当前位置:网站首页>Hibernate architecture introduction and environment construction (very detailed)
Hibernate architecture introduction and environment construction (very detailed)
2022-06-25 23:34:00 【_ Qilixiang】
Catalog
4 Hiberate Environment construction and various preparations ( Very detailed )
5 Writing rules of entity classes
1 Three layer architecture
1、web layer :struts2 frame
2、service layer :spring frame
3、dao layer :hiberate frame ( The database is crud operation )
MVC thought :model-view-controller
2 hiberate summary
stay javaEE In the three-tier architecture dao layer .
Hibernate The bottom is JDBC, Yes JDBC It was packaged , The advantage is that you don't need to write complex JDBC Code and SQL The statement implements .
Hibernate It's an open source 、 Lightweight ( It can be used directly without relying on other things 、 Import very few jar package ) Framework
Hibernate edition :Hibernate3.x、4.x、5.x;4.x Is an over version
3 ORM thought
Hibernate Is an open source object relational mapping (orm-Object Relational Mapping) frame .
Hibernate This idea is used to crud operation .
Web Stage javaBean class , In the Framework phase, it is called Entity class .
Let entity classes and database tables have a one-to-one correspondence .
Attributes of a class -- The fields in the table correspond to
You don't need to directly manipulate database tables , The direct operation table corresponds to the entity class object .
Jdbc Code :
Class.forName(“com.oracle.jdbc.driver”);
Connection = DriverManager.getConnection();
(url,username,password)
String sql=””;
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = ps.excuteQuery();
// Traversal result set
// Release resources Entity class
Public class User{
Private int userid;
Private String username;
Private String password;
//set、get
}Database table :
Create table t_user(
Userid number not NULL AUTO_INCREATEMENT,
username varchar2(100),
password varchar2(100)
);Use the configuration file to complete one-to-one correspondence
Hibernate Encapsulated objects Session:
User user = new User();
User.setUserName(“”);
Session.save(user); //session The method in 4 Hiberate Environment construction and various preparations ( Very detailed )
Basic preparation
First step : Import Hibernate Of jar package
require Folders and JPA In folder jar You have to import .
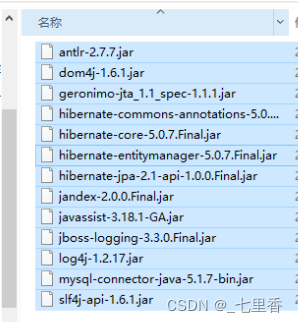
Because use Hibernate Log information is output from time to time ,Hibernate There is no log output in itself jar package , You need to import other logs jar The package supports these outputs .
2、 Create entity class
Hibernate Require an attribute in the entity class ( Such as id) Is the only one. .( Such as the primary key in the table )
private int userid;
3、 Create table (hibernate Automatically create )
4、 Configure the mapping relationship between entity classes and database tables -- Configuration file implementation
establish xml The configuration file : Configuration file name and location are not required , But it's usually called :hbm.xml; The location is created under the package of the entity class .
First introduced xml constraint , Currently in hibernate Most of them are dtd constraint ; stay hibernate The constraint file for (hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd) Copy the created from xml.
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd" >Configure a correspondence

Create core profile
The location and name are fixed . Location --src Next ; name --hibernate.cfg.xml

hibernate.cfg.xml Templates
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!--1. Configuration database information , There must be -->
<!-- Configure the dialect of the database , Such as :MySQL The middle page is limit,oracle Medium is rownum; Give Way hibernate Identify statements or keywords in different databases -->
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.OracleDialect</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:XE</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">abc</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">abc</property>
<!--2. To configure hibernate Information , There is nothing -->
<!-- Output bottom layer SQL -->
<property name="hibernate.show_sql">true </property>
<!-- To the underlying SQL format , Formatting is not displayed on one line -->
<property name="hibernate.format_sql">true</property>
<!-- Automatically generate or update database tables , Written words , The table will be created automatically -->
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<!-- 3. Register map file -->
<mapping resource="com/wl/entity/User.hbm.xml" /> <!-- With src For the relative path , If in src Next , Is directly User.hbm.xml -->
<!-- notes :hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto The value of is create Indicates that a new table will be created each time ;
The value is create-drop It's closing SessionFactory Delete the fairy sword table ;
The value is update( Common values ) If the first runtime database does not have a corresponding table , A new table will be created , But if there is a corresponding data table , No longer create the corresponding data table -->
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
Copy in dtd constraint :
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"hibernate In operation , Only the core configuration file... Will be loaded , Other configuration files will not load .
The following three parts are basically configured only once , After that, it is seldom modified .
The first part : Configuration database information
The second part : To configure hibernate Information
The third part : Put the configuration file into the core configuration file
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibernate</property>Add operation steps
First step : load hibernate Core profile
The second step : establish Sessionfactory Factory object
The third step : Use Sessionfactory establish session object
Step four : Open transaction , Manual creation is recommended
Step five :curd operation
Step six : Commit transaction
Step seven : close resource
Change is only the fifth step , Other general purpose fixing .
Test the whole code
package com.wl.test;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.wl.entity.User;
import com.wl.utils.HibernateUtils;
/*
* add to :save()
* modify :update()
* Delete :delete()
* according to id Inquire about :get()
*/
public class InsertDemo {
/*
* modify
*/
@Test
public void updateDemo(){
// Configuration cfg = new Configuration();
// cfg.configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = HibernateUtils.getSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
User user = new User();
user.setUserid(4);
user.setUsername("rrr");
user.setPassword("rrr");
user.setAddress("AAAAA");
session.update(user);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
/*
* Insert
*/
@Test
public void insertDemo1(){
SessionFactory sessionFactory = HibernateUtils.getSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("wl9");
user.setPassword("000002");
user.setAddress("XXXXX");
session.save(user);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
/*
* Insert
*/
@Test
public void insertDemo(){
// First step : load hibernate Core profile , Will be in src Look under hibernate.cfg.xml
Configuration cfg = new Configuration();
cfg.configure();
// The second step : Read the contents of the core configuration file , To create Sessionfactory Factory object ; In the process , According to the mapping relationship , Create tables in the configuration database .
SessionFactory sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
// The third step : Use Sessionfactory establish session object , It's like connecting connection
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
// Step four : Open transaction , Manual creation is recommended
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// Step five :curd operation , Such as add operation
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("123");
user.setPassword("000002");
user.setAddress("XX");
// call session The method inside implements adding
session.save(user);
// Step six : Commit transaction
transaction.commit();
// Step seven : close resource
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
}
Effect validation
1 Whether the table has been created ;
2 Whether records have been added .
Console :
There are five sentences :
Hibernate:
update
t_user
set
username=?,
password=?,
address=?
where
userid=?
Hibernate:
select
hibernate_sequence.nextval
from
dual
Hibernate:
insert
into
t_user
(username, password, address, userid)
values
(?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate:
select
hibernate_sequence.nextval
from
dual
Hibernate:
insert
into
t_user
(username, password, address, userid)
values
(?, ?, ?, ?)In the database :

