当前位置:网站首页>Do you really understand the cache penetration, cache breakdown and cache avalanche in rotten street?
Do you really understand the cache penetration, cache breakdown and cache avalanche in rotten street?
2022-06-23 21:14:00 【Su San Shuo Technology】
Preface
For students engaged in back-end development , cache Has become one of the indispensable technologies in the project .
you 're right , Caching can significantly improve the performance of our system . But if you don't use it well , Or lack of relevant experience , It will also bring many unexpected problems .
Today, let's talk about if caching is introduced into the project , The following three major problems that may bring us . Let's see if you've got it ?
1. Cache penetration problem
In most cases , The purpose of caching is : In order to reduce the pressure of database , Improve the performance of the system .
1.1 How do we use cache ?
In general , If a user requests to come , Check the cache first , If there is data in the cache , Then return directly . If it doesn't exist in the cache , Then check the database again , If there is , Then put the data into the cache , Then return . If it doesn't exist in the database , Then directly return to failure .
The flow chart is as follows :
The picture above must be familiar to the boys , Most caches are used like this .
1.2 What is cache penetration ?
But if the following two special situations occur , such as :
- user-requested id Does not exist in cache .
- Malicious users forge nonexistent id Initiate request .
The result of such a user request is : Every time I can't find data from the cache , You need to query the database , At the same time, the data is not found in the database , I can't put it in the cache . in other words , Every time this user requests to come , You have to query the database once .
The red arrow in the figure indicates the route taken each time .
Obviously , Caching doesn't work at all , It's like being through The same , Every time I visit the database .
That's what we're talking about : Cache penetration problem .
If the cache is penetrated at this time , The number of requests for direct database is very large , The database may hang up because it can't bear the pressure . Purring .
So here comes the question , How to solve this problem ?
1.3 Calibration parameters
We can treat users id Make a test .
For example, you are legal id yes 15xxxxxx, With 15 At the beginning . If the user passed in 16 At the beginning id, such as :16232323, Parameter verification fails , Directly intercept relevant requests . This can filter out some malicious forged users id.
1.4 The bloon filter
If there is less data , We can put the data in the database , One that's all in memory map in .
This can be very fast to identify , Whether the data exists in the cache . If there is , Then let it access the cache . If it doesn't exist , Then reject the request directly .
But if there's too much data , Tens of millions or hundreds of millions of data , Put it all in memory , Obviously, it will take up too much memory space .
that , Is there any way to reduce memory space ?
answer : That's what you need to use The bloon filter 了 .
The bottom layer of Bloom filter is used bit Arrays store data , The default value of the elements in this array is 0.
When the bloom filter is first initialized , All existing in the database key, After a series of hash Algorithm ( such as : Three times hash Algorithm ) Calculation , Every key Will calculate multiple positions , Then set the element values at these locations to 1.
after , A user key When you ask to come , Then use the same hash Algorithm calculation position .
- If the element values in multiple locations are 1, That means key Already exists in the database . At this time, it is allowed to continue to operate backward .
- If there is 1 The element values at more than locations are 0, That means key Does not exist in the database . The request can then be rejected , And return directly .
Using Bloom filters does solve the cache penetration problem , But it also brings two problems :
- There are misjudgments .
- There is a data update problem .
Let's see why there are misjudgments ?
As I said above , When data is initialized , For each key Through many times hash Algorithm , Calculate some positions , Then set the element values at these locations to 1.
But we all know hash The algorithm will appear hash Conflicting , That is to say, different key, It's possible to calculate the same position .
The subscript in the figure above is 2 Your position appears hash Conflict ,key1 and key2 Calculated the same position .
If there are tens of millions or hundreds of millions of data , In the bloom filter hash The conflict will be very obvious .
If a user key, After many times hash Calculated position , Its element value , It happens to be by others key Initialization is 1. here , There was a miscarriage of justice , Originally this key It doesn't exist in the database , But the bloom filter is confirmed to exist .
