当前位置:网站首页>Introduction, architecture and principle of kubernetes
Introduction, architecture and principle of kubernetes
2022-07-24 06:42:00 【Magic dance Tsinghua】
Official website document address :https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/home/ (k8s There are official detailed documents , The best way to learn is to go to the official website )
kubernetes brief introduction
Kubernetes It is an automatic container arrangement platform , It is responsible for the deployment of applications 、 Application flexibility and application management . It can provide many functions , Generally speaking kubernetes It is a container cloud steward , It manages and orchestrates containers ,kubernetes The following functions can be provided :
Service discovery and load balancing
Kubernetes have access to DNS Name or own IP Address disclosure container , If the flow into the container is large , Kubernetes Can load balance and distribute network traffic , So that the deployment is stable
Storage choreography
Kubernetes Allows you to automatically mount the storage system of your choice , For example, local storage 、 Public cloud providers, etc .
Automatic deployment and rollback
You can use Kubernetes Describes the required state of the deployed container , It can transfer the actual state at a controlled rate Change to the desired state . for example , You can automate Kubernetes To create a new container for your deployment , Delete existing containers and use all their resources for new containers .
Automatically complete the packing calculation
Kubernetes Allows you to specify what each container needs CPU And memory (RAM). When the container specifies a resource request ,Kubernetes Better decisions can be made to manage the container's resources .
Self repair
Kubernetes Restart the failed container 、 Replace the container 、 Kill does not respond to user-defined Health check container , And don't advertise the service to the client until it's ready .
Key and configuration management
Kubernetes Allows you to store and manage sensitive information , For example, password 、OAuth Token and ssh secret key . You can deploy and update the key and application configuration without rebuilding the container image , There is no need to expose the key in the stack configuration
… etc.
kubernetes Cluster architecture
kubernetes It uses master-node framework .
Master As the central control node , Will go with Node Make a connection . client ( such as UI/CLI etc. ) Only with Master Connect , Send the desired state or order to Master,Master These commands or states will be sent to the corresponding nodes , Carry out the final execution
- master: Master node , There may be a lot of
- node: Work node , quite a lot , The application of real work

working principle
Master
Kubernetes Of Master There are four main components :kube-apiserver、kube-controller、kube-scheduler as well as etcd, As shown in the figure below . We usually call it Master The node is the control surface (Control Plane), This of the control surface 4 Components make global decisions about the cluster ( For example Pod Schedule to a suitable node ), And detecting and responding to cluster Events .
master There are some core components on the node :
- Controller Manager: Control Manager , It is used to manage the cluster state
- etcd: Key value database , It's a distributed storage system ,API Server All the original information needed in is placed in etcd in ,etcd Itself is a highly available system , adopt etcd Guarantee the whole Kubernetes Of Master High availability of components
- scheduler: Scheduler ,“ Scheduler ” As the name implies, it is to complete the scheduling operation , This component monitors those newly created Pod, And select the node that conforms to the regulation to let Pod Run on . The factors considered in scheduling decision include single Pod and Pod Aggregate resource requirements 、 Hardware / Software / Policy constraints 、 Affinity and anti affinity norms 、 Data location 、 Interference between workloads, etc .
- api server:api gateway , As the name suggests, it is used to deal with API Operation of the ,Kubernetes All of the components in will be associated with API Server Connect , There is no independent connection between components , Rely on a API Server To transmit messages

