当前位置:网站首页>How to do research on plant endophytes? Special topic on Microbiology
How to do research on plant endophytes? Special topic on Microbiology
2022-06-24 12:38:00 【Liuyongxin Adam】
Content guide
1. Secret and powerful plant endophytes
2. Indistinguishable endophytes
3. Better sequencing methods for Endophytic Bacteria in plants
3.1 LNA-16S The principle of sequencing to identify endophytic bacteria
3.2 LNA-16S The proportion of endophytic bacteria identified by sequencing is as high as 99%
4. Research ideas and methods of plant endophytes
4.1 A detailed explanation of representative cases
4.2 Summary of research ideas and methods
1. Secret and powerful plant endophytes
In the course of plant growth , Will encounter and interact with many different kinds of microorganisms , This may be why plants can be colonized on land . Plant chloroplasts and mitochondria use nuclear encoded proteins to replicate their DNA, Unlike those proteins involved in nuclear genome replication , These proteins are specially constructed for replication in the organelle environment . These organelle localized proteins originate from bacterial and phage genes , This supports the endosymbiosis theory of their origin and is established as an endosymbiont . therefore , This kind of little-known microorganism , Silence plays a unique role in plants , They are called endophytes (Endophyte).
Endophytes are defined as living in plants at one or all stages , It does not form obviously infected microorganisms , Contains endophytic bacteria 、 Endophytic fungi and endophytic actinomycetes . Their fame is as obscure as their existence , Until later, people separated them from the plant , It turns out that there are microorganisms in plants . Almost all plants have endophytic bacteria , Many plants cannot even survive without endophytes ( chart 1)[1]. Endophytic bacteria live in the special environment of plants for a long time , And coevolution with the host , In the process of evolution, the two formed a mutually beneficial symbiotic relationship , On the one hand, plants provide photosynthetic products and minerals for endophytes to grow , On the other hand, endophytes play an important role in the growth, development and phylogenetic evolution of the host .