If the bloom filter determines a certain key There is , There may be a miscarriage of justice . If you judge a key non-existent , Then it must not exist in the database .
Usually , The misjudgment rate of Bloom filter is still relatively small . Even if there are a few misjudged requests , Direct access to the database , But if the number of visits is not large , It has little impact on the database .
Besides , If you want to reduce the misjudgment rate , You can add hash function , Used in the figure 3 Time hash, Can be added to 5 Time .
Actually , The most fatal problem with the bloom filter is : If the data in the database is updated , The bloom filter needs to be updated synchronously . But it is two data sources with the database , There may be data inconsistencies .
such as : A new user has been added to the database , The user data needs to be synchronized to bloom filter in real time . But due to network anomalies , Synchronization failed .
At this time, the user's request came , Because the bloom filter does not have this key The data of , So the request was rejected directly . But this is a normal user , Also by Intercept 了 .
Obviously , If such a normal user is intercepted , Some businesses are intolerable . therefore , Bloom filter depends on the actual business scenario before deciding whether to use , It helps us solve the cache penetration problem , But at the same time, it brings new problems .
1.5 Cache null
It uses a bloom filter , Although it can filter out many non-existent users id request . But in addition to increasing the complexity of the system , There are two problems :
- The bloom filter has been killed by mistake , It may also filter the requests of a small number of normal users .
- If the user information changes , Need real-time synchronization to bloom filter , Otherwise there will be problems .
therefore , Usually , We rarely use Bloom filters to solve cache penetration problems . Actually , There is another simpler solution , namely : Cache null .
When a user id Not found in cache , I can't find it in the database , The user also needs to be id cached , It's just that the value is empty . So later requests , Take the same user id When making a request , You can get empty data from the cache , Straight back , Without having to check the database again .
The optimized flow chart is as follows :
The key point is whether you can find the data from the database or not , Put the results into the cache , Just if you don't find the data , The value in the cache is empty .
2. Cache breakdown problem
2.1 What is cache breakdown ?
occasionally , When we access hotspot data . such as : We buy a hot product in a mall .
To ensure access speed , Usually , The mall system will put the commodity information into the cache . But if at some point , The item is expired .
here , If a large number of users request the same product , But the item is invalid in the cache , All of a sudden, these user requests are directly connected to the database , It may cause excessive pressure on the database at the moment , And just hang up .
The flow chart is as follows :
that , How to solve this problem ?
2.2 Lock
The root cause of excessive database pressure is , Because too many requests access the database at the same time .
If we can limit , Only one request can access a at a time productId Database commodity information , It doesn't solve the problem ?
answer : you 're right , We can use Lock The way , Implement the above functions .
The pseudocode is as follows :
try {
String result = jedis.set(productId, requestId, "NX", "PX", expireTime);
if ("OK".equals(result)) {
return queryProductFromDbById(productId);
}
} finally{
unlock(productId,requestId);
}
return null;Lock when accessing the database , Prevent multiple identical productId Requests to access the database at the same time .
then , You also need a piece of code , Put the results queried from the database , Put it back in the cache . There are many ways , I'm not going to expand here .
2.3 Automatic renewal
The cache breakdown problem is due to key Expired, resulting in . that , Let's change our thinking , stay key It's about to expire , Automatically renew it , No OK 了 ?
answer : you 're right , We can use job To assign to key Automatic renewal .
for instance , We have a classification function , The set cache expiration time is 30 minute . But there is one. job every other 20 Once per minute , Automatically update the cache , Reset the expiration time to 30 minute .
So you can make sure , The classification cache will not expire .
Besides , There are many requests for third-party platform interfaces , We often need to call a get first token The interface of , Then use this token As a parameter , Request the real business interface . Generally obtained token It has a validity period , such as 24 Failure after hours .
If we request each other's business interface every time , You have to call once to get token Interface , Obviously it's more troublesome , And the performance is not very good .
