当前位置:网站首页>Advanced Mathematics (Seventh Edition) Tongji University exercises 1-7 personal solutions
Advanced Mathematics (Seventh Edition) Tongji University exercises 1-7 personal solutions
2022-06-23 05:44:00 【Navigator_ Z】
Advanced mathematics ( The seventh edition ) Tongji University exercises 1-7
1. When x → 0 when , 2 x − x 2 And x 2 − x 3 phase Than , which One individual yes high rank nothing poor Small ? \begin{aligned}&1. \ When x \rightarrow 0 when ,2x-x^2 And x^2-x^3 comparison , Which is the higher order infinitesimal ?&\end{aligned} 1. When x→0 when ,2x−x2 And x2−x3 phase Than , which One individual yes high rank nothing poor Small ?
Explain :
because by lim x → 0 ( 2 x − x 2 ) = 0 , lim x → 0 ( x 2 − x 3 ) = 0 , lim x → 0 x 2 − x 3 2 x − x 2 = lim x → 0 x − x 2 2 − x = 0 , the With When x → 0 when , x 2 − x 3 yes Than 2 x − x 2 high rank Of nothing poor Small . \begin{aligned} &\ \ because \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}(2x-x^2)=0,\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}(x^2-x^3)=0, \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}{\frac{x^2-x^3}{2x-x^2}}=\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}{\frac{x-x^2}{2-x}}=0,\\\\ &\ \ So when x \rightarrow 0 when ,x^2-x^3 It's better than 2x-x^2 Infinitesimal of higher order . & \end{aligned} because by x→0lim(2x−x2)=0,x→0lim(x2−x3)=0,x→0lim2x−x2x2−x3=x→0lim2−xx−x2=0, the With When x→0 when ,x2−x3 yes Than 2x−x2 high rank Of nothing poor Small .
2. When x → 0 when , ( 1 − c o s x ) 2 And s i n 2 x phase Than , which One individual yes high rank nothing poor Small ? \begin{aligned}&2. \ When x \rightarrow 0 when ,(1-cos\ x)^2 And sin^2\ x comparison , Which is the higher order infinitesimal ?&\end{aligned} 2. When x→0 when ,(1−cos x)2 And sin2 x phase Than , which One individual yes high rank nothing poor Small ?
Explain :
because by lim x → 0 ( 1 − c o s x ) 2 = 0 , lim x → 0 s i n 2 x = 0 , lim x → 0 ( 1 − c o s x ) 2 s i n 2 x = lim x → 0 ( 1 2 x 2 ) 2 x 2 = lim x → 0 1 4 x 2 = 0 , the With When x → 0 when , ( 1 − c o s x ) 2 yes Than s i n 2 x high rank Of nothing poor Small . \begin{aligned} &\ \ because \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}(1-cos\ x)^2=0,\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}sin^2\ x=0,\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}{\frac{(1-cos\ x)^2}{sin^2\ x}}=\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}{\frac{\left(\frac{1}{2}x^2\right)^2}{x^2}}=\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}{\frac{1}{4}x^2}=0,\\\\ &\ \ So when x \rightarrow 0 when ,(1-cos\ x)^2 It's better than sin^2\ x Infinitesimal of higher order . & \end{aligned} because by x→0lim(1−cos x)2=0,x→0limsin2 x=0,x→0limsin2 x(1−cos x)2=x→0limx2(21x2)2=x→0lim41x2=0, the With When x→0 when ,(1−cos x)2 yes Than sin2 x high rank Of nothing poor Small .
3. When x → 1 when , nothing poor Small 1 − x and ( 1 ) 1 − x 3 , ( 2 ) 1 2 ( 1 − x 2 ) yes no Same as rank , yes no etc. price ? \begin{aligned}&3. \ When x \rightarrow 1 when , An infinitesimal 1-x and (1)1-x^3,(2)\frac{1}{2}(1-x^2) Same order or not , Is it equivalent ?&\end{aligned} 3. When x→1 when , nothing poor Small 1−x and (1)1−x3,(2)21(1−x2) yes no Same as rank , yes no etc. price ?
