当前位置:网站首页>Tensorrt Paser loading onnx inference use
Tensorrt Paser loading onnx inference use
2022-06-23 16:39:00 【loong_ XL】
Reference resources :
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42357472/article/details/125333979
Be careful :paser Refer to trt.OnnxParser Load conversion
1、 Environmental Science
The environment is still used docker, Reference resources
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42357472/article/details/125333979
docker pull nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:22.05-py3
## function
docker run --gpus all -it -d --rm nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:22.05-py3
1) here tensorrt The version is 8.0 above , Will report a mistake AttributeError: ‘tensorrt.tensorrt.Builder’ object has no attribute ‘max_workspace_size’
Then comment out these lines directly
#builder.max_workspace_size = 1 << 60 # ICudaEngine Execution time GPU The most needed space
#builder.max_batch_size = max_batch_size
#builder.fp16_mode = fp16_mode
#config.max_workspace_size = 1 << 30 # 1G
2) No, pycuda The package needs to be installed
pip install pycuda
2、TensorRT Paser Use
Reference resources :https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42357472/article/details/124100236
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44533869/article/details/125223704
1)pytorch turn onnx
import onnx
import torch
import torchvision
# 1. Defining models
model = torchvision.models.resnet50(pretrained=True).cuda()
# 2. Define input & Output
input_names = ['input']
output_names = ['output']
image = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224).cuda()
# 3.pt turn onnx
onnx_file = "./resnet50.onnx"
torch.onnx.export(model, image, onnx_file, verbose=False,
input_names=input_names, output_names=output_names,
opset_version=11,
dynamic_axes={"input":{0: "batch_size"}, "output":{0: "batch_size"},})
# 4. Check onnx Calculation chart
net = onnx.load("./resnet50.onnx")
onnx.checker.check_model(net) # Check whether the file model is correct
# 5. Before and after optimization & verification
# Before optimization
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
output1 = model(image)
2)onnx turn trt
# coding utf-8
import os
import time
import torch
import torchvision
import numpy as np
import pycuda.autoinit
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import tensorrt as trt
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = '0'
TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.VERBOSE)
class HostDeviceMem(object):
def __init__(self, host_mem, device_mem):
"""
host_mem: cpu memory
device_mem: gpu memory
"""
self.host = host_mem
self.device = device_mem
def __str__(self):
return "Host:\n" + str(self.host) + "\nDevice:\n" + str(self.device)
def __repr__(self):
return self.__str__()
def build_engine(onnx_file_path, engine_file_path, max_batch_size=1, fp16_mode=False, save_engine=False):
"""
Args:
max_batch_size: Specify the size in advance to allocate the video memory
fp16_mode: Whether to adopt FP16
save_engine: Whether to save the engine
return:
ICudaEngine
"""
if os.path.exists(engine_file_path):
print("Reading engine from file: {}".format(engine_file_path))
with open(engine_file_path, 'rb') as f, trt.Runtime(TRT_LOGGER) as runtime:
return runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read()) # Deserialization
# In case of dynamic input , You need to explicitly specify EXPLICIT_BATCH
EXPLICIT_BATCH = 1 << (int)(trt.NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag.EXPLICIT_BATCH)
# builder Create a calculation chart INetworkDefinition
with trt.Builder(TRT_LOGGER) as builder, builder.create_network(EXPLICIT_BATCH) as network, builder.create_builder_config() as config, trt.OnnxParser(network, TRT_LOGGER) as parser: # Use onnx Parser binding calculation diagram
# Dynamic input profile Optimize
profile = builder.create_optimization_profile()
profile.set_shape("input", (1, 3, 224, 224), (8, 3, 224, 224), (8, 3, 224, 224))
