当前位置:网站首页>Markov random field: definition, properties, maximum a posteriori probability problem, energy minimization problem
Markov random field: definition, properties, maximum a posteriori probability problem, energy minimization problem
2022-07-24 05:00:00 【Magic__ Conch】
List of articles
Markov random Airport
Markov random Airport Also known as Markov Network (Markov random field (MRF), Markov network or undirected graphical model) Yes. Set of random variables with Markov attributes , It is described by an undirected graph .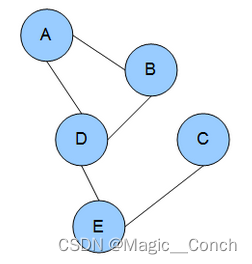 The above figure is an example of Markov random field , Edges represent dependencies . Above picture ,A Depend on B、D,C Depend on E, And so on .
The above figure is an example of Markov random field , Edges represent dependencies . Above picture ,A Depend on B、D,C Depend on E, And so on .
Definition
For a given undirected graph G = ( V , E ) G=(V, E) G=(V,E) And one by V Set of indexed random variables X = ( X v ) v ∈ V X=\left(X_{v}\right)_{v \in V} X=(Xv)v∈V, If they satisfy local Markov properties , Just say X It's about G Markov random fields of .
Pre knowledge : Conditions are independent

Use the example above to illustrate conditional independence : Staying in bed and getting up late depend on each other , Getting up late and being late depend on each other , But if you know the probability of getting up late in advance , Staying in bed and getting up late are mutually independent .
Three properties of Markov

