当前位置:网站首页>线程池
线程池
2022-06-23 15:25:00 【weixin_43766298】
1.线程池总结

public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//========================定长==========================
ExecutorService ftp = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
//newFixedThreadPool使用的构造函数
/* public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); }*/
//========================可缓存==========================
ExecutorService ctp = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//newCachedThreadPool使用的构造函数
/* public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()); }*/
//========================定时==========================
ScheduledExecutorService stp = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
//newScheduledThreadPool使用的构造函数
/* public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) { return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize); }*/
//========================单例==========================
ExecutorService ste = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
//newSingleThreadExecutor使用的构造函数
/*public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() { return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService (new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>())); }*/
}
2.阻塞队列和非阻塞队列

//==============================非阻塞队列===============================
ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> clq = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
//入队
clq.add("a");
clq.add("b");
clq.add("c");
//查看队列头
String peek = clq.peek();
System.out.println("peek = " + peek);//a
System.out.println("clq.size() = " + clq.size());//3
//出队
String poll = clq.poll();
System.out.println("poll = " + poll);//a
System.out.println("clq.size() = " + clq.size());//2
System.out.println("=================================");
//======================阻塞队列=======================================
BlockingQueue<String> bq = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(2);
// bq.add("a");
//bq.add("b");
// bq.add("c");//java.lang.IllegalStateException: Deque full
//todo:offer 和 add一样都是入队,但是offer可以等待一定时间看能否可以插入
bq.offer("a");
bq.offer("b");
System.out.println("bq.poll() = " + bq.poll());
//阻塞3秒,看能不能把c放进队列中
bq.offer("c",3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("bq.poll() = " + bq.poll());
System.out.println("bq.poll() = " + bq.poll());
//阻塞5秒,等待是否有可被取出的元素
System.out.println("bq.poll() = " + bq.poll(5,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
2.线程池原理
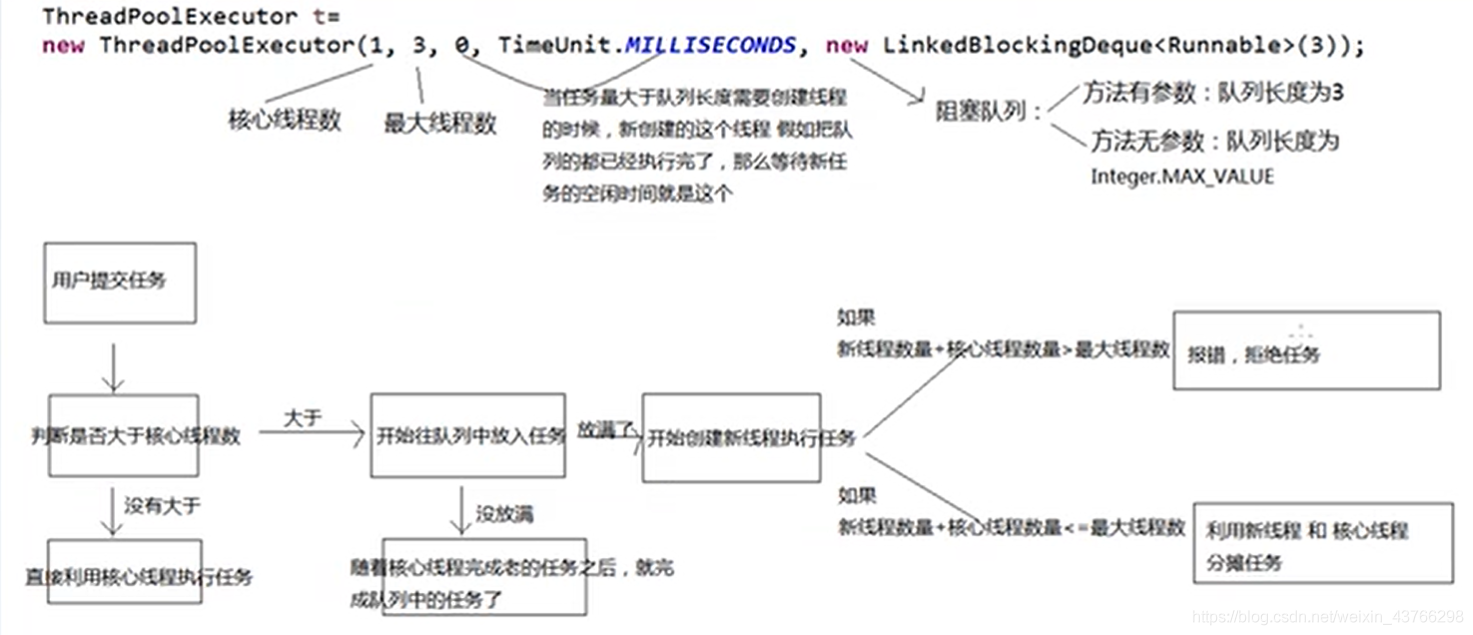
3.线程池测试和分析
public static void main(String[] args){
ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//使用的是无边界队列,来一个任务创建一个线程
/* 根据需要创建线程, 但可用时将重用以前构造的线程的线程池。 这些池通常可提高其执行很多短期异步任务的程序的性能。 调用execute (如果可用)将重用以前构造的线程。 如果没有现有线程可用,一个新的线程将被创建并添加到池中。 尚未使用的60秒的线程将终止并从缓存中删除。 因此保持空闲的时间足够长池不会消耗任何资源*/
/* public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()); }*/
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
es.execute(()-> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()));
}
es.shutdown();
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
/* 创建一个线程池, 该线程池可重用固定数量的线程, 在共享的无边界队列上操作。 在任何时候,最多{nThreads}个线程将是活动的处理任务。 如果在所有线程都处于活动状态时提交了其他任务, 则它们将在队列中等待,直到线程可用为止。 如果任何线程由于执行过程中的失败而终止在关机之前,如果需要一个新线程将代替执行后续任务。 池中的线程将存在,直到明确地shutdown*/
/*public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); }*/
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
fixedThreadPool.execute(()-> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()));
}
fixedThreadPool.shutdown();
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
/*创建一个线程池,该线程池可以安排命令在给定的延迟后运行或定期执行。 @param corePoolSize即使在空闲时也要保留在池中的线程数*/
/*public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) { return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize); }*/
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
//delay(3):延时三秒执行任务
scheduledThreadPool.schedule(()-> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()),3,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
//initialDelay(2) :第一次执行前延时时间 period(1) 连续执行之间的时间间隔
//scheduledThreadPool.scheduleAtFixedRate(()-> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()),2,1,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
scheduledThreadPool.shutdown();
ExecutorService singlePool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
/*创建一个使用单个worker线程的操作无界队列的执行人。 (不过请注意,如果这个单一线程终止由于停机前执行过程中出现故障, 如果需要执行后续任务,将会有新取而代之。)的任务是保证顺序地执行, 并且不超过一个任务将是积极的在任何给定的时间。 与其他等效newFixedThreadPool(1)所返回的执行保证无需重新配置为使用其他的线程。*/
/* public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() { return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService (new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>())); }*/
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
singlePool.execute(()-> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()));
}
singlePool.shutdown();
}
边栏推荐
- 数组自带的方法
- mysql 系列:总体架构概述
- Solution to the problem that MySQL cannot be started in xampp
- 电荷泵原理讲义,电压是怎么“泵”上去的?
- 云上探“店”,云商店全新升级!
- Analysis of graphical level-1 programming problem of Electronic Society: cat and mouse
- How to open a stock account? Is online account opening safe?
- Important knowledge of golang: sync Cond mechanism
- MySQL中json_extract函数说明
- labelme的JSON文件转成COCO数据集格式
猜你喜欢