config.add_optimization_profile(profile)
# analysis onnx file , Fill in the calculation diagram
if not os.path.exists(onnx_file_path):
quit("ONNX file {} not found!".format(onnx_file_path))
print('loading onnx file from path {} ...'.format(onnx_file_path))
with open(onnx_file_path, 'rb') as model:
print("Begining onnx file parsing")
if not parser.parse(model.read()): # analysis onnx file
print('ERROR: Failed to parse the ONNX file.')
for error in range(parser.num_errors):
print(parser.get_error(error)) # Print parsing error log
return None
last_layer = network.get_layer(network.num_layers - 1)
# Check if last layer recognizes it's output
if not last_layer.get_output(0):
# If not, then mark the output using TensorRT API
network.mark_output(last_layer.get_output(0))
print("Completed parsing of onnx file")
# Use builder establish CudaEngine
print("Building an engine from file{}' this may take a while...".format(onnx_file_path))
# engine=builder.build_cuda_engine(network) # Non dynamic input uses
engine = builder.build_engine(network, config) # Dynamic input uses
print("Completed creating Engine")
if save_engine:
with open(engine_file_path, 'wb') as f:
f.write(engine.serialize())
return engine
def allocate_buffers(engine):
inputs, outputs, bindings = [], [], []
stream = cuda.Stream()
for binding in engine:
size = trt.volume(engine.get_binding_shape(binding)) * engine.max_batch_size # Non dynamic input
# size = trt.volume(engine.get_binding_shape(binding)) # Dynamic input
size = abs(size) # What we got above size(0) It could be negative , It can lead to OOM
dtype = trt.nptype(engine.get_binding_dtype(binding))
host_mem = cuda.pagelocked_empty(size, dtype) # Create lock memory
device_mem = cuda.mem_alloc(host_mem.nbytes) # cuda Allocate space
bindings.append(int(device_mem)) # binding Buffer address in the calculation diagram
if engine.binding_is_input(binding):
inputs.append(HostDeviceMem(host_mem, device_mem))
else:
outputs.append(HostDeviceMem(host_mem, device_mem))
return inputs, outputs, bindings, stream
def inference(context, bindings, inputs, outputs, stream, batch_size=1):
# Transfer data from CPU to the GPU.
[cuda.memcpy_htod_async(inp.device, inp.host, stream) for inp in inputs]
# Run inference.
# If you create network It explicitly specifies batchsize, Use execute_async_v2, Otherwise use execute_async
context.execute_async_v2(bindings=bindings, stream_handle=stream.handle)
# Transfer predictions back from the GPU.
[cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(out.host, out.device, stream) for out in outputs]
# gpu to cpu
# Synchronize the stream
stream.synchronize()
# Return only the host outputs.
return [out.host for out in outputs]
def postprocess_the_outputs(h_outputs, shape_of_output):
h_outputs = h_outputs.reshape(*shape_of_output)
return h_outputs
if __name__ == '__main__':
onnx_file_path = "resnet50.onnx"
fp16_mode = False
max_batch_size = 1
trt_engine_path = "resnet50.trt"
# 1. establish cudaEngine
engine = build_engine(onnx_file_path, trt_engine_path, max_batch_size, fp16_mode)
# 2. Apply the engine to different GPU Configure the execution environment on
context = engine.create_execution_context()
inputs, outputs, bindings, stream = allocate_buffers(engine)
# 3. Reasoning
output_shape = (max_batch_size, 1000)
dummy_input = np.ones([1, 3, 224, 224], dtype=np.float32)
inputs[0].host = dummy_input.reshape(-1)
# In case of dynamic input , The following settings are required
context.set_binding_shape(0, dummy_input.shape)
t1 = time.time()
trt_outputs = inference(context, bindings=bindings, inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, stream=stream)
t2 = time.time()
# because tensorrt The output is a one-dimensional vector , need reshape To the specified size
feat = postprocess_the_outputs(trt_outputs[0], output_shape)
***docker In the container ipython Testing in the environment 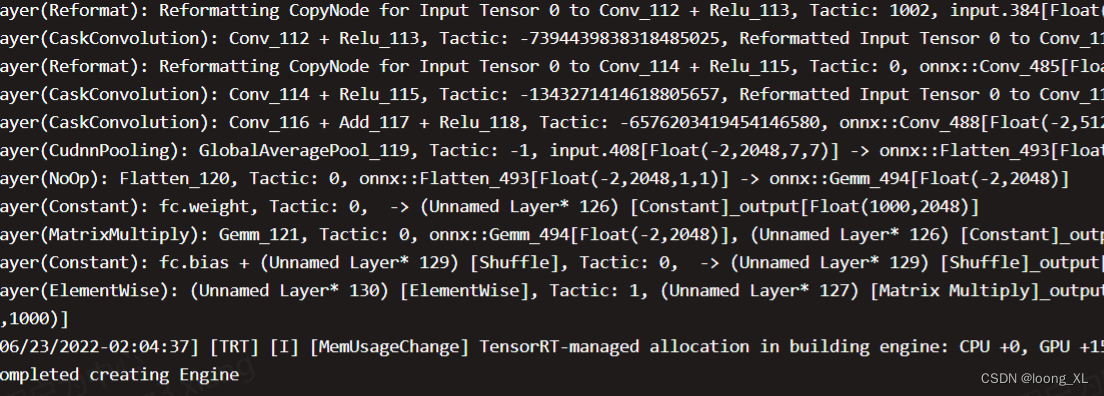

