当前位置:网站首页>MySQL multi table operation
MySQL multi table operation
2022-06-22 22:35:00 【Fire eye Dragon】
Multi table relation
Concept : In actual development , A project usually requires multiple tables to complete .
Multi table relationships can be summarized as : one-on-one 、 One to many / For one more , Many to many
One to one relationship
- A student has only one ID card , One ID card can only correspond to one student
- Add a unique foreign key to any table , Point to the other party's primary key , Ensure a one-to-one relationship
- Generally, one-to-one relationships are rare , Tables that encounter one-to-one relationships are best consolidated tables
One to many / For one more
- There are many employees in a department , An employee can only correspond to one department
- No matter how many parties establish foreign keys , A primary key that points to a party of one
Many to many relationship
- A student can choose many courses , A course can also be chosen by many students
- Many to many relationships are implemented with the help of a third intermediate table . The middle table contains at least two fields , A many to many relationship , Split into a one to many relationship , The middle table must have at least two foreign keys , These two foreign keys point to the primary keys of the original two tables
Foreign key constraints
Concept :MySQL Foreign key constraints (FOREIGN KEY) Is a special field of the table , Often used with primary key constraints . For two tables that have an association , The table where the primary key in the associated field is located is the primary table ( Parent table ), The table where the foreign key is located is the slave table ( Sub table ).
characteristic
When defining a foreign key , The following rules need to be followed :
- The primary table must already exist in the database , Or the table that is currently being created
- The primary key must be defined for the primary table
- Gradually cannot contain control , But null values are allowed in foreign keys . in other words , Each non null value of the primary and secondary foreign keys appears in the specified primary key , The content of this foreign key is correct
- Specify the column name or combination of column names after the table name of the main table . This column or combination of columns must be the primary key or candidate key of the main table
- The number of columns in the foreign key must be the same as the number of columns in the primary key of the primary table
- The data type of the column in the foreign key must be the same as the corresponding data type in the primary table primary key
Create foreign key constraints
Method 1 :
[constraint< Foreign key name >] foreign key Field name [, Field name 2,……] references < Main table name > Primary key column 1[, Primary key column 2……]
for example :
-- Create department table , Main table
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS dept(
deptno VARCHAR(20) PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(20)
);
-- Create an employee table , From the table , And create dept_id Foreign key constraints
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS emp(
eid VARCHAR(20) PRIMARY KEY,
ename VARCHAR(20),
age INT,
dept_id VARCHAR(20),
CONSTRAINT emp_fk FOREIGN KEY (dept_id) REFERENCES dept(deptno)
);
Method 2 :
alter table < Data table name > add constraint < Foreign key name > foreign < Name > references < Main table name >(< Name >);
for example :
-- Create department table , Main table
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS dept2(
deptno VARCHAR(20) PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(20)
);
-- Create an employee table , From the table , And create dept_id Foreign key constraints
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS emp2(
eid VARCHAR(20) PRIMARY KEY,
ename VARCHAR(20),
age INT,
dept_id VARCHAR(20)
);
ALTER TABLE emp2 add CONSTRAINT emp2_fk FOREIGN KEY(dept_id) REFERENCES dept2(deptno);
Insert data into
-- Foreign key constraint operation
-- 1. Add master table data
-- notes : You must first add data to the main table
INSERT INTO dept VALUES('1001',' R & D department ');
INSERT INTO dept VALUES ('1002', ' The sales department ');
INSERT INTO dept VALUES ('1003', ' Finance Department ');
INSERT INTO dept VALUES ('1004', ' The personnel department ');
-- 2. Add data from table
-- notes : When adding data to the slave table , The value of the foreign key column must depend on the primary key column of the primary table
INSERT INTO emp VALUES('1',' Xiao feng ',20,'1001');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES('2', ' Duan Yu ', 21, '1001');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES('3', ' False bamboo ', 23, '1001');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES('4', ' Violet ', 18, '1002');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES('5', ' Sweeping monk ', 35, '1002');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES('6', ' Li Qiushui ', 33, '1003');
INSERT INTO emp VALUES('7', ' Jiu Mo Zhi ', 50, '1003');
Data deletion
-- 3. Delete data
-- notes :
-- 1. When the data of the master table is dependent on the slave table , Can't delete
-- 2. The data from the table can be deleted at will
DELETE FROM dept WHERE deptno=1004;
DELETE FROM emp WHERE eid='7';
Delete foreign key constraint
Concept : When a foreign key constraint is not required in a table , You need to remove it from the table . Once the foreign key is deleted , You will contact the relationship between the master table and the slave table .