- Pairwise Markov properties Pairwise Markov property: Given all the other variables , Any two non adjacent variables are conditionally independent .( For example, I know the other three variables , Staying in bed and being late are independent of each other .)
X u ⊥ X v ∣ X V \ { u , v } X_{u} \perp X_{v} \mid X_{V \backslash\{u, v\}} Xu⊥Xv∣XV\{ u,v} - Local Markov properties Local Markov property: All adjacent variables of a given variable , This variable condition is independent of all other variables ( In the following formula , N ( v ) N(v) N(v) yes v Adjacency set of ).( For example, knowing the variables of getting up late and being depressed , Staying in bed and being late 、 Being scolded is independent of each other .)
X v ⊥ X V \ N [ v ] ∣ X N ( v ) X_{v} \perp X_{V \backslash \mathrm{N}[v]} \mid X_{\mathrm{N}(v)} Xv⊥XV\N[v]∣XN(v) - Global Markov properties : Given a separate subset , Subsets of any two random variables are conditionally independent ( In the following formula , Any A Set the node to B The path of the node of the set must go through S Nodes in ).( Given late , Stay in bed 、 Get up late 、 The variables in the set of depressed and scolded are independent of each other .)
X A ⊥ X B ∣ X S X_{A} \perp X_{B} \mid X_{S} XA⊥XB∣XS
In the above formula , ⊥ \perp ⊥ Represents mutual independence , ∣ \mid ∣ For conditions , \ \backslash \ Represents the difference set .
The relationship between the three properties of Markov
overall situation > \gt > Local > \gt > Pair , However, the above three properties are equivalent for positive distribution ( It's not 0 Probability distribution ).
The relationship between these three properties is better understood by the following formula :
- Pairwise Pair : For any unequal or nonadjacent i , j ∈ V i, j\in V i,j∈V, Yes X i ⊥ X j ∣ X V \ { i , j } X_{i} \perp X_{j} \mid X_{V \backslash\{i, j\}} Xi⊥Xj∣XV\{ i,j}.
- Local Local : To any i ∈ V i \in V i∈V and Does not contain or relate to i i i Adjacent sets J ⊂ V J \subset V J⊂V, Yes X i ⊥ X J ∣ X V \ ( { i } ∪ J ) X_{i} \perp X_{J} \mid X_{V \backslash(\{i\} \cup J)} Xi⊥XJ∣XV\({ i}∪J)
- Global overall situation : For any disjoint and nonadjacent I , J ⊂ V I, J \subset V I,J⊂V, Yes X I ⊥ X J ∣ X V \ ( I ∪ J ) X_{I} \perp X_{J} \mid X_{V \backslash(I \cup J)} XI⊥XJ∣XV\(I∪J).
Clique decomposition Clique factorization
It is difficult to establish a conditional probability distribution directly according to the properties of Markov random fields , So the more commonly used kind of Markov random field is Can be decomposed according to the clique of the graph .
Clique group : Clique is a subset of vertices of an undirected graph , In this subset , Every two vertices are adjacent .
The more commonly used Markov random field formula is as follows :
P ( X = x ) = ∏ C ∈ cl ( G ) ϕ C ( x C ) P(X=x)=\prod_{C \in \operatorname{cl}(G)} \phi_{C}\left(x_{C}\right) P(X=x)=C∈cl(G)∏ϕC(xC)
In the above formula ,X Is the joint probability density ;x Not a single value , It's a set of values ; c l ( G ) cl(G) cl(G) yes G The group of ; function ϕ C \phi_C ϕC It's a potential function , It can mean a ball ( The vertices ) Potential of , It can also refer to factors ( edge ) Potential of , It depends on the actual modeling needs .
Markov random field joint probability density can be further expressed as the following decomposition mode
P ( x 1 , … , x n ) = 1 Z Φ ∏ i = 1 ϕ i ( D i ) P\left(x_{1}, \ldots, x_{n}\right)=\frac{1}{Z_{\Phi}} \prod_{i=1} \phi_{i}\left(D_{i}\right) P(x1,…,xn)=ZΦ1i=1∏ϕi(Di)
among , Z Φ Z_{\Phi} ZΦ Is the normalization factor of the joint probability distribution , It is usually called partition function (partition function). D i D_i Di Is a collection of random variables , factor ϕ i ( D i ) \phi_{i}\left(D_{i}\right) ϕi(Di) It is a mapping from the set of random variables to the field of real numbers , be called Potential function or factor
Φ = { ϕ i ( D i ) , … , ϕ K ( D K ) } p ~ ( x 1 , … , x n ) = ∏ i = 1 ϕ i ( D i ) Z Φ = ∑ x 1 , … , x n p ~ ( x 1 , … , x n ) \begin{aligned} &\Phi=\left\{\phi_{i}\left(D_{i}\right), \ldots, \phi_{K}\left(D_{K}\right)\right\} \\ &\tilde{p}\left(x_{1}, \ldots, x_{n}\right)=\prod_{i=1} \phi_{i}\left(D_{i}\right) \\ &Z_{\Phi}=\sum_{x_{1}, \ldots, x_{n}} \tilde{p}\left(x_{1}, \ldots, x_{n}\right) \end{aligned} Φ={ ϕi(Di),…,ϕK(DK)}p~(x1,…,xn)=i=1∏ϕi(Di)ZΦ=x1,…,xn∑p~(x1,…,xn)
Example of Markov random field