chart 1. Microorganisms colonize and grow on various parts of plants
Some metabolites produced by endophytic bacteria can stimulate the growth and development of plants , Improve the resistance of host plants to biotic or abiotic stresses . Because pathogenic microorganisms and endophytic bacteria occupy the same niche in plants , Therefore, endophytic bacteria can also be inoculated to control pathogens in plants . Besides , Endophytic fungi have many other benefits for plant growth : Nitrogen fixation 、 Dissolved phosphorus 、 Produce plant hormones , Change root morphology 、 Regulate penetration 、 Increase the output of iron phosphate carrier 、 Enhance dissolution activity and regulate stomata ( chart 2)[1].
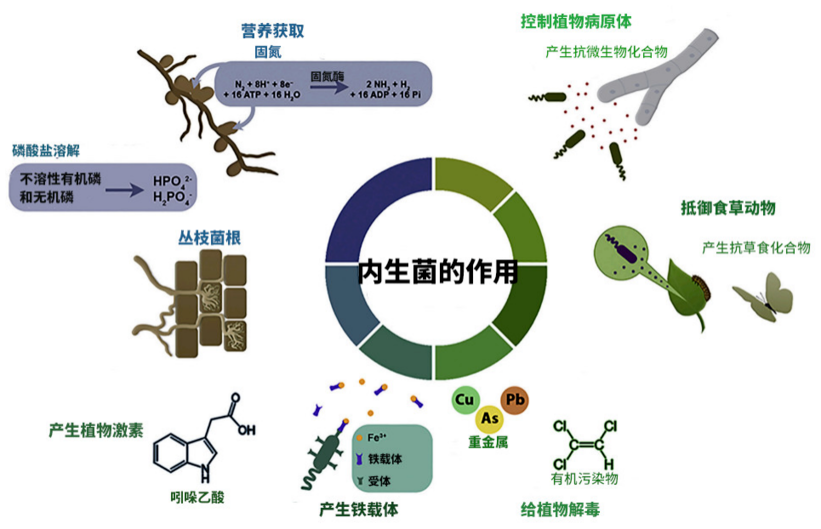
chart 2. The role of plant endophytes
The number of endophytes present in various plants 、 Species and plant species 、 Living environment 、 Growth stage 、 There is a close relationship between nutrition supply and their genotypes . Faster growing plants have more endophytes than slower growing plants ; The number of endophytic bacteria in the plants with long growth time is more than that in the plants just growing [2]. For humans , Endophytes have many unknowns , For example, how the metabolites of endophytes promote the growth mechanism of crop yield and effective components of medicinal plants , And the use of endophytic bacteria in biological fertilizers can improve plant nutrition , It has great research prospects in many fields .
2. Indistinguishable endophytes
It is not easy to detect plant endophytic bacteria, especially endophytic bacteria , This is because the mitochondria of plants 16S rDNA (Mt16S)、 chloroplast 16S rDNA (Ct16S) With bacteria 16S rDNA Show... In full length 70% The above sequence homology , The conserved region has higher sequence homology . This makes in use 16S Primer amplification of plant endophytic bacteria , A large number of plant sources will be produced in the amplified library DNA (Mt16S and Ct16S) Pollution ( The proportion can be as high as 99% above ), It seriously interferes with the subsequent analysis of endophytic bacteria data .
So , The researchers used a variety of methods to minimize the plant source DNA Interference of , such as :
1) Using primers 799F/1193R(V)(16S Of V5-V7) Amplification can produce products that do not contain Ct16S Amplification products of , And for most plants Mt16S The interference of about... Is removed 750 bp To remove the product of [3]. This method is limited to the plant species tested , For example, it is not applicable to rice ;
2) Redesign bacteria 16S Specific primers ( Including the introduction of base mutations ) To reduce the plant source DNA Interference of , It can increase the proportion of identified endophytic bacteria to a certain extent [4];
3) Adopt nested PCR, The first step is to use a pair of primers to amplify a part 16S Sequence , In the second step, another pair of primers is used to start from PCR In the product 16S Specific variable areas of, such as V4, Finally, the diversity of endophytic bacteria was analyzed [5]; We used a similar scheme to identify endophytic bacteria , Can reduce the plant source DNA The proportion of to 20~30%, But it will still fluctuate due to different plant species or plant organs ;
4) utilize CRISPR/Cas9 In the system Cas9 Nuclease and specificity guide RNA(gRNA) stay PCR Targeted elimination of plant sources during amplification DNA Sequence . This method can be applied to the root and leaf of rice DNA The pollution is from 63.2% and 99.4% Down to 2.9% and 11.6%[6];
5) Using locking nucleotides (Locked Nucleic Acid,LNA) Or peptide nucleic acid (Peptide Nucleic Acid,PNA) As PCR Clamp on PCR Block the plant source during amplification DNA Extension of [7,8,9].
If you will LNA Technology and the nest we have used PCR Whether the combination can reduce the interference of plant source sequences to a greater extent , Get a higher percentage of endophytic bacteria data , And it can also have a wider range of species applicability ?
3. Better sequencing methods for Endophytic Bacteria in plants
3.1 LNA-16S The principle of sequencing to identify endophytic bacteria
LNA It is a nucleotide analogue , By adding a to the ribose “2 '-O,4'-C- Methylene ” Bridge chain , Lock the spatial conformation of the sugar ring , Improve the stability of nucleic acid complementary chain binding , So as to improve the specificity of chain binding ( chart 1)[10]. By using LNA The oligonucleotide sequence can be Tm Value to fine tune . Usually in primer / Each time one is added to the probe LNA, Thermal stability can be improved 3~8 ℃. Add multiple... To one probe LNA, It can greatly improve the stability of the combination between the probe and the target segment . Based on the above advantages , with LNA The oligonucleotide sequence of is often used in PCR primer 、 Double labeled probe 、 In situ hybridization probes and molecular beacons .LNA There is also a disadvantage , Compared with traditional primers , Each composite one LNA Bases are hundreds of times more expensive than conventional bases .

