当前位置:网站首页>线程同步之互斥量(互斥锁)
线程同步之互斥量(互斥锁)
2022-06-26 03:56:00 【StudyWinter】
1 同步的概念
所谓同步, 即同时起步,协调一致。不同的对象, 对“同步” 的理解方式略有不同。 如,设备同步,是指在两个设备之间规定一个共同的时间参考; 数据库同步, 是指让两个或多个数据库内容保持一致,或者按需要部分保持一致; 文件同步, 是指让两个或多个文件夹里的文件保持一致等等。
而编程中、 通信中所说的同步与生活中大家印象中的同步概念略有差异。“同” 字应是指协同、协助、互相配合。主旨在协同步调,按预定的先后次序运行。
2 线程同步的概念
同步即协同步调,按预定的先后次序运行。线程同步,指一个线程发出某一功能调用时,在没有得到结果之前,该调用不返回。同时其它线程为保证数据一致性,不能调用该功能。
“同步”的目的,是为了避免数据混乱,解决与时间有关的错误。实际上,不仅线程间需要同步,进程间、信号间等等都需要同步机制。因此, 所有“多个控制流,共同操作一个共享资源” 的情况,都需要同步。
3 为什么要有线程同步

- 共享资源,多个线程都可对共享资源操作 [容易产生冲突]
- 线程操作共享资源的先后顺序不确定
- cpu处理器对存储器的操作一般不是原子操作
举个例子:
两个线程都把全局变量增加1,这个操作平台需要三条指令完成。
从内存读到寄存器 →寄存器的值加1 →将寄存器的值写会内存。
如果此时线程A取值在寄存器修改还未写入内存,线程B就从内存取值就会导致两次操作实际上只修改过一次。或者说后一次线程做的事情覆盖前一次线程做的事情。实际上就执行过一次线程。
4 互斥量 mutex
4.1 基本概念
- Linux 中提供一把互斥锁 mutex(也称之为互斥量)。
- 每个线程在对资源操作前都尝试先加锁,成功加锁才能操作,操作结束解锁。
- 资源还是共享的,线程间也还是竞争的,但通过“锁”就将资源的访问变成互斥操作,而后与时间有关的错误也不会再产生了。
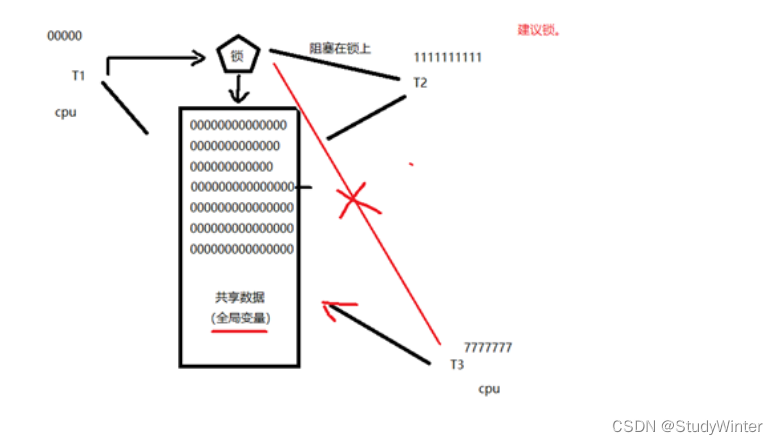
锁的使用:建议锁!对公共数据进行保护。所有线程【应该】在访问公共数据前先拿锁再访问。但,锁本身不具备强制性。
4.2 借助互斥锁管理共享数据实现同步
主要应用函数:
pthread_mutex_init
pthread_mutex_destory
pthread_mutex_lock
pthread_mutex_trylock
pthread_mutex_unlock以上5个函数的返回值都是:成功返回0,失败返回错误号。pthread_mutex_t 类型,其本质是一个结构体。为简化理解,应用时可忽略其实现细节,简单当成整数看待。pthread_mutex_t mutex;变量mutex只有两种取值:0,1。
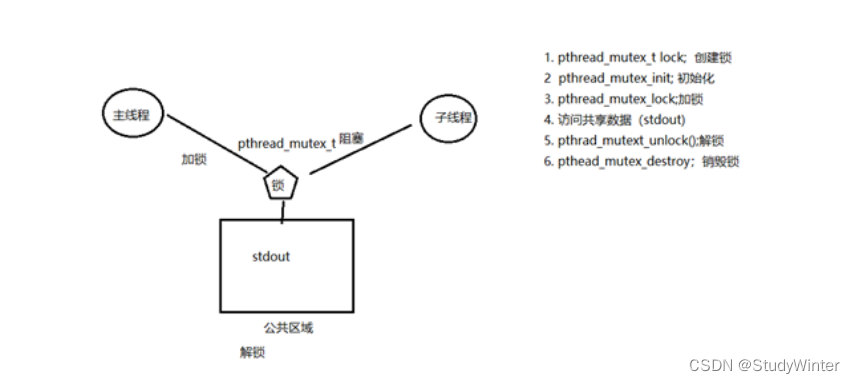
使用mutex(互斥量、互斥锁)一般步骤【重点】
pthread_mutex_t 类型。
1 pthread_mutex_t lock; 创建锁
2 pthread_mutex_init; 初始化 1
3 pthread_mutex_lock;加锁 1-- --> 0
4 访问共享数据(stdout)
5 pthrad_mutext_unlock();解锁 0++ --> 1
6 pthead_mutex_destroy;销毁锁pthread_mutex_init函数
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,
const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr)
// 这里的restrict关键字,表示指针指向的内容只能通过这个指针进行修改
// restrict关键字:
// 用来限定指针变量。被该关键字限定的指针变量所指向的内存操作,必须由本指针完成。初始化互斥量:
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); // 第1种:动态初始化。
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; // 第2种:静态初始化pthread_mutex_destroy 函数
销毁一个互斥锁
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);pthread_mutex_lock 函数
加锁。 可理解为将 mutex--(或 -1),操作后 mutex 的值为 0 。
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);pthread_mutex_unlock 函数
解锁。 可理解为将 mutex ++(或 +1),操作后 mutex 的值为 1。
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);pthread_mutex_trylock 函数
尝试加锁
int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);加锁与解锁
lock 与 unlock:
lock 尝试加锁,如果加锁不成功,线程阻塞,阻塞到持有该互斥量的其他线程解锁为止。
unlock 主动解锁函数, 同时将阻塞在该锁上的所有线程全部唤醒,至于哪个线程先被唤醒,取决于优先级、调度。默认:先阻塞、先唤醒。
例如: T1 T2 T3 T4 使用一把 mutex 锁。 T1 加锁成功,其他线程均阻塞,直至 T1 解锁。 T1 解锁后, T2 T3 T4 均被唤醒,并自动再次尝试加锁。
可假想 mutex 锁 init 成功初值为 1。 lock 功能是将 mutex--。而 unlock 则将 mutex++。
lock 与 trylock:
lock 加锁失败会阻塞,等待锁释放。
trylock 加锁失败直接返回错误号(如: EBUSY),不阻塞。
使用锁实现互斥访问共享区:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
// 定义全局互斥锁
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
// 初始化互斥锁
// mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
void *tfn(void *arg)
{
srand(time(NULL));
int res;
while (1)
{
// 加锁
res = pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_lock error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
printf("hello");
// 模拟长时间操作共享资源
sleep(rand() % 3);
printf("world\n");
// 解锁
res = pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_unlock error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
sleep(rand() % 3);
}
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// 定义线程
pthread_t tid;
srand(time(NULL));
// 初始化互斥锁
int res = pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_init error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
// 创建线程
res = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, tfn, NULL);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
while (1)
{
// 加锁
res = pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_lock error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
printf("HELLO");
// 模拟长时间操作共享资源
sleep(rand() % 3);
printf("WORLD\n");
// 解锁
res = pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_unlock error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
sleep(rand() % 3);
}
// 回收线程
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
// 销毁互斥锁
res = pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
if (res != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_unlock error:%s\n", strerror(res));
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}执行

