicated line ), No conflict , Buildable VLAN Flow control ;
- shortcoming : The switch hung up , All stations connected to the switch are connected .
- Full duplex and half duplex
- full duplex : Receive and send at the same time , It's like a phone ;
- Half duplex : Send only or accept only , It's like a walkie talkie ;
3.2.4 according to MAC Address forwarding
- Ethernet switch ( Switching hub ): Automatically record the corresponding... Of each port through the self-study process MAC Address ( According to the target of each frame in the data link layer MAC Address ) And stored in the forwarding table (Forwarding Table) in .
- The contents of this forwarding table do not need to be manually set by the user on each terminal or switch , Instead, it can be generated automatically
- host A And host B The communication between them is only between the ports to which they are connected
- When the number of equipment increases , The forwarding table becomes larger , Retrieval forwarding time extension , It is necessary to divide the network into multiple data links and adopt hierarchical management .
- Switch forwarding mode :
- Store and forward : Check FSC Forward after , It can avoid the frame destroyed by collision or the wrong frame caused by noise ;
- Direct forwarding : Instead of recording the whole frame, you only need to know the target address and forward it directly , The delay is short but the error frame cannot be checked .
3.2.5 Loop detection technology
- Avoid data frames being continuously forwarded in the loop , To avoid this cycle , You need to configure a bridge that solves circular forwarding , Make a detour , Improve disaster recovery capability .
- There are two solutions :
- Spanning tree method : Each bridge is at each 1-10s Internal exchange BPDU(Bridge Protocol Data Unit) package , So as to determine which ports are used and which are not , In order to eliminate the loop .
In case of failure , It takes tens of seconds , To solve this problem IEEE Put forward RSTP(Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol) Method . - Source routing : Determine which bridge is used to transmit the source address of data . And write RIF(Routing Information Field), according to RIF Send the frame to the destination address .
- Spanning tree method : Each bridge is at each 1-10s Internal exchange BPDU(Bridge Protocol Data Unit) package , So as to determine which ports are used and which are not , In order to eliminate the loop .
3.2.6 VLAN( Virtual LAN )
- Use a device with VLAN The bridge of Technology , There's no need to actually modify the network wiring ;
- VALN Technology attached to the bridge /2 Layer switch , You can cut off everything VALN All direct communications ;
- The switch distinguishes multiple network segments according to ports ( For heterogeneous network segments, routers are required to communicate ), Use TAG VLAN Use one for each network segment VLAN ID identification , When transmitting frames in a switch , Add this to the Ethernet header VID label , This value determines which network segment to send data frames to .
3.3 Ethernet
Connection form of Ethernet : Early morning shared media , Now the switch is exclusive ( Unshared media type ).
The classification of Ethernet :1000BASE-SX, 10BASE2 And so on . In Ethernet, the transmission speed is determined by the clock frequency .1K = 1000,1M = 1000K.
Ethernet history :
- Half duplex CSMA/CD;
- FDDI(Fiber Distributed Data Interface), Fiber distributed data interface , It is a LAN data transmission standard , It provides higher speed data communication capability than Ethernet at that time (10Mbps) And token network (4 or 16 Mbps) The ability of .
- ATM Switching technology ,CAT UTP Cable development
- Full duplex switch exclusive
Ethernet frame format :
- Lead code (preamble),“101010…” Eight bytes in total , The leading code ends with SFD(Start Frame Delimiter), Its value is “11”.
- Ethernet frame body :14 Bytes ,6 The target of the byte MAC + 6 Source of bytes MAC + 2 The upper protocol type of bytes (IP:0800,ARP:0806;RARP:8035);
- Types are usually passed along with data , Indicates the type of network protocol on the next layer of Ethernet
- data :46 To 1500 byte ;
- FCS(Frame Check Sequence, Frame detection sequence ):4 byte , Check the frame for damage , Because if there is electronic noise interference in the communication process , It will lead to the occurrence of garbled bits .