chart 1. DNA、RNA and LNA Structure diagram of nucleotides
To test our previous conjecture , In the nest PCR Identification of endophytic bacteria , introduce LNA primer , Whether it can further reduce the interference of plant source sequences , And get a wider range of plant species applicability , We did the following experiments :
Reference resources [8,11] Primer sequences and methods , Synthesized with conventional bacteria PCR Primers have overlapping sequences , And for plant organelles such as Ct16S and Mt16S The uniqueness of LNA primer . In the first round PCR Before reaction , Add three pairs of primers at the same time , Two pairs of belts LNA And specifically bind to each other Ct16S and Mt16S The primers for , One pair is without LNA Conventional specific binding bacteria 16S The primers for ( Full length can be amplified 16S). because LNA Primed Tm It's worth more , So at higher temperatures (70℃) Time can be compared with Ct16S and Mt16S Gene annealing . after , Because the base position of the overlapping part has been LNA Primer binding anchoring , On reaching the lower Tm When the value of , Such as 54℃ when , routine 16S Primers can no longer be annealed with plant organelle genes , meanwhile LNA Primed 3’ Terminal primers are phosphorylated , Cannot extend sequence ( chart 2). therefore , Keep going PCR amplification , Only the full length of the bacteria will be amplified 16S Sequence , And inhibit the amplification of plant organelle genes .
Then proceed to the second round PCR reaction , Use the routine 16S Amplification primer ( With sequencing primers and barcode), Such as V4 or V3-V4, For the first round PCR The product is amplified ( That is, the construction of amplified sub library ). The amplified product was purified , It can be used for on-line sequencing . We call this 16S Sequenced as LNA-16S Sequence .

chart 2. LNA-PCR working principle [11]
3.2 LNA-16S The proportion of endophytic bacteria identified by sequencing is as high as 99%
LNA-16S Sequencing to determine whether endophytic bacteria behave as we expected ? We use LNA-16S(V4) The endophytic bacteria in the roots and leaves of many monocotyledons and dicotyledons were sequenced , And non LNA The nest of PCR-16S(V4), routine 16S V3-V4 as well as V5-V6 The sequencing results are compared ( chart 3).
Whether monocotyledons or dicotyledons , Whether it's a root sample or a leaf sample , stay LNA-16S Sequencing can identify a very high proportion of endophytic bacteria , The average proportion is 98.86%, Up to 99.83%. Accordingly , The highest proportion of plant source sequences is only 2.02%, The lowest is only 0.17%( surface 1).
In our test 4 Identification methods of endophytic bacteria , Integrated endophytic bacteria and plant sources DNA High ratio , And the wide applicability and performance of plant species and organs ,LNA-16S Sequencing is the best . therefore , We will LNA-16S Sequencing is the preferred method to identify endophytic bacteria in plants , Provide detection services for researchers .

chart 3. LNA-16S Sequencing and others 16S Comparison of sequencing in identification of endophytic bacteria in plants
LNA:LNA-16S Sequence (V4),V4: Not LNA The nest of PCR-16S Sequence ,V3V4: routine 16S V3-V4 Sequence ,V5V6: routine 16S V5-V6 Sequence ,ER: Monocotyledon root samples ,EL: Monocotyledon leaf samples ,DR: Dicotyledon root samples ,DL: Dicotyledon leaf samples
surface 1. 4 Kind of 16S Comparison of the proportion of endophytic bacteria obtained by sequencing method (%)

More Than This , in consideration of V3-V4 Is more often amplified 16S Variable area , We further compare LNA-16S(V3-V4) and LNA-16S(V4) Results of sequencing identification of endophytic bacteria in plants ( chart 4). It turns out that ,LNA-16S(V3-V4) The total proportion of endophytic bacteria identified on plant roots and leaves and the composition of dominant bacterial groups were sequenced LNA-16S(V4) Sequencing is basically similar , It can limit the interference of plant source sequence in a very small range . Besides ,LNA-16S(V3-V4) There will be more bacteria at each classification level identified by sequencing .

chart 4. LNA-16S(V3-V4) Sequencing and LNA-16S(V4) Comparison of sequencing in identification of endophytic bacteria in plants ( Take dicotyledons for example )
4. Research ideas and methods of plant endophytes
Endophytic fungi of plants ( Including endophytic bacteria and endophytic fungi ) In plant growth and development , Resistant to infection by viruses and germs 、 Resistance to abiotic stresses such as drought 、 Heavy metal pollution plays a key role , Therefore, the study of plant endophytes is also an important part of plant biology .
Here are some typical research cases of endophytes , To help readers better understand the research ideas and experimental design of plant endophytes .
4.1 A detailed explanation of representative cases
Case study 1: Characteristics of endophytic bacterial community in Ginkgo biloba leaves during development