select dbms_metadata.get_ddl('TABLE', ‘T_USER’) from dual;
![]()
or desc see :

5 Writing rules of entity classes
- Property private , Provide get/set Method .
- Have an attribute as the unique value , If you use id Distinguish between unique values .
- For the data type of entity class, it is recommended to use the wrapper type of basic data type , Such as Integer,Character, Everything else is capitalized
If you use int Express score,int score=0; The score is 0 when , At this point, if you want to show that the students have not taken the exam, you can't realize , because int score=null; It's wrong. . It's time to use Integer score = null;
6 Primary key growth strategy
Primary key : stay Hibernate Persistent classes in all have an identity attribute , Unique to identify the instance , This attribute maps to the primary key of the database table .
key generator :<generator class=" generation "/>
The values of the generation method are :
increment: Indicates to obtain the maximum primary key value of the table in the database , and +1 As the new primary key .
identity: Automatic growth , Mainly used in mysql,db2.
Sequence:Hibernate Generate identifiers based on the underlying database sequence , The condition is that the database should support sequences . Applies to proxy primary keys .
native:( This method is generally selected during development ) Automatic growth ,Hibernate From the database identity,sequence( Sequence ),hilo( High low algorithm ) Select an appropriate method to generate a primary key , stay mysql Use identity, stay Oracle Select... In the middle sequence( Sequence ).
uuid: Use UUID Algorithm generates string type primary key ( It is mainly used for distributed deployment ).
Use uuid when , Change the primary key of the entity class to String type , Change the configuration file to uuid.
Run the encapsulated tool class , See the effect :

Run the test data :
![]()
in other words , When using uuid When a policy is generated as a primary key , You need to set the primary key to String type .
边栏推荐
- How to download the software package of CDH version
- C. Yet Another Card Deck-Educational Codeforces Round 107 (Rated for Div. 2)
- C. Planar Reflections-CodeCraft-21 and Codeforces Round #711 (Div. 2)
- Applets - view and logic
- 转载: QTableWidget详解(样式、右键菜单、表头塌陷、多选等)
- Implementation of importing vscode from PDM
- Fegin client entry test
- Qt自定义实现的日历控件
- 信息学奥赛一本通 1353:表达式括号匹配(stack) | 洛谷 P1739 表达式括号匹配
- Sword finger offer 46 Translate numbers to strings (DP)
猜你喜欢

转载: QTableWidget详解(样式、右键菜单、表头塌陷、多选等)

Ble Low Power Bluetooth networking process and Bluetooth role introduction

UE4\UE5 蓝图节点Delay与Retriggerable Delay的使用与区别

BI-SQL丨存储过程(一)

LM small programmable controller software (based on CoDeSys) note XVII: PTO pulse function block

Rk3568+ Hongmeng industrial control board industrial gateway video gateway solution

What is Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI)?

RepOptimizer: 其实是RepVGG2

二进制、16进制、大端小端

UE4_ Ue5 combines the offline voice recognition plug-in for speech recognition
随机推荐
How to add cartoon characters to the blog park?
头歌 第3关:使用线程锁(Lock)实现线程同步
毕业旅行 | 伦敦5日游行程推荐
[opencv450 samples] inpaint restores the selected region in the image using the region neighborhood
character string
go中全类型等值判断解析&综合汇总
统计字符串中不同回文子序列的个数
记一次beego通过go get命令后找不到bee.exe的坑
指针强化与提高
After xampp restarts, the MySQL service cannot be started.
UE4_ Ue5 combines the offline voice recognition plug-in for speech recognition
UE4 学习记录二 给角色添加骨架,皮肤,及运动动画
YUV444、YUV422、YUV420、YUV420P、YUV420SP、YV12、YU12、NV12、NV21
C. Planar Reflections-CodeCraft-21 and Codeforces Round #711 (Div. 2)
Ble Low Power Bluetooth networking process and Bluetooth role introduction
【opencv450-samples】读取图像路径列表并保持比例显示
[2023 proofreading and bidding questions] Part 1: Measurement Technology FPGA post (roughly analytical version)
cookie、session、token
28 rounds of interviews with 10 companies in two and a half years (including byte, pinduoduo, meituan, Didi...)
What aspects should we start with in the feasibility analysis of dry goods?