Method :
alter table < Table name >drop foreign key< Foreign key constraint name >;
for example :
ALTER TABLE emp2 drop FOREIGN KEY emp2_fk;
Many to many relationship
In many to many relationships ,A One row of the table corresponds to B Multiple lines of ,B Corresponding to one line of A Multiple lines of , We Yao added a new middle table , To build many to many relationships .
-- Create student table student( Left main table )
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS student(
sid INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
name VARCHAR(20),
age INT,
gender VARCHAR(20)
);
-- Create a curriculum course( The main table on the right )
CREATE TABLE course(
cid INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
cidname VARCHAR(20)
);
-- Create middle table student_course/score( From the table )
CREATE TABLE score(
sid INT,
cid INT,
score DOUBLE
);
-- Create foreign key constraints ( two )
ALTER TABLE score ADD FOREIGN KEY(sid) REFERENCES student(sid);
ALTER TABLE score ADD FOREIGN KEY(cid) REFERENCES course(cid);
-- Add data to the student table
INSERT INTO student VALUES(1,' Little dragon female ',18,' Woman '),(2,' Violet ',19,' Woman '),(3,' Zhou Zhiruo ',20,' male ');
-- Add data to the curriculum
INSERT INTO course VALUES(1,' Chinese language and literature '),(2,' mathematics '),(3,' English ');
-- Add... To the intermediate table
INSERT INTO score VALUES(1,1,78),(1,2,75),(2,1,88),(2,3,90),(3,2,80),(3,3,65);
notes : When modifying and deleting , Intermediate slave tables can be deleted and modified at will , However, the primary tables on both sides are subject to the data dependent on the secondary tables and cannot be deleted or modified
Multi table joint query
Concept : Multi table query is to query two or more tables at the same time , Because sometimes when users are viewing data , The data to be displayed comes from multiple tables .
Multi table query has the following categories :
- Cross-join query ( Produce Cartesian product )
grammar :select * from A,B; - Internal connection query ( Keywords used inner join – inner It can be omitted )
Implicit inner join :select * from A,B where Conditions ;
Display inner connection :select * from A inner join B on Conditions ; - External connection query ( Keywords used outer join --outer It can be omitted )
The left outer join :left outer join
select * from A left outer join B on Conditions ;
Right connection :right outer join
select * from A right outer join B on Conditions ;
Full outer join :full outer join
select * from A full outer join B on Conditions ; - Subquery
select Nesting of - Table self association
Use one table as multiple tables
Prepare to query data
Next, prepare the data for multi table query , Be careful , Foreign key constraints have no effect on multi table queries .
-- Create department table
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS dept3(
deptno varchar(20) PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(20)
);
-- Create an employee table
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS emp3(
eid VARCHAR(20) PRIMARY KEY,
ename VARCHAR(20),
age INT,
dept_id VARCHAR(20)
);
-- to dept3 Add data
INSERT INTO dept3 VALUES('1001',' R & D department ');
INSERT INTO dept3 VALUES ('1002', ' The sales department ');
INSERT INTO dept3 VALUES ('1003', ' Finance Department ');
INSERT INTO dept3 VALUES ('1004', ' The personnel department ');
-- to emp3 Add data
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('1',' Xiao feng ',20,'1001');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('2', ' Duan Yu ', 21, '1001');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('3', ' False bamboo ', 23, '1001');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('4', ' Violet ', 18, '1002');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('5', ' Sweeping monk ', 35, '1002');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('6', ' Li Qiushui ', 33, '1003');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('7', ' Jiu Mo Zhi ', 50, '1003');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('8',' Tong lao ',60,'1003');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('9',' Murongbo ',58,'1003');
Cross-join query
- The cross join query returns the Cartesian product of all data rows of the connected two tables
- Cartesian product can be understood as that each row of one table matches any row of another table
- If A Table has m Row data ,B Table has n Row data , Then return to m*n Row data
- Cartesian product will produce a lot of redundant data , Other queries in the later stage can be filtered based on the set
Method :
select * from surface 1, surface 2, surface 3……;
for example :
SELECT * FROM dept3,emp3;
Internal connection query
Inner join query to find the intersection of multiple tables
Method :
Implicit ——selsect * from A,B where Conditions ;
