当前位置:网站首页>Learning diary - (routing and switching technology) dynamic routing (RIP protocol) and static routing
Learning diary - (routing and switching technology) dynamic routing (RIP protocol) and static routing
2022-07-23 12:50:00 【Make money and marry sweet】
One 、 Related knowledge
1、 Dynamic routing
- Dynamic routing is the communication between routers in the network , Passing routing information , The process of using the received routing information to calculate the route and update the routing table .
- Adapt to the changes of network structure in real time
- Suitable for large-scale networks 、 Complex network topology
- There are multiple network protocols , Common are RIP、OSPF、EIGRP etc.
- flexible , But it costs a lot
- Automatically exchange routing information , No administrator configuration required
2、RIP Routing protocol
- RIP Is a distance vector routing protocol , Internal gateway protocol , Applied in autonomous systems .
- RIP Use hops as the only measure of path selection .
- The number of hops cannot exceed 15.
- Every time 30s Broadcast a message working process .
Two 、 Related examples
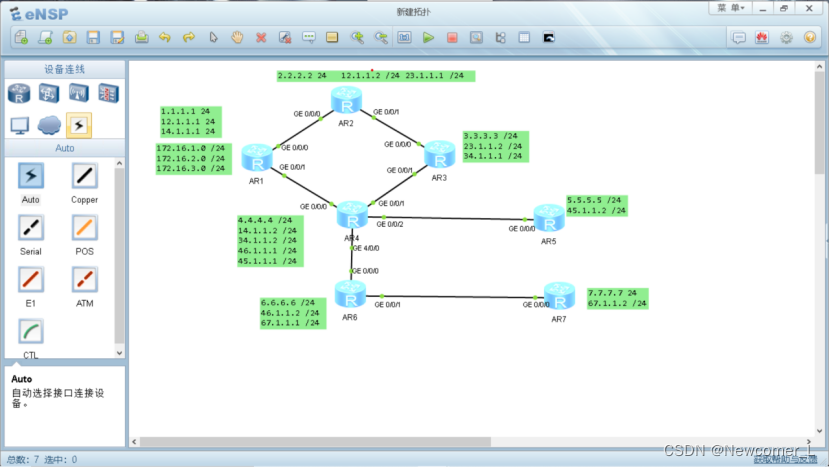
1、 topology
The... Of the host is omitted here IP Address configuration diagram , Readers configure themselves according to their own needs , Like me Gateways are all set 192.168.1/2/3.254

2、 Related codes :
In the routing table R representative RIP S It's static
Route 1:
Router>en
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#host
Router(config)#hostname R1
R1(config)#int g
R1(config)#int gigabitEthernet 0/0
R1(config-if)#ip add
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.254 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no sh
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
R1(config-if)#e
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int gigabitEthernet 0/1
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to up
R1(config-if)#e
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int gigabitEthernet 0/2
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/2, changed state to up
R1(config-if)#e
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/2, changed state to up
R1(config)#route rip This section is about configuration RIP agreement , Be careful :RIP The configured network segment is the direct connection network segment with the router .
R1(config-router)#net
R1(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0
R1(config-router)#network 192.168.12.0
R1(config-router)#network 192.168.13.0
R1(config-router)#ver
R1(config-router)#version 2( Version number )
R1(config-router)#end
R1#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
R1#show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.1.254/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
R 192.168.2.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.12.2, 00:00:09, GigabitEthernet0/1 (R It stands for RIP agreement )
R 192.168.3.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.13.2, 00:00:13, GigabitEthernet0/2 ([120/1],120 Represents management distance ,1 Representative expenses )
192.168.12.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 192.168.12.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
192.168.13.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.13.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/2
L 192.168.13.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/2
R 192.168.23.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.12.2, 00:00:09, GigabitEthernet0/1
[120/1] via 192.168.13.2, 00:00:13, GigabitEthernet0/2
Route 2:
Router>en
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#host
Router(config)#hostname R2
R2(config)#int g
R2(config)#int gigabitEthernet 0/0
R2(config-if)#ip add
R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.2.254 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shu
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
R2(config-if)#e
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#int gigabitEthernet 0/1
R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to up
R2(config-if)#e
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#int gigabitEthernet 0/2
R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/2, changed state to up
R2(config-if)#e
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/2, changed state to up
R2(config)#route rip This section is about configuration RIP agreement , Be careful :RIP The configured network segment is the direct connection network segment with the router .
R2(config-router)#net
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.2.0
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.12.0
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.23.0
R2(config-router)#ver
R2(config-router)#version 2
Route 3:
Router>en
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#host
Router(config)#hostname R3
R3(config)#int g
R3(config)#int gigabitEthernet 0/0
R3(config-if)#ip add
R3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.3.254 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no sh
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
R3(config-if)#e
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#int gigabitEthernet 0/1
R3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.13.2 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to up
R3(config-if)#
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#int gigabitEthernet 0/2
R3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/2, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/2, changed state to up
R3(config-if)#e
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#route rip This section is about configuration RIP agreement , Be careful :RIP The configured network segment is the direct connection network segment with the router .
R3(config-router)#net
R3(config-router)#network 192.168.3.0
R3(config-router)#network 192.168.13.0
R3(config-router)#network 192.168.23.0
R3(config-router)#ver
R3(config-router)#version 2
R3(config-router)#
R3(config-router)#end
R3#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
R3#show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
R 192.168.1.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.13.1, 00:00:05, GigabitEthernet0/1
R 192.168.2.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.23.1, 00:00:11, GigabitEthernet0/2
192.168.3.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.3.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.3.254/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
R 192.168.12.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.23.1, 00:00:11, GigabitEthernet0/2
[120/1] via 192.168.13.1, 00:00:05, GigabitEthernet0/1
192.168.13.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.13.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 192.168.13.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
192.168.23.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.23.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/2
--More--
result :
PC1 ping PC2

