当前位置:网站首页>Oracle database self study notes
Oracle database self study notes
2022-06-26 08:02:00 【qq_ forty-five million seven hundred and thirty-two thousand fi】
summary

edition

PL/SQL brief introduction


Create an account , Connect to database
Log in as an administrator first : ./as sysdba Then create a user name and password , to grant authorization , Just connect and log in

Oracle data type



Modify table
Modify the name of the table , Change column names , Add columns , Modify the column ( data type , length , The default value is ), Delete column
Modify the name of the table
rename student to studentsadd to address- Column
alter table students add address varchar2(2);modify address Column
alter table students modify address varchar2(200);Change column names address by stu_address
alter table students rename column address to stu_address;Delete column stu_address
alter table students drop column stu_address;
DML Data operation language
- insert data ( The data type here is :number,varchar2,char,date)
insert into students values(1,‘xiaoming’,‘f’,1.23,‘01-12 month -1997’);
insert into students(id,name)values(2,‘admin’); - update Modifying data
update students set height =1.45,birth=‘12-12 month -1998’ where id=2; - delete Delete data
delete from students where id=2;
TCL Transaction control language
commit,rollback
truncate Clear the table
truncate table students;
select Basic syntax of statements
select*from emp;
Arithmetic operator + - * /
selecte ename,sal*12 from emp;
Alias the list
select ename as name;
distinct: Remove duplicate lines
select distinct deptno from emp;
Strings and string functions

- Returns the value of a string connection
select concat(‘hello’,‘students’)from dual; The virtual table is used here , Because the link string does not need a table
select ‘sdfsa’||'sdfaf’from dual; there || Function and concat It's the same thing - Returns the length of the string ;
select length(‘sfasfd’)from dual;
select length(ename)from emp;// Return the length of the field in the table - upper,lower,initcap
upper All characters are capitalized ,lower All characters become lowercase ,initcap The first letters of all words are capitalized
select upper(ename),lower(ename),initcap(‘i am students’)from emp; - Functions that intercept strings
trim: Intercept both sides of the string select trim(‘e’ from ‘ehelle’)from dual;
ltrim: Intercept the left side of the string select ltrim(‘ehelle’,‘e’)from dual;
rtrim: Intercept the right side of the string select rtrim(‘ehelle’,‘e’)from dual; - Complement function : Not enough digits , Will be made up $ Symbol
Left filling :lpad Right complement : rpad
select lpad(sal,10,’ $ ‘)from emp;
select rpad(sal,10,’ $ ')from emp; - Intercept function substr( String to intercept , Start with number one , section ? How many characters )
select substr(‘hello’,2,3)from dual; - Get the index of the character ( I don't know much about anything )
select instr(‘hello’,‘l’)from dual;
Numeric types and numeric functions
- round( Floating point data , Reserve the number of digits ) Round function
select round(23.237,2)from dual;
** Be careful :** If the reserved digits are negative , Indicates the number of bits intercepted to the integer digit ; If the reserved digits are 0, Indicates that only integers are reserved - Truncation function trunc( Floating point data , Reserve the number of digits )
select trunc(234.342,2)from dual; - mod The remainder of two numbers
select mod(3,2)from dual; - ceil and floor
ceil: Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to one decimal
floor: Returns the largest integer less than or equal to one decimal
select ceil(45.234)from dual; select floor(45.234)from dual;
Date type and date function
- sysdate Get current system time systimestamp The time format obtained is more accurate , Time zone can be displayed
select sysdate from dual; It's not accurate to seconds , The following functions can be used for conversion
select to_char(sysdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss’)from dual;
select systimestamp from dual; - to_char Convert date type to string type
to_char( date , Format string )
Format specification :
for example : Convert the system time to the following format 2017 year 12 month 1 Japan
select to_char(sysdate,‘yyyy" year "mm" month "dd" Japan "’)from dual; - to_date( character string , Format string ) Convert string date to date type
select to_date(‘2000-01-01’,‘yyyy-mm-dd’)from dual; - last_day Returns the last day of the current month
select last_day(sysdate)from dual; - next_day Return the date of today one month later
select add_months(sysdate,1)from dual; - months_between Returns the number of months between two dates
select months_between(sysdate,hiredate)from emp; - next_day The day of the week next to the current date
select next_day(sysdate,2)from dual; This is back next week 1 Date
NULL And general functions
null Do arithmetic , The result is null
Use generic functions to solve this problem
The generic function :nvl nvl2
select nvl(null,2)from dual; Indicates that the first value is not empty , Returns the value of the first , Otherwise return the second value
select nvl2(1,2,3)from dual; Indicates that the first value is not empty , Just return the second value , Otherwise, return to the third
nvl solve null problem ( here comm May be null)
select ename,sal+nvl(comm,0)from emp;
Or use nvl2
select ename,sal+nvl2(comm,comm,0)from emp;
Import test table

