当前位置:网站首页>(to be added) games101 job 7 improvement - knowledge you need to know to realize micro surface model
(to be added) games101 job 7 improvement - knowledge you need to know to realize micro surface model
2022-06-24 21:45:00 【flashinggg】
Catalog
Microplane theory Microfacet Theory
Micro surface BRDF The implementation of the
1 Normal distribution function D
Trowbridge-Reitz Distribution (GGX Distribution ) The formula
Surface roughness Edit the value
Micro surface material model
Microfacet Material, It is also a realistic material model , At the same time PBR(Physicallly-Based-Rendering Based on physical rendering ) Something based on .
Involved in previous work BRDF, namely Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function, Bidirectional reflection distribution function , Microsurface model is based on physics BRDF, It is also the most commonly used kind of physics BRDF,Disney Priciple BRDF Also added
Microplane theory Microfacet Theory
The following is my understanding of the micro plane theory in combination with the course content .
in real life , The surfaces of objects are irregular , There will be potholes when you look closer , This means that these pitted surfaces reflect light in different directions . But for every small surface , Incident light is only divided into reflected light and refracted light . Based on this , Microsurface model assumptions :① The size of the micro surface is smaller than the colored area and larger than the visible wavelength ; The surface of an object is its appearance from a distance (diffuse、glossy), From a close view, there are tiny 、 A flat geometric surface ,② These flat geometric surfaces conform to the laws of geometric optics , Can be seen as a very small mirror ;③ Light is only ejected once between micro surfaces (single-bounce), The light emitted after one shot does not change the shading result .( About assumptions ③, The multiple ejection of light shown in the figure below is not considered here , There will be a separate post on subsurface scattering technology )

With these assumptions , The key to solve the micro surface material model is : Solve the distribution of micro surface orientation , To be specific Normal distribution of micro surface . Here's the picture , For the relationship between two typical materials and normal distribution : Normal set ->glossy; Normal divergence ->diffuse.

Micro surface BRDF The implementation of the
We often use Cook-Torrance BRDF To achieve Microfacet:
Cook-Torrance BRDF
Cook-TorranceBRDF The diffuse reflection and specular reflection of the micro surface are considered , The formula is as follows :

among : —— The ratio of refracted light to incident light ;
—— The ratio of refracted light to incident light ;
 —— The proportion of reflected light to incident light ;
—— The proportion of reflected light to incident light ;
 —— Diffuse reflection (diffuse) Of BRDF;
—— Diffuse reflection (diffuse) Of BRDF;
 —— Specular reflection (specular) Of BRDF;
—— Specular reflection (specular) Of BRDF;
Diffuse term
Diffuse BRDF It's a constant term , Diffuse reflection bounces evenly in the hemispherical direction , From before GAMES101 The result of radiometry calculation in class , You can write the formula for diffuse reflection directly :

Specular items
The formula is as follows :

among , Is the incidence direction ;
Is the incidence direction ; Is the exit direction ;
Is the exit direction ; Is the half angle vector (halfway vector), That is, the intermediate vector between the two ;
Is the half angle vector (halfway vector), That is, the intermediate vector between the two ; For Fresnel term ;
For Fresnel term ; For the shadow occlusion function ;
For the shadow occlusion function ; Is the normal distribution function .
Is the normal distribution function .
It is worth mentioning that ,Cook-Torrance BRDF Specular items of the model (specular reflection) It's based on Torrance-Sparrow BRDF A complete isotropic material reflection model , And then apply it to the result of graphics . This value is used to depict the highlight of the material . Diffuse reflection diffuse Item is used to depict the shading of materials , The following are the diffuse items
Next, the normal distribution function 、 Shadow shading coefficient and Fresnel term .
1 Normal distribution function D
The first thing to be clear about is , The normal distribution function has Phong Distribution 、Beckmann Distribution 、GGX Distribution (Trowbridge-Reitz Distribution ), The following will only be combined with GGX Distribution to introduce the normal distribution function .
Normal distribution function (Normal Distribution Fuction),NDF, Write it down as : . On the definition of normal distribution function ,How Is The NDF Really Defined? – Nathan Reed’s coding blog That's how it's described in :“NDF statistically describes the microscopic shape of the surface as a distribution of microfacet orientations.”, namely : The shape of micro surface is described as the distribution of surface orientation . at present , The mainstream normal distribution function has changed from the traditional Blinn-Phong The distribution and Beckmann Distribution , Developed to be closer to the appearance of real-world materials GGX Distribution .
. On the definition of normal distribution function ,How Is The NDF Really Defined? – Nathan Reed’s coding blog That's how it's described in :“NDF statistically describes the microscopic shape of the surface as a distribution of microfacet orientations.”, namely : The shape of micro surface is described as the distribution of surface orientation . at present , The mainstream normal distribution function has changed from the traditional Blinn-Phong The distribution and Beckmann Distribution , Developed to be closer to the appearance of real-world materials GGX Distribution .
GGX Distribution profile