Node
Kubernetes Of Node It's really running the business load , Each business load will be loaded with Pod Form operation . One Pod Run in one or more containers , To really run these Pod The component of is called kubelet, That is to say Node The most critical component on , It passes through API Server Receive what you need Pod State of operation , And then submit this Container Runtime Components ( A simple understanding is what we usually call a container ) in .
node node (worker Work node ):
- kubelet: This is the most important component running on each work node ,kubelet Receive a set of PodSpecs( That is to say Pod The expected state of ), Make sure these PodSpecs The container described in is running and healthy .
- kube-proxy: agent . Agent network ,kube-proxy Maintain network rules on nodes . These network rules allow you to interact with Pod Network communication . It is the realization of Kubernetes Service Important components of the concept .
- Pod: Pod yes Kubernetes A minimum scheduling and resource unit of . The user can go through Kubernetes Of Pod API Produce a Pod, Give Way Kubernetes For this Pod To schedule , That is to put it in a certain Kubernetes Running on managed nodes . One Pod It's an abstraction of a set of containers , It will contain one or more containers .
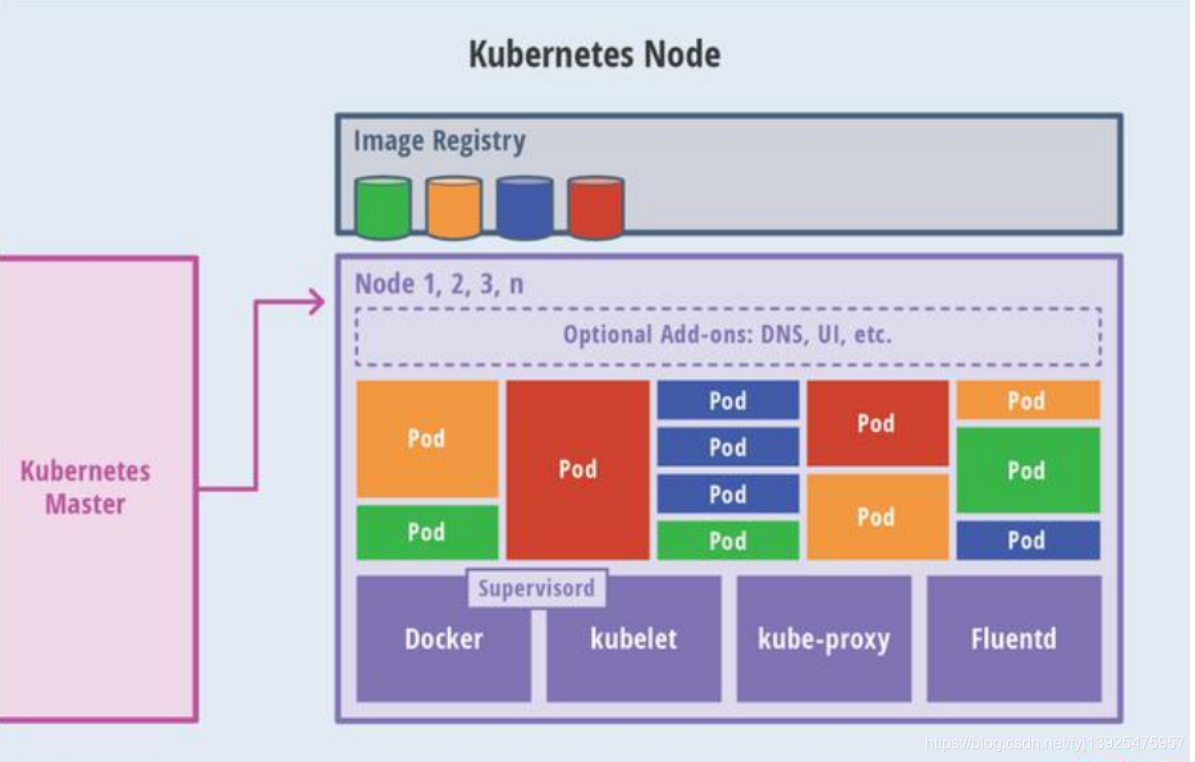
Master and node The node interaction is shown in the following figure :