Journal Publishing :Front. Microbiol.
Influencing factors :5.640
Time of publication :2021.10.4
research objective : The composition and abundance of endophytic bacteria in Ginkgo biloba leaves were analyzed , And the effect of flavonoids on endophytic bacterial community
Subjects of study : Endophytic fungi in Ginkgo leaves
Research methods :16S Sequence
Number of samples :5 Some time ×3 tree ×3 A repetition , share 45 individual

Research design :
Choose three wild ginkgo trees ( namely S1、S2 and S3), from 4 Month to 8 When ginkgo leaves begin to grow in June , Collect leaf samples every month . Divide the crown of each tree into 3 Parts of , From the ground 5 ~ 7 m Collect at 200 g Healthy leaves as samples for each part . All in all 5 A point in time from 3 From a tree 45 Blade samples . After the sample is transported to the laboratory , Each sample was divided into three parts for phytochemical analysis 、 Endophytic bacteria isolation and DNA extract . be used for DNA The extracted part needs to be surface sterilized , And freeze in liquid nitrogen , And then in -80°C Store... Under . use 16S Sequencing analysis of endophytic bacteria in Ginkgo leaves , The effects of flavonoids and other compounds on Endophytic community were also discussed .
Research conclusion :
It is the first time to reveal the bacterial communities in different growth stages of Ginkgo leaves . Ginkgo biloba leaves in different growth stages and under the influence of flavonoids , There were significant differences in bacterial communities in different periods .Spearman Correlation analysis shows that , There is a strong correlation between endophytic bacteria and flavonoids . The in vitro culture experiment provided further evidence for the effect of flavonoids on microorganisms .Tax4Fun2 The results of the prediction show that , Flavonoids may affect the changes of bacterial community in Ginkgo leaves at different growth stages .

chart 1 Endophytic bacterial community diversity index

chart 2. RDA(A) and VPA(B) To analyze the relationship between endophytic bacterial community and environmental variables in Ginkgo leaves
>> View full text interpretation
reference :
Deng Y, et al. Endophytic Bacterial Communities of Ginkgo biloba Leaves During Leaf Developmental Period. Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 4;12:698703.
Case study 2: Studies on the community structure of endophytic bacteria from different rice varieties in cadmium polluted paddy fields


Journal Publishing :Front. Microbiol.
Influencing factors :5.640
Time of publication :2021.11.16
research objective : Investigation in cadmium (Cd) Endophytic bacterial communities in roots of different rice varieties growing in Polluted Paddy Fields .
Subjects of study : Endophytic fungi in rice roots
Research methods :16S Sequence
Number of samples :5 varieties ×2 Some time ×3 A repetition , common 30 individual

Research design :
According to the Cd The rice varieties to be tested were divided into two groups : low Cd Accumulation level RBQ、728B and NX1B(LA Varieties ), And high Cd Accumulation level BB and S95B(HA Varieties ). A randomized block design was used in the field experiment , Before using , Fully plough the land , It is divided into 15 Districts (200 ×60 cm), The interval between each zone is 40 cm. A zone has three columns , One column has 10 A hole , Two seedlings are planted in each hole . Each rice variety has 3 A repetition ( District ). After transplanting 30 d( Vegetative growth period ) and 60 d( Reproductive growth period ) Collect rice root samples respectively . For each rice variety , Sample in each area by diagonal sampling method 5 A single plant , And mix the roots . The root sample is divided into two parts : Part for 16S Sequence , The other part is used to isolate endophytic bacteria . In the vegetative growth period 5 Root samples of rice varieties were named RBQ1、728B1、NX1B1、BB1 and S95B1, The root sample in the reproductive growth period is named RBQ2、728B2、NX1B2、BB2 and S95B2.
Research conclusion :
For the first time, a detailed description of Cd Endophytic flora of rice roots under water stress , And for understanding endophytic bacteria 、 The interaction between plants and heavy metal pollution provides insights .

chart 1. nutrition (A) And reproduction (B) Co-occurrence network diagram of period samples

chart 2. LEfSe and Venn Graph analysis

chart 3. Prediction of gene function of Endophytic Bacteria Community
>> View full text interpretation
reference :
Chu C, et al. Unveiling Endophytic Bacterial Community Structures of Different Rice Cultivars Grown in a Cadmium-Contaminated Paddy Field. Front Microbiol. 2021 Nov 16;12:756327.
Case study 3: Effects of interaction between rhizosphere and endophytic microbial communities on cotton growth in Xinjiang