- Different versions Ethernet The first part of the agreement is different , Like with VLAN The Ethernet frame format in the switch of contains VALN Additional 4 byte : type 16bits + Priority 3bits + CFI 1bit(1 Indicates source routing )+ VALN ID 12bits
3.4 wireless communication
- Types of wireless communication
- wireless PAN(Personal Area Net): bluetooth ;
- wireless LAN:Wi-Fi;
- wireless MAN(Metropolitan):WiMAX;
- wireless RAN(Regional):
- wireless WAN:3G,4G.
- IEEE802.11 Defines wireless LAN Part of the physical layer and data link layer in the protocol (MAC layer ), Means wireless LAN A means of communication
- Media access control uses CSAM/CD Allied CSAM/CA(Collision Avoidance), The wireless base station is adopted and the communication is realized through the high base station .
- The physical layer adopts electromagnetic wave or infrared ray
- Different physical layers have different applicable frequency bands :2.4GHz and 5GHz Two kinds of .
3.5 PPP(Point-to-Point Protocol)
PPP The protocol is a pure data link layer protocol , It has nothing to do with the physical layer . Ethernet uses coaxial cable and twisted pair cable , It can decide 0,1 What kind of electronic signal should be interpreted . Use PPPoE(PPP over Ethernet) perhaps ASDL Access to the Internet
LCP(Link Control Protocol) and NCP(Network Control Protocol)
- LCP, Not dependent on the top , Mainly responsible for establishing and disconnecting , Set the maximum receiving unit (MRU, Maximum Receive Unit), Set the user authentication protocol (PAP,Password Authentication Protocol or CHAP, Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol) And whether the communication quality is monitored .
- NCP, Rely on the top , The upper level is IP When is IPCP, be responsible for IP Address setting and whether to TCP/IP First compression ;
- PAP Second handshake for user name and password verification , Password plaintext propagation ,CHAP Use a one-time password , Prevent listening .
PPP Protocol frame format : And HDLC(High Level Data Link Protocol) The agreement is similar to , The first is “01111110”, All middle bytes cannot be consecutive 6 More than one 1, Continuous... Occurs when sending 5 individual 1 You must add one 0, Continuous... Occurs when receiving 5 individual 1 And followed by 0 Must delete .
PPPoE: Pure Ethernet has no verification function , You cannot charge by time without setting up and disconnecting processing . use PPPoE You can use PPP The verification function of makes ISP Effective management of terminal clients .
PPPoE Data frame : Ethernet 14 byte + PPPoE 6 byte + PPP 2 byte + data + FCS;
3.6 Other data links
1.ATM:
- ATM It is a connection oriented data link . Similar telephone , But you can establish connections with multiple opposite ends ;
- ATM No Ethernet FDDI Send limit for , When the data is large, it will cause network congestion and even the network will enter the convergence state ( It's too crowded , The router or switch is unable to complete packet processing , So the packet is lost ). To prevent this ,ATM Bandwidth restriction rules are added to .
- Synchronous and asynchronous ,TDM For synchronous transmission , There will be many free time slots , Low utilization ;ATM stay TDM Insert data into the gap of , Add... For identification sequence VPI(Virtual Path Identifier) And VCI(Virtual Channel Identifier) Etc ;
- Syncing ABCD Each has its own transmission time slot . Even if there is no data to send , It will also occupy time slots , Or you have to send empty data .
- In asynchrony, the destination address is specified in the packet header , Therefore, data is sent only when necessary .
- ATM Agreement with the upper layer : In general use AAL(ATM Adapter Layer), The upper level is IP When is AAL5, take IP TCP The first part is encapsulated in AAL5 Divided into 192 A cell (48 byte ) send out , Lost an entire send failure . adopt AAL5 Tail verification information integrity .
2.POS(Packet over SDH/SONET It's a kind of SDH A protocol for packet communication on .SDH Is the physical layer specification for digital signal transmission over optical fiber .
