当前位置:网站首页>Debian10 LVM logical volumes
Debian10 LVM logical volumes
2022-06-23 01:26:00 【Halyace】
Basic terminology
come from Baidu Encyclopedia -LVM
- Physical storage medium (PhysicalStorageMedia)
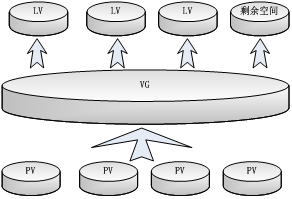
Refers to the physical storage device of the system : disk , Such as :/dev/hda、/dev/sda etc. , It's the bottom storage unit of the storage system .- Physical volume (Physical Volume,PV)
Refers to a disk partition or a device that logically has the same function as a disk partition ( Such as RAID), yes LVM Block of basic storage logic , But with the basic physical storage medium ( Such as zoning 、 Disks, etc ) Compare , But contains and LVM Related management parameters .- The volume group (Volume Group,VG)
It's similar to not LVM Physical disks in the system , It consists of one or more physical volumes PV form . You can create one or more... On a volume group LV( Logic volume ).- Logic volume (Logical Volume,LV)
It's similar to not LVM Disk partition in the system , Logical volumes are built on volume groups VG above . In the logical volume LV You can build a file system ( such as /home perhaps /usr etc. ).- Physical block (Physical Extent,PE)
PE Is a physical volume PV The basic division unit of , Having a unique number PE Yes, it can be. LVM The smallest unit of addressing .PE The size of is configurable , The default is 4MB. So physical volumes (PV) By basic units of equal size PE form .- Logic block (Logical Extent,LE)
Logic volume LV It is also divided into addressable basic units , be called LE. In the same volume group ,LE The size and PE It's the same , And one to one .
One 、 establish LVM Logical volumes and mount
# install lvm2
apt install lvm2
# see scsi Bus
ls /sys/class/scsi_host
# View results host0 host1 host2
# scanning host0
echo '- - -' > /sys/class/scsi_host/host0/scan
# scanning host1
echo '- - -' > /sys/class/scsi_host/host1/scan
# scanning host2
echo '- - -' > /sys/class/scsi_host/host2/scan
# Check the disk Find a new hard disk /dev/sdb
fdisk --list
# Use cfdisk Initialize disk
# Use GPT Partition establish Linux LVM Type of zoning
cfdisk /dev/sdb
# Check the disk New partition found /dev/sdb1
fdisk --list
# establish pv( Physical volume )
# Parameters 1 Device path
pvcreate /dev/sdb1
# see pv list
pvs
# see pv details
pvdisplay
# establish vg( The volume group )
# Parameters 1 -s PE size ( One vg most 65534 individual PE 256M Of vg The maximum capacity is 16T)
# Parameters 2 vg name
# Parameters 3 pv name
vgcreate -s 128M vg0 /dev/sdb1
# see vg list
vgs
# see vg details
vgdisplay
# establish lv( Logic volume )
# Parameters 1 -L Logical volume size ( Actual capacity 10G 500G etc. )
# Parameters 1 -l Logical volume size (80%Free 100%VG etc. )
# Parameters 2 -n Logical volume name
# Parameters 3 vg0 For use vg Group
lvcreate -l 100%Free -n vdisk0 vg0
# see lv list
lvs
# see lv details
lvdisplay
# Check out the hard disk Find out /dev/mapper/vg0-vdisk0 Logic volume
fdisk --list
# Format logical volume
mkfs.ext4 /dev/vg0/vdisk0
# Create mount point
mkdir -p /opt/vdisk0
# Mount logical volumes
mount /dev/vg0/vdisk0 /opt/vdisk0
# see UUID
blkid /dev/vg0/vdisk0
# Check out the file system
df -h
# Power on auto mount
# Add a row UUID=xxxxxxxx /opt/vdisk0 ext4 defaults 0 0
# < file system > < Mount point > < Partition type > < Options > <dump Backup > < Check sector >
nano /etc/fstab
Two 、LVM command
| command | purpose |
|---|---|
| pvchange | Change the properties of the physical volume |
| pvck | Check physical volume metadata |
| pvcreate | Initialize a disk or partition for LVM Use |
| pvdisplay | Show properties of physical volume |
| pvmove | Move physical volumes |
| pvremove | Delete physical volume |
| pvresize | adjustment LVM2 The size of the disk or partition used |
| pvs | View the list of physical volumes |
| pvscan | Scan all disks of the physical volume |
| vgcfgbackup | Backup volume group configuration |
| vgcfgrestore | Restore volume group configuration |
| vgchange | Change the properties of the volume group |
| vgck | Check volume group metadata |
| vgconvert | Transform volume group metadata format |
| vgcreate | Create a volume group |
| vgdisplay | Display the properties of the volume group |
| vgexport | Export volume groups |
| vgextend | Append physical volumes to volume groups |