A brief introduction GGX This symbol ,GGX We often see it in various places . Actually GGX Distribution is Walter Wait for someone in the paper Microfacet Models for Refraction through Rough Surfaces (cornell.edu)
A new microsurface distribution function mentioned in , This function can simulate the transmission effect of rough surface , The following figure shows the use GGX Rendering of a glass ball effect :


GGX Distribution is Walter And others , In his opinion NDF Follow the following equation :

among , —— Indicates macro ( From afar ) A small flat area on the surface ;
—— Indicates macro ( From afar ) A small flat area on the surface ; —— The direction is
—— The direction is  The total area of all small flat areas .
The total area of all small flat areas .
This formula shows that ,NDF Does not mean density , It's a unit area 、 The area of a microplane per unit solid angle . Integral of the above formula :

among , —— The area of a micro surface projected onto a macro surface ; The right side of the equation represents the integral of the solid angle of the positive hemisphere , The left indicates in all directions
—— The area of a micro surface projected onto a macro surface ; The right side of the equation represents the integral of the solid angle of the positive hemisphere , The left indicates in all directions  The microplane area and , And the sum of the projected areas of the micro surface in all directions of the macro surface is equal to
The microplane area and , And the sum of the projected areas of the micro surface in all directions of the macro surface is equal to  . So the right side of the equation should be equal to 1.
. So the right side of the equation should be equal to 1.

Besides ,GGX There is also a limit to the distribution : For any viewing direction  , Yes :
, Yes :

The geometric meaning of this formula is shown in the figure below :
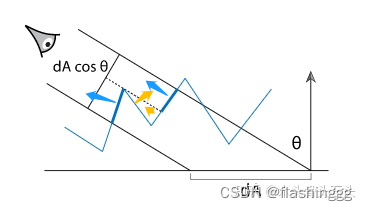
You can see , In the direction  On , To find the projected area on a macroscopic surface , If the orientation shown in the above figure is Orange arrow Micro surface of , The positive and negative offsets after the projection , The rest is facing Blue arrow The projection and . So the projection can be expressed as
On , To find the projected area on a macroscopic surface , If the orientation shown in the above figure is Orange arrow Micro surface of , The positive and negative offsets after the projection , The rest is facing Blue arrow The projection and . So the projection can be expressed as  .
.
Trowbridge-Reitz Distribution (GGX Distribution ) The formula
Also known as GGX Distribution , The paper Microfacet Models for Refraction through Rough Surfaces The form given in is :

The simplified formula can be used for calculation :