Show ——selsect * from A inner join B on Conditions ;
for example :
-- Create department table
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS dept3(
deptno varchar(20) PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(20)
);
-- Create an employee table
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS emp3(
eid VARCHAR(20) PRIMARY KEY,
ename VARCHAR(20),
age INT,
dept_id VARCHAR(20)
);
-- to dept3 Add data
INSERT INTO dept3 VALUES('1001',' R & D department ');
INSERT INTO dept3 VALUES ('1002', ' The sales department ');
INSERT INTO dept3 VALUES ('1003', ' Finance Department ');
INSERT INTO dept3 VALUES ('1004', ' The personnel department ');
-- to emp3 Add data
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('1',' Xiao feng ',20,'1001');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('2', ' Duan Yu ', 21, '1001');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('3', ' False bamboo ', 23, '1001');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('4', ' Violet ', 18, '1002');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('5', ' Sweeping monk ', 35, '1002');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('6', ' Li Qiushui ', 33, '1003');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('7', ' Jiu Mo Zhi ', 50, '1003');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('8',' Tong lao ',60,'1003');
INSERT INTO emp3 VALUES('9',' Murongbo ',58,'1003');
SELECT * FROM dept3,emp3;
-- Query the employees of each department
-- Implicit inner join
SELECT * FROM dept3,emp3 WHERE deptno = dept_id;
SELECT * FROM dept3 a,emp3 b WHERE a.deptno =b.dept_id;
-- Display inner connection
SELECT * FROM dept3 INNER JOIN emp3 ON deptno = dept_id;
SELECT * FROM dept3 a INNER JOIN emp3 b ON a.deptno =b.dept_id;
-- Query the employees of the R & D department
-- Implicit inner join
SELECT * FROM dept3 a,emp3 b WHERE a.deptno =b.dept_id AND name =' R & D department ';
-- Display inner connection
SELECT * FROM dept3 a JOIN emp3 b ON a.deptno = b.dept_id AND name = ' R & D department ';
-- Query the employees of R & D department and sales department
SELECT * FROM dept3 a JOIN emp3 b on a.deptno = b.dept_id and (name= ' R & D department ' or name = ' The sales department ');
SELECT * FROM dept3 a JOIN emp3 b on a.deptno = b.dept_id and name in (' R & D department ',' The sales department ');
-- Query the number of employees in each department , And sort in ascending order
SELECT
a.name,a.deptno,COUNT(*) ' Number of employees '
FROM
dept3 a JOIN emp3 b on a.deptno = b.dept_id GROUP BY a.deptno ORDER BY COUNT(*) ;
-- The number of queries is greater than or equal to 3 The department in charge of the , And in descending order of the number of people
SELECT
a.deptno,a.name,COUNT(*) as total_cnt
FROM
dept3 a JOIN emp3 b on a.deptno = b.dept_id
GROUP BY
a.deptno,a.name HAVING total_cnt >=3 ORDER BY total_cnt DESC;
External connection query
External connection is divided into left external connection (left outer join)、 Right connection (right outer join), Full outer join (full outer join).
notes :oracle There are fulll join, But in the MySQL in full join The support is not good , We can use union To achieve the goal .
Method :
The left outer join :left outer join
select * from A left outer join B on Conditions ;
Right connection :right outer join
select * from A right outer join B on Conditions ;
Full outer join :full outer join
select * from A full outer join B on Conditions ;
for example :
-- External connection query
SELECT * FROM dept3 a LEFT OUTER JOIN emp3 b ON a.deptno = b.dept_id;
SELECT * FROM dept3 a LEFT JOIN emp3 b ON a.deptno = b.dept_id;
-- SELECT * FROM A LEFT JOIN B on Conditions 1 RIGHT JOIN C on Conditions 2 RIGHT JOIN D on Conditions 3;
-- Check which departments have employees , Which departments have no employees
SELECT * FROM dept3 a RIGHT OUTER JOIN emp3 b ON a.deptno = b.dept_id;
SELECT * FROM dept3 a RIGHT JOIN emp3 b ON a.deptno = b.dept_id;
-- SELECT * FROM A RIGHT JOIN B on Conditions 1 RIGHT JOIN C on Conditions 2 RIGHT JOIN D on Conditions 3;
-- Realize full external connection
-- Use union Keyword to realize the union of left outer connection and right outer connection
-- union Splice the two long training results up and down , And remove the weight
SELECT * FROM dept3 a LEFT OUTER JOIN emp3 b ON a.deptno = b.dept_id
UNION
SELECT * FROM dept3 a RIGHT JOIN emp3 b ON a.deptno = b.dept_id;
-- union all It is to splice the two long training results up and down , No weight removal
SELECT * FROM dept3 a LEFT OUTER JOIN emp3 b ON a.deptno = b.dept_id
UNION ALL
SELECT * FROM dept3 a RIGHT JOIN emp3 b ON a.deptno = b.dept_id;
Subquery
Concept : A subquery is a complete query statement of values , Nested several small queries with different functions , So as to complete the complex query together , Popular point is to include select nested queries .