Journal Publishing :Front. Microbiol.
Influencing factors :5.640
Time of publication :2021.12.06
research objective : Effects of the interaction between rhizosphere soil and endophytes on cotton growth were studied
Subjects of study : Rhizosphere soil + Endophytic fungi in cotton roots
Research methods :16S Sequence +ITS Sequence
Number of samples :(7 A region ×4 Period ×3 A repetition )×2, common 336 individual

Research design :
On the north slope and south foot of Tianshan Mountain 7 Cotton seedlings were randomly collected from cotton planting areas in four regions 、 bud 、 Flowers and catkins 4 Samples of diseased and healthy plants at growing stages . The samples collected include roots and rhizosphere soil ( From the root surface 0-3 mm) be used for 16S and ITS Sequence .

chart 1 Research design
Research conclusion :
It was found that the rhizosphere colony was mainly proteus 、 Acidobacteria 、 Spores 、 Actinomycetes 、 Chloromycetes 、 Bacteroides 、 Ascomycetes 、 Mortierella 、 Basidiomycetes . The abundance of endophytic bacteria and rhizosphere bacteria and fungi in diseased cotton plants were higher than that in healthy plants . Endophytic bacteria and rhizosphere bacteria have nothing in common OTUs. The distribution of dominant bacteria in different cotton rhizosphere soils and roots is different , The dominant bacteria are Pseudomonas and pantomycetes , The dominant bacteria Alternaria alternata and cephalosporin were the most abundant . Sampling points in different ecological areas , Endophytes and Rhizosphere Microflora of cotton from south to North Xinjiang OTUs The total is on the rise . During the whole cotton growing period , There were significant differences in composition and diversity between rhizosphere microorganisms and endophytes .

chart 2 Rhizosphere and endophytic bacteria / Horizontal community composition of fungi

chart 3 Rhizosphere and endophytic bacteria from different sampling sites and different growth stages / fungus PCoA analysis

chart 4 Correlation network analysis of rhizosphere and endosphere microbial communities in genus level cotton
>> View full text interpretation
reference :
Shi Y, et al. Differentiation and Variability in the Rhizosphere and Endosphere Microbiomes of Healthy and Diseased Cotton (Gossypium sp.). Front Microbiol. 2021 Dec 6;12:765269.
Case study 4: Multinomial analysis revealed the mechanism of endophytic bacteria promoting the growth and salt tolerance of Agropyron


Journal Publishing :International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Influencing factors :5.924
Time of publication :2021.10.30
research objective : Explore how endophytic bacteria affect the growth and salt tolerance of Agropyron
Subjects of study : Rhizosphere soil 、 Agropyron root endophytic bacteria 、 Agropyron metabolome
Research methods :16S Sequence 、 Metabolome detection

Research design :
Collect soil from three different areas , In different salts (50 mM,200 mM and 350 mM) Plant wheatgrass under . Take the root of each process , After surface disinfection , use 16S Sequencing for endophytic bacterial analysis . Then, endophytic bacteria were isolated and cultured from the leaves and roots of Agropyron . After two rounds of screening, endophytic bacteria that promote plant growth (PGPE), Grow them with the seeds of Agropyron , By measuring the growth of Agropyron 1 Fresh weight and root length after weeks , To evaluate the growth promoting effect of each strain . The characteristics of promoting plant growth of selected strains were determined and phylogenetic analysis was carried out . Last , Vaccination PGPE 2 and 4 Metabonomics analysis of Agropyron under different treatments .
Research conclusion :
The two strains of endophytic bacteria have the function of promoting plant growth . Only 4 Strain No IAA, and 2 Strain No. 1 promotes plant growth , But it doesn't produce IAA Or any other test character . The metabolic profile highlights salt stress and inoculation PGPE Differences in metabolites in offspring . especially , In planting PGPE Of plants , The abundance of some metabolites has increased , For example, those with TCA loop 、ABC Transporters are metabolites related to photosynthesis ( chart 7). Salinity also affects the metabolism of Agropyron , Results in changes in compatible solute and polyamine content . by comparison , The contents of many substances in the simulated inoculated plants under salt stress were higher than those in the inoculated strains 2 or 4 All the plants showed a downward trend under salt stress , These results indicated that these strains alleviated the effects of salt stress .