Explain :
( 1 ) because by lim x → 1 1 − x 1 − x 3 = lim x → 1 1 1 + x + x 2 = 1 3 , the With When x → 1 when , nothing poor Small 1 − x And 1 − x 3 Same as rank . ( 2 ) because by lim x → 1 1 − x 1 2 ( 1 − x 2 ) = lim x → 1 2 1 + x = 1 , the With When x → 1 when , nothing poor Small 1 − x And 1 2 ( 1 − x 2 ) etc. price . \begin{aligned} &\ \ (1)\ because \lim_{x \rightarrow 1}\frac{1-x}{1-x^3}=\lim_{x \rightarrow 1}\frac{1}{1+x+x^2}=\frac{1}{3}, So when x \rightarrow 1 when , An infinitesimal 1-x And 1-x^3 Isomorphism .\\\\ &\ \ (2)\ because \lim_{x \rightarrow 1}\frac{1-x}{\frac{1}{2}(1-x^2)}=\lim_{x \rightarrow 1}\frac{2}{1+x}=1, So when x \rightarrow 1 when , An infinitesimal 1-x And \frac{1}{2}(1-x^2) Equivalent . & \end{aligned} (1) because by x→1lim1−x31−x=x→1lim1+x+x21=31, the With When x→1 when , nothing poor Small 1−x And 1−x3 Same as rank . (2) because by x→1lim21(1−x2)1−x=x→1lim1+x2=1, the With When x→1 when , nothing poor Small 1−x And 21(1−x2) etc. price .
4. Prove bright : When x → 0 when , Yes \begin{aligned}&4. \ prove : When x \rightarrow 0 when , Yes &\end{aligned} 4. Prove bright : When x→0 when , Yes
( 1 ) a r c t a n x ∼ x ; ( 2 ) s e c x − 1 ∼ x 2 2 \begin{aligned} &\ \ (1)\ \ arctan\ x \sim x;\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ (2)\ \ sec\ x-1 \sim \frac{x^2}{2} & \end{aligned} (1) arctan x∼x; (2) sec x−1∼2x2
Explain :
( 1 ) Make x = t a n t , t = a r c t a n x , When x → 0 when , t → 0 . because by lim x → 0 a r c t a n x x = lim t → 0 t t a n t = 1 , the With When x → 0 when , a r c t a n x ∼ x . ( 2 ) because by lim x → 0 s e c x − 1 x 2 2 = lim x → 0 1 − c o s x c o s x 1 2 x 2 = lim x → 0 1 c o s x = 1 , the With When x → 0 when , s e c x − 1 ∼ x 2 2 . \begin{aligned} &\ \ (1)\ Make x=tan\ t,t=arctan\ x, When x \rightarrow 0 when ,t \rightarrow 0. because \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{arctan\ x}{x}=\lim_{t \rightarrow 0}\frac{t}{tan\ t}=1,\\\\ &\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ So when x \rightarrow 0 when ,arctan\ x \sim x.\\\\ &\ \ (2)\ because \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{sec\ x-1}{\frac{x^2}{2}}=\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{\frac{1-cos\ x}{cos\ x}}{\frac{1}{2}x^2}=\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{1}{cos\ x}=1,\\\\ &\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ So when x \rightarrow 0 when ,sec\ x -1 \sim \frac{x^2}{2}. & \end{aligned} (1) Make x=tan t,t=arctan x, When x→0 when ,t→0. because by x→0limxarctan x=t→0limtan tt=1, the With When x→0 when ,arctan x∼x. (2) because by x→0lim2x2sec x−1=x→0lim21x2cos x1−cos x=x→0limcos x1=1, the With When x→0 when ,sec x−1∼2x2.