characteristic
There are four types of data that can be returned by sub queries :
- Single row single row : What is returned is a specific column of content , It can be understood as a single value data
- Single row and multiple columns : Returns the daily use of multiple columns in a row of data
- Multi row single row : Returns the contents of the same column in multiple rows of records , It is equivalent to giving an operating range
- Multiple rows and columns : The result of the query is a temporary table
Basic subquery
-- A subquery is a value in a complete query statement , Nested several small queries with different functions , So as to complete the complex query together , Popular point is to include select Nested queries
-- Query the information of the oldest employee , The display information contains the employee number 、 Employee name 、 Age of employee
-- step :
-- 1. Query maximum age
SELECT MAX(age) FROM emp3;
-- 2. Compare the age of each employee with the maximum age , Equality satisfies the condition
SELECT * FROM emp3 WHERE age = (SELECT MAX(age) FROM emp3);
-- Query the employee information of R & D department and sales department , Include employee number 、 Employee name
-- Mode one : Relational query
SELECT * FROM dept3 a JOIN emp3 b ON a.deptno = b.dept_id AND ( name in(' R & D department ',' The sales department '));
-- Mode two : Subquery
-- step :
-- 1. First, check the Department numbers of the R & D department and the sales department
SELECT deptno FROM dept3 WHERE name in(' R & D department ',' The sales department ');
-- 2. The department number of the employee is 1001 or 1002
SELECT * FROM emp3 WHERE dept_id in (SELECT deptno FROM dept3 WHERE name in(' R & D department ',' The sales department '));
-- Check the R & D department 20 Information about employees under the age of , Include employee number 、 Employee name , Department name
-- Mode one : Relational query
SELECT * FROM dept3 a JOIN emp3 b ON a.deptno = b.dept_id AND (name = ' R & D department 'AND age <20);
-- Mode two : Subquery
-- step :
-- 1. Query the information of R & D department in the Department table
SELECT * FROM dept3 WHERE name = ' R & D department ';
-- 2. Query the employee table for persons younger than 20 Year old employee information
SELECT * FROM emp3 WHERE age < 20;
-- 3. Associate the results of the above two queries
SELECT *
FROM
(SELECT * FROM dept3 WHERE name = ' R & D department ') t1
JOIN
(SELECT * FROM emp3 WHERE age < 20) t2 ON t1.deptno = t2.dept_id;
Subquery keyword
In subquery , There are some common logical keywords , These keywords can provide us with rich query functions , The main keywords are as follows :
- ALL keyword
- ANY keyword
- SOME keyword
- IN keyword
- EXISTS keyword
ALL keyword
Method :
select …… from…… where c > all ( Query statement )
Equivalent to
select ……from …… where c > result1 and c > result2 and c > result3
characteristic :
- ALL: Compared with the ownership returned by the subquery, it is TRUE Then return to true
- ALL It can be done with =、>、>=、<、<=、<> Combine to use , Respectively equal to 、 Greater than 、 Greater than or equal to 、 Less than 、 Less than or equal to 、 Not all the data in it
- ALL Indicates that the value in the specified column must be greater than each value in the subquery set , That is, it must be greater than the maximum value of the sub query set ; If it is less than, it is less than the minimum value of the sub query set . In the same way, you can exit other comparison operators
for example :
-- 1. Query age is greater than ‘1003’ Employee information of all ages in the Department
SELECT * FROM emp3 WHERE age > all (SELECT age FROM emp3 WHERE dept_id = '1003');
-- 2. Query employee information that does not belong to any department
SELECT * FROM emp3 WHERE dept_id <> all(SELECT deptno FROM dept3 );
ANY and SOME
Method :
select …… from…… where c > any( Query statement )
Equivalent to
select ……from …… where c > result1 or c > result2 or c > result3
characteristic :
- ANY: Compare with any word returned by the subquery as true Then return to ture
- ANY It can be done with =、>、>=、<、<=、<> Combine to use , Respectively equal to 、 Greater than 、 Greater than or equal to 、 Less than 、 Less than or equal to 、 It does not mean that any of the data is combined