The local potential function is not directly related to the edge probability density .
Paired Markov random fields and their applications
The formula of paired Markov random fields is as follows :
1 Z Φ ∏ p ∈ V ϕ p ( x p ) ∏ ( p , q ) ∈ E ϕ p q ( x p , x q ) \frac{1}{Z_{\Phi}} \prod_{p \in V} \phi_{p}\left(x_{p}\right) \prod_{(p, q) \in E} \phi_{p q}\left(x_{p}, x_{q}\right) ZΦ1p∈V∏ϕp(xp)(p,q)∈E∏ϕpq(xp,xq)
Image processing problems can often be defined in MRF The maximum a posteriori probability problem on :
max x p ( x ) ∝ ∏ p ∈ V ϕ p ( x p ) ∏ ( p , q ) ∈ E ϕ p q ( x p , x q ) \max _{\mathbf{x}} p(\mathbf{x}) \propto \prod_{p \in V} \phi_{p}\left(x_{p}\right) \prod_{(p, q) \in E} \phi_{p q}\left(x_{p}, x_{q}\right) xmaxp(x)∝p∈V∏ϕp(xp)(p,q)∈E∏ϕpq(xp,xq)
The o p ( x ) p(x) p(x) At the very least ,x The value of , As shown in the figure below .
The maximum a posteriori reasoning problem is equivalent to the energy minimization problem , Make θ p ( x p ) = − log ϕ p ( x p ) , θ p q ( x p , x q ) = − log ϕ p q ( x p , x q ) \theta_{p}\left(x_{p}\right)=-\log \phi_{p}\left(x_{p}\right), \theta_{p q}\left(x_{p}, x_{q}\right)=-\log \phi_{p q}\left(x_{p}, x_{q}\right) θp(xp)=−logϕp(xp),θpq(xp,xq)=−logϕpq(xp,xq), Yes :
min x E ( x ) = ∑ p ∈ V θ p ( x p ) + ∑ ( p , q ) ∈ E θ p q ( x p , x q ) \min _{x} E(\mathbf{x})=\sum_{p \in V} \theta_{p}\left(x_{p}\right)+\sum_{(p, q) \in E} \theta_{p q}\left(x_{p}, x_{q}\right) xminE(x)=p∈V∑θp(xp)+(p,q)∈E∑θpq(xp,xq)
Assumption of potential function : The value of continuous pixels is continuous .
边栏推荐
- Why can't I hide folders? Solutions to the hidden folders on the computer that can still be seen
- 招聘| 嵌入式軟件(单片机)工程师
- Format problem handling
- Little black leetcode journey: 100 same trees
- Black one-stop operation and maintenance housekeeper 10 records ro
- 排序——QuickSort
- Chapter VI more supervision training
- 利用a*启发式搜索解决迷宫寻路问题
- LabVIEW master VI freeze pending
- E d-piece system is nfdavi oriented, reaching a high level for engineers
猜你喜欢

Post SQL era: edgedb 2.0 Release Notice
![GOM engine starts M2 prompt: [x-fkgom] has been loaded successfully. What should I do if it gets stuck?](/img/32/df602f294e009c9462d955b1819ffe.png)
GOM engine starts M2 prompt: [x-fkgom] has been loaded successfully. What should I do if it gets stuck?

Journey of little black leetcode: 590. Post order traversal of n-ary tree

Division of training set, verification set and test set in link prediction (take randomlinksplit of pyg as an example)

Kingbase V8R6集群安装部署案例---脚本在线一键扩容

Jiang Xingqun, senior vice president of BOE: aiot technology enables enterprise IOT transformation

greatest common divisor
The x-fkgom supporting the GOM engine key.lic is authorized to start
Array force buckle (continuously updated)

Zhaoyi innovation gd25wdxxk6 SPI nor flash product series comes out
随机推荐
黑色的的一站式运维管家 10条记录RO
Kingbase v8r6 cluster installation and deployment case - script online one click expansion
力扣146题:LRU缓存
Which is better, Xiaomi current treasure or yu'e Bao? Detailed comparison and introduction of the differences between Xiaomi current Bao and Alibaba yu'e Bao
Hcde city closed door meeting successfully held in Nanjing station
How can I open and view the bin file? Diagram of reading method of bin file backed up by router
Recruitment | embedded software (MCU) Engineer
Print leap years between 1000 and 2000
LabVIEW主VI冻结挂起
C language: generation of random numbers
Xiaohongshu joins hands with HMS core to enjoy HD vision and grow grass for a better life
Threejs+shader drawing commonly used graphics
Introduction and use of pycharm debugging function
Face algorithms
Godson leader spits bitterness: we have the world's first performance CPU, but unfortunately no one uses it!
yum 查看某个命令由哪个安装包提供
Pony activation tool appears cannot open file k:\oemsf solution
MGRE and OSPF comprehensive experiment
Icml2022 | rock: causal reasoning principle on common sense causality
uniapp学习