RIP Contrast with static
Route 1:
en
R1#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R1(config)#ip route 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.12.2
R1(config)#ip route 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.13.2
R1(config)#ip route 192.168.23.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.12.2
R1(config)#do show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.1.254/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
S 192.168.2.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.12.2
S 192.168.3.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.13.2
192.168.12.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 192.168.12.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
192.168.13.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.13.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/2
L 192.168.13.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/2
S 192.168.23.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.12.2
Route 2:
R2>en
R2#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R2(config)#ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.12.1
R2(config)#ip route 192.168.13.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.12.1
R2(config)#ip route 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.23.2
R2(config)#do show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
S 192.168.1.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.12.1
192.168.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.2.254/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
S 192.168.3.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.23.2
192.168.12.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 192.168.12.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
S 192.168.13.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.12.1
192.168.23.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.23.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/2
L 192.168.23.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/2
Route 3:
R3>en
R3#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R3(config)#ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.13.1
R3(config)#ip route 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.13.1
R3(config)#ip route 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.23.1
R3(config)#do show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
S 192.168.1.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.13.1
S 192.168.2.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.23.1
192.168.3.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.3.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.3.254/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
S 192.168.12.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.13.1
192.168.13.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.13.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 192.168.13.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
192.168.23.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.23.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/2
L 192.168.23.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/2
summary : When the network is equipped with RIP Routing protocol and static routing , The network will enable static routing , Why? ?
Because of the priority , The management distance ratio of static routing RIP(120) Small , So I will use static routing .
In the routing table R representative RIP S It's static
This article will be finished here , come on. !!
边栏推荐
- Overview of OpenSSL self visa process
- Article on the basic technology needed to build hybrid app
- 即时通讯WebSocket
- How many seats do you need for 1000 people to eat in 2 hours?
- Analysis of inheritablethreadlocal and Alibaba's transmittablethreadlocal design ideas
- Unity3d:UGUI源碼,Rebuild優化
- HCIP---BGP相关配置
- 第五周作业
- Reading Phoenix Architecture - History and knowledge of RPC
- LeetCode题解汇总
猜你喜欢
DHCP second experiment

HCIP-第一次实验

Super easy to use packet capturing tool tcpdump

Unity在URP管线下使用TriLib插件加载模型材质不正确的问题

C#(CSharp) 微信公众号开发一 基本配置

【读书笔记《凤凰架构》- 构架可靠的大型分布式系统.周志明】(一)

unity3d:UGUI源码EventSystem输入系统常见问题
Unity3d:ugui, UI and special effect particle level, bakemesh above 2018.2, particles between two images and in Scrollview

GameFramework:资源热更代码分析,检查版本信息,下载版本文件,校验版本文件,得到更新文件数量,下载文件,TaskPool

Hcip --- HCIA knowledge review (I)
随机推荐
详解TCP分段与IP分片
学习日记(路由与交换技术)——浮动静态路由和缺省路由
HCIP---GRE协议和MGRE环境,以及OSPF协议的相关知识点
学习日记——(路由与交换技术)网络地址转换 NAT技术
GameFramework:资源热更代码分析,检查版本信息,下载版本文件,校验版本文件,得到更新文件数量,下载文件,TaskPool
Explain the establishment of TCP connection in detail
浅做一下思科实验吧!
[bootloader architecture and brushing process based on UDS service]
HCIP-HCIA知识回顾(二)
学习日记——(路由与交换技术)三层交换机
Unity3d:ugui, UI and special effect particle level, bakemesh above 2018.2, particles between two images and in Scrollview
How to solve too many if statements
学习日记——(路由与交换技术)单臂路由
OSPF和RIP的路由扩展配置
Unity3d: special effect object pool, timeout delete GameObject in the pool, GC weight
学习日记——(路由与交换技术)OSPF协议
C# 自定义栈(Stack)
HCIP---OSPF细节讲解
MySQL性能优化,索引优化
LSM-tree(Log Structured-Merge Tree)的理解