当前位置:网站首页>【leetcode天梯】链表 · 203 移除链表元素
【leetcode天梯】链表 · 203 移除链表元素
2022-07-23 17:30:00 【kikokingzz】

题目描述:
给你一个链表的头节点
head和一个整数val,请你删除链表中所有满足Node.val == val的节点,并返回新的头节点 。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]示例 2:
输入:head = [], val = 1
输出:[]示例 3:
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
输出:[]题目链接:
203. 移除链表元素 - 力扣(LeetCode) https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/
解题思路:
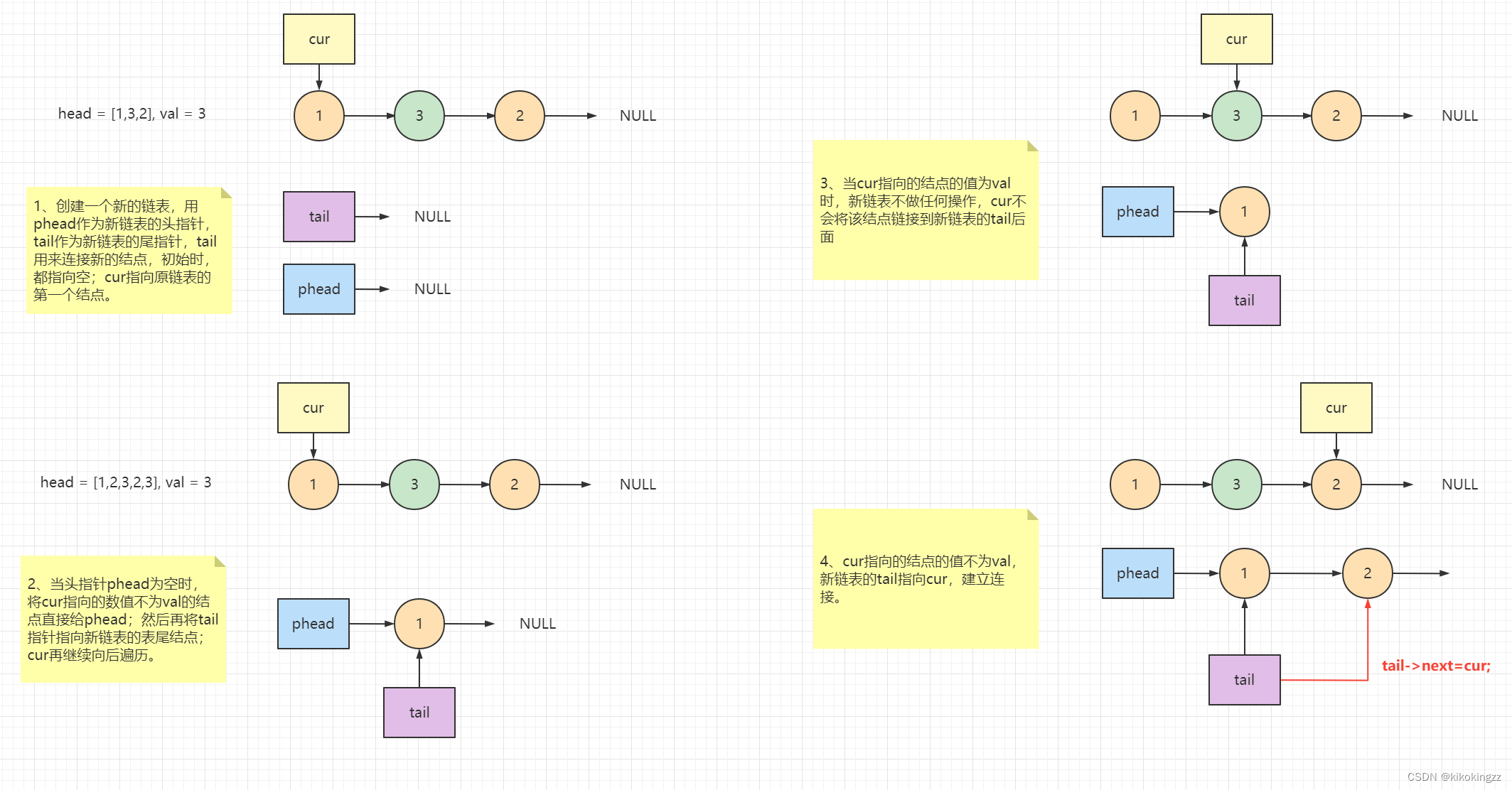
常规法1:建立一个新链表接收
我们想到使用三个指针,用一个指针phead来建立一个新链表,指向新链表表头;再用一个指针tail指向新链表中最后一个结点;最后一个指针cur用来遍历原链表,cur挨个向后遍历,遇到数值不是val的结点,就将新链表的尾结点指向这个结点。
使用上述办法,需要注意的就是新链表的最后一个结点需要指向NULL,判断条件是当cur指向空时,表明原链表已经遍历完了,这时就应该将新链表的尾巴,即tail的next指向NULL。
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){ struct ListNode* phead = NULL; //phead是新链表的头指针 struct ListNode* tail = NULL; //tail指向新链表的最后一个结点 struct ListNode* cur = head; //cur用来遍历原链表 while(cur) { if(cur->val!=val) //当遇到值不为val的结点时 { if(phead==NULL) //如果此时新的链表为空 { phead=cur; //将该结点赋予给新链表 tail=cur; //尾指针也指向这唯一的一个结点 } else { tail->next=cur; //将尾指针的next指向cur tail=cur; //将尾指针更新到新链表的最后一个结点 } cur=cur->next; //cur继续向后遍历 } else //当遇到的值为val的结点时 { cur=cur->next; } } //当cur一直运行到空,此时新链表的最后一个结点的指向还没有确定 if(tail!=NULL) //如果新链表不为空的话 { tail->next=NULL; //将最后一个结点的next指向空 } return phead; }
总结一下:使用这种方式,其实相当于重新规划出一片空间进行组合,这时的空间复杂度就达到了O(N),对此我们打算尝试,能否直接对原链表直接进行操作呢?于是,我们想到了第二种办法,就是断开指定的结点。
常规法2:断开指定的结点
这种方式我们仍然采用三个指针,但是这三个指针都指向原链表,只不过指向的位置各不相同,我们设置一个指针cur用来遍历整个单链表,设置一个指针after指向cur的后一个结点,设置一个指针prev指向cur 的前一个结点,当cur指向的结点的值为val时,就将prev的next指向after,进而断开与cur指向的结点的连接,并将cur给free掉。
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){ struct ListNode* prev = NULL; struct ListNode* after = NULL; //tail指向新链表的最后一个结点 struct ListNode* cur = head; //cur用来遍历原链表 if(head==NULL) return NULL; //如果是空链表,直接跳出 head=NULL; //这一步是为了当原链表的值全为val时,可以直接返回NULL after=cur->next; //after为cur的后一个结点 while(cur) //当after为空时,说明cur已经遍历完了原链表,跳出循环 { if(cur->val!=val)//当cur指向的结点的值不为val时 { if(prev==NULL) //如果此时prev指向空,就将第一个保留结点赋给prev { prev=cur; head=prev; //新链表的头结点由此时第一个保留结点决定 } else //当prev不为空时 { prev=cur; } cur=after; //cur向后走一步 if(after!=NULL) after=after->next; //after向后走一步 } else //当cur指向的结点的值为val时 { if(prev!=NULL) { prev->next=after; //prev的next指向after free(cur); //释放cur指向的结点空间 cur=after; //cur向后走一步 if(after!=NULL) after=after->next; //after向后走一步 } else { cur=after; //cur向后走一步 if(after!=NULL) after=after->next; //after向后走一步 } } } return head; }
