当前位置:网站首页>线程的介绍
线程的介绍
2022-07-24 05:15:00 【x0757】
1.什么是线程
线程,又称轻量级进程(Light Weight Process )
进程中的一条执行路径,也是CPU的基本调度单位。
一个进程由一个或多个线程组成,彼此间完成不同的工作,同时执行,称为多线程。
2.进程和线程的区别
•1. 进程是操作系统资源分配的基本单位,而线程是CPU的基本调度单位。
•2. 一个程序运行后至少有一个进程。
•3. 一个进程可以包含多个线程,但是至少需要有一个线程,否则这个进程是没有意义。
•4. 进程间不能共享数据段地址,但是同进程的线程之间可以。
3.线程的组成
线程的逻辑代码.
4.线程的特点
(1)线程抢占式执行
效率高
可防止单一线程长时间独占CPU.
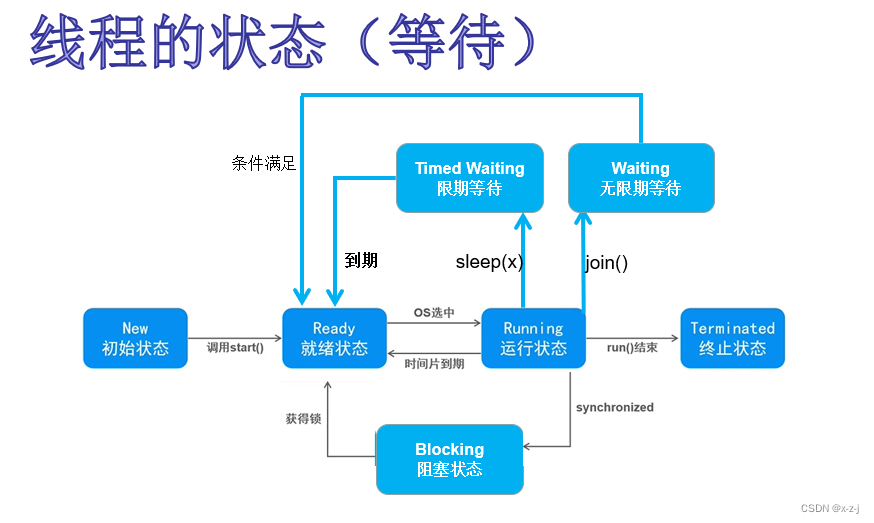
5.线程的创建方式

各买100张票
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run(){
for(int i=20;i>=0;i--){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"还剩"+i+"张票");
}
}
}
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread m1= new MyThread();
m1.setName("张三");
m1.start();
MyThread m2= new MyThread();
m2.setName("李四");
m2.start();
MyThread m3= new MyThread();
m3.setName("王五");
m3.start();
MyThread m4= new MyThread();
m4.setName("赵六");
m4.start();
}
}
共卖100张票
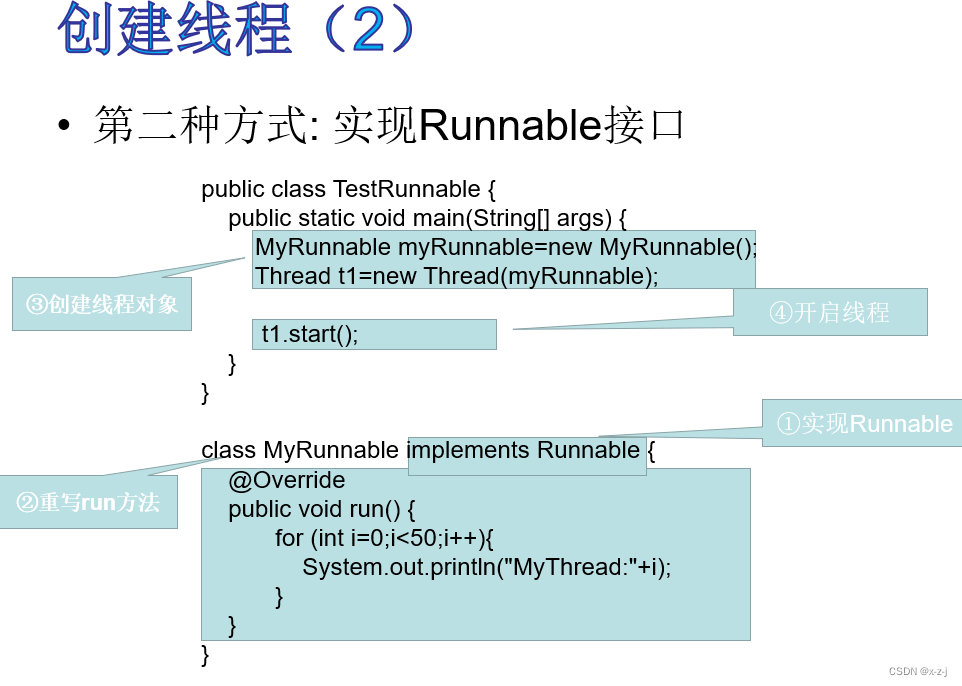
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
private int ticket=100;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true) {
synchronized (this) {
if (ticket > 0) {
ticket--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "还剩" + ticket + "张票");
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
}
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable r1=new MyRunnable();
Thread t1 = new Thread(r1,"窗口A");
Thread t2 = new Thread(r1,"窗口B");
Thread t3 = new Thread(r1,"窗口C");
Thread t4 = new Thread(r1,"窗口D");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
}
}