It's important to note that ,Kubernetes Of Node It will not interact directly with users , Its interaction will only be through Master, User pass Master Send information to the node .Kubernetes Every Node On , Will run the components mentioned just now .
Principle of component interaction
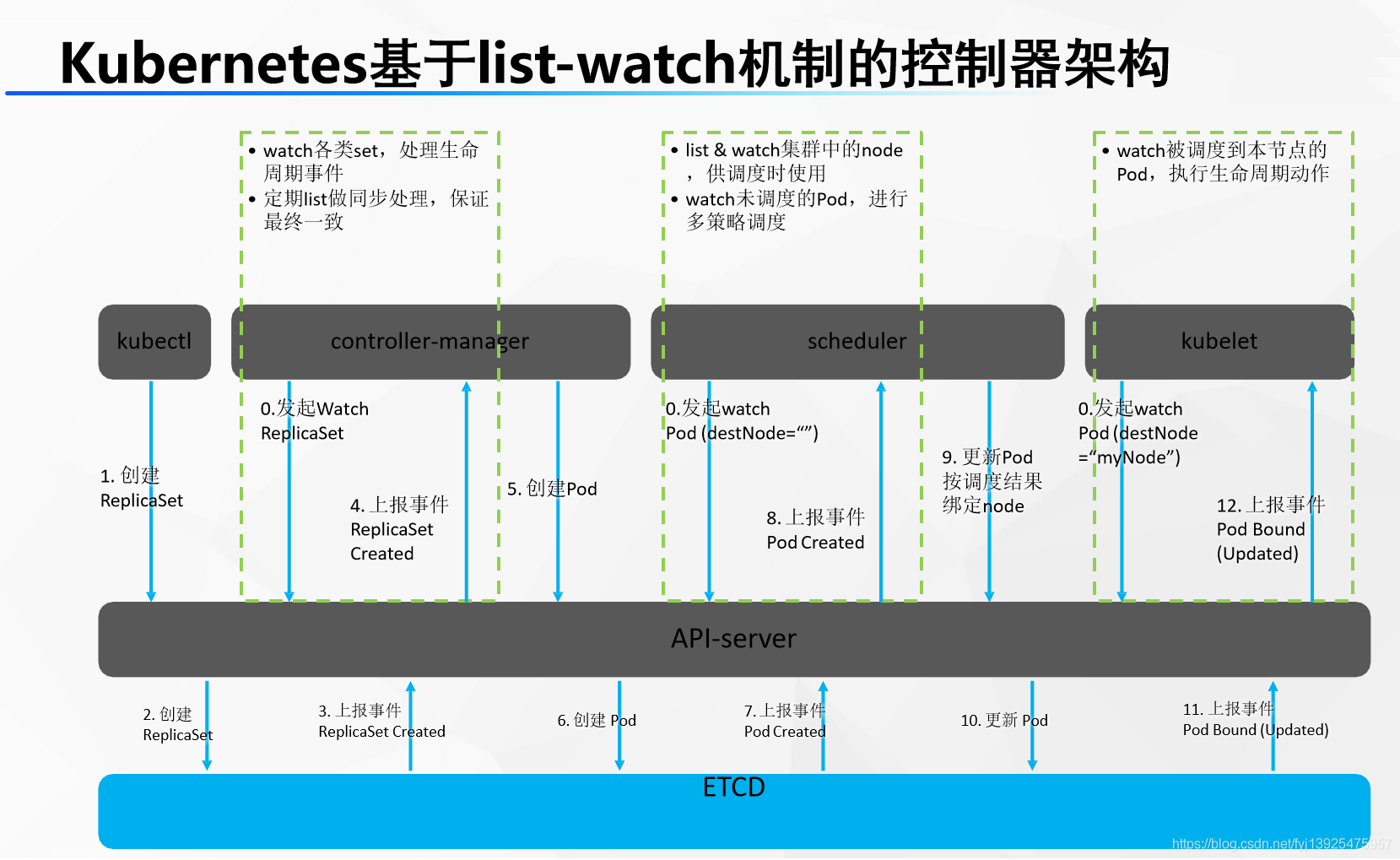
Want to make k8s Deploy a tomcat? The whole interaction process is as follows :
- Power on defaults to all nodes kubelet、master Node scheduler( Scheduler )、controller-manager( Control Manager ) Keep monitoring master Of api-server Changes in events (for ::)
- Programmers use command-line tools : kubectl ; kubectl create deploy tomcat --image=tomcat8( tell master Let the cluster use tomcat8 Mirror image , Deploy a tomcat application )
- kubectl The command line content is sent to api-server,api-server Save the creation information to etcd
- etcd to api-server Report the incident , Said someone just saved a message for me .( Deploy Tomcat[deploy])
- controller-manager Listen to the api-server Events ,( Deploy Tomcat[deploy])
- controller-manager Deal with this ( Deploy Tomcat[deploy]) Events .controller-manager Will generate Pod Deployment information for 【pod Information 】
- controller-manager hold Pod Give your information to api-server, Save it to etcd
- etcd Report the incident 【pod Information 】 to api-server.
- scheduler Special monitoring 【pod Information 】 , Get 【pod Information 】 The content of , Calculation , See which node is suitable for deploying this Pod【pod Information after scheduling node: node-02)】
- scheduler hold 【pod Information after scheduling (node: node-02)】 hand api-server Save to etcd
- etcd Report the incident 【pod Information after scheduling (node: node-02)】, to api-server
- Of other nodes kubelet Special monitoring 【pod Information after scheduling (node: node-02)】 event , Cluster all nodes kubelet from api-server Got it. 【pod Information after scheduling (node: node-02)】 event
- For each node kubelet Judge whether it belongs to you ;node-02 Of kubelet It was his business to find out
- node-02 Of kubelet Start this pod. Report to master All the information currently started
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Combination of grep and regular

Special effects - click the mouse, and a random color of love will appear

Server hardware and RAID configuration practice

目录和文件管理

grep与正则的搭配使用

Special effects - bubble tailing occurs when the mouse moves

【媒体控制器】开源项目学习笔记(基于Arduino Micro开发板)
Go environment construction and start

Customize MVC 3.0

Account and authority management
随机推荐
Special effects - mouse click, custom DOM follow move
Difference between PX and EM and REM
进程和计划任务管理
Flex layout
Solution: exit status 1 and exit status 145 appear when the console uses NVM to control the node version
Windows下bat脚本备份MySQL数据库
LM393 voltage comparator and its typical circuit introduction
【LVGL(5)】标签的(label)用法
NFS共享服务及实验
Crud of MySQL
Disk management and file system
Directory and file management
Batch implementation of key based authentication using sshpass
history命令历史记录中加时间
sql server 同步数据库 跨网段无公网ip几个常见小问题问题
JSP tag 02
Install agent and proxy using custom ZABBIX package (version 4.0.5)
Rsync (I): basic commands and usage
SSH远程访问及控制
object-oriented