imp system/admin fromuser=scott touser=scott file=d:/scott.dmp
Operator
- any and all Conditional operator

Query salary greater than (2500,3000,5000) Employee information
selec*from emp where sal>any(2500,3000,5000); - Other operators between… and…,like, is null
between… and…
likeRepresents a placeholder
Aggregate functions
min(),max(),sum(),avg(),count()
All aggregate functions are ignored null The calculation of
for example :select avg(comm)from emp; There are only those that are not empty comm Only rows participate in the operation
** There is a conclusion ( Although I don't quite understand ):** Columns not contained by the grouping function , Must be rough now group by Behind
Relational query
When querying two tables , If you do not specify query criteria , The result would be the Cartesian product of two tables .
for example :select emp.*,dname,loc from emp,dept;
** Internal connection query :** Find out the data that meets the conditions …inner join …on…
for example : Check the basic information of employees , Department name
select emp.*,dname
from emp inner join dept
on emp.deptno=dept.deptno
Use table aliases
select e.,dname
from emp e inner join dept d
on emp.deptno=dept.deptno
About alias specification : To use aliases , that sql The alias should be used everywhere in the statement , No use, no use
Omit inner join Internal connection query
select e.,dname from emp e,dept d where e.deptno=d.deptno( namely : By default, the inner join query is used )
** Be careful :** Multi table join query , link n Tables , At least have n-1 Valid conditions
External connection query
In addition to finding out the data that meet the conditions , We should also find out the data that do not meet the conditions
** classification :** Left outer connection query , Right outer connection query , Full external connection query
Left lateral :…left join…on…
Right outside :…right join…on…
Full outer join :…full join…on…
Self connect query
This is achieved by virtualizing the table into two tables with aliases , Can make equivalent or unequal connection
for example : Query the employee's name and the name of other department managers
select e.ename,m.ename
from emp e,emp m
where e.mgr=m.empno
Subquery
According to the execution order of sub query and main query, it is divided into : Standard subquery ( Execute subquery first ) Correlation subquery ( Execute main query first )
Examples of related sub queries : Query employee information whose salary exceeds the average salary of the Department
select*from emp e where sal>(select avg(sal)from emp where deptno=e.deptno);
First, execute the main query , Then use the results of the main query for the sub query
select*from emp group by deptno having sal>avg(sal)
Paging query
 **rownum:* Query a row and add a row number , from 1 Start adding... In sequence
**rownum:* Query a row and add a row number , from 1 Start adding... In sequence
for example :
Query all the data in the first row of the table :
select emp. from emp where rownum=1;
Query all the data in the first three rows of the table :
select emo.* from emp where rownum<=3;
Query all data after three rows in the table :
select emo.* from emp where rownum>=3;
** Be careful :* There is not a single piece of data here , because rownum Is a pseudo column , That is, find out a line number assigned to it , The first data line number is 1, We can't find out , There is no way to check the others
take rownum As data that can be used in the result set , This is achieved through the inline view
The above query can be implemented in the following ways :
select from (select emp.,rownum rn from emp)where rn>=3
The realization of paging function
selectfrom(select emp.*,rownum rn from emp)where rn between 11 and 20;
decode Functions and case sentence
 for example : Look up the employee table , Calculate the amount of bonus according to the position of the employee
for example : Look up the employee table , Calculate the amount of bonus according to the position of the employee
Position is manager:12 Double salary ; analyst:11 Double salary ; other : The original wage
select ename,job,sal,
decode(job,‘manager’,sal12,
‘analyst’,sal11,
‘salseman’,sal*5,
sal)bonus
from emp;
---------------- Use case Realization
select ename,job,sal,case job when ‘manager’ then sal12
when ‘analyst’ then sal1.1
when ‘salseman’ then sal*5
else sal
end bonus
from emp;
Count the number of people ,analyst/manager Belong to vip, Everything else belongs to operation,vip and opeation Count
select decode(job,
‘manager’,‘vip’,
‘analyst’,‘vip’,
‘operation’) job,
count(*)
from emp
group by decode(job,
‘manager’,‘vip’,
‘analyst’,‘vip’,
‘operation’);
Sorting function
for example : Group by Department , According to sal Sort
**row_number(): ** If the same data is encountered during sorting , The ranking will increase in turn , There won't be the same ranking
select ename,deptno,sal,
row_number()
over(partition by deptno order by sal)
as emp_no
from emp
**rank(): ** If the same data is encountered during sorting , The ranking will be the same , But the ranking of the next data will jump
select ename,deptno,sal,
rank()
over(partition by deptno order by sal)
as emp_no
from emp
**dense_rank(): ** If the same data is encountered during sorting , The ranking will be the same , The ranking of the next data will not jump
select ename,deptno,sal,
dense_rank()
over(partition by deptno order by sal)
as emp_no
from emp
Set operations