3.FDDI It is called distributed ray data interface , Use token ring (Token Ring), It is easy for the network to converge when the traffic is large
3.7 The public network
1. Analog phone lines : Analog telephone lines are dial-up Internet access using the audio bandwidth of telephone lines , A modem is required to connect the computer to the telephone line “ cat ” Convert digital signals into analog signals .·
2.ADSL: An extension of analog telephone lines . Use the high-speed line between the telephone set and the exchange of the Telecommunications Bureau , Attach a separator , Turn the audio signal on ( Low frequency ) And digital signals ( high frequency ) Isolate to avoid noise interference , The digital signal enters the digital line , The audio signal enters the audio line .
3.FTTH(Fiber to the Home): Use ONU(Optical Network Unit) Connect the computer to an optical fiber , Be responsible for the conversion between optical signals and electronic signals
4.VPN: It is used to connect remote areas
IP-VPN:IP-VPN Is in IP The connection of layers
- Use MPLS(Multiprotocol Label Switching) technology stay IP The packet is attached with a message called a tag for transmission control , For each user MPLS Different labels , Through MPLS Network time can easily determine the target address , In this way, multiple different users' VPN Information through MPLS Net , Form a closed private network , User level bandwidth control is also available .
- IPsec Technical right IP Package for authentication and encryption , Build a closed private network on the Internet . Use IPsec Technology can be connected to the company's intranet from the outside .
Wide area Ethernet : Use on Ethernet VLAN Realization VPN.
5. Public wireless LAN:Wi-Fi,HotSpot
IP(Internet Protocol) agreement
4.1 IP Internet protocol
- TCP/IP The heart of the Internet layer . This floor is mainly composed of IP and ICMP(Internet Control Message Protocol) form .
- The core role of the network layer : Realize point-to-point data packet transmission across different data link layers . The data link layer can only transfer packets between nodes of the same data link .
host : Equipped with IP Address , But the device that does not perform route control ;
Router : That is to say IP Device with address and routing control capability .
The relationship between network layer and data link layer :
- The data link layer is responsible for the communication between two directly connected devices ;
- The network layer is responsible for the communication between two devices that are not directly connected ;
- For example, there is a place of departure on the itinerary ( The sender IP) And destination ( The receiver IP), It takes a train , The plane , And buses ( Data link layer ) To get to
4.2 IP Basic knowledge of
- Three modules :IP Addressing , route ,IP Subcontracting and subcontracting ;
4.2.1 IP Address belongs to network layer address
- IP Address is used to identify the target address for communication among all hosts connected to the network ,TCP/IP All hosts or routers in communication must set their own IP Address .
- The physical layer or data link layer, such as the bridge or switching hub, is forwarding packets , Unwanted IP Address .
4.2.2 Route control (Routing): Send the packet data to the final destination address .
- Hop:IP Packets are forwarded in a hop of the network ,IP Routing is also called multi hop routing , Each interval determines the path of the packet to be forwarded in the next hop .
- a jump : A section of a data frame that utilizes the layered function below the dlink layer ;
- IP It is equivalent to purchasing the next one marked at each transfer MAC The address of the ticket .
- Routing control table (Routing Table): Record IP Which router should the data be sent to in the next step .
4.2.3 Abstraction of data link
- IP The upper layer protocol does not care what the data link layer protocol is , Therefore, the address of the data link can be abstracted as IP Address .
- The difference between different data link layers lies in , Maximum transmission unit (Maximum Transmission Unit) Different (Ethernet 1500 byte ,FDDI 4352 byte , ATM 9180 byte ).
- IP Shard processing (IP Fragmentation) Handle , To omit by subcontracting MTU The difference of , Thus abstracting the data link layer , The upper layer protocol cannot see the details of the network structure .
4.2.4 IP It's connectionless
- Simple and high speed , It can be handed over to the upper layer when there is a connection (TCP) Handle ;
- The host needs to monitor the network , Accept the package sent to you ;
- There will be a lot of redundant communication .
