当前位置:网站首页>MIP nerf: anti aliasing multiscale neural radiation field iccv2021
MIP nerf: anti aliasing multiscale neural radiation field iccv2021
2022-06-24 00:17:00 【tzc_ fly】

Aliasing phenomenon
Data collection , If the sampling frequency does not satisfy the Nyquist sampling theorem , It may cause aliasing of sampled signals .
When the sampling frequency setting is unreasonable , That is, the sampling frequency is lower than 2 Times the signal frequency , It will cause the original high-frequency signal to be sampled into a low-frequency signal . As shown in the figure below , The red signal is the original high frequency signal , However, the sampling frequency does not meet the requirements of the sampling theorem , The actual sampling points are shown as blue solid points in the figure , Connect these blue actual sampling points into a curve , It is obvious that this is a low frequency signal .
Equal time sampling of continuous signals , If the sampling frequency does not satisfy the sampling theorem , The sampled signal frequency will be aliased , That is, high-frequency signals are mixed into low-frequency signals .
For the image , The high-frequency information of the image is the part with steep gray change , The aliasing part of the image, that is, the high-frequency content, is represented as the low-frequency content , That is what we call fuzzy phenomenon ( Close observation ), And jagged edge appearance ( Long distance observation ).
NeRF Excellent results can be generated only when the distance between the camera and the object is fixed , When the camera zooms in , Blurring and jagging occur when you zoom out of the scene . The reason is that the sampling frequency is lower than the frequency of the real original signal , To solve this problem , We can : Improve sampling rate or roughly remove high-frequency components ( Use low-pass filter to smooth the edge ).
- NeRF( Left ) There are short-range blur and long-range aliasing ,Mip-NeRF( Right )
NeRF Only one light is emitted for each pixel , If you emit multiple rays , Improved sampling rate , To some extent, it can solve the problems of blur and aliasing , But this method greatly increases the amount of calculation , Efficiency is too low , So ,mip-nerf A scheme of using cone to replace light is proposed .
Mip-NeRF summary
mip From Latin ( A small space for many things ), In computer graphics ,mipmapping Is a kind of accelerated rendering , Techniques for reducing image aliasing . In short ,mipmapping The main picture is reduced to a series of pictures which are reduced in turn , And save these smaller images with lower resolution . This strategy is called pre-filtering, The computational burden of anti aliasing is concentrated on Preprocessing : No matter what needs to be done later on texture How many times to render , Only the first preprocessing is needed .
Mip-NeRF The background is : During rendering , If NeRF At every pixel use single ray Come on sample scene ,(NeRF When rendering ) There will be blurring (blurred) And serrations (aliased) The situation of , This is usually due to the resolution of multiple pictures corresponding to the same scene (resolution) Caused by inconsistency ( Due to different camera distances , Cause the relative sampling frequency to change , Thus causing signal distortion ). The simplest solution is rendering time , For each pixel use multiple rays. But yes. NeRF It's not realistic , Because along a ray Rendering requires query One MLP Hundreds of times .
Mip-NeRF Solutions and NeRF There is an essential difference :NeRF Rendering is based on ray Of , However Mip-NeRF Is based on conical frustums( Cone ) Of , And is anti-aliased( Anti aliasing ) Of . Final ,Mip-NeRF And NeRF Faster than having 、 smaller 、 More accurate advantages , More suitable for handling multiscale The data of .
Location code IPE
Classic location coding ( be used for Transformer And neural radiation fields ) Map a single point in space to a feature vector , Each element in the vector is generated by a sine curve with exponentially increasing frequency : γ w ( x ) = s i n ( w x ) , γ ( x ) = [ γ 2 l ( x ) ] l = 0 L − 1 \gamma_{w}(x)=sin(wx),\gamma(x)=[\gamma_{2^{l}}(x)]_{l=0}^{L-1} γw(x)=sin(wx),γ(x)=[γ2l(x)]l=0L−1 here , We show how these eigenvectors change with the movement of points in one-dimensional space ( Make L = 5 L=5 L=5):
mip-nerf Of integrated positional encoding Consider... In space Gaussian regions, Not a point of infinity . This provides a natural way , You can put the space “region” As query Input to is based on coordinate The neural network of . The expected value of each location code has a simple form : E x ∼ N ( μ , σ 2 ) [ γ w ( x ) ] = s i n ( w μ ) e x p ( − ( w σ ) 2 / 2 ) E_{x\sim N(\mu,\sigma^{2})}[\gamma_{w}(x)]=sin(w\mu)exp(-(w\sigma)^{2}/2) Ex∼N(μ,σ2)[γw(x)]=sin(wμ)exp(−(wσ)2/2) We can see , When considering broader region when ( vision ), High frequency information will automatically shrink to zero , So as to provide more low-frequency information for the network . With region narrow ( Close up ), These position characteristic signals will be close to the classical position coding .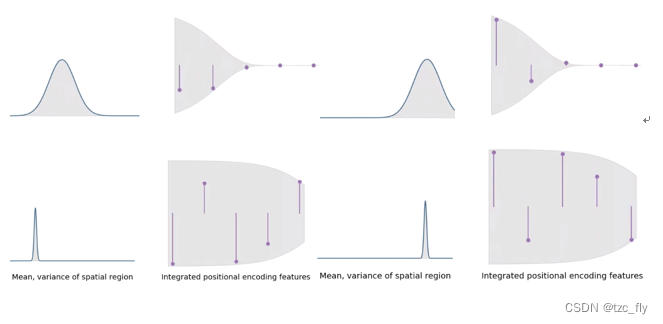
This dynamic setting , bring nerf Process the vision and automatically filter the high-frequency information , The sawtooth phenomenon is relieved ( That is, remove the high-frequency components in the scene ), Recover the processing of high-frequency information when processing close range .
Mip-NeRF
Use IPE To train NeRF To generate antialiasing rendering .mip-nerf Instead of casting an infinitely wide ray per pixel , Instead, it projects a complete 3D Cone . For each query point along the ray , We consider its associated cone truncated cone . The same point in the observation space of two cameras at different positions may produce different conical truncated cones , As shown in the figure below :
We fit multivariate Gauss to a conical truncated cone , And use the above IPE establish MLP The input eigenvector of the network .
Intuitive to see , The advantage of using cone rendering is : The cone reflects the shape and size of a point in the scene , Because from different perspectives , The shape and size of a point are different , That is, conical truncated cone ( Trapezoid in the picture above ) The size and shape of . Reflected in the calculation is the camera in different positions , The expected values of position codes for the same observation point are different .
Introduction