| vgimport | Import volume group |
| vgimportclone | Import and rename duplicate volume groups ( For example, hardware snapshot ) |
| vgmerge | Merge two volume groups |
| vgmknodes | Recreate volume group directories and logical volume special files |
| vgreduce | Reduce volume groups by deleting one or more physical volumes |
| vgremove | Remove the volume group |
| vgrename | Rename volume group |
| vgs | Volume group list |
| vgscan | Scan all disks of the volume group |
| vgsplit | Split the volume group in two , Move any logical volume from one volume group to another by moving the entire physical volume |
| lvchange | Change the properties of the logical volume |
| lvconvert | Convert logical volumes from linear to mirror or snapshot |
| lvcreate | Create a logical volume in an existing volume group |
| lvdisplay | Show properties of logical volume |
| lvextend | Expand the size of the logical volume |
| lvreduce | Reduce the size of the logical volume |
| lvremove | Delete logical volume |
| lvrename | Rename logical volume |
| lvresize | Resize logical volume |
| lvs | List of logical volumes |
| lvscan | scanning ( All disks ) The logical volume |
| lvmconfig | Show lvm Configuration information |
| lvmdiskscan | Scan right LVM2 All visible devices |
| lvmdump | Create... For diagnostic purposes lvm2 memory dump |
3、 ... and 、LVM Capacity expansion
# see scsi Bus
ls /sys/class/scsi_host
# View results host0 host1 host2
# scanning host0
echo '- - -' > /sys/class/scsi_host/host0/scan
# scanning host1
echo '- - -' > /sys/class/scsi_host/host1/scan
# scanning host2
echo '- - -' > /sys/class/scsi_host/host2/scan
# Check the disk Find a new hard disk /dev/sdc
fdisk --list
# Use cfdisk Initialize disk
# Use GPT Partition establish Linux LVM Type of zoning
cfdisk /dev/sdc
# Check the disk New partition found /dev/sdc1
fdisk --list
# establish pv( Physical volume )
# Parameters 1 Device path
pvcreate /dev/sdc1
# see VG
vgdisplay
# Use vgextend hold pv Expand to vg0
# Parameters 1 vg The volume group
# Parameters 2 pv Physical volume
vgextend vg0 /dev/sdc1
# see VG Found free space :Free PE/Size 239/<29.88 GiB
vgdisplay
# lv Capacity expansion /dev/vg0/vdisk0
# Parameters 1 -l Adjust by percentage
# Parameters 2 lv Logic volume
lvextend -l +100%FREE /dev/vg0/vdisk0
# Resize partition Expand all spaces by default
resize2fs -p /dev/vg0/vdisk0
# View the adjusted partition
df -h
3、 ... and 、LVM Volume reduction
# View partition mount
df -h
# Unload mount
umount /opt/vdisk0
# Check partition
e2fsck -f /dev/vg0/vdisk0
# Resize partition to 20G
resize2fs -p /dev/vg0/vdisk0 20G
# Mount logical volumes
mount /dev/vg0/vdisk0 /opt/vdisk0
# lv The logical volume capacity is adjusted to 20G( Be careful : Could damage data )
lvreduce -L 20G /dev/vg0/vdisk0
# View partition mount
df -h
# see vg Available space
vgdisplay
边栏推荐
- E-R diagram
- Explain the startup process of opengauss multithreading architecture in detail
- Webdriver and selenium Usage Summary
- C#.NET万能数据库访问封装类(ACCESS、SQLServer、Oracle)
- Pat class A - 1007 maximum subsequence sum
- 62. 不同路径
- [ZOJ] P3228 Searching the String
- LeetCode 206. Reverse linked list (iteration + recursion)
- Add expiration time for localstorage
- Sélecteur de hiérarchie
猜你喜欢

Hierarchy selector

Lexical Sign Sequence

How to calculate the position of gold ETF

Yyds dry inventory solution sword finger offer: print the binary tree into multiple lines

How about precious metal spot silver?

Xiaobai operates win10 to expand Disk C (allocate disk D memory to Disk C) and the test is valid for many times

SAP mm me27 create intra company sto order

B tree and b+ tree

Psychological analysis of the safest spot Silver

3D printing microstructure
随机推荐
Shell 日志与打印输出
Installation record of ros1noetic in Win 11
Similar to attention NLP
OSPF综合实验
C language student achievement ranking system
崔鹏团队:万字长文梳理「稳定学习」全景图
Up the Strip
62. different paths
LINQ 查询
BGP联邦综合实验
Requête linq
Xiaobai operates win10 to expand Disk C (allocate disk D memory to Disk C) and the test is valid for many times
【机器学习-西瓜书】更文挑战【Day1】:1.1 引言
It's still like this
Day500: keyboard line
cadence SPB17.4 - allegro - 优化指定单条电气线折线连接角度 - 折线转圆弧
[hdu] P6964 I love counting
Day367: valid complete square
Unit of RMB in words
OSPF experiment in mGRE environment