- TCP And IP The division of labor makes it easier for each layer to focus on one task
- IP Only responsible for sending data to the target host , that TCP Is responsible for ensuring that the opposite host does receive data .
4.3 IP Address Basics
4.3.1 IP The definition of address
IP Address by 32 Bit positive integers represent .IP The address is processed in binary form inside the computer . Single class cannot be recognized, so decimal and “.” Separated representation .
- One host or one network card can have 1 More than one IP, A router can have 2 More than one IP.
4.3.2 IP The address consists of two parts: network and host .
- The network ID must ensure that the addresses of each segment connected to each other are not duplicated ;
- The host identification must ensure that each host in the same segment does not repeat ;
- The router forwards through the network ID ;
- The subnet mask is used to distinguish the network ID from the host ID
4.3.3 IP Classification of addresses
- A class : The first is 0 Of IP Address ,0.0.0.0 - 127.0.0.0.1 To 8 Bit is the network ID ,9 To 32 Bit is the host identification , The maximum number of hosts in a network segment 16777214 individual ;
- B class : The first is 10 Of IP Address ,128.0.0.1 - 191.255.0.0. 1 To 16 Bit is the network ID ,17-32 Bit is the host identification , The maximum number of hosts in a network segment 65534 individual ;
- C class : front 3 Position as 110 Of IP Address ,192.168.0.0 - 239.255.255.0. 1 To 24 Bit is the network identifier ,25-32 Is the host id , The upper limit of network segment hosts is 254( Remove all for 0 And all are 1) individual ;
- D class : front 4 position 1110 Of IP Address .224.0.0.0 - 239.255.255.255, No host id , For multicast .
- special : The host ID cannot all be 0 or 1, All for 0 yes IP Use when the address is not available , All for 1 It's a broadcast address .
Broadcast address :172.20.0.0/16(B class ) The broadcast address of is 172.20.255.255
- Local radio : Broadcast in this network . such as 192.168.0.0/24 Under the circumstances , The address is 192.168.0.255.
- Direct broadcast : Broadcasting between different networks .192.168.0.0/24 Sent by the host 192.168.1.255/24 Your broadcast will be forwarded to 192.168.1.1 To 192.168.1.254 All hosts of .
4.3.5 IP multicast
- Multicast is used to send packets to all hosts in a particular group . Need to be able to penetrate the router , And it can only send data packets to specific hosts .
- Multicast use D Class address , after 28 Bit is the multicast group number .224.0.0.0 To 239.255.255.255 Is the available range , among 224.0.0.0 To 224.0.0.255 The scope of does not require routing control . Setting a multicast address outside this range will send multicast packets to all members of the group in the whole network .
- In addition to the address, you also need IGMP(Internet Group Management Protocol) Protocol and other support .
4.3.6 Subnet mask
- Subnet mask : An identification code that subdivides network addresses into ratios A,B,C A more granular network like a network , take A,B,C The address is used as the subnet address , Cut into multiple sub physical networks . Avoid waste caused by direct use of classified addresses ;
- The subnet mask is the same as IP Same as 32 position , The corresponding network identification bit is 1, The host identification bit is 0, This represents the length of the network . For example, the length of the network ID is 26 The subnet mask of is 255.255.255.192, Another expression is IP Add... After the address /26
- The subnet mask can flexibly specify the length of the network id
4.3.7 CIDR(Classless Inter-Domain Routing) And VLSM(Variable Length Subnet Mask)
- CIDR: because A,B Class address is seriously insufficient ,C Class address capacity is too small ,CIDR Will be continuous C Class addresses are merged into one network , Increased the maximum number of hosts ;
- VLSM: The mechanism for modifying the subnet mask length of each department within the organization , Dynamically divide the number of hosts .
4.3.8 Global address and private address
- Private network IP Address :A class (10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255);B class (172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255);C class (192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255).
- Global network IP Address : Except private IP An address other than .
- School , Companies and other organizations use private terminals IP, Use global... On servers or routers IP. Use NAT Technology conversion IP The address can be private IP Connected to the Internet ;
- overall situation IP The address is unique , private IP Only unique within the domain .
