当前位置:网站首页>Basic OJ exercise of binary tree-
Basic OJ exercise of binary tree-
2022-07-23 12:38:00 【Diving boy requests to fight】
Binary tree
According to the rules , The traversal of binary tree has : Before the order / Middle preface / The recursive structure of post order traverses :
The former sequence traversal (Preorder Traversal Also called preorder traversal )—— The operation of accessing the root node occurs before traversing its left and right subtrees .
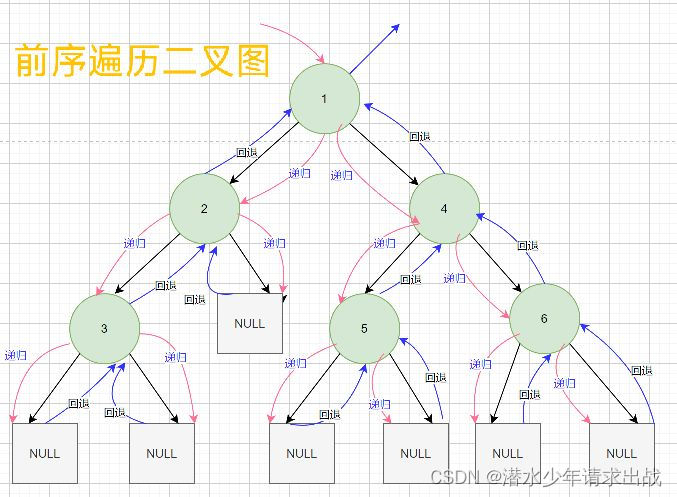
Preface 、 Middle order and post order traversal are similar
Preorder traversal results :1 2 3 4 5 6
Middle order traversal result :3 2 1 5 4 6
Subsequent traversal results :3 1 5 6 4 1In the sequence traversal (Inorder Traversal)—— The operation of accessing the root node occurs in traversing its left and right subtrees ( between ).
After the sequence traversal (Postorder Traversal)—— The operation to access the root node occurs after traversing its left and right subtrees .
Topic link
1. link : Single valued binary trees
2. link : Same tree
3. link : Symmetric binary tree
4. link : Preorder traversal of two tree
5. link : Middle order traversal of binary trees
6. link : Postorder traversal of binary trees
Their thinking :
1. Traversing the binary tree , And each node value is compared with the value of the root node , If it is not equal to the value of the root node , Is not a single valued tree .
2. Traversing the binary tree , And the value of a tree node is compared with that of another book , If it is not equal to the value of the root node , It's not the same tree .
3. First divide into two trees , Traversing the binary tree , And the value of a tree node is compared with that of another book , If it is not equal to the value of the root node , It's not the same tree , That is, it is not a symmetric tree .
Code :
1. Single valued tree
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
bool BTd(struct TreeNode* root, int x)
{
if(root==NULL)
return true;
if(root->val != x)
return false;
return BTd(root->left, x) && BTd(root->right, x);
}
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return true;
int a = root->val;
return BTd(root, a);
}
2. Same tree
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q)
{
if(p==NULL && q==NULL)
return true;
if(p==NULL || q==NULL)
return false;
if(p->val != q->val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left, q->left) && isSameTree(p->right, q->right);
}
3. Symmetric tree
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q)
{
if(p==NULL && q==NULL)
return true;
if(p==NULL || q==NULL)
return false;
if(p->val != q->val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left, q->right) && isSameTree(p->right, q->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return true;
struct TreeNode* p=root->left;
struct TreeNode* q=root->right;
return isSameTree(p, q);
}
4. Preorder traversal of two tree
remind : We need to send the address of the subscript of the array , In this way, you can ensure that you use one when recursing i,( for example ; The left and right nodes of the root , After the left node is used up i Self increment , Will not affect the right node i.)
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
/** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */
int BTSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
return 1+BTSize(root->left)+BTSize(root->right);
}
void preorder(struct TreeNode* root, int* a, int* pi)
{
if(root==NULL)
return;
a[(*pi)++]=root->val;
preorder(root->left, a, pi);
preorder(root->right, a, pi);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize = BTSize(root);
int* a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize * 4);
if(a==NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
int i=0;
preorder(root, a, &i);
return a;
}
5 Middle order traversal of binary trees
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
/** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */
int BTSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
return 1+BTSize(root->left)+BTSize(root->right);
}
void inorder(struct TreeNode* root, int* a, int* pi)
{
if(root==NULL)
return;
inorder(root->left, a, pi);
a[(*pi)++]=root->val;
inorder(root->right, a, pi);
}
int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize=BTSize(root);
int* a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize * 4);
if(a==NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
int i=0;
inorder(root, a, &i);
return a;
}
6. Postorder traversal of binary trees
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
/** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */
int BTSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return root==NULL?0:1+BTSize(root->left)+BTSize(root->right);
}
void postorder(struct TreeNode* root, int* a, int* pi)
{
if(root==NULL)
return;
postorder(root->left, a, pi);
postorder(root->right, a, pi);
a[(*pi)++]=root->val;
}
int* postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize=BTSize(root);
int* a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize * 4);
if(a==NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail");
}
int i=0;
postorder(root, a, &i);
return a;
}
Feel the watching of friends .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
![[AUTOSAR candrive 1. learn the function and structure of candrive]](/img/f6/662512bddab70e75367d212029fc23.png)
[AUTOSAR candrive 1. learn the function and structure of candrive]

Data mining scenario - false invoice

二叉树基础oj练习-
输入三角形边长,求面积
Object based - two classic classes

Baidu Shen Shuo: focus on the scene, deeply cultivate the industry, and bring practical results to enterprise Digitalization
C语言小项目——学生成绩管理系统

匿名上位机v7波形显示

Enter the triangle side length and calculate the area

常见的排序—交换排序
随机推荐
AWK 程序设计语言
K-nucleotide frequencies (KNF) or k-mer frequencies
嵌入式从入门到精通(入土)——超详细知识点分享2
高分子合成工艺学复习考题
[introduction to AUTOSAR com 4.com service layer module]
鋼結構基本原理複習
Summary of video coding and decoding related data
【AUTOSAR COM 1.通信协议栈介绍】
Interpretation of the paper: develop and verify the deep learning system to classify the etiology of macular hole and predict the anatomical results
Blog building 4: how to add your blog to Baidu and Google
解决谷歌chrome浏览器双击没反应,不能启动(亲测好用)
3.2daydayup draw inferences from one instance: three days of fishing and two days of net learning
输入三角形边长,求面积
The CUDA version of pytorch installed by anconda is inconsistent with the CUDA version of the system
【Autosar CP通用 1.如何阅读Autosar官方文档】
(1)ASIO
Review of basic principles of steel structure
Object based - two classic classes
Uni native plug-in development -- Youmeng one click login
[AUTOSAR com 3. signal sending and receiving process tx/rx]