5. benefit use etc. price nothing poor Small Of sex quality , seek Next Column extremely limit : \begin{aligned}&5. \ Using the property of equivalent infinitesimal , Find the following limit :&\end{aligned} 5. benefit use etc. price nothing poor Small Of sex quality , seek Next Column extremely limit :
( 1 ) lim x → 0 t a n 3 x 2 x ; ( 2 ) lim x → 0 s i n ( x n ) ( s i n x ) m ( n , m by just whole Count ) ; ( 3 ) lim x → 0 t a n x − s i n x s i n 3 x ; ( 4 ) lim x → 0 s i n x − t a n x ( 1 + x 2 3 − 1 ) ( 1 + s i n x − 1 ) \begin{aligned} &\ \ (1)\ \ \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{tan\ 3x}{2x};\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ (2)\ \ \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{sin(x^n)}{(sin\ x)^m}\ (n,m As a positive integer );\\\\ &\ \ (3)\ \ \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{tan\ x-sin\ x}{sin^3\ x};\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ (4)\ \ \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{sin\ x-tan\ x}{(\sqrt[3]{1+x^2}-1)(\sqrt{1+sin\ x}-1)} & \end{aligned} (1) x→0lim2xtan 3x; (2) x→0lim(sin x)msin(xn) (n,m by just whole Count ); (3) x→0limsin3 xtan x−sin x; (4) x→0lim(31+x2−1)(1+sin x−1)sin x−tan x
Explain :
( 1 ) lim x → 0 t a n 3 x 2 x = lim x → 0 s i n 3 x 2 c o s 3 x ⋅ x = lim x → 0 ( 3 2 ⋅ 1 c o s 3 x ⋅ s i n 3 x 3 x ) = 3 2 ( 2 ) lim x → 0 s i n ( x n ) ( s i n x ) m = lim x → 0 x n x m = { 0 , n > m , 1 , n = m , ∞ , n < m . ( 3 ) lim x → 0 t a n x − s i n x s i n 3 x = lim x → 0 s i n x − s i n x ⋅ c o s x c o s x ⋅ s i n 3 x = lim x → 0 1 − c o s x c o s x ⋅ s i n 2 x = lim x → 0 1 2 c o s x ⋅ s i n 2 x x 2 = 1 2 ( 4 ) lim x → 0 s i n x − t a n x ( 1 + x 2 3 − 1 ) ( 1 + s i n x − 1 ) = lim x → 0 s i n x ( 1 − s e c x ) 1 3 x 2 ⋅ 1 2 s i n x = lim x → 0 − 1 2 x 2 1 6 x 2 = − 3 \begin{aligned} &\ \ (1)\ \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{tan\ 3x}{2x}=\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{sin\ 3x}{2cos\ 3x \cdot x}=\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\left(\frac{3}{2} \cdot \frac{1}{cos\ 3x} \cdot \frac{sin\ 3x}{3x}\right)=\frac{3}{2}\\\\ &\ \ (2)\ \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{sin(x^n)}{(sin\ x)^m}=\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{x^n}{x^m}=\begin{cases}0,n \gt m,\\\\ 1,n =m,\\\\ \infty,n \lt m.\end{cases}\\\\ &\ \ (3)\ \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{tan\ x-sin\ x}{sin^3\ x}=\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{sin\ x-sin\ x \cdot cos\ x}{cos\ x \cdot sin^3\ x}=\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{1-cosx}{cos\ x \cdot sin^2\ x}=\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{1}{2cos\ x \cdot \frac{sin^2\ x}{x^2}}=\frac{1}{2}\\\\ &\ \ (4)\ \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{sin\ x-tan\ x}{(\sqrt[3]{1+x^2}-1)(\sqrt{1+sin\ x}-1)}=\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{sin\ x(1-sec\ x)}{\frac{1}{3}x^2 \cdot \frac{1}{2}sin\ x}=\lim_{x \rightarrow 0}\frac{-\frac{1}{2}x^2}{\frac{1}{6}x^2}=-3 & \end{aligned} (1) x→0lim2xtan 3x=x→0lim2cos 3x⋅xsin 3x=x→0lim(23⋅cos 3x1⋅3xsin 3x)=23 (2) x→0lim(sin x)msin(xn)=x→0limxmxn=⎩⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎧0,n>m,1,n=m,∞,n<m. (3) x→0limsin3 xtan x−sin x=x→0limcos x⋅sin3 xsin x−sin x⋅cos x=x→0limcos x⋅sin2 x1−cosx=x→0lim2cos x⋅x2sin2 x1=21 (4) x→0lim(31+x2−1)(1+sin x−1)sin x−tan x=x→0lim31x2⋅21sin xsin x(1−sec x)=x→0lim61x2−21x2=−3
6. Prove bright nothing poor Small Of etc. price Turn off system have Yes Next Column sex quality : \begin{aligned}&6. \ It is proved that the equivalence relation of infinitesimal has the following properties :&\end{aligned} 6. Prove bright nothing poor Small Of etc. price Turn off system have Yes Next Column sex quality :