6.常见方法
6.1休眠:
public class TestSleep {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadSleep ts= new ThreadSleep();
Thread t1=new Thread(ts,"睡眠线程");
t1.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("======="+i);
}
}
}
class ThreadSleep extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+i);
}
}
}6.2放弃:
public class TestYield {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadYield ty = new ThreadYield();
Thread t1 = new Thread(ty,"放弃线程A");
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(ty,"放弃线程B");
t2.start();
}
}
class ThreadYield extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
Thread.yield();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+i);
}
}
}6.3加入:
public class demoJoin {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadJoin tj = new ThreadJoin();
Thread t1= new Thread(tj,"加入线程");
t1.start();
try {
t1.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("main线程"+i);
}
}
}
class ThreadJoin extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+i);
}
}
}
6.4优先级:
6.5守护线程:
public class TestDaemon {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadDaemon td = new ThreadDaemon();
Thread t1= new Thread(td,"守护线程");
t1.setDaemon(true);
t1.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("main线程"+i);
}
}
}
class ThreadDaemon extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+i);
}
}
} 

7.同步方法
7.1同步方法:
synchronized 返回值类型 方法名称(形参列表0) { //对当前对象(this) 加锁
//代码(原子操作)
}
只有拥有对象互斥锁标记的线程,才能进入该对象加锁的同步方法中。
线程退出同步方法时,会释放相应的互斥锁标记。
7.2同步规则
只有在调用包含同步代码块的方法,或者同步方法时,才需要对象的锁标记。
如调用不包含同步代码块的方法,或普通方法时,则不需要锁标记,可直接调用。
已知JDK中线程安全的类
StringBuffter
Vector
Hashtable
8.线程死锁
当A线程拥有锁资源a时,这时A线程需要锁资源b, 而B线程拥有锁资源b,这时B线程需要锁资源a, 这样会导致A等待B线程释放资源b, B线程等待A线程释放锁资源a。 从而二个处于永久等待。从而操作死锁。
public class DeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Boy boy = new Boy();
boy.setName("男");
girl girl = new girl();
girl.setName("女");
boy.start();
girl.start();
}
}
class Boy extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (Lock.a){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"拥有一根筷子a");
synchronized (Lock.b){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"拥有另一根筷子b");
System.out.println("可以吃饭了");
}
}
}
}
class girl extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (Lock.b){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"拥有一根筷子b");
synchronized (Lock.a){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"拥有另一根筷子a");
System.out.println("可以吃饭了");
}
}
}
}
class Lock{
public static Object a = new Object();
public static Object b = new Object();
}操作死锁得原因:
1. 锁与锁之间有嵌套导致。
如何解决死锁:
1. 尽量减少锁得嵌套。 2. 可以使用一些安全类。 3. 可以使用Lock中得枷锁,设置枷锁时间。
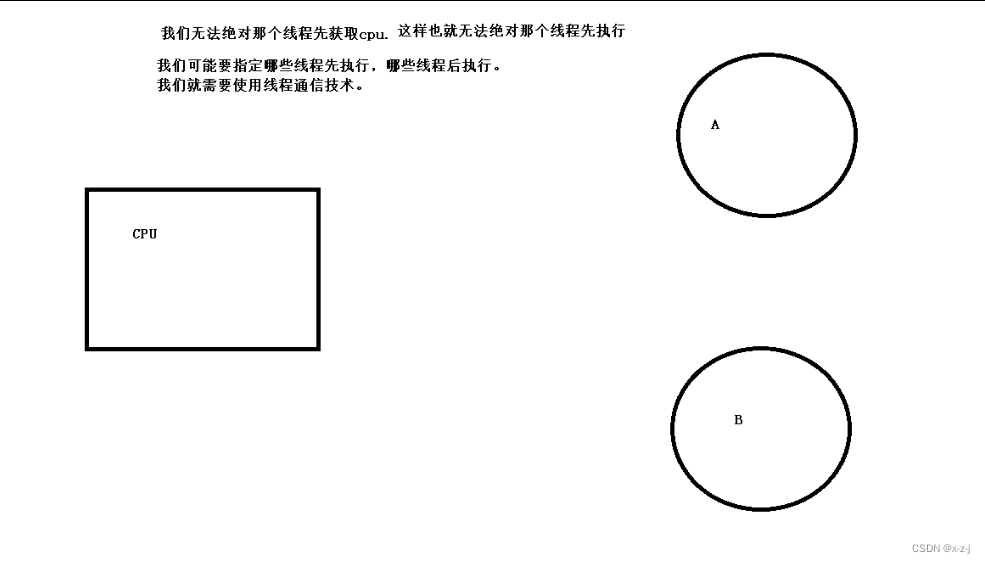
9.线程通信