Redis集群操作的方法

stylegan3:alias-free generative adversarial networks

Analysis of graphical level-1 programming problem of Electronic Society: cat and mouse

golang 重要知识:定时器 timer
Sorting out and summarizing the handling schemes for the three major exceptions of redis cache

stylegan2:analyzing and improving the image quality of stylegan

Matlab| sparse auxiliary signal denoising and pattern recognition in time series data

JS garbage collection

Important knowledge of golang: sync Once explanation

MQ消息中间件理论详解
随机推荐
139. word splitting
Thymeleaf——学习笔记
SQL窗口函数怎么使用
Web篇_01 了解web开发
C. Product 1 Modulo N-Codeforces Round #716 (Div. 2)
System design and analysis - Technical Report - a solution for regularly clearing verification code
The running rabbit fell
Sfod: passive domain adaptation and upgrade optimization, making the detection model easier to adapt to new data (attached with paper Download)
Object
JS garbage collection
PHP 2D array insert
要买的理财产品年限长,划算吗?
get_edges
他山之石 | 微信搜一搜中的智能问答技术
自监督学习(SSL)Self-Supervised Learning
How can genetic testing help patients fight disease?
labelme的JSON文件转成COCO数据集格式
stylegan2:analyzing and improving the image quality of stylegan
《利用CAS实现自旋锁》
Charge pump principle handout, how is the voltage "pumped"?