UNION Combine : After the union of two sets , Merge the results of the two sets into one piece and remove the duplicate parts .
UNION ALL Combine : After the union of two sets , The repetition will not be removed .
INTERSECT intersection : Show data that exists in both result sets at the same time
MINUS Cross sets : Only data in the first result set that does not exist in the second result set
for example : The inquiry work is manager Of employees and salaries are greater than 2500 The employees'
select ename,job,sal from emp
where job=‘manager’
union (union all intersect minus)
select ename,job,sal from emp
where sal>2500
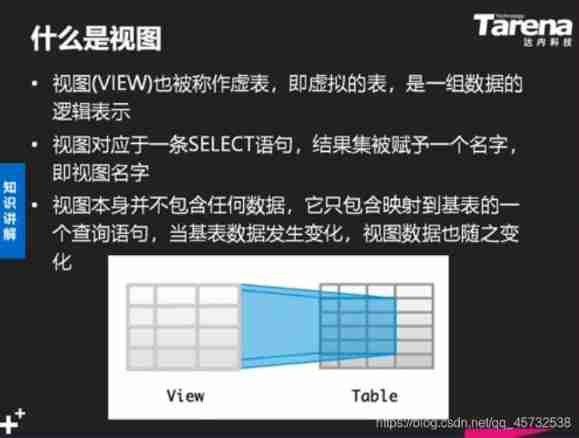
View


Create view :create or replace view view_name
as
select Clause
Add... Here or replace Express : If it doesn't exist, create a view , Modify the view if it exists
for example :create or replace view v_emp as select ename,hiredate from emp;
Read only view read only
create or replace view v_emp
as
select ename,hiredate
from emp
with read only;
Delete view drop
drop view v_emp;
Sequence
** What is sequence :** Is a database object used to generate unique data values
** effect :** The primary key value used to generate the table
The definition of sequence :
create sequence dept_seq
start with 100
increment by 10
Usage sequence :
nextval: Get the next value on the sequence
select dept_seq.nextval from dual;
currval: Get the current value on the sequence
select dept_seq.currval from dual;
Delete sequence :
drop sequence dept_seq
Indexes





Create index
create index index_name on table_name(column): Indicates which column of which table is used to create the index
When I make the following query, I will automatically use the index to improve the query efficiency :select*from emp where ename =‘king’;
Delete index
drop index emp_ename;
constraint