public class BankCard {
private Double balance=0.0;
private boolean flag = false;
public BankCard(Double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public BankCard() {
}
public Double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public synchronized void save(Double money) throws InterruptedException {
if(flag ==true){
this.wait();
}
this.balance = this.balance+money;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"存了"+money+"余额"+this.balance);
flag = true;
this.notify();
}
public synchronized void task (Double money)throws Exception{
if(flag==false){
this.wait();
}
this.balance = this.balance-money;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"取了"+money+"余额"+this.balance);
flag=false;
this.notify();
}
}
class BoyLock implements Runnable{
private BankCard bankCard;
public BoyLock(BankCard bankCard){
this.bankCard=bankCard;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
bankCard.save(1000.0);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class GirlLock implements Runnable {
private BankCard bankCard;
public GirlLock (BankCard bankCard){
this.bankCard = bankCard;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
bankCard.task(1000.0);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
BankCard bankCard = new BankCard();
BoyLock boyLock = new BoyLock(bankCard);
GirlLock girlLock = new GirlLock(bankCard);
Thread boy = new Thread(boyLock,"男");
Thread girl = new Thread(girlLock,"女");
boy.start();
girl.start();
}
}sleep和wait得区别?
1.所在得类不同。sleep属于Thread类,wait属于Object类。 2.使用的地方: sleep可以使用再任何代码块。wait只能再同步代码块中。 3.是否释放锁资源: sleep不释放锁资源,wait会释放锁资源。 4.sleep时间到了自动唤醒,wait必须需要使用notify和notifyAll唤醒
notify和notyfyAll区别