Now , We can take what we got for the first time token cached , When requesting the other party's business interface, get the information from the cache token.
meanwhile , There is one job Every once in a while , Like every other 12 Request once every hour token Interface , Keep refreshing token, To reset token The expiration time of .
2.4 Cache does not fail
Besides , For many popular key, In fact, there is no need to set the expiration time , Make it permanent .
For example, popular products participating in second kill activities , Because of this kind of goods id There is not much , In the cache, we can not set the expiration time .
Before the second kill , We first use a program to query the data of goods from the database in advance , Then synchronize to the cache , Do it ahead of time preheating .
After a period of time after the second kill , We will have a Delete manually These useless caches can .
3. Cache avalanche problem
3.1 What is a cache avalanche ?
I've talked about cache breakdown earlier .
Cache avalanche is an upgraded version of cache breakdown , Cache breakdown is about a hot key It doesn't work , And the cache avalanche says there are multiple hot key Simultaneous failure . look , If a cache avalanche occurs , The problem is more serious .
There are currently two kinds of cache avalanches :
- There are a lot of popular caches , Simultaneous failure . Will result in a large number of requests , Access database . And the database is likely to be unable to withstand the pressure , And just hang up .
- Cache server down Machine. , It may be a problem with the machine hardware , Or computer room network problems . All in all , This makes the entire cache unusable .
In the final analysis, there are a lot of requests , Through cache , And direct access to the database .
that , How to solve this problem ?
3.2 Expiration time plus random number
To solve the cache avalanche problem , First of all, we should try to avoid cache invalidation at the same time .
This requires us not to set the same expiration time .
Based on the set expiration time , Add another 1~60 Random number of seconds .
Actual expiration time = Expiration time + 1~60 Random number of seconds
So even in the case of high concurrency , Set the expiration time for multiple requests at the same time , Because of the existence of random numbers , There won't be too many same expiration key.
3.3 High availability
For cache servers down The situation of the machine , When doing system design in the early stage , Can do some high availability Architecture .
such as : If used redis, Sentinel mode can be used , Or cluster mode , Avoid single node failure leading to the whole system redis Service unavailability .
After using sentinel mode , When a master When the service is offline , The master One of the following slave Service upgrade to master service , Replace offline master The service continues to process the request .
3.4 service degradation
If you do a high availability Architecture ,redis The service still hung up , What to do ?
Now , You need to downgrade the service .
We need to configure some default bottom data .
There is a global switch in the program , Such as the 10 Requests in the last minute , from redis Failed to get data from , Then the global switch is on . Later new requests , Get the default data directly from the configuration center .
Of course , There needs to be a job, Go from... At regular intervals redis Get data in , If you can get data twice in the last minute ( This parameter can be set by yourself ), Turn off the global switch . Later requests , It can be normal from redis Get data from .
I need to say something special , The scheme is not applicable to all scenarios , It needs to be determined according to the actual business scenario .
边栏推荐
- The substring() method in. JS can be used to intercept all characters after the specified string
- C WPF new open source control library: newbeecoder Nbtreeview of UI
- Authentication can be as simple as this - use the API gateway to protect your API security
- How to view the role of PMO in agile organizations?