Neural radiation fields (NeRF) Has become a compelling strategy , Used to learn representation from images 3D Objects and scenes , To render a new view with photorealistic realism . Even though NeRF And its variants have achieved impressive results in a series of view composition tasks , but NeRF The rendering model is flawed , May cause excessive blurring ( Close up ) And serrations ( vision ).NeRF The traditional discrete sampling is replaced by a continuous volume function , It is parameterized as a multilayer perceptron (MLP), The perceptron inputs from the 5D coordinate (3D Location and 2D Look in the direction ) Scene attributes mapped to this location ( Bulk density and emissivity determined by viewing angle ). To render the color of a pixel ,NeRF A ray will be cast through this pixel , And output it to its volume representation , Sample queries along this ray MLP Get scene properties , Combine these values into a single color .
Although when all training and test images only observe the scene content from a roughly constant distance , This method works well ( As in the NeRF And most of the follow-up work ), but NeRF Rendering shows obvious flaws in less artificial scenes . When the training image observes the scene content at multiple resolutions , Recovered NeRF Rendering in close-up view ( Observe the situation closely ) Is too vague , In the far view ( Long distance observation ) Contains jagged . A simple solution is to adopt the strategy used in offline ray tracing : Oversampling each pixel by pushing multiple rays into their footsteps . But for the neural volume representation ( Such as NeRF) Come on , This method is expensive , Because rendering a ray requires querying MLP Hundreds of times , It will eventually take several hours to reconstruct a scene .
In this paper , We start with the... Used to prevent aliasing in the computer graphics rendering pipeline mipmapping Method .mipmap In fact, it is a multi-resolution image pyramid structure .
Our solution is called mip-NeRF(multum in parvo-NeRF, Such as “mipmap”).mip-NeRF The input is one Three dimensional Gaussian distribution , Is the integral of the radiation field region. Pictured 1 Shown , And then we can query by every distance along the cone mip-NeRF, The pixel is rendered using a Gaussian distribution approximating the cone section corresponding to the pixel . In order to 3D Location and its surroundings Gaussian region Encoding , We propose a new feature representation : Integrated position coding (IPE,integrated positional encoding). This is a NeRF The location code of (PE) Promotion of , It allows space region Characterized compactly , Not a single point in space .
- chart 1:NeRF(a) Point to point along the ray traced through the pixel from the camera projection center x \textbf{x} x sampling , d \textbf{d} d Is the direction of observation , Then use position coding PE γ γ γ Code these points , To generate features γ ( x ) γ(\textbf{x}) γ(x).Mip-NeRF(b) Instead, it is interpreted as a three-dimensional conical frustum defined for camera pixels . then , Use our integrated location code (IPE) These conical truncated cones are characterized ,IPE Its working principle is to use multivariate Gauss approximation to truncate cone , Then calculate the integral on the Gauss coordinate position coding E [ γ ( x ) ] E[γ(\textbf{x})] E[γ(x)].
Mip-NeRF Greatly improved NeRF The accuracy of the . On a challenging multi-resolution benchmark proposed by us ,mip-NeRF be relative to NeRF Can reduce on average 60% Error rate .Mip-NeRF The scale aware structure of also allows us to NeRF For layered sampling "coarse" and "fine"MLP Merge into a single MLP in . therefore ,mip-NeRF Slightly faster than NeRF, And it has half the parameters .
Method
When replacing rays with cones , Sampling is no longer a discrete set of points , But a continuous conical cutting platform (conical frustum), This can solve NeRF The problem of the volume and size of the light observation range is ignored .
In order to simplify the calculation , We use 3D Gaussian To approximate conical frustum( Conical frustum ), And propose to use IPE Instead of PE.IPE Defined as Gaussian distribution positional encoding The expectation of .
Gaussian There are many advantages of distribution , One of them is linear transformation . take positional encoding Rewritten in matrix form , Input Gaussian distribution for operation , It is equivalent to transforming the mean and covariance of Gaussian distribution .
First ,PE The matrix form of is :
Be careful , x \textbf{x} x It's spatial location , d \textbf{d} d Is the direction of observation , We define μ t \mu_{t} μt Is the sampling point t t t The average distance from the corresponding cone section to the camera ( The average distance along the light ), in addition , σ t 2 \sigma_{t}^{2} σt2 Is the variance of the distance along the ray , σ r 2 \sigma_{r}^{2} σr2 Is the variance of the distance perpendicular to the light .
We can get the sampling point t t t Gaussian distribution of the corresponding cone section : u = o + μ t d \textbf{u}=\textbf{o}+\mu_{t}\textbf{d} u=o+μtd Σ = σ t 2 ( d d T ) + σ r 2 ( I − d d T ∣ ∣ d ∣ ∣ 2 2 ) \Sigma=\sigma_{t}^{2}(\textbf{d}\textbf{d}^{T})+\sigma_{r}^{2}(\textbf{I}-\frac{\textbf{d}\textbf{d}^{T}}{||\textbf{d}||_{2}^{2}}) Σ=σt2(ddT)+σr2(I−∣∣d∣∣22ddT) We encode the position of Gaussian distribution , The position coding must obey Gaussian distribution , And the mean and variance are : u γ = Pu \textbf{u}_{\gamma}=\textbf{P}\textbf{u} uγ=Pu Σ γ = P Σ P T \Sigma_{\gamma}=\textbf{P}\Sigma\textbf{P}^{T} Σγ=PΣPT According to this Gaussian distribution , We can get IPE: γ ( u , Σ ) = E x ∼ N ( u γ , Σ γ ) [ γ ( x ) ] \gamma(\textbf{u},\Sigma)=E_{\textbf{x}\sim N(\textbf{u}_{\gamma},\Sigma_{\gamma})}[\gamma(\textbf{x})] γ(u,Σ)=Ex∼N(uγ,Σγ)[γ(x)] = [ sin ( u γ ) ∘ e x p ( − ( 1 2 ) d i a g ( Σ γ ) ) , cos ( u γ ) ∘ e x p ( − ( 1 2 ) d i a g ( Σ γ ) ) ] T =[\text{sin}(\textbf{u}_{\gamma})\circ exp(-(\frac{1}{2})diag(\Sigma_{\gamma})),\text{cos}(\textbf{u}_{\gamma})\circ exp(-(\frac{1}{2})diag(\Sigma_{\gamma}))]^{T} =[sin(uγ)∘exp(−(21)diag(Σγ)),cos(uγ)∘exp(−(21)diag(Σγ))]T d i a g ( Σ γ ) = [ d i a g ( Σ ) , 4 d i a g ( Σ ) , . . . , 4 L − 1 d i a g ( Σ ) ] T diag(\Sigma_{\gamma})=[diag(\Sigma),4diag(\Sigma),...,4^{L-1}diag(\Sigma)]^{T} diag(Σγ)=[diag(Σ),4diag(Σ),...,4L−1diag(Σ)]T among , ∘ \circ ∘ by element-wise The product of . d i a g diag diag Is the diagonal of the matrix .mip-nerf Sampling with truncated cones , Information of different scales is considered , So just learn one MLP Can represent coarse-grained and fine-grained information .
Discuss