- Indicates that the value in the specified column must be greater than any value in the subquery , That is, it must be greater than the minimum value in the sub query set . In the same way, you can exit the case of other comparison operators
- SOME and ANY It does the same thing ,SOME It can be understood as ANY Another name for
for example :
-- Query age is greater than ‘1003’ Employee information of any employee age in the Department
SELECT * FROM emp3 WHERE age > ANY(SELECT age FROM emp3 WHERE dept_id='1003') and dept_id <>'1003';
SELECT * FROM emp3 WHERE age > SOME(SELECT age FROM emp3 WHERE dept_id='1003') and dept_id <>'1003';
IN keyword
Method :
select …… from…… where c in( Query statement )
Equivalent to
select ……from …… where c = result1 or c = result2 or c = result3
characteristic :
- IN keyword , Used to determine the value of a record , Whether in the specified set
- stay IN Add... Before the keyword not You can reverse the conditions
-- Query the employee information of R & D department and sales department , Include employee number 、 Employee name
SELECT eid,ename FROM emp3 WHERE dept_id in (SELECT deptno FROM dept3 WHERE name in (' R & D department ',' The sales department '));
EXISTS keyword
Method :
select……from……where exists ( Query statement )
characteristic :
- The subquery if “ There are data results ”( Return at least one row of data ), Then EXISTS() As the result of the “true”, Outer query execution
- The subquery if “ No data results ”( No data returned ), Then EXISTS() As the result of the “false”, The outer query does not execute
- EXISTS The following sub query does not return any actual data , Only return true or false , When true is returned where Conditions established
- Be careful ,EXISTS Keywords are more than IN The operation efficiency of keywords is high , therefore , In actual development , Especially when there is a large amount of data , Recommended EXISTS keyword
for example :
-- Query whether the company has a value greater than or equal to 60 Year old employees , Output if there is
SELECT * FROM emp3 a WHERE EXISTS(SELECT * FROM emp3 WHERE a.age >= 60);
SELECT * FROM emp3 a WHERE eid in(SELECT eid FROM emp3 WHERE a.age >= 60);
-- Query the employee information of the Department
SELECT * FROM emp3 a WHERE EXISTS(SELECT * FROM dept3 b WHERE a.dept_id=b.deptno);
SELECT * FROM emp3 a WHERE dept_id in(SELECT deptno FROM dept3 b WHERE a.dept_id=b.deptno);
Self association query
Concept :MySQL For information query, you need to perform association query on the table itself , That is, a table is associated with itself , Use one table as multiple tables . Note that the table must be aliased during self association .
Method 1 :
select Field list from surface 1 a, surface 1 b where Conditions ;
Method 2 :
select Field list from surface 1 a [left] join surface 1 b on Conditions ;
for example :
-- Create table , And establish self correlation constraints
CREATE TABLE t_sanguo(
eid INT PRIMARY KEY,
ename VARCHAR(20),
manager_id INT,
FOREIGN KEY(manager_id) REFERENCES t_sanguo(eid)
);
INSERT INTO t_sanguo VALUES(1,' Liu Xie ',NULL);
INSERT INTO t_sanguo VALUES(2,' Liu bei ',1);
INSERT INTO t_sanguo VALUES(3, ' Guan yu ', 2);
INSERT INTO t_sanguo VALUES(4, ' Zhang Fei ', 2);
INSERT INTO t_sanguo VALUES(5, ' Cao Cao ', 1);
INSERT INTO t_sanguo VALUES(6, ' Xu Chu ', 5);
INSERT INTO t_sanguo VALUES(7, ' Dianwei ', 5);
INSERT INTO t_sanguo VALUES(8, ' king of Wu in the Three Kingdoms Era ', 1);
INSERT INTO t_sanguo VALUES(9, ' Zhou Yu ', 8);
INSERT INTO t_sanguo VALUES(10, ' Lu Su ', 8);
-- Make association query
-- 1. Query the information of each person in the three countries and his superiors
SELECT * FROM t_sanguo a,t_sanguo b WHERE a.manager_id = b.eid;
SELECT a.ename, b.ename FROM t_sanguo a,t_sanguo b WHERE a.manager_id = b.eid;
-- 2. Query all tasks and superiors
SELECT a.ename, b.ename FROM t_sanguo a LEFT JOIN t_sanguo b on a.manager_id = b.eid;
-- 3. Query all tasks 、 The superior , Superior such as : Zhang Fei Liu bei Liu Xie
SELECT a.ename, b.ename FROM t_sanguo a LEFT JOIN t_sanguo b on a.manager_id = b.eid LEFT JOIN t_sanguo c on b.manager_id = c.eid;
Multi table operation exercises
边栏推荐
- Analysis of open API design specification
- RapidEye快鸟、SPOT卫星遥感影像数据
- VS代码一键整理快捷键
- volume rendering
- [path planning] week 1: hodgepodge
- liunx 安装mysql
- Why do you think it is common for Chinese people to earn more than 10000 yuan a month?