- 【5分钟玩转Lighthouse】快速使用长安链
- Full instructions for databinding
- Excel text function
- Cloudbase init considerations
- Summary of multiple methods for obtaining the last element of JS array
- How PMO uses two dimensions for performance appraisal
猜你喜欢
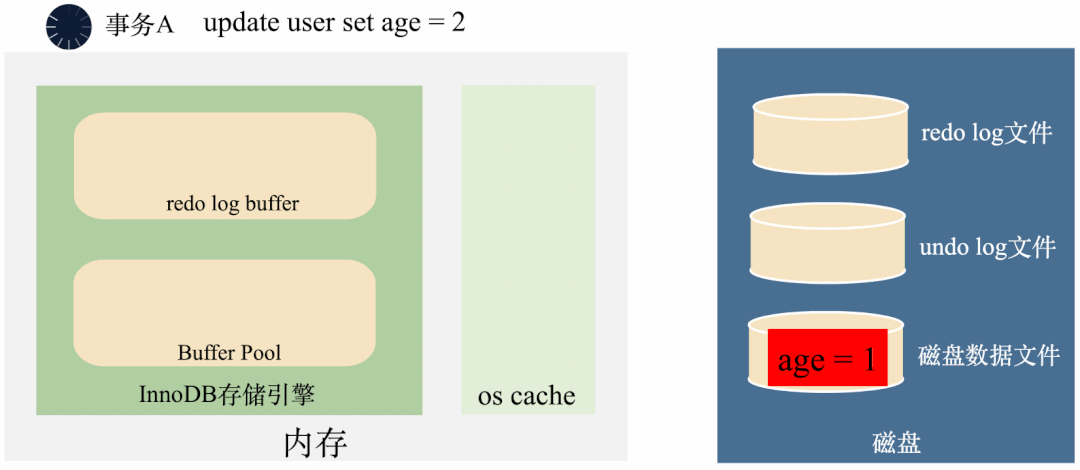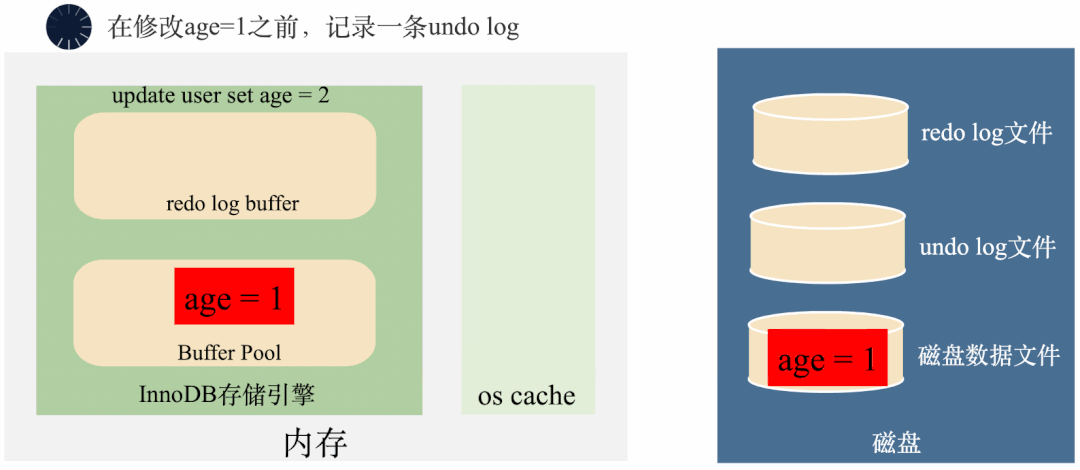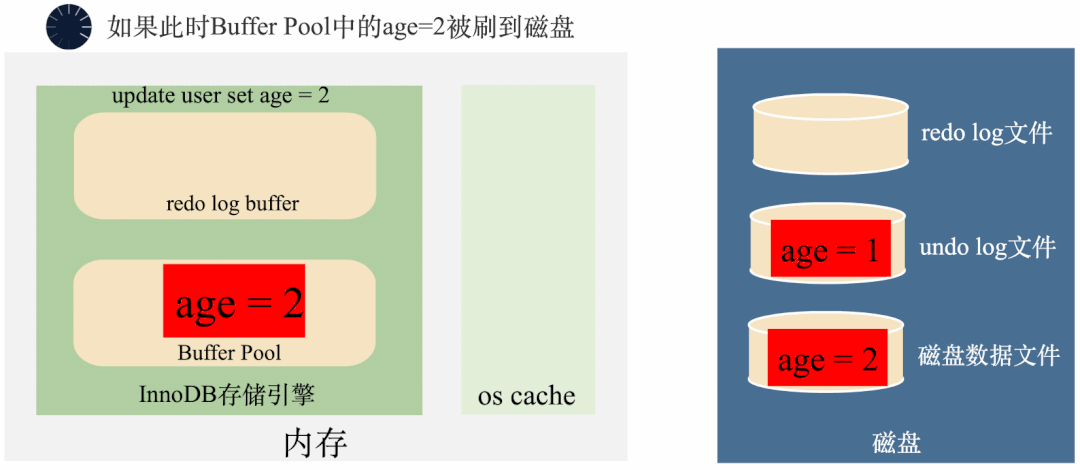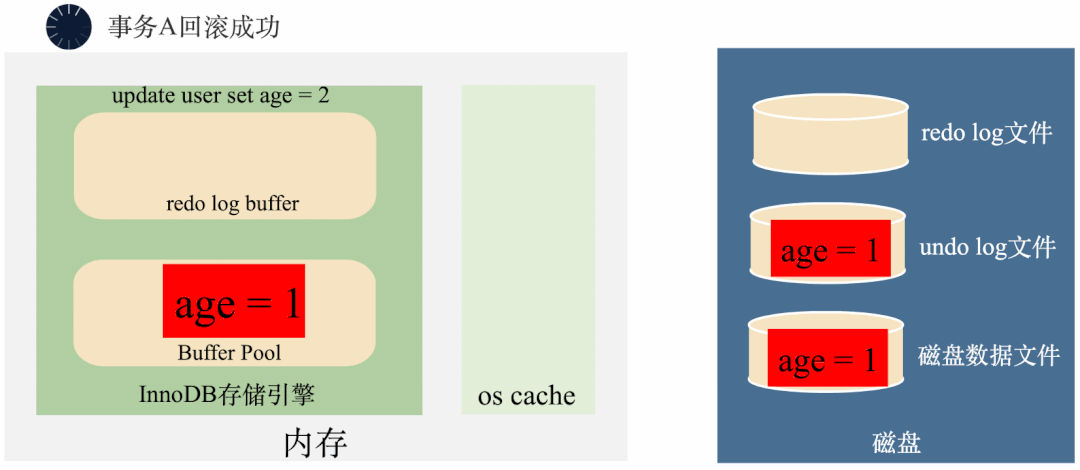
3000 frame animation illustrating why MySQL needs binlog, redo log and undo log

How does PMO select and train project managers?

How to gradually improve PMO's own ability and management level

New SQL syntax quick manual!

How to view the role of PMO in agile organizations?
Application of JDBC in performance test

What are the main dimensions of PMO performance appraisal?

Steps for formulating the project PMO strategic plan

How PMO uses two dimensions for performance appraisal

Applet development framework recommendation
随机推荐
Overview of digital circuits
Applet development framework recommendation
Row height, (top line, middle line, baseline, bottom line), vertical align
Use Tencent cloud lightweight application server to build an unlimited network disk -zpan building tutorial
What cloud disk types does Tencent cloud provide? What are the characteristics of cloud disk service?
Whether the offsetwidth includes scroll bars
. Net cloud native architect training camp (rgca four step architecture method) -- learning notes
[development skills] how to add "live broadcast" status display bar on easynvr platform
How to make a material identification sheet
[typescript] some summaries in actual combat
[sap-hcm] report jump to pa30/pa40 instance
How to dispose of the words on the picture? How do I add text to a picture?
QPS fails to go up due to frequency limitation of public network CLB bandwidth
Making CSR file for face core
How to solve the problem of large traffic audio audit? What are the common approval methods?
Is it possible to transfer files on the fortress server? How to operate?
How to separate image processing? What should I pay attention to when separating layers?
Emmet syntax specification
WinDbg loads mex DLL analysis DMP file
Troubleshooting of black screen after easynvr is cascaded to the upper platform and played for one minute