How to define constraints
There are two ways , Below sql It's all reflected in
create table test1(tid number(4) primary key,
name varchar2(30) not null, // These two add constraints when creating table fields
email varchar2(40),
gender char(1),
constraint email_un unique(email),
constraint gender_ck check(gender=‘F’ or gender=‘M’)// These two are to add constraints to the fields after they are created , And specify the constraint name
)
Foreign keys
Be careful : A table with a primary key is called a primary key table ; A table with foreign keys is called a foreign key table 
create table dept1(
deptno number(4) primary key,
dname varchar2(30),
loc varchar2(40)
)
create table emp1(
empno number(4) primary key,
ename varchar2(30),
deptno,
constraint emp1_dept_fk foreign key(deptno)references dept1(deptno) // Here is to deptno Field add foreign key constraint
)
** Be careful :** After adding foreign key constraints to the table , The value in this field must exist in the primary key list , Otherwise, an error will be reported
insert into dept1 values(10,‘it’,‘beijing’);
insert into emp1 values(1,‘admin’,10);
insert into emp1 values(2,‘admin’,20);
Add constraints to table fields
alter table Table name to add add constraint t2_pk primary key( The name of the field to add );
PL/SQL — It's a programming language





–1. Only the execution part is defined
begin
dbms_output.put_line(‘hello !’);
end;
–2. Contains the declaration and execution part
declare
v_ename varchar2(30);– Defining variables
begin
select ename into v_ename from emp– Find out the values in the table and assign them to variables
where empno=7839;
dbms_output.put_line(v_ename);– Output the value of the variable
end;
–3. Contains examples of declaration execution and exception sections
declare
v_ename varchar2(30);– Defining variables
begin
select ename into v_ename from emp– Find out the values in the table and assign them to variables
where empno=123;
dbms_output.put_line(v_ename);– Output the value of the variable
exception
when no_data_found then -- When this exception occurs, execute the following command
dbms_output.put_line(‘ Check no one !’);** Be careful :** Here the string should use single quotation marks
end;
identifier

Variable


Define basic data types 
The column type of the reference table
** Format :** Table name . Field name %type
for example :
Record type
Format :
type Type name is record(
Variable name 1,
Variable name 2,
…
);
for example :
Reference record type
Format : Table name %rowtype
Flow control statement
IF sentence


if give an example
--if
declare
v_age number(3):=18;
begin
if(v_age>=18) then
dbms_output.put_line(' You can get a driver's license !');
end if;
end;
--if else
declare
v_age number(3):=10;
begin
if(v_age>=18) then
dbms_output.put_line(' You can get a driver's license !');
else
dbms_output.put_line(' You can't get a driver's license !');
end if;
end;
-- if elseif else
declare
v_age number(3):=12;
begin
if(v_age>=18) then
dbms_output.put_line('>=18');
elsif(v_age>=16) then
dbms_output.put_line('>=16');
elsif(v_age>=12) then
dbms_output.put_line('>=12');
else
dbms_output.put_line('default!');
end if;
end;
while Loop statement



-- Print 1 To 10
--loop loop
declare
v_x number(4):=1;
begin
loop
dbms_output.put_line(v_x);
v_x:=v_x+1;
exit when v_x>10;-- You can change this line to if(v_x>10)then exit;end if;
end loop;
end;
--while loop
declare
v_x number(4):=1;
begin
while v_x<=10 loop
dbms_output.put_line(v_x);
v_x:=v_x+1;
end loop;
end;
--for loop
begin
for i in 1..10 loop
dbms_output.put_line(i);
end loop;
end;
The cursor
Pointer to query result , Which record does the pointer point to , What is extracted is the data of which record 
** Be careful :** Every time a piece of data is fetched from the cursor , The cursor pointer moves down 
The use of cursors
-- Inquire about 10 Name and salary of the employee in department No
declare
v_ename emp.ename%type;
v_sal emp.sal%type;
cursor emp_cursor is select ename,sal from emp where deptno<100;
begin
open emp_cursor;
fetch emp_cursor into v_ename,v_sal;
while emp_cursor%found loop
dbms_output.put_line(v_ename||','||v_sal);
fetch emp_cursor into v_ename,v_sal;-- The purpose of this line is to manually move the pointer down
end loop;
end;
Parameterized cursors
The query parameters are not written , You can query which department you want to transfer in
declare
v_ename emp.ename%type;
v_sal emp.sal%type;
cursor emp_cursor(p_deptno number) is select ename,sal from emp where deptno<p_deptno;-- Here, a formal parameter is defined when defining a cursor ,
begin -- Pass in an argument when opening the cursor
open emp_cursor(100);
fetch emp_cursor into v_ename,v_sal;
while emp_cursor%found loop
dbms_output.put_line(v_ename||','||v_sal);
fetch emp_cursor into v_ename,v_sal;
end loop;
end;
The cursor for loop
declare
cursor emp_cursor is
select ename,sal from emp where deptno<100;
begin
for e in emp_cursor loop
dbms_output.put_line(e.ename||','||e.sal);
end loop;
end;
Cursors with parameters for loop
declare
cursor emp_cursor(p_deptno number) is
select ename,sal from emp where deptno<p_deptno;
begin
for e in emp_cursor(1200) loop
dbms_output.put_line(e.ename||','||e.sal);
end loop;
end;
Use of implicit cursors
there sql Is an implicit cursor 
abnormal