- Fundamentals of shell programming (Part 7: branch statement -if)
- The link added in the bottom menu cannot jump to the secondary page
- Linux安装Mysql(包成功!!)
猜你喜欢

leetcode. 11 --- container with the most water

KDD'22 | 阿里: 基于EE探索的精排CTR预估

What are the methods of software stress testing and how to select a software stress testing organization?

Registration of spa project development

新捷途X70S上市8.79万起,空间安全越级,不愧是网红国民大7座SUV
![[GWCTF 2019]mypassword XSS](/img/26/3611fd5aae21ea004dcfcc2c623328.png)
[GWCTF 2019]mypassword XSS

In the third week of June, the main growth ranking list (BiliBili platform) of station B single feigua data up was released!
Task cache compilation caused by gradle build cache
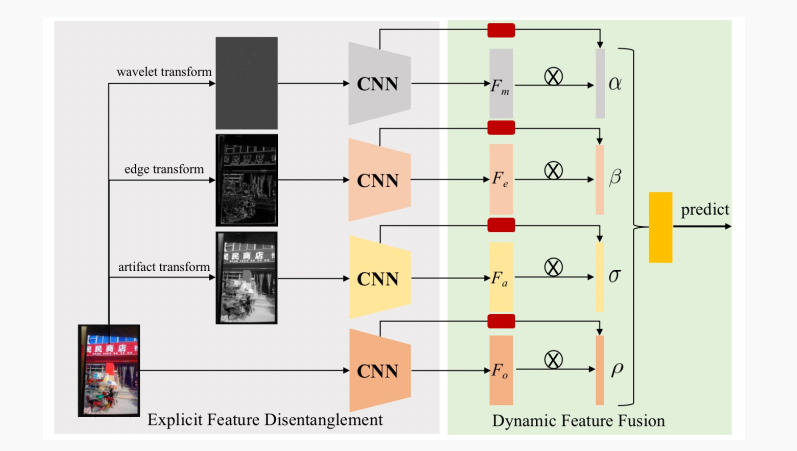
Cvpr2022 𞓜 feature decoupling learning and dynamic fusion for re captured images

Las point cloud data thinning in ArcGIS
随机推荐
≥ server2012r2 system, disable some planned tasks of the system
【论文解读】关于基于视觉无人机自主降落平台的论文梳理
Solution to cache inconsistency
Implementation of depth traversal adjacency table in Figure 6-7
自助图书馆系统-Tkinter界面和openpyxl表格综合设计案例
In the third week of June, the main growth ranking list (BiliBili platform) of station B single feigua data up was released!
5分钟快速上线Web应用和API(Vercel)
SPA项目开发之动态树+数据表格+分页
Fundamentals of shell programming (Part 7: branch statement -if)
【ROS】ROSmsg cakin_make编译错误
Query es page subscript exceeds 10000
[mavros] mavros startup Guide
The required reading for candidates | PMP the test on June 25 is approaching. What should we pay attention to?
[recommended by Zhihu knowledge master] castle in UAV - focusing on the application of UAV in different technical fields
Liunx installing MySQL
【象棋人生】01 人生如棋
How much do you know about the cause of amplifier distortion?
322. change exchange
Is it bad for NFT that the market starts to cool down?
Redis error reporting and common configurations
