当前位置:网站首页>Notes on brushing questions (19) -- binary tree: modification and construction of binary search tree
Notes on brushing questions (19) -- binary tree: modification and construction of binary search tree
2022-06-26 15:14:00 【Dream of becoming a skinhead!】
Catalog
List of articles
Brush notes ( One )– An array type : Dichotomy
Brush notes ( Two )– An array type : Double finger needling
Brush notes ( 3、 ... and )– An array type : The sliding window
Brush notes ( Four )– An array type : simulation
Brush notes ( 5、 ... and )– List type : Basic topics and operations
Brush notes ( 6、 ... and )– Hashtable : Basic topics and ideas
Brush notes ( 7、 ... and )– character string : Classic title
Brush notes ( 8、 ... and )– Double pointer : Sum of two numbers and extension
Brush notes ( Nine )– character string :KMP Algorithm
Brush notes ( Ten )– Stacks and queues : Basic topics
Brush notes ( 11、 ... and )– Stacks and queues :Top-K problem
Brush notes ( Twelve )– review : Sorting algorithm
Brush notes ( 13、 ... and )– Binary tree : Traversal in front, middle and back order ( review )
Brush notes ( fourteen )– Binary tree : Sequence traversal and DFS,BFS
Brush notes ( 15、 ... and )– Binary tree : Attribute related topics
Brush notes ( sixteen )– Binary tree : Modification and construction
Brush notes ( seventeen )– Binary search tree : About attributes
Brush notes ( eighteen )– Binary tree : The common ancestor problem
Preface
The last blog of binary tree !!! The second part is the backtracking algorithm !! start doing sth. !
Bibliography
701. Insert operation in binary search tree
The title links are as follows :
701. Insert operation in binary search tree
The screenshot of the title is as follows :
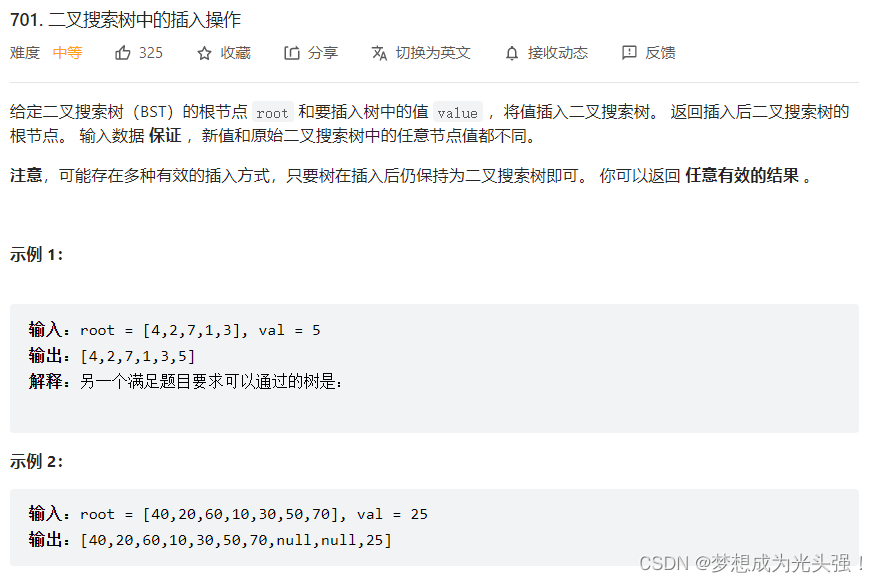
Binary search tree here the problem must pay attention to a very important skill , Is its postorder traversal , Because of the particularity of post order traversal of binary search tree , So most of the time, topics evolve according to post order traversal .
recursive _DFS
public class Insert operation in binary search tree {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
// If the current node is empty, it will go to the bottom , At this point, you can directly construct a new node
if(root == null) return new TreeNode(val);
// Judge the relationship between the value of the current node and the left and right subtrees , So as to determine the next step
if(root.val > val){
root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left,val);
}else{
root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right,val);
}
return root;
}
}
iteration _BFS
How to say the insertion operation of binary tree , In fact, it is a process of continuous traversal . But in the process of traversal , To save the values of two nodes , That is, the values of the current node and the previous node .
public class Insert operation in binary search tree _ Iterative writing {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root == null) return new TreeNode(val);
// Define two node pointers , Used to save the current node and the previous node
TreeNode parent = root,key = root;
while(key != null){
parent = key;
key = key.val < val ? key.right : key.left;
}
// Pay attention , Here, if the value of the inserted node is equal to the current node , The value of the current node will be overwritten
if(parent.val > val) parent.left = new TreeNode(val);
else if(parent.val < val) parent.right = new TreeNode(val);
return root;
}
}
450. Delete nodes in binary search tree
The title links are as follows :
450. Delete nodes in binary search tree
The screenshot of the title is as follows :