总结一下:说真的,这种方法写着写着就觉得好蠢,因为设置了一个after指针,导致弄巧成拙了,还需要讨论当after指针为空时的情况,所以这种方式不可取!万万不可取啊!
常规法3:断开指定的结点
为什么又来一遍,因为这次我们只需要使用两个指针就可以搞定,并且操作更加简单。我们这次只设置两个指针。
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){ struct ListNode* prev = NULL; struct ListNode* cur = head; //cur用来遍历原链表 while(cur) { if(cur->val==val) //当cur指向的结点的值为val时 { if(prev==NULL) //这种情况说明,原链表的第一个结点的值就是val { head=cur->next; //将链表的头指针指向cur的后一个结点 free(cur); //删除cur指向的结点 cur=head; //cur向后走一步 } else //这种情况下,prev的值不为空 { prev->next=cur->next; //将prev的next指向cur的后一个结点 free(cur); //删除cur cur=prev->next; //cur向后走一步 } } else //当cur指向的结点值不为val时 { prev=cur; cur=cur->next; //cur向后走一步 } } return head; }
总结一下:这种解法就较为中规中矩一些,尤其是通过灵活地将head进行移动的方式,避免了链表第一个结点就需要删除,导致head为空的情况发生。讲道理,head为空或者不为空这个问题导致了上述代码复杂,即头指针的值可能会发生修改导致了代码复杂,我们能不能将头指针值的修改这个操作变得简单一些呢?
常规法4:哨兵法
我们发现,上面这么多方法其实都略微复杂,复杂的本质在于当我们输入的数值为下面这些情况时:
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7 输出:[]原链表的头指针的值会发生变化,进而导致程序设计时,必须要去考虑头指针为空的情况,这就会使得我们要额外去考虑头指针为空的情况。但是当我们设置一个哨兵位后,所有的操作,其实都众生平等了!
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){ struct ListNode* phead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); //建立一个哨兵位 struct ListNode* prev=phead; //prev起初指向哨兵位 struct ListNode* cur=head; //cur指向原链表的第一个结点 phead->next=head; //哨兵位处于原链表第一个结点之前 while(cur) //cur为空时,说明cur已经遍历完原链表了 { if(cur->val==val) //当cur指向的结点需要被删除 { prev->next=cur->next; free(cur); cur=prev->next; } else //当cur指向的结点不需要被删除时 { prev=cur; cur=cur->next; } } head=phead->next; //返回的链表是不带哨兵位的,所以将新链表的头赋值为哨兵的后一个结点 free(phead); //释放哨兵位 return head; }
总结一下:这种解法告诉我们,当我们设置的一个链表的头指针可能会发生值修改时,我们可以直接采用一种哨兵位的思想进行处理,较为方便。
边栏推荐
- 【论文阅读】GETNext: Trajectory Flow Map Enhanced Transformer for Next POI Recommendation
- Labyrinth DP integration
- Notes of benthos
- FPGA implementation of IIC bus of IIC protocol (II) (single read / write drive)
- Detailed explanation: tmp1750 chip three channel linear LED driver
- [shutter -- layout] flexible layout (flex and expanded)
- Cell array processing
- You must execute multiple requests and catch errors. Using try catch is not elegant
- Synopsys TCL of Tcl language (3) (Digital IC)
- Recognition engine ocropy- & gt; ocropy2-> Ocropus3 summary
猜你喜欢