可以看到,主线程和子线程在访问共享区时就没有交叉输出的情况了。
4.3 互斥锁的使用技巧
注意事项:
尽量保证锁的粒度, 越小越好。(访问共享数据前,加锁。访问结束【立即】解锁。)
互斥锁,本质是结构体。 我们可以看成整数。 初值为 1。(pthread_mutex_init() 函数调用成功。)
加锁: --操作, 阻塞线程。
解锁: ++操作, 唤醒阻塞在锁上的线程。
try锁:尝试加锁,成功--。失败,返回。同时设置错误号 EBUSY
边栏推荐
- Li Kou 79 word search
- Detailed explanation of widget construction process of fluent
- chrome页面录制,重放功能
- [Flink] a brief analysis of the writing process of Flink sort shuffle
- Oracle technology sharing Oracle 19.14 upgrade 19.15
- In the matter of getting customers at sea, how can advertisers play besides digital advertising?
- ABP framework Practice Series (II) - Introduction to domain layer
- (15) Blender source code analysis flash window display menu function
- Quanergy欢迎Lori Sundberg出任首席人力资源官
- I/O 虚拟化技术 — VFIO
猜你喜欢

High performance computing center roce overview

商城风格也可以很多变,DIY 了解一下

面了个字节拿25k出来的测试,算是真正见识到了基础的天花板

线程同步之读写锁

Detailed explanation of globalkey of flutter

When the tiflash function is pushed down, it must be known that it will become a tiflash contributor in ten minutes

ABP framework Practice Series (II) - Introduction to domain layer

Intelligent manufacturing learning videos and books

外包干了四年,人直接废了。。。

Unity移动端游戏性能优化简谱之 以引擎模块为划分的CPU耗时调优
随机推荐
2022.6.24-----leetcode.515
IEDA 突然找不到了compact middle packages
开源!ViTAE模型再刷世界第一:COCO人体姿态估计新模型取得最高精度81.1AP
Contains an object field at offset position
JS to achieve the effect