chart 1. Rhizosphere soil microorganisms (a-c) And endophytic bacteria (d-f) The number of

chart 2. A family of Endophytic Bacteria of Agropyron aestivum growing in three different soils

chart 3. Of the metabolites of Agropyron aestivum in different treatments PCA analysis
>> View full text interpretation
reference :
Kataoka R, et al. Metabolomics Analyses Reveal Metabolites Affected by Plant Growth-Promoting Endophytic Bacteria in Roots of the Halophyte Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 30;22(21):11813.
4.2 Summary of research ideas and methods
The overall research idea is not obviously different from that of other environmental microbiome (>> This article explains how to do environmental microbiome research ). The research content of plant endophytes mainly focuses on the identification of endophytes 、 Effects on the growth and development of host plants 、 Counteract the effects of adverse responses 、 The effects of Endophytes and other environmental microorganisms, such as rhizosphere soil microorganisms, on the growth and development of host plants and stress resistance .
In particular , Do monoomic research , It is suggested to do multi object research , It can be the study of endophytic bacteria and endophytic fungi , It can also be the study of roots 、 stem 、 Endophytes in leaves , It can also be rhizosphere soil microorganisms and endophytes ; Do multiomics research , It is still preferred to combine with the metabolome , It can also be the transcriptome or proteome of the co host ; Endophytic bacteria generally do not recommend macrogenomics , Because the host DNA The proportion is too high . In the experimental design , The most common is different treatment × At different times , Different varieties × At different times . A striking difference in the study of endophytes is , Many studies have involved the isolation, culture and functional verification of endophytic bacteria . About the number of sample repetitions , Also like other environmental microbiomes , We recommend the number of repetitions per sample ≥ 5 individual .
reference :( Slide to see )
1. Papik J, Folkmanova M, Polivkova-Majorova M, et al. The invisible life inside plants: Deciphering the riddles of endophytic bacterial diversity. Biotechnol Adv. 2020 Nov 15;44:107614.
2. Wu W, Chen W, Liu S, et al. Beneficial Relationships Between Endophytic Bacteria and Medicinal Plants. Front Plant Sci. 2021 Apr 22;12:646146.
3. Bai Y, Müller D B, Srinivas G, et al. (2015). Functional overlap of the Arabidopsis leaf and root microbiota. Nature 528, 364–369.
4. Chen L, et al. Designing specific bacterial 16S primers to sequence and quantitate plant endo-bacteriome. Sci China Life Sci. 2022 May;65(5):1000-1013.
5. Yu J, et al. Design and application of specific 16S rDNA-targeted primers for assessing endophytic diversity in Dendrobium officinale using nested PCR-DGGE. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Nov;97(22):9825-36.
6. Song L, and Xie K. (2020). Engineering CRISPR/Cas9 to mitigate abundant host contamination for 16S rRNA gene-based amplicon sequencing. Microbiome 8, 80.
7. Ikenaga M, Sakai M. Application of Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA) oligonucleotide-PCR clamping technique to selectively PCR amplify the SSU rRNA genes of bacteria in investigating the plant-associated community structures. Microbes Environ. 2014 Sep 17;29(3):286-95.
8. Ikenaga M, et al. Improvements in Bacterial Primers to Enhance Selective SSU rRNA Gene Amplification of Plant-associated Bacteria by Applying the LNA Oligonucleotide-PCR Clamping Technique. Microbes Environ. 2018 Sep 29;33(3):340-344.
9. Matsumoto H, Fan X, Wang Y, et al. (2021). Bacterial seed endophyte shapes disease resistance in rice. Nat Plants 7, 60–72.
10. Singh S. K, et al. (1998). LNA (locked nucleic acids): synthesis and high-affinity nucleic acid recognition. Chem. Commun. 4, 455-456.
11. Yu Z H, Ikenaga M, Sakai M, et al.(2021). Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA) Oligonucleotide PCR Clamping Method for Investigating the Plant Endophyte Bacteria. // Microbiome Protocols eBook. Bio-101: e2003525.
Related reading
Recent Cell Tumor microbiome , Do you all know ?| Special topics on Microbiology
Official announcement CP! Tumor microbiome × Exome | Special topics on Microbiology 
Guess you like
iMeta brief introduction Highly quoted articles High color value drawing imageGP Network analysis iNAP
iMeta Web tools Metabolism group MetOrigin Meggie cloud Lactation prediction DeepKla
iMeta review Intestinal flora Plant flora Oral flora Protein structure prediction
10000+: Flora analysis Babies and dogs Rhapsody of syphilis carry DNA Hair Nature
Series of tutorials : Introduction to microbiome Biostar Microbiome Macro genome
Expertise : Academic charts High score article Shengxin Scripture An indispensable person
Article to read : Macro genome Parasite benefits Evolutionary tree Necessary skills : put questions to Search for Endnote
Amplification analysis : Chart interpretation Analysis process Statistical mapping
16S Function prediction PICRUSt FAPROTAX Bugbase Tax4Fun
Biological science : Intestinal bacteria Life on the human body Great leap forward in life Cell warfare The mystery of human body
Written in the back
To encourage readers to communicate and quickly solve scientific research difficulties , We established “ Macro genome ” Discussion groups , There are already domestic and foreign 6000+ Researchers join . Please add editor in chief wechat meta-genomics Bring you into the group , Be sure to remark “ full name - Company - Research direction - The title / grade ”. Please indicate your identity for the senior title , There are also microorganisms at home and abroad PI Cooperation and exchange of group supply . Ask for help with technical problems , First read 《 How to ask questions gracefully 》 Learn how to solve problems , Unresolved intra group discussions , Don't talk about problems in private , Help colleagues .
Click to read the original text , Jump to the latest article catalog to read
边栏推荐
- The programmer's graduation project is still bald after a year
- Practice of dynamic load balancing based on open source tars
- Opencv learning notes - loading and saving images
- Jenkins pipeline syntax
- 一纸英雄帖,激起千层浪,横跨10国,一线大厂都派人来了!-GWEI 2022-新加坡
- Getting started with scrapy
- Istio practical skills: using prism to construct multi version test services
- How to calculate the bandwidth of video transmission? How much bandwidth is required to transmit 4K video?
- Programmer: after 5 years in a company with comfortable environment, do you want to continue to cook frogs in warm water or change jobs?
- Kubernetes practical skills: use cert manager to issue free certificates for DNSPod domain names
猜你喜欢