Predefined exceptions
This exception is defined in the program , There is an exception name and its corresponding number
–no_data_found
declare
v_ename emp.ename%type;
begin
select ename into v_ename from emp where empno=111;
dbms_output.put_line(v_ename);
exception -- This means that this is an exception handling block
when no_data_found then -- This is an exception where the data is not found
dbms_output.put_line(' There is no such person ');
end;
–to_many_rows
declare
v_ename emp.ename%type;
begin
select ename into v_ename from emp where empno<10000;
dbms_output.put_line(v_ename);-- There is no way to use a variable to accept multiple types of values
exception
when too_many_rows then
dbms_output.put_line(' Too many values returned ');
end;
–others You can match multiple exception types If there are multiple exceptions to handle ,others Be sure to put it at the end
Non predefined exception
It is also an exception defined in the program , Only the number without exception name **
How to handle non predefined exceptions : Because non predefined exceptions have only numbers but no names , So we need to declare an exception variable before processing , Bind the custom exception name and number when calling a function , The next process is the same
declare
e_exception exception;
pragma exception_init(e_exception,-02291);-- Bind exception name and exception number
begin
insert into emp values(119,'admin',null,null,null,50);
exception
when e_exception then
dbms_output.put_line(' No, 50 Department No ');
dbms_output.put_line(' Wrong number '||sqlcode||','||' error message '||sqlerrm);
end;
Two functions commonly used in exceptions :sqlcode Returns the number of the current exception ;sqlerrm Returns the description of the current exception
Functions and stored procedures
Just give ps/sql Give the block a name , If you use function The name , This block is a function , If you use proceder Is the process 


function
– Returns the system date function ( No arguments ),'yyyy-mm-dd’
create or replace function getDate
return varchar2
is
v_date varchar2(12);
begin
v_date:=to_char(sysdate,'yyyy-mm-dd');
return v_date;
end;
-- Call function
declare
v_date varchar2(12);
begin
v_date:=getDate; -- Call function , No parameters are required
dbms_output.put_line(v_date);
end;
– Return the employee's name by the employee's number
create or replace function getName(p_empno number)
return varchar2
is
v_ename emp.ename%type;
begin
select ename into v_ename from emp
where empno=p_empno;
return v_ename;
end;
-- Call function
declare
v_ename varchar2(30);
begin
v_ename:=getName(1200);
dbms_output.put_line(v_ename);
end;
– Returns the sum of two data , Bad
– Because there are two values to be returned , So the output parameter is used here p_x
– The other two are the default input parameters
create or replace function getResult(p_a number,p_b number,p_x out number)
return number
is
v_sum number(4);
begin
v_sum:=p_a+p_b;
p_x:=p_a-p_b;
return v_sum;
end;
**-- Call function **
declare
v_result number(4);
v_x number(4);
begin
v_result:=getResult(2,1,v_x);
dbms_output.put_line(v_result);
dbms_output.put_line(v_x);
end;
The process
The difference between a function and a procedure is that a function must have a return value , But the procedure has no return value , But a procedure can define output parameters , So the process can also complete the output function
– The process ( The keyword has changed , Everything else is the same )
– Return system date
create or replace procedure getDate1(p_date out varchar2)
is
begin
p_date:=to_char(sysdate,'yyyy-mm--dd');
end;
-- Call function
declare
v_date varchar(12);
begin
getDate1(v_date);
dbms_output.put_line(v_date);
end;
package
Equivalent to a set or combination , A collection of related procedures and functions
Be similar to Java The concept of classes in languages ,