11. Basic concepts of neural network
![Redis [2022 latest interview question]](/img/32/7efbc52f97eb3be90c7fa2e6863758.png)
Redis [2022 latest interview question]

正则化不同导致的tuple错误

Source code analysis of ThreadPoolExecutor

Lendingclub loan status business details current, charge off, issued, full paid, grace period

界面设计四大原则

Navigation component of jetpack compose uses

作为一名后台开发人员,你必须知道的两种过滤器
![[shutter -- layout] flexible layout (flex and expanded)](/img/03/0f07a56487f8e91045f9e893e9f96c.png)
[shutter -- layout] flexible layout (flex and expanded)
【论文阅读】GETNext: Trajectory Flow Map Enhanced Transformer for Next POI Recommendation
随机推荐
还在用Xshell?你out了,推荐一个更现代的终端连接工具
FPGA实现IIC协议(一)IIC总线协议
TODO FIXME BUG TAG FEATURE 等配置
FPGA flash reading and writing based on SPI
What is stack and the difference between stacks
[shutter -- layout] linear layout (row and column)
Todo fix bug tag feature and other configurations
Redis [2022 latest interview question]
SQL statement exercise
not all arguments converted during string formatting
[2022] [paper notes] terahertz quantum well——
Building virtual private network based on softther
FPGA实现IIC协议(二)之IIC总线的FPGA实现(单次读写驱动)
J9数字论:数字行业的FOMO现象我们应该怎么克服?
Mbio | the sun Chaomin formation of Ocean Institute has verified in situ the new pathway of microbial mediated elemental sulfur formation in the deep sea
Recognition engine ocropy- & gt; ocropy2-> Ocropus3 summary
Rapid establishment of devstack cloud computing platform
Learn and understand Architecture Design from business development
How to understand: common code block, construction block, static block? What does it matter?
基于FPGA的UART接口设计