( 1 ) α ∼ α ( since back sex ) ; ( 2 ) if α ∼ β , be β ∼ α ( Yes call sex ) ; ( 3 ) if α ∼ β , β ∼ γ , be α ∼ γ ( Pass on Deliver sex ) \begin{aligned} &\ \ (1)\ \ \alpha \sim \alpha( reflexivity );\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ (2)\ \ if \alpha \sim \beta, be \beta \sim \alpha( symmetry );\\\\ &\ \ (3)\ \ if \alpha \sim \beta,\beta \sim \gamma, be \alpha \sim \gamma( Transitivity ) & \end{aligned} (1) α∼α( since back sex ); (2) if α∼β, be β∼α( Yes call sex ); (3) if α∼β,β∼γ, be α∼γ( Pass on Deliver sex )
Explain :
( 1 ) because by lim α α = 1 , the With α ∼ α ; ( 2 ) because by α ∼ β , namely lim α β = 1 , the With lim β α = 1 , namely β ∼ α ; ( 3 ) because by α ∼ β , β ∼ γ , namely lim α β = 1 , lim β γ = 1 , the With lim α γ = lim ( α β ⋅ β γ ) = lim α β ⋅ lim β γ = 1 , namely α ∼ γ \begin{aligned} &\ \ (1)\ because \lim{\frac{\alpha}{\alpha}}=1, therefore \alpha \sim \alpha;\\\\ &\ \ (2)\ because \alpha \sim \beta, namely \lim{\frac{\alpha}{\beta}}=1, therefore \lim{\frac{\beta}{\alpha}}=1, namely \beta \sim \alpha;\\\\ &\ \ (3)\ because \alpha \sim \beta,\beta \sim \gamma, namely \lim{\frac{\alpha}{\beta}}=1,\lim{\frac{\beta}{\gamma}}=1, therefore \lim{\frac{\alpha}{\gamma}}=\lim\left(\frac{\alpha}{\beta}\cdot \frac{\beta}{\gamma}\right)=\lim{\frac{\alpha}{\beta}} \cdot \lim{\frac{\beta}{\gamma}}=1, namely \alpha \sim \gamma & \end{aligned} (1) because by limαα=1, the With α∼α; (2) because by α∼β, namely limβα=1, the With limαβ=1, namely β∼α; (3) because by α∼β,β∼γ, namely limβα=1,limγβ=1, the With limγα=lim(βα⋅γβ)=limβα⋅limγβ=1, namely α∼γ
边栏推荐
- 软件设计开发笔记2:基于QT设计串口调试工具
- AHA C language Chapter 7 you can do more with it (talks 27-28)
- CF [1700d] D. River locks (DP, bisection, Mathematics)
- Introduction to JDBC (IV) - use of Druid connection pool