** Be careful :** The package body name must be the same as the package name you defined
– Definition dept Examples of adding, deleting, modifying, and querying tables , By package
– Definition package
create or replace package depttools
is
function addDept(p_deptno number,p_dname varchar2,
p_loc varchar2)return number;
function updateDept(p_deptno number,p_dname varchar2,
p_loc varchar2)return number;
procedure getAll;
procedure deleteDept(p_deptno number);
end;
– Define package entities
create or replace package body depttools
is
--addDept The implementation of the
function addDepts(p_deptno number,p_dname varchar2,p_loc varchar2)return number
is
begin
insert into dept values(p_deptno,p_dname,p_loc);-- Implicit cursors are used here
if sql%found then
commit; -- Submit after successful execution
return 1;
else
return 0;
end if
end;
--updateDept The implementation of the
function updateDept(p_deptno number,p_dname varchar2,
p_loc varchar2)return number
is
begin
update dept set dname=p_dname,loc=p_loc where deptno=p_deptno;
if sql%found then
commit;
return 1;
else
return 0;
end if;
end;
--getAll The implementation of the
procedure getAll
is
cursor dept_cursor is select*from dept;
begin
for d in dept_cursor loop
dbms_output.put_line(d.deptno||','||d.dname);
end loop;
end;
--deleteDept The implementation of the
procedure deleteDept(p_deptno number)
is
begin
delete from dept where deptno=p_deptno;
commit;
end;
end;
– test
declare
v_x number;
begin
v_x:=depttools.addDept(50,'HR','BEIJING');
v_x:=depttools.updateDept(50,'IT','HANGZHOU');
depttools.deleteDept(50);
end;
SELECT*from EMP;
边栏推荐
- The long path of Xiao Sha (graph theory, Euler diagram)
- PyTorch-12 GAN、WGAN
- Baoyan postgraduate entrance examination interview - Network
- Click the button to call the system browser to open Baidu home page
- Livevideostackcon | evolution of streaming media distribution for online education business
- Detailed explanation and code implementation of soft voting and hard voting mechanism in integrated learning
- [UVM practice] Chapter 2: a simple UVM verification platform (4) the ultimate masterpiece of UVM: sequence
- 我想造SQL数据(存储结构)
- Pycharm settings
- Chapter VII (structure)
猜你喜欢

Color code

Basic use of swiperefreshlayout, local refresh of flutterprovider

Detailed explanation and code implementation of soft voting and hard voting mechanism in integrated learning

Web technology sharing | webrtc recording video stream

Data governance: from top project to data culture!

Apache inlong graduated as a top-level project with a million billion level data stream processing capability!

The 9th zero code training camp is officially open for registration! (Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou and Shenzhen)

Quickly upload data sets and other files to Google colab ------ solve the problem of slow uploading colab files

JMeter performance testing - Basic Concepts

Chapter 4 (functions and preprocessing)
随机推荐
Pic 10B parsing
OSPF design principles, commands take H3C as an example
我想要股票账户优惠开户,如何操作?手机开户安全么?
Informatics Orsay all in one 1354: bracket matching test
Win11 open folder Caton solution summary
What are the characteristics of digital factory in construction industry
Rewrite string() method in go language
Project management learning
信息学奥赛一本通 1355:字符串匹配问题(strs)
Redis (4) -- Talking about integer set
Chapter 4 (functions and preprocessing)
ReW_ p
Basic use of swiperefreshlayout, local refresh of flutterprovider
Flower instruction WP
JWT in go
Is it legal to open an account for compass stock trading software? Is it safe?
Junit
Livevideostackcon | evolution of streaming media distribution for online education business
Chapter VIII (classes and objects)
Hand drawn style chart library chart Implementation principle of xkcd