This topic , It can be roughly divided into the following steps
1. Find the node to be deleted
2. Classify the nodes to be deleted
<1> The node to be deleted is a leaf node
<2> The left subtree of the node to be deleted is empty
<3> The right subtree of the node to be deleted is empty
<4> The left and right subtrees of the node to be deleted are sound
3. Delete the corresponding node
The specific code is as follows :
public class Delete operation in binary search tree {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
TreeNode cur = root;// Pointer to the current
TreeNode parent = null;// Record the last traversal node
// Find the node to be deleted
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val > key){
parent = cur;
cur = cur.left;
}else if(cur.val < key){
parent = cur;
cur = cur.right;
}else{
break;
}
}
if(cur == null) return root;// If the node to be deleted is not found , Just return to the root node ( The test cases are also included here [] The situation of )
if(cur.left == null){
//1. The left subtree is empty ( It may be the root node ) At the same time processing
if(parent == null){
// The identification of this situation is added here because the node to be deleted may be the root node
root = cur.right;
}else{
if(parent.left == cur) parent.left = cur.right;
else parent.right = cur.right;
}
cur.right = null;
}
else if(cur.right == null){
//2. The right subtree is empty ( It may be the root node )
if(parent == null){
// The identification of this situation is added here because the node to be deleted may be the root node
root = cur.left;
}else {
if (parent.left == cur) parent.left = cur.left;
else parent.right = cur.left;
}
cur.left = null;
}
else{
// This is the last case , That is, the left and right subtrees of the current node are , This one is special , The deletion here needs a different form
// This deletion is to find a suitable node value to overwrite
parent = cur;
TreeNode fac = cur.right;// This node is used to find the maximum value of the left subtree or the minimum value of the right subtree
// In general, our choice is the minimum value of right subtree
while(fac.left != null){
parent = fac;
fac = fac.left;
}
// Overwrite the current node to be deleted after finding it
cur.val = fac.val;
if(parent.left == fac){
// If the found node is the left child tree of the parent node
parent.left = fac.right;
}else{
// If the found node is the right subtree of the parent node
parent.right = fac.right;
}
}
return root;
}
}
669. Prune the binary search tree
The title links are as follows :
669. Prune the binary search tree
The screenshot of the title is as follows :

How to say the pruning here , Although it is a simple question , But the pruning process is actually very painful .
public class Prune the binary search tree {
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
if(root == null) return null;
// Then there is post order traversal , First, traverse the left and right subtrees
root.left = trimBST(root.left,low,high);
root.right = trimBST(root.right,low,high);
// Then start with the root node of the current tree
// If the root node does not meet the requirements , Then deal with the left and right subtrees
if(root.val < low) return trimBST(root.right,low,high);
if(root.val > high) return trimBST(root.left,low,high);
return root;
}
}
108. Convert an ordered array to a binary search tree
The title links are as follows :
108. Convert an ordered array to a binary search tree
The screenshot of the title is as follows :
public class Turn an ordered array into a binary search tree {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length == 0) return null;
return solve(nums,0, nums.length);
}
// It's not very complicated , Because it is no different from building a normal binary tree , Because its value is very fixed , It's always taken from the middle .
public TreeNode solve(int[] nums,int left,int right){
// if left > right Just go back to one null Nodes are fine
if(left >= right) return null;
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = solve(nums,left,mid);
root.right = solve(nums,mid + 1,right);
return root;
}
}
538. Convert binary search tree to accumulation tree
The title links are as follows :
538. Convert binary search tree to accumulation tree
The screenshot of the title is as follows :

Although this question is medium , But it's not very difficult . Our middle order traversal is a left subtree >> The root node >> Right subtree , But the traversal method required here is right subtree >> The root node >> The left subtree , So just change the order .
public class Binary search tree is transformed into cumulative tree {
int num;
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return null;
solve(root);
return root;
}
public void solve(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return;
solve(root.right);
root.val += num;
num = root.val;
solve(root.left);
}
}
边栏推荐
- Database - sequence
- R语言dplyr包bind_rows函数把两个dataframe数据的行纵向(竖直)合并起来、最终行数为原来两个dataframe行数的加和(Combine Data Frames)
- 【小程序实战系列】小程序框架 页面注册 生命周期 介绍
- Kubernetes的pod
- Unity C # e-learning (10) -- unitywebrequest (2)
- The R language cartools package divides data, the scale function scales data, and the KNN function of the class package constructs a k-nearest neighbor classifier
- Function: crypto JS encryption and decryption
- 券商经理给的开户二维码安全吗?找谁可以开户啊?
- Redis-集群
- 集群中命令的执行过程
猜你喜欢