among :
 : Surface roughness , Generally in [0,1] Between , The bigger the coarser ;
: Surface roughness , Generally in [0,1] Between , The bigger the coarser ;
 : Macro surface normal vector ;
: Macro surface normal vector ;
 : Micro plane normal vector , Same as above , That is, the intermediate vector between the incident direction and the outgoing direction .
: Micro plane normal vector , Same as above , That is, the intermediate vector between the incident direction and the outgoing direction .
Surface roughness  The value of
The value of
About the value of surface roughness , The reference article says so :“ In Disney principle coloring model Disney principled shading model in , It is recommended that the roughness be controlled by  Expose to users , among
Expose to users , among  yes 0 To 1 User interface roughness parameter value of , It can make GGX The distribution changes in a more linear way , And this method is more practical , A lot of use GGX Distributed engines and games use this mapping method .” there
yes 0 To 1 User interface roughness parameter value of , It can make GGX The distribution changes in a more linear way , And this method is more practical , A lot of use GGX Distributed engines and games use this mapping method .” there  Express
Express , Roughness .
Implementation code
float DistributionGGX(float NdotH, float roughness) {
float a2 = roughness * roughness;
float pi = 3.1415;
float m = NdotH * NdotH * (a2 - 1) + 1;
return a2 / (pi * m * m);// Note that the denominator cannot be 0, The real use needs to give a minimum value
}So here we go , Enough to write GGX Density distribution function code , If you want to know more about how the formula is pushed , You can take a closer look at the derivation process in the paper .
Here we can understand : Why say and Phong and Beckmann comparison ,GGX Closer to the truth ? because GGX It can better show the dissipation of metal highlights ( trailing ) effect , Here you can refer to Fundamentals of graphics rendering : Micro surface material model - You know (zhihu.com) The explanation in one article :
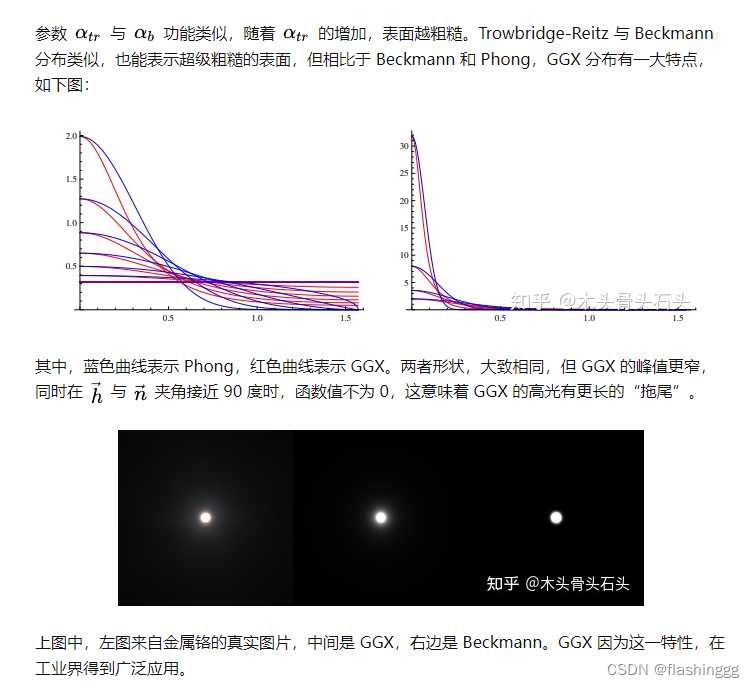
because GGX The highlight has a longer tail , So in Represent real metal surfaces It's better when .
2 Shadow occlusion function G
The micro surface is uneven , From different observation directions, it is inevitable that one surface will be blocked by another surface ( Here's the picture , Source watermark ). among , light illumination Occlusion is called self shadowing ; From line of sight viewing Looking at the past, being blocked is called self occlusion .
BSDF A geometric function is defined  It is used to simulate the light caused by mutual occlusion of micro surfaces Energy loss The phenomenon of , This function is called the shadow occlusion function , It is not difficult to see from the definition that , The value of this function should also be from [0,1] Of . meanwhile , Geometric functions have two forms :
It is used to simulate the light caused by mutual occlusion of micro surfaces Energy loss The phenomenon of , This function is called the shadow occlusion function , It is not difficult to see from the definition that , The value of this function should also be from [0,1] Of . meanwhile , Geometric functions have two forms :
—— The micro plane is in a single direction ( The direction of the light
 or Direction of sight
or Direction of sight  ) Upper visible scale , Light corresponds to Masking function masking function; Line of sight corresponds to Shadow function shadowing function.
) Upper visible scale , Light corresponds to Masking function masking function; Line of sight corresponds to Shadow function shadowing function.
—— The proportion of a microplane that is commonly visible in the direction of illumination and line of sight , be called Joint shadowing function joint masking-shadowing function.
among , from
Derived from , At the same time, the geometric function in general micro surface material calculation refers to
Smith Masking function
Smith Masking function , namely Smith masking function. Since the nature of self shadowing is the same as that of self occlusion , Only visible micro surfaces can contribute to coloring , therefore Smith They are considered to be independent of each other , With the following product Smith Function:

among  Denotes the incident and outgoing directions respectively , The corresponding words are light source and observation direction .
Denotes the incident and outgoing directions respectively , The corresponding words are light source and observation direction .
Smith The shadowing function is very accurate for random surfaces , but For some non random surfaces 、 The accuracy of repetitive pattern representation will be reduced ( For example, the highly repetitive structure of fabrics ). Therefore, some special patterns will be used for the repeated structure pattern of cloth shading model To calculate .
Disney Implementation method