- Implementation of MySQL custom sequence number
- Meteorological mapping software panoply tutorial (updated from time to time)
- June 22, 2022: golang multiple choice question, what does the following golang code output? A:3; B:1; C:4; D: Compilation failed. package main import ( “fmt“ ) func mai
- 1010 Radix
- visdom的使用
- What if win11 cannot record audio? Solution of win11 unable to input sound
猜你喜欢

Leetcode 797: all possible paths

2022年中国重卡智能化升级专题研究
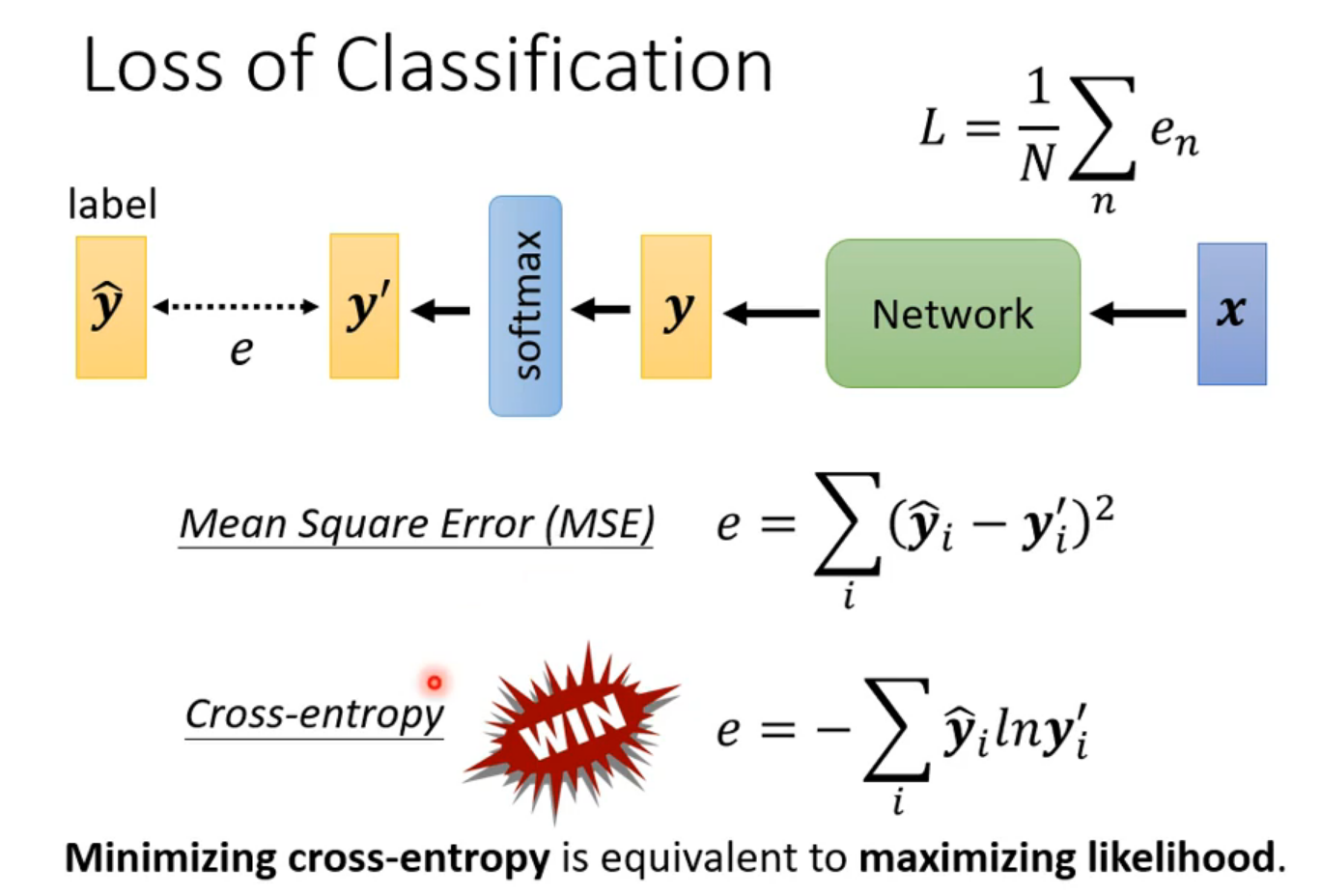
Lihongyi, machine learning 5 Tips for neural network design
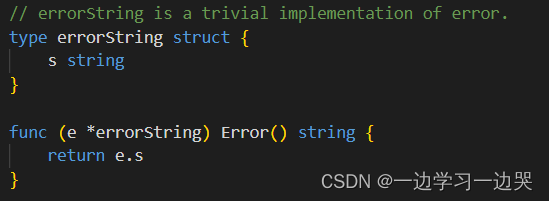
Go language - custom error
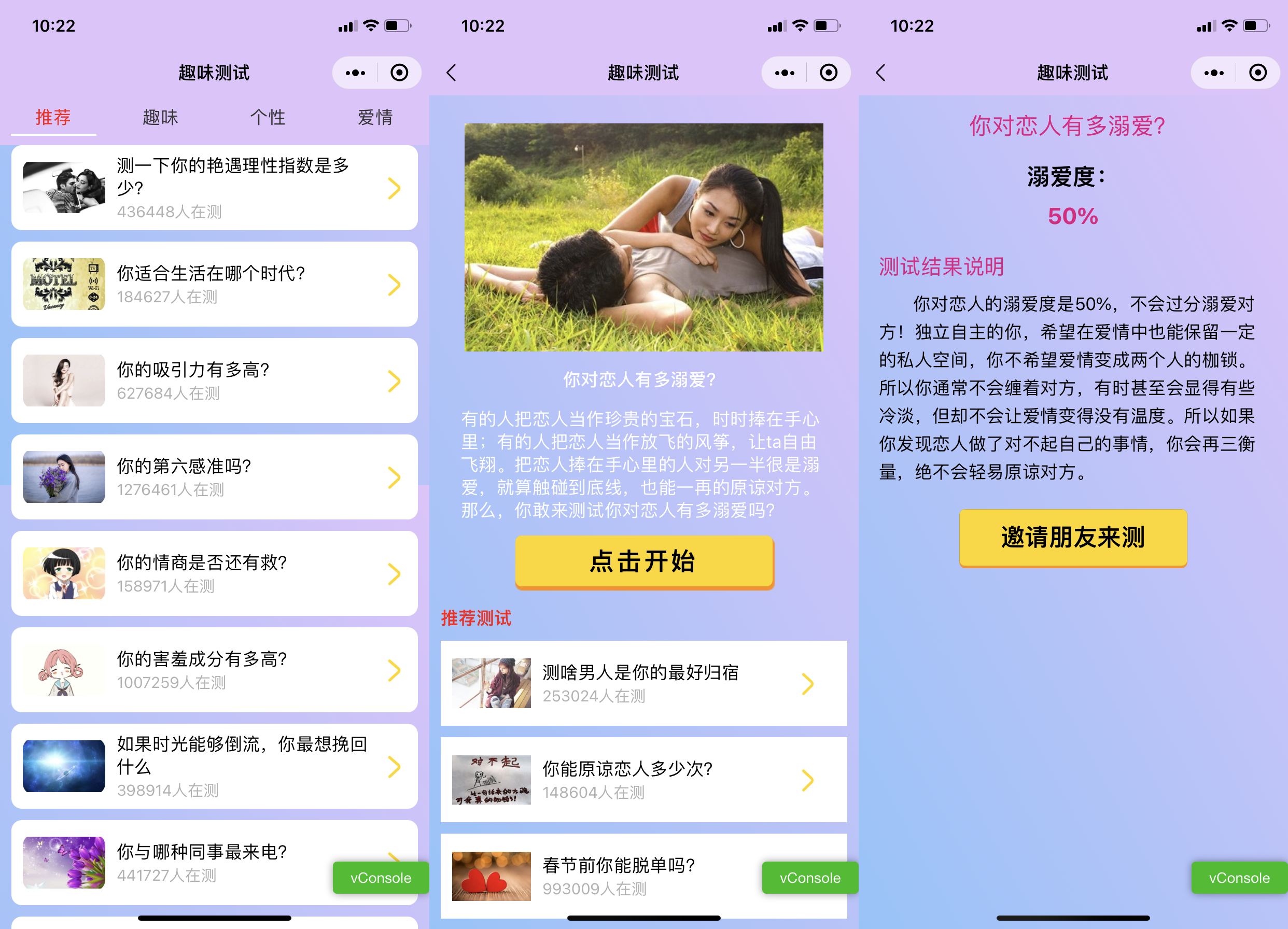
Wechat applet: a new interesting test

软件设计开发笔记2:基于QT设计串口调试工具

Differences between fs4059a and fs5080e charging chips

Markdown add background color to the picture

JDBC introductory learning (II) encapsulation tool class

Qimen dunjia assistant decision software
随机推荐
软件设计开发笔记2:基于QT设计串口调试工具
STC 32-bit 8051 MCU development example tutorial I development environment construction
MySQL面试真题(二十四)——行列互换
Introduction to JDBC (IV) - use of Druid connection pool
Go grouping & sorting
云原生数据库是未来数据库的天下
Facing new challenges and becoming a better self -- an advanced technology er
A bit of knowledge - folding forging and Damascus steel
MySQL面试真题(二十九)——案例-找到爱看的电影
数字藏品——新的投资机遇
CF [1700d] D. River locks (DP, bisection, Mathematics)
Arctime makes Chinese and English subtitle video
Common wireless charging and transmitting IC chips
英集芯ip6806无线充电方案5W过Qi认证外围精简14颗器件
数字藏品到底有什么魔力?目前有哪些靠谱的团队在开发
Mobile power fast charging qc3.0 scheme chip ip5318 fast charging scheme
Webrtc[47] - a common way for webrtc to save YUV data
C prime plus notes d'apprentissage - 2, constantes et formatage io (I / o)
STC 32比特8051單片機開發實例教程 一 開發環境搭建
When I was young, I thought my father was omnipotent