4.3.9 Who decides the global address
- ICANN(Internet Corporation For Assigned Names and Numbers) Conduct management ;
- about FTTH and ASDL service ,ISP Be responsible for dynamic allocation to users IP Address , Users are not required to apply for global IP;
- ICMP,traceroute Generally used for network diagnosis ,whois Command query ip The manager information corresponding to the address .
4.4 Route control
Routing control table (Routing Table): Indicate the router or host that should be sent to .
- Static routing control : Administrator settings ;
- Dynamic routing control : Self study function ;
- IP The protocol always thinks that the routing table is correct , The routing table consists of “ Routing protocol ” Made of .
4.4.1 IP Address and routing control
- The routing control table records the network address and the address that should be sent to the router next . Take out IP It's the first one IP Address , Find out and IP Address of the network address The same record , Forward to the corresponding router ;
- If there are multiple records with the same network address , Choose the most appropriate network address ( The maximum number of the same digits is );
- If the location of the next router in the routing table records the location of a host or router network card IP Address , It indicates that the destination address of the transmission belongs to the same link .
Special routing :
- Default route : A record that can match any address in the routing table ,0.0.0.0/0 or default, Note that this is not IP Address .
- Host routing :IP Address /32, The corresponding subnet mask is 255.255.255.255, be called Host Route, It means the whole IP All addresses should participate in the routing, not the network address part .
- Loopback address :localhost,127.0.0.1, Used for network communication between programs on the same computer , Use the address , Packets do not flow back to the network .
4.4.2 Aggregation of routing control tables
- The larger the routing table , Memory CPU The more consumption , The more time it takes to find the routing table , Forwarding performance is degraded ;
- Routing information aggregation can significantly reduce the number of routing table entries ; for example :192.168.2.0/24 -> B, 192.168.3.0/24 -> B Can be combined into 192.168.2.0/23 -> B, Reduce the subnet mask by one bit to expand the selection range .
4.5 IP Segmentation processing and reconstitution processing
1. Data links are different ,MTU Different ;IP Of MTU The scope is 68 - 65535.
2.IP Fragmentation (IP Fragmentation): Fragmentation will be processed only when the network encounters a relatively large message that cannot be sent out at once . The router performs fragmentation ( With 8 A multiple of a byte ), Reorganized by the target host .
- for example :A - FDDI(4352)- Router - Ethernet(1500)- B On the Internet , host A Sent out a 4324 A bag the size of B, When a packet passes through a router, it is split into 1472,1480,1372 Of 3 Share , And pass Ethernet Send to B,B according to IP The first identification code is recombined . If a fragment is lost, the whole packet will be invalidated .
3. route MTU Discovery technology (Path MTU Discovery):
- Implemented by the operating system , Reduce the burden on routers .
- Path MTU: from A To B It is not necessary to divide into pieces MTU, That is, the smallest in the path MTU( Network flow algorithm ), Then, the sending host follows the Path MTU Send after slicing , So as to avoid fragmentation on the router and reduce the burden on the router .
- UDP(User Datagram) Implementation process in case of :
- For the first time, it is not divided into pieces ,IP The slice prohibition flag of the first part of the packet is set to 1;
- Routers lose packets without fragmentation , And return a ICMP Unreachable messages will send messages on the data link MTU Send to host ;
- according to MTU Slice and resend , If no new ICMP That is, the last time MTU For appropriate MTU value .
- TCP Under the agreement ,TCP Will be based on MTU To calculate the MSS Maximum segment length , According to MSS Send datagram .IP Layers do not participate in slicing .