【2022国赛模拟】摆(bigben)——行列式、杜教筛

《回归故里》阅读笔记

How can a shell script (.Sh file) not automatically close or flash back after execution?

一纸英雄帖,激起千层浪,横跨10国,一线大厂都派人来了!-GWEI 2022-新加坡
[mysql_16] variables, process control and cursors

微医CodeReview工具链

巴比特 | 元宇宙每日必读:618成绩已然揭晓,在这份还算满意的答卷背后,数字藏品做出了多少贡献?...

WPF从零到1教程详解,适合新手上路

文本转语音功能上线,可以体验专业播音员的服务,诚邀试用

一文讲透植物内生菌研究怎么做 | 微生物专题
随机推荐
Essential key steps in the construction of e-commerce live broadcast source code
How to apply for new bonds is it safe to open an account
mLife Forum | 微生物组和数据挖掘
Post processing - deep camera deformation effects
Kubernetes practical technique: setting kernel parameters for pod
Opencv learning notes - Discrete Fourier transform
Is it safe to open an account for how many new bonds you can apply for
How to open a new bond? Is it safe to open an account
Smart photovoltaic energy - visualization of photovoltaic power generation energy management and control in the park
A "full cloud" journey of a quasi financial system
I'm in Shenzhen. Where can I open an account? Is it safe to open an account online now?
Installation and operation of libuv
[tke] GPU node NVIDIA Tesla driver reinstallation
How to evaluate software development projects reasonably?
Can Tencent's tendis take the place of redis?
一文讲透植物内生菌研究怎么做 | 微生物专题
How to develop mRNA vaccine? 27+ pancreatic cancer antigen and immune subtype analysis to tell you the answer!
Discussion on redis communication protocol
What are the low threshold financial products in 2022? Not much money
About me, a 19 line programmer
![[mysql_16] variables, process control and cursors](/img/c3/91ffb21431cf891747d6d09b554d0d)