- chart 2:NeRF Location code used PE( Left ) and mip-nerf Integrated position coding IPE( Right ). because NeRF Sample along each ray , And encode all frequencies , For those high frequency features ( Sampling frequency exceeded ) It will always cause the rendering to be aliased . By integrating... On each bay PE features , When the sampling frequency period is the same as IPE The interval size of is smaller than that of ,IPE The high frequency dimension of the feature shrinks to zero , Avoid aliasing .
The figure above visualizes IPE and PE The difference between one-dimensional features of .IPE The behavior of features is intuitive : If the frequency period in the position coding is less than the construction IPE Interval width of the feature ( under these circumstances , On this interval PE The oscillation will be repeated ), Then the characteristic at this frequency will be reduced to 0.IPE Feature is an effective anti aliasing location coding , The size and shape of the space volume can be gently encoded .
IPE Each sampling can ensure that it is relative to IPE The high frequency feature of feature interval is weakened , Because the Gaussian distribution of each cone always follows IPE The characteristic interval changes dynamically
Mip-NeRF The main contribution is to improve the sampling method , Use a cone instead of a point in the light , For the sake of calculation , A three-dimensional Gaussian distribution is proposed region Approximate conical truncated cone , According to the characteristics of Gaussian distribution , Get the Gaussian distribution corresponding to the position coding , Sampling position coding from this Gaussian distribution , And calculate the expected position code as the last .
The position coding which obeys Gauss distribution can automatically when the sampling frequency is low (IPE When the feature interval is wide ) Weakening high frequency features , So as to alleviate the aliasing phenomenon . This sampling design itself determines that it is suitable for multi-scale situations , therefore ,Nerf Of the two MLP Can be combined into one MLP.
边栏推荐
- setfacl命令的基本用法
- What is the difference between overload and override?
- 【第25天】给定一个长度为 n 的数组,统计每个数出现的次数 | 计数哈希
- Return, const, volatile keywords
- Jimureport building block report - table linkage chart topic
- 如何利用數倉創建時序錶
- Building a digital software factory -- panoramic interpretation of one-stop Devops platform
- How to use data warehouse to create time series
- Index principle and filling factor in database
- 合成大西瓜小游戏微信小程序源码/微信游戏小程序源码
猜你喜欢
![[traffic light identification] traffic light identification based on Matlab GUI [including Matlab source code 1908]](/img/0e/3103c4c5dd664196c85db9b30bcaf5.png)
[traffic light identification] traffic light identification based on Matlab GUI [including Matlab source code 1908]