Refer to the above figure , Defined function ,, Indicates that the normal direction is
 The microsurfaces are looking in the direction
The microsurfaces are looking in the direction  The proportion of the surface that is not occluded . According to the one discussed above GGX The provisions of the , For any viewing direction
The proportion of the surface that is not occluded . According to the one discussed above GGX The provisions of the , For any viewing direction  , Yes :
, Yes :

Then there is :

among , It is used to eliminate the micro surface facing away from the observation direction .
It is used to eliminate the micro surface facing away from the observation direction .
Write it down to simplify  The calculation of , It is assumed that it is independent of the orientation of the micro surface , You can bring it up . And then the angle with the line of sight is greater than and less than
The calculation of , It is assumed that it is independent of the orientation of the micro surface , You can bring it up . And then the angle with the line of sight is greater than and less than  The microsurface area and of the , Named as
The microsurface area and of the , Named as  and
and  , obtain :
, obtain :

According to this formula , combination  Can deduce accurate
Can deduce accurate  .
.
among : , Remapping the roughness to reduce the extreme gain of glossy surfaces , Make the roughness change smoother .
, Remapping the roughness to reduce the extreme gain of glossy surfaces , Make the roughness change smoother .
Implementation code
// Yes G1 The implementation of the
float SmithG_GGX(float NdotV, float roughness) {
float r = 0.5 + roughness / 2.0f;
float m = r * r + (1 - r * r) * NdotV * NdotV;
return 2.0f * NdotV / (NdotV + std::sqrt(m));
}
// The light source direction and observation direction are calculated respectively ggx1 and ggx2, Multiply to get G
float GeometrySmith(Vector3f N, Vector3f V, Vector3f L, float roughness) {
float NdotV = std::max(dotProduct(N, V), 0.0f);
float NdotL = std::max(dotProdoct(N, L), 0.0f);
float ggx1 = SmithG_GGX(NdotL, roughness);
float ggx2 = SmithG_GGX(NdotV, roughness);
return ggx1 * ggx2;
}UE4 Method -SchlickGGX
UE4 The method adopted is to use Schlick The approximate Smith To calculate geometric functions , Please refer to this article for specific calculation :
graphics |PBR:Schlick Approximate method - You know (zhihu.com)

among :
Implementation code
float GeometrySchlickGGX(float NdotV, float roughness) {
float r = roughness + 1;
float k = r * r / 8;
float m = NdotV / NdotV * (1.f - k) + k;
return NdotV / m;
}
// The light source direction and observation direction are calculated respectively ggx1 and ggx2, Multiply to get G
float GeometrySmith(Vector3f N, Vector3f V, Vector3f L, float roughness) {
float NdotV = std::max(dotProduct(N, V), 0.0f);
float NdotL = std::max(dotProdoct(N, L), 0.0f);
float ggx1 = GeometrySchlickGGX(NdotL, roughness);
float ggx2 = GeometrySchlickGGX(NdotV, roughness);
return ggx1 * ggx2;
}In addition to the above two methods, there are other , If you want to know, you can read this article :PBR GGX Specular G Geometric functions - Nuggets (juejin.cn)
3 Fresnel term F
Is to calculate the proportion of reflected light . For the calculation of the Fresnel effect and the Fresnel term, it is necessary to 5 In the introduction , I won't repeat it here , Post code directly , What you want to know can be moved GAMES101 Homework 5- Understand the code from beginning to end &Whitted Ray tracing _flashinggg The blog of
Implementation code
Here, the calculation function of the Fresnel term in the framework is directly posted :
// Fresnel equation , And homework 5 identical
void fresnel(const Vector3f &I, const Vector3f &N, const float &ior, float &kr) const
{
float cosi = clamp(-1, 1, dotProduct(I, N));
float etai = 1, etat = ior;
if (cosi > 0) { std::swap(etai, etat); }
// Compute sini using Snell's law
float sint = etai / etat * sqrtf(std::max(0.f, 1 - cosi * cosi));
// Total internal reflection
if (sint >= 1) {
kr = 1;
}
else {
float cost = sqrtf(std::max(0.f, 1 - sint * sint));
cosi = fabsf(cosi);
float Rs = ((etat * cosi) - (etai * cost)) / ((etat * cosi) + (etai * cost));
float Rp = ((etai * cosi) - (etat * cost)) / ((etai * cosi) + (etat * cost));
kr = (Rs * Rs + Rp * Rp) / 2;
}What is? BSDF
BSDF(Bidirectional Scattering Distribution Function,S That means “ scattering ”), Describes how light scatters on the surface of an object , It reflects the corresponding relationship between the incident and outgoing intensity of light . What we talked about before Reflection model BRDF and Transmission model BTDF(T finger Transmittance, transmission ) yes BSDF The model results are limited to reflection and transmission respectively .BSDF Itself is BRDF and BTDF Comprehensive effect .
Disney Principle BRDF
Disney There is a set of its own based on micro surface theory BRDF Implementation model , Form the following :