4.6 IPv6
1.IPv6 The necessity of :IPv6 Is to fundamentally solve IPv4 The problem of address exhaustion ;
2.IPv6 Characteristics :
- IP Address expansion and routing control table aggregation :IP Addresses adapt to the hierarchical structure of the Internet , Allocate appropriate IP Address , Avoid route table expansion ;
- Performance improvement : The length of the package head is fixed (40 byte ), Do not use the first inspection code , Simplify the head structure , Reduce the routing burden , The router does not partition ;
- Support for plug and play
- Using authentication and encryption functions : prevent IP forge , Prevent wiretapping (IPsec)
- multicast ,Mobile IP
3.IPv6 Address notation :
- The length is 128 position , Every time 16 Bit use : separate , And continuous 0 You can use two : separate , Only one address can appear ::.
- for example : 1080:0:8:800:200C:417A It can be written. 1080::8:800:200C:417A
4.IPv6 The structure of the address :
Global unicast address : Unicast communication between different networks ( other );
- Format :48 Bit wide area network + 16 Bit site internal + 64 Bit host id (64 Bit version MAC Address or relevant random temporary address )
The only local address : Unicast communication between different network segments (1111 110);
- Format : 7 The bit 1111 110 + 1 The bit L( Usually it is 1)+ 40 Bit global ID( Random decision ) + 16 Bit subnet ID + 64 Bit interface ID
5. Link local unicast address : Unicast communication between the same network segment (1111 1110 10);
- Format :10 The bit 1111 1110 10 + 54 The bit 0 + 64 Bit interface ID(64 Bit version MAC)
Multicast address :1111 1111;
Loopback address :::1/ 128;
Undefined :::/128;
6.IPv6 Handle in sections :IPv6 Sharding is only carried out at the sending end , The router does not partition , So the path MTU Discovery is essential .IPv6 Minimum MTU by 1280, For embedded systems, it is directly set to 1280 that will do .
4.7 IPv4 The first one
edition :4 The bit ,IPv4 = 4, IPv6 = 6;
The length of the first (IHL: Internet Header Length):4 The bit ,IP Head size , When there is no option, it is 5;
Distinguish between service (TOS,Type of Service): Surface service quality , Priority , Minimum delay , Maximum throughput, etc , But the implementation is too complex to be used ; Divided into DSCP and ECN paragraph :
- DSCP(Differential Services Codepoint): The quality control , Priority, etc ;
- ECN(Explicit Congestion Notification): Report network congestion = The first 6 position ECT(ECN-Capable Transport)+ The first 7 position CE(Congestion Experienced);ECT Give the upper layer agreement TCP Report whether to handle ECN,CE Indicates whether there is congestion , Appears as 1.
Total length :16 The bit , therefore IP The maximum package size is 65535 byte ;
identification (ID):16 The bit , For fragment recombination , Self increasing . Even if ID Same source IP And target IP Different words are not the same piece ;
sign (Flags):3 The bit ,0 = Whether to use ;1 = Whether it is divided into pieces or not ;2 = Whether the partition is the last package ;
Slice offset (Fragment Offset):13 The bit , Represents the position of each segment relative to the original data ;
Time to live (TTL,Time To Live):8 The bit , It actually indicates how many routes can be transferred , Without a reduction 1, by 0 Packet loss at ;
agreement (Protocol):8 The bit , Express IP Which agreement does the next header belong to .
Head check sum (Header Checksum):16 The bit , Verify only the header , Make sure IP The packets are not destroyed .
source address (Source Address):32 The bit ;
Destination address (Destination Address):32 The bit ;
optional : Variable length , Experimental or diagnostic use ;
fill (Padding): The first one is not 32 Integer multiples of bits 0;
4.8 IPv6 The first one
- In order to reduce the burden of routers, the first checksum is omitted ( because TCP and UDP There is a data integrity verification mechanism in , You can rely on the upper layer protocol to complete the verification mechanism ), Therefore, the router does not need to calculate the first checksum , Improve packet forwarding efficiency ;
- To cooperate with 64 Bit computer processing ,IPv6 The first parts of all are 8 Byte formation ;
- edition : IPv6 = 6;
- Traffic class (Traffic Class): amount to TOS;
- Stream label (Flow Label):20 The bit , Prepare for quality of service , Set to... When not in use 0; Only in stream labels , source address , A stream is considered only when the destination addresses are consistent ;
- Payload length (Payload Length): Expand the header plus all the lengths of the data ;
- Next first (Next Header): Indicates the next header , Can expand the first , Or the upper layer agreement ;
- Jump limit (Hop Limit): amount to IPv4 Of TTL;
- Source address and destination address ;
- Expand the first :IPv6 The length of the head is fixed , Cannot add optional , Use extended header , Put it in IPv6 The first and TCP/UDP Between the first one , You can set Next Header To expand the first part, the expansion function is introduced : Load encryption , First certification ,IPv6 Slicing and other functions .