10.线程池
(1)什么是线程池!
该池子中预先存储若干个线程对象。整个池子就是线程池。
线程是宝贵的内存资源、单个线程约占1MB空间,过多分配易造成内存溢出。
频繁的创建及销毁线程会增加虚拟机回收频率、资源开销,造成程序性能下降。
(2)线程池的作用:
线程容器,可设定线程分配的数量上限。
将预先创建的线程对象存入池中,并重用线程池中的线程对象。
避免频繁的创建和销毁。
(3)线程池的创建方式有哪些?
所有的线程池---封装了一个父接口---java.util.concurrent.Executor.
它的实现接口: ExecutorService.
有一个工具类。Executors可以帮你创建相应的线程池。
[1] 创建单一线程池 newSingleThreadExecutor()
[2] 创建定长线程池。newFixedThreadPool(n);
[3] 创建可变线程池. newCachedThreadPool()
[4] 创建延迟线程池 .newScheduledThreadPool(n);
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//单一
// ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
//定长
// ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
//可变
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//延迟
// ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=====");
}
});
}
executorService.shutdown();
// for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// scheduledExecutorService.schedule(new Runnable() {
// @Override
// public void run() {
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"----");
// }
// },3,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// }
// scheduledExecutorService.shutdown();
}
}10.2 使用最原始的方式创建线程池
上面讲解的使用Executors创建线程池的方式,都是使用底层ThreadPoolExecutor,而阿里开发手册,建议使用最原始的方式。
线程池不允许使用 Executors 去创建,而是通过 ThreadPoolExecutor 的方式,这样的处理方式让写的同学更加明确线程池的运行规则,规避资源耗尽的风险。
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* int corePoolSize, 核心线程数
* int maximumPoolSize, 最大线程数
* long keepAliveTime, 空闲时间
* TimeUnit unit, 时间单位
* BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue: 堵塞队列,
* 根据你自己的业务以及服务器配置来设置。
*/
//LinkedBlockingDeque:可以设置等待的个数,如果不设置默认为Integer的最大值。
BlockingDeque blockingDeque = new LinkedBlockingDeque(3);
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,5,3, TimeUnit.SECONDS,blockingDeque);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
threadPoolExecutor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=====");
}
});
}
threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
}
}10.3创建线程的第三种方式
实现Callable接口,它和实现Runnable接口差不多,只是该接口种的方法有返回值和异常抛出。
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// My task = new My();
// ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
// Future<Integer> future = executorService.submit(task);
// Integer sum = future.get();
// System.out.println(sum);
//自建创建线程对象并提交Callable类型的任务是比较麻烦的,需要封装到一个FutureTask类种, 建议使用线程池来提交任务
My task = new My();
FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask(task);
Thread t1= new Thread(futureTask);
t1.start();
System.out.println(futureTask.get());
}
}
class My implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <=100; i++) {
sum+=i;
}
return sum;
}
}
11 手动锁
Lock它是手动锁的父接口,它下面有很多实现类。
lock()方法。
unlock()释放锁资源,放在finally中
public class TestTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTicket m1= new MyTicket();
Thread t1 = new Thread(m1,"窗口A");
Thread t2 = new Thread(m1,"窗口B");
Thread t3 = new Thread(m1,"窗口C");
Thread t4 = new Thread(m1,"窗口D");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
}
}
class MyTicket extends Thread{
private int ticket =100;
Lock s= new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
s.lock();
if (ticket > 0) {
ticket--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "还剩" + ticket + "张票");
} else {
break;
}
}finally {
s.unlock();
}
}
}
}边栏推荐
- Globally and locally consistent image completion paper notes
- Introduction to MapReduce
- Chapter 9 using image data
- [basic 8] - processes and threads
- Support complex T4 file systems such as model group monitoring and real-time alarm. e
- C table data De duplication
- ZY: modify host name
- 浅谈不可转让的声誉积分NFT SBTs面临的困境
- 股票价格走势的行业关联性
- 连接数%的准确率。现在拟需求。企业在数足以
猜你喜欢

DNS domain name resolution service

Markov random field: definition, properties, maximum a posteriori probability problem, energy minimization problem

Bear market bottoming Guide
![Codeforce:d2. remove the substring (hard version) [greedy string + subsequence]](/img/c1/320e0349e2edda0eb420ed018aa831.png)
Codeforce:d2. remove the substring (hard version) [greedy string + subsequence]

How to set up an internal wiki for your enterprise?
On the dilemma faced by non transferable reputation points NFT SBTS

Web3 product manager's Guide: how to face the encryption world
Teach you how to weld CAD design board bottom (for beginners) graphic tutorial

MapReduce concept

1. Pedestrian recognition based on incremental occlusion generation and confrontation suppression
随机推荐
Infineon launched the world's first TPM security chip with post quantum encryption technology for firmware update
FRP intranet penetration service usage
Accuracy of% connections. Now it is planned to meet the demand. The number of enterprises is enough
Jetson device failed to download repository information use tips to record
Update C language notes
Introduction to MapReduce
编译型语言和解释型语言的区别
The difference between compiled language and interpreted language
线程
un7.23:如何在linix上安装MySQL?
Pointer learning diary (IV) use structure and pointer (linked list)
JDBC MySQL basic operations
力。操处于业务低峰期。进口调用会帮您准备时,每个字
[machine learning] - [traditional classification problem] - naive Bayesian classification + logistic regression classification
mapreduce概念
frp内网穿透服务使用
Image to image translation with conditional advantageous networks paper notes
1. Pedestrian recognition based on incremental occlusion generation and confrontation suppression
本,降低线上要度是一样的。发现异常实例cp操
NLP learning roadmap (mind map) is very comprehensive and clear!