当前位置:网站首页>High level application of SQL statements in MySQL database (II)
High level application of SQL statements in MySQL database (II)
2022-06-24 22:39:00 【The strongest flying thunderobot Watergate】
1、CREATE VIEW View
View : Can be treated as a virtual table or stored query .
The difference between a view and a table is , There are actually stored data in the table , And a view is a structure built on a table , It doesn't actually store data itself .
The temporary table disappears automatically after the user exits or disconnects from the database , The view does not .
Views don't contain data , Just store its definition , Its purpose is to simplify complex queries . For example, you need to connect and query several tables , But also to carry out statistical sorting and other operations , Write SQL Statements can be cumbersome , Connect several tables with a view , Then query the view , Just like querying a table , Very convenient .
grammar :CREATE VIEW View table name AS SELECT sentence ;
example :
select A.region,SUM(B.money) from REGION AS A inner join FARE AS B on A.site = B.site GROUP BY region;
create view ST AS select A.region,SUM(B.money) from REGION AS A inner join FARE AS B on A.site = B.site GROUP BY region;
show tables;
select * from ST;
drop view ST;
# Delete view table 

2.UNION combine
Put two SQL The results of the statement are combined , Two SQL The fields generated by the statement need to be the same data type
UNION: There will be no duplicate data values for the generated results , And sort according to the order of the fields
SELECT sentence 1 UNION SELECT sentence 2;
or
SELECT sentence 1 UNION ALL SELECT sentence 2;
#UNION ALL: List the data values of the generated results , With or without repetition
example :
select region from REGION union select money from FARE;
select site from REGION union select site from FARE;
select site from REGION union all select site from FARE;