边栏推荐
- very good
- [golang] leetcode intermediate - the kth largest element in the array &
- Leetcode daily [2022 - 02 - 17]
- How can the intelligent transformation path of manufacturing enterprises be broken due to talent shortage and high cost?
- Illustrated with pictures and texts, 700 pages of machine learning notes are popular! Worth learning
- Feature Engineering in simple terms – a practice guide based on openmldb (Part 1)
- 2022 oceanbase technical essay contest officially opened | come and release your force
- Desktop network error display red ×, Component failed to start
- Compile 6relayd using the cross compiler
- OLED driven learning based on ssd1306 (II): addressing mode of ssd1306
猜你喜欢
MySQL lock

Sqlmap for interface security testing
Yunzhisheng atlas supercomputing platform: computing acceleration practice based on fluid + alluxio (Part 2)

PIP command -fatal error in launcher: unable to create process using How to resolve the error after migrating the virtual environment?
MySQL installation tutorial
Detailed explanation of unified monitoring function of multi cloud virtual machine

Molecular dynamics - basic characteristics of molecular force field
This is a simple and cool way to make large screen chart linkage. Smartbi will teach you

Install JDK, MySQL and nexus under Linux (tar package installation)
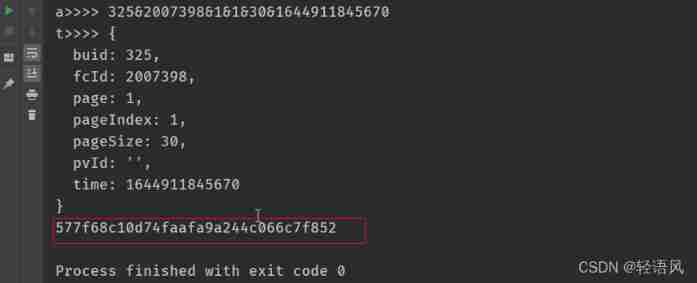
Jingxi Pinpin wechat applet -signstr parameter encryption
随机推荐
R language momentum and Markowitz portfolio model implementation
Splunk series: Splunk data import (II)
How can the intelligent transformation path of manufacturing enterprises be broken due to talent shortage and high cost?
[distributed system design profile (1)] raft
Vbpr (visual Bayesian personalized ranking) paper summary
[machine learning] machine learning from zero to mastery -- teaching you how to use decision tree to predict contact lens types
Several ways to obtain domain administrator privileges
Idea implements hot deployment
[phase 23] phased summary of spring recruitment practice (Alibaba cloud has OC)
Analysis and cleaning of kdevtmpfsi virus content
[opencv] opencv from introduction to mastery -- detailed explanation of input and output XML and yaml files
Desktop network error display red ×, Component failed to start
Causes and solutions of unreliable JS timer execution
A new paradigm for large model application: unified feature representation optimization (UFO)
Paddledtx v1.0 has been released, and its security and flexibility have been comprehensively improved!
Decipher the AI black technology behind sports: figure skating action recognition, multi-mode video classification and wonderful clip editing
Molecular dynamics - basic characteristics of molecular force field
How does jest expose specific problems in complex judgment conditions?
"Space guard soldier" based on propeller -- geosynchronous geostationary orbit space target detection system
Redis common principles interview