# 4. Speed comparison
model = torchvision.models.resnet50(pretrained=True).cuda()
model = model.eval()
dummy_input = torch.zeros((1, 3, 224, 224), dtype=torch.float32).cuda()
t3 = time.time()
feat_2 = model(dummy_input)
t4 = time.time()
feat_2 = feat_2.cpu().data.numpy()
mse = np.mean((feat - feat_2) ** 2)
print("TensorRT engine time cost: {}".format(t2 - t1))
print("PyTorch model time cost: {}".format(t4 - t3))
print('MSE Error = {}'.format(mse))
边栏推荐
- 亚朵更新招股书:继续推进纳斯达克上市,已提前“套现”2060万元
- Pytorch: saving and exporting models
- Can the hbuilderx light theme be annotated?
- 图扑软件以轻量化建模构建智慧城市
- openGauss数据库源码解析系列文章—— 密态等值查询技术详解(下)
- 电感参数有哪些?怎么选择电感?
- R语言ggplot2可视化水平箱图(Horizontal boxplot with coord_flip)、并添加抖动数据点显示分布情况(jittered points)
- Golang write file code example
- JS common error reporting and exception capture
- Image saving: torchvision utils. save_ image(img, imgPath)
猜你喜欢

Safe and comfortable, a new generation of Qijun carefully interprets the love of the old father

get_ edges
聚焦:ZK-SNARK 技术
![Generating binary search balanced tree [using tree recursion]](/img/b3/f8edf45bdfdced7c3698088dbf7d84.png)
Generating binary search balanced tree [using tree recursion]
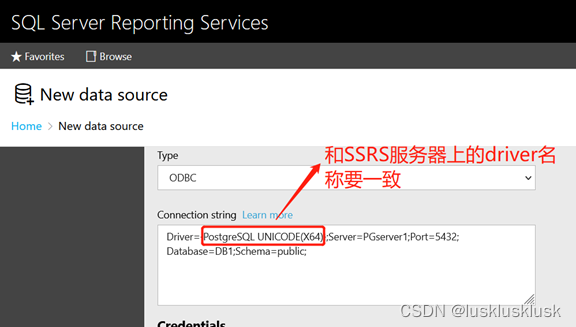
How to configure PostgreSQL data source on SSRs page

stylegan2:analyzing and improving the image quality of stylegan
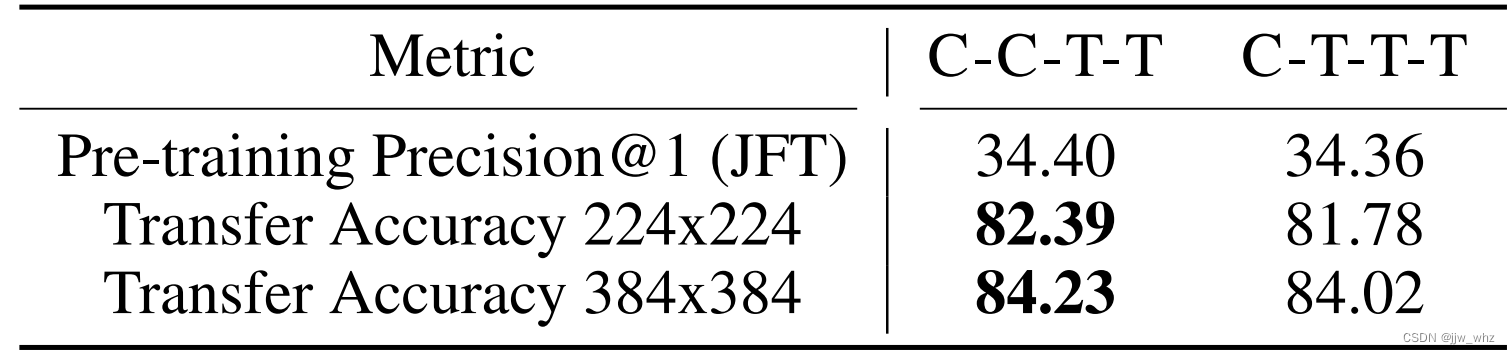
CoAtNet: Marrying Convolution and Attention for All Data Sizes翻译

Interpreting the 2022 agile coaching industry status report

测试的重要性及目的
![Leetcode: question d'entrevue 08.13. Empiler la boîte [DFS en haut + mémoire ou tri en bas + DP]](/img/22/220e802da7543c2b14b7057e4458b7.png)
Leetcode: question d'entrevue 08.13. Empiler la boîte [DFS en haut + mémoire ou tri en bas + DP]
随机推荐
Apache基金会正式宣布Apache InLong成为顶级项目
Opengauss database source code analysis series articles -- detailed explanation of dense equivalent query technology (Part 1)
IFLYTEK neuroimaging disease prediction program!
R语言使用tidyquant包的tq_transmute函数计算持有某只股票的天、月、周收益率、ggplot2使用条形图(bar plot)可视化股票月收益率数据、使用百分比显示Y轴坐标数据
Case analysis of camera power supply disturbed, seriously affecting image quality
聚焦:ZK-SNARK 技术
stylegan3:alias-free generative adversarial networks
get_ edges
Leetcode 450. Delete node in binary search tree
Short video platform development, click the input box to automatically pop up the soft keyboard
短视频平台开发,点击输入框时自动弹出软键盘
Improving efficiency or increasing costs, how should developers understand pair programming?
解读2022年度敏捷教练行业现状报告
你女朋友也能读懂的LAMP架构
TQ of R language using tidyquant package_ The transmute function calculates the daily, monthly and weekly returns of a stock. Ggplot2 uses the bar plot to visualize the monthly return data of the stoc
How to select an oscilloscope? These 10 points must be considered!
炒股买股票需要怎么选择呢?安全性不错的?
golang二分查找法代码实现
How is it cheaper to open a stock account? Is it safe to open an account online now?
相机电源受干扰案例分析,严重影响画质