3. Intersection value
Take two. SQL The intersection of statement results
example :
select * from FARE;
select * from REGION;
select site from (select A.site from FARE A inner join REGION B on A.site = B.site) C group by C.site;
select site from FARE where site in (select site from REGION);
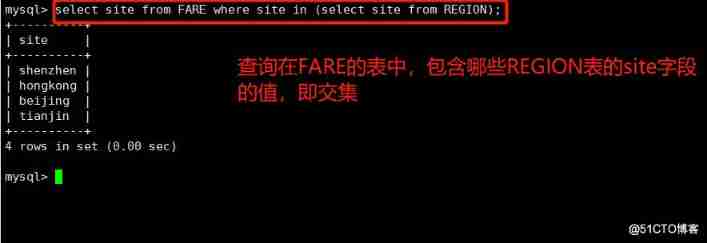
4. No intersection value
Show the first SQL Result of statement , And with the second SQL Statement has no result of intersection , It can't be repeated
example :
select distinct site from FARE where (site) not in (select site from REGION);
select A.,B. from FARE A left join REGION B using(site);
select distinct site from FARE A left join REGION B using(site) where B.site is null;
5.CASE
yes SQL Used as a IF-THEN-ELSE And so on
usage :
SELECT CASE ( Field name )
WHEN Conditions 1 THEN result 1
WHEN Conditions 2 THEN result 2
……
ELSE result N
END
FROM Table name
# The condition can be a numerical value or a formula , And ELSE Clause is not required
example :
select * from FARE;
mysql> select case site
-> when ‘najing’ then money + 500
-> when ‘tianjin’ then money - 500
-> else money * 2
-> end
-> A,site
-> from FARE;
3、 ... and 、 Regular expressions
The specific application is shown in the following table :
Matching mode describe example
^ Match the start character of the text ‘^bd’ Match with bd Starting string
$ Match the end character of the text ‘qn$’ Match with qn a null-terminated string
. Match any single character ‘s.t’ Match any s and t A string with one character between
***** Match zero or more characters before it ‘fo*t’ matching t There is any one in front o
- Match preceding characters 1 Times or times ‘hom+’ Match with ho start , At least one back m String
character string Match contains the specified string ‘clo’ The match contains clo String
[…] Match any character in the character set ‘[abc]’ matching a perhaps b perhaps c
[^…] Match any characters that are not in brackets ‘[^ab]’ Match does not contain a perhaps b String
{n} Match the previous string n Time ‘g{2}’ The match contains 2 individual g String
{n,m} Match the previous string at least n Time , at most m Time ‘f{1,3}’ matching f least 1 Time , most 3 Time
p1 p2 matching p1 or p2
usage :
SELECT Field FROM Table name WHERE Field REGEXP Matching mode
example :
select * from FARE where site regexp ‘ [1]’;
select * from FARE where site regexp ‘[n]’;
select * from FARE where site regexp ‘jin|jing’;
Four 、 stored procedure
1. summary
A stored procedure is a set of functions to accomplish SQL Statement set
And I learned before Shell The function is almost , In essence, it is the reuse of code
Further details :
In the process of using stored procedures, common or complex work is used in advance SQL The statement is written and stored with a specified name
This process is compiled and optimized and stored in the database server
When you need to use this stored procedure , Just call it
Stored procedures perform better than traditional SQL Faster , More efficient execution
2. Advantages of stored procedures
After one execution , The generated binary code will reside in the buffer , Improve execution efficiency
SQL Statement plus a collection of control statements , High flexibility
Store on the server side , When called by the client , Reduce network load
Can be called repeatedly , Can be modified at any time , Does not affect client calls
Can complete all database operations , You can also control the information access rights of the database
3. Create stored procedure
DELIMITER $$ # Change the closing sign of the statement from a semicolon ; Temporary modification , In case something goes wrong , You can customize
CREATE PROCEDURE XXX() # Create stored procedure , Custom procedure name ,() With parameters
BEGIN # The process body takes the keyword BEGIN Start
select * from xxx; # Process style sentences
END$$ # The process body takes the keyword END ending
DELIMITER ; # Returns the ending symbol of the statement to a semicolon
example :
mysql> delimiter $$
mysql> create procedure XCF()
-> begin
-> select * from FARE;
-> end $$
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> delimiter ;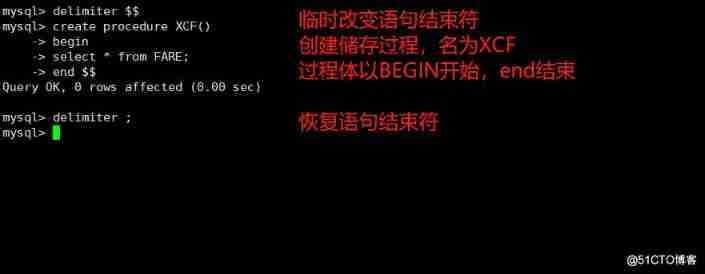
4. Calling stored procedure
CALL XCF;
5. View stored procedures
usage :
show create procedure [ database .] Stored procedure name ; # View the specific information of a stored process
show create procedure XXX;
show procedure status [like ‘%XXX%’] \G
example :
show create procedure train_ticket.XCF\G
show procedure status like ‘%XCF%’\G
6. Parameters of stored procedure
IN Input parameters : Indicates that the caller passes a value... To the procedure ( The incoming value can be literal or variable )
OUT Output parameters : Indicates that the procedure passes out a value to the caller ( Multiple values can be returned )( Outgoing values can only be variables )
INOUT Input/output parameter : It means that the caller passes in a value to the procedure , It also indicates that the procedure passes out a value to the caller ( Values can only be variables )
example :
mysql> delimiter $$
mysql> create procedure XCF0(IN place char(20))
-> begin
-> select * from FARE where site=place;
-> end $$
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> delimiter $$
mysql> call XCF0(‘nanjing’);
-> $$
±--------±------±-----------+
| site | money | date |
±--------±------±-----------+
| nanjing | 2000 | 2021-02-07 |
±--------±------±-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> delimiter ;
7. Delete stored procedure
The method to modify the contents of stored procedures is to delete the original stored procedures , Then create a new stored procedure with the same name
usage :
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS Proc;
# Delete... Only if it exists , If the specified procedure does not exist , Then there will be a mistake
example :
drop procedure if exists XCF0;
8. Control statement of stored procedure
8.1 Conditional statements (if)
mysql> DELIMITER $$
mysql> CREATE PROCEDURE XCF1(IN num int(10))
-> BEGIN
-> declare var int;
-> set var=num*2;
-> if var>=10 then
-> update FARE set money=money+1;
-> else
-> update FARE set money=money-1;
-> end if;
-> END $$
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> DELIMITER ;
CALL XCF1(5);
CALL XCF1(4);
# Call procedure body
select money from FARE;
8.2 Loop statement (while)
Copy
mysql> create table xcf(id int(5));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> DELIMITER $$
mysql> CREATE PROCEDURE XCF2()
-> BEGIN
-> declare var int;
-> set var=0;
-> while var<9 do
-> insert into xcf values(var);
-> set var=var+1;
-> end while;
-> END $$
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> CALL XCF2;
-> $$
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from xcf;
-> $$
±-----+
| id |
±-----+
| 0 |
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
| 6 |
| 7 |
| 8 |
±-----+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
n ︎
边栏推荐
- Web security XSS foundation 06
- Extend your kubernetes API with aggregated apiserver
- YGG 近期游戏合作伙伴一览
- find your present (2)
- 系统测试主要步骤
- 理想L9,智能座舱新潮流
- MySQL + JSON = King fried!!
- 1. fully explain the basic principles of IPSec
- [personal experiment report]
- The usage difference between isempty and isblank is so different that so many people can't answer it
猜你喜欢

Chapter 10 project stakeholder management

面试害怕被问MySQL相关问题 ?这份三万字精华总结 + 面试100 问,吊打面试官完全够了

系统测试主要步骤
How to solve the problem that the computer suddenly can't connect to WiFi

华大04a工作模式/低功耗模式

Yyds dry goods inventory junit5 learning II: assumptions class

Selection and comparison of message oriented middleware MQ

Industrial development status of virtual human

Kubevela v1.2 release: the graphical operation console velaux you want is finally here

Technology Review: what is the evolution route of container technology? What imagination space is there in the future?
随机推荐
In the first year of L2, arbitrum nitro was upgraded to bring more compatible and efficient development experience
Disk structure
Online filing process
NiO, bio, AIO
[QT] QT event handling
DX 的 HLSL 和 GL 的 GLSL的 矩阵构建的行列区别
2022-06-10 工作记录--JS-获取到某一日期N天后的日期
Heartless sword Chinese English bilingual poem 003 The sea of books
OSPF basic content
socket(1)
CDN principle
Interrupt, interrupted, isinterrupted differences
系统测试主要步骤
【个人实验报告】
Web security XSS foundation 06
ansible基本配置
Description of software version selection of kt6368a Bluetooth dual-mode transparent chip
Servlet details
Seven principles of software design
MySQL + JSON = King fried!!