What is the use of AI technology in the medical field?

Revit API: schedule viewschedule

超标量处理器设计 姚永斌 第3章 虚拟存储器 --3.1~3.2 小节摘录

What should I pay attention to in the interview of artificial intelligence technology?

数字化工厂可以分为哪两类

985本3Android程序员40天拿下阿里P6口头offer,面试成功后整理了这些面试思路

Chaos engineering, learn about it

【面试经验包】面试被吊打经验总结(一)

C语言:利用自定义函数排序
随机推荐
【图像检测显著图】基于matlab失真提示鱼眼图显著图计算【含Matlab源码 1903期】
C语言:关于矩阵右移问题
Learn PWN from CTF wiki - ret2text
Revit API: schedule viewschedule
. Net
智能制造时代下,MES管理系统需要解决哪些问题
Chaos engineering, learn about it
Android App bundle exploration, client development interview questions
Drag and drop report design - new features of jimureport 1.4.0
Comment utiliser l'entrepôt de données pour créer une table de synchronisation
Three Solution to the problem of inaccuracy in radiographic testing under the condition of non full screen canvas of JS
【虹科案例】3D数据如何成为可操作的信息?– 对象检测和跟踪
[digital signal] spectrum refinement based on MATLAB analog window function [including Matlab source code 1906]
[image detection saliency map] calculation of fish eye saliency map based on MATLAB distortion prompt [including Matlab source code 1903]
Solve the problem of project dependency red reporting
国内首款开源MySQL HTAP数据库即将发布,三大看点提前告知 石原子科技重磅推出
【红绿灯识别】基于matlab GUI红绿灯识别【含Matlab源码 1908期】
[technical grass planting] use the shared image function to realize the offline switching from CVM to LH
[traffic light identification] traffic light identification based on Matlab GUI [including Matlab source code 1908]
如何入门机器学习?