among :DIFFUSE—— Sub surface scattering of nonmetals
See here , Implementation work 7 There is no problem with the improvement of micro surface material in , There will be another post to introduce the specific implementation code .
And then I will summarize other expanded contents from the study of micro surface materials , for example PBR What else is there besides the micro surface ?Disney Principle What is it? ? wait ...
Reference resources
Fundamentals of graphics rendering : Micro surface material model - You know (zhihu.com)
How Is The NDF Really Defined? – Nathan Reed’s coding blog (reedbeta.comd
边栏推荐
- Memcached comprehensive analysis – 5 Memcached applications and compatible programs
- Football information query system based on C language course report + project source code + demo ppt+ project screenshot
- The first day of handwritten RPC -- review of some basic knowledge
- Direct attack on "three summers" production: good harvest news spreads frequently and summer broadcasting is in full swing
- Failed to open after installing Charles without any prompt
- 升哲科技 AI 智能防溺水服务上线
- Pattern recognition - 0 introduction
- CondaValueError: The target prefix is the base prefix. Aborting.
- 123. 买卖股票的最佳时机 III
- leetcode_191_2021-10-15
猜你喜欢

关于Unity中的transform.InverseTransformPoint, transform.InverseTransofrmDirection

VirtualBox虚拟机安装Win10企业版

Memcached comprehensive analysis – 2 Understand memcached memory storage
![[精选] 多账号统一登录,你如何设计?](/img/df/9b4fc11a6971ebe8162ae84250a782.png)
[精选] 多账号统一登录,你如何设计?

The first day of handwritten RPC -- review of some basic knowledge

Blender's landscape

Introduce the overall process of bootloader, PM, kernel and system startup

【Camera基础(二)】摄像头驱动原理和开发&&V4L2子系统驱动架构

Why are life science enterprises on the cloud in succession?

手动事务的几个类
随机推荐
TCP Jprobe utilization problem location
力扣每日一题-第26天-496.下一个更大元素Ⅰ
[camera Foundation (II)] camera driving principle and Development & v4l2 subsystem driving architecture
leetcode-201_2021_10_17
JMeter implementation specifies concurrent loop testing
TCP specifies the source port
力扣每日一题-第25天-496.下一个更大元素Ⅰ
leetcode1863_2021-10-14
Tso hardware sharding is a header copy problem
XTransfer技术新人进阶秘诀:不可错过的宝藏Mentor
memcached全面剖析–5. memcached的应用和兼容程序
Functional analysis of ebpf tracepoint
Web project deployment
【产品设计研发协作工具】上海道宁为您提供蓝湖介绍、下载、试用、教程
Notes_ Vlan
【吴恩达笔记】卷积神经网络
Tutorial on obtaining JD cookies by mobile browser
The most important thing at present
Blender's landscape
架构实战营 第 6 期 毕业总结
 The value of
The value of