Redis-集群

【ceph】CEPHFS 内部实现(一):概念篇--未消化

Bank of Beijing x Huawei: network intelligent operation and maintenance tamps the base of digital transformation service
![[tcapulusdb knowledge base] tcapulusdb doc acceptance - create business introduction](/img/05/8ec56393cac534cb5a00c10a1a9f32.png)
[tcapulusdb knowledge base] tcapulusdb doc acceptance - create business introduction

【文件】VFS四大struct:file、dentry、inode、super_block 是什么?区别?关系?--编辑中
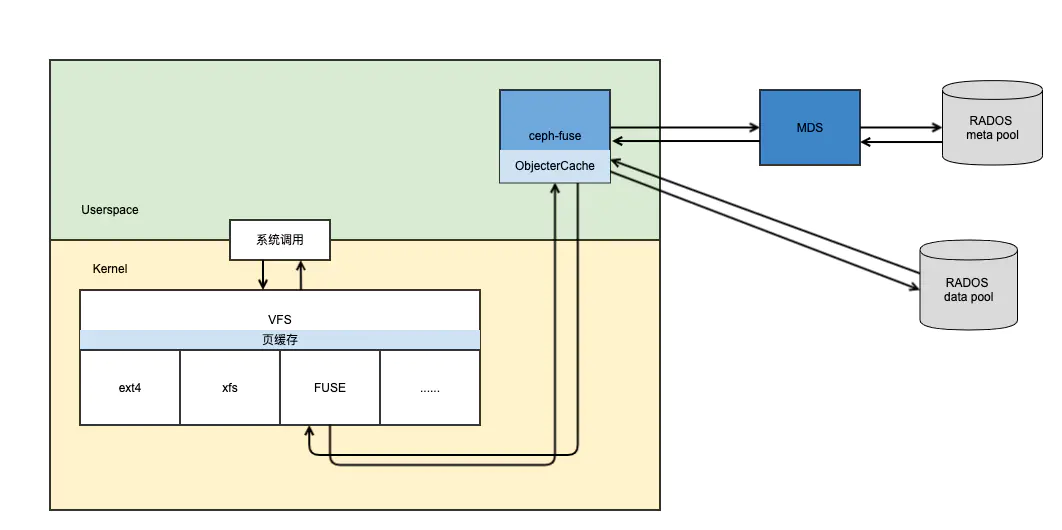
【ceph】CephFS 内部实现(二):示例--未消化

【TcaplusDB知识库】TcaplusDB系统管理介绍
![[tcapulusdb knowledge base] Introduction to tcapulusdb general documents](/img/7b/8c4f1549054ee8c0184495d9e8e378.png)
[tcapulusdb knowledge base] Introduction to tcapulusdb general documents
![[CEPH] cephfs internal implementation (II): example -- undigested](/img/87/6eb214550faf1f0500565c1610ff3b.png)
[CEPH] cephfs internal implementation (II): example -- undigested
Advanced operation of MySQL database basic SQL statement tutorial
随机推荐
R语言caTools包进行数据划分、scale函数进行数据缩放、class包的knn函数构建K近邻分类器
Talk about the RPA direction planning: stick to simple and valuable things for a long time
View touch analysis
Sikuli automatic testing technology based on pattern recognition
一键分析硬件/IO/全国网络性能脚本(强推)
通过券商经理的开户链接开股票账户安全吗?还是去证券公司开户安全?
Function: crypto JS encryption and decryption
[CEPH] cephfs internal implementation (II): example -- undigested
TCP congestion control details | 1 summary
SAP 销售数据 实际发货数据导出 销量
Database - sequence
The heavyweight white paper was released. Huawei continues to lead the new model of smart park construction in the future
Pytoch deep learning code skills
Unity C # e-learning (10) -- unitywebrequest (1)
【TcaplusDB知识库】TcaplusDB运维单据介绍
Smoothing data using convolution
1. accounting basis -- several major elements of accounting (general accounting theory, accounting subjects and accounts)
使用RestCloud ETL Shell组件实现定时调度DataX离线任务
The intersect function in the dplyr package of R language obtains the data lines that exist in both dataframes and the data lines that cross the two dataframes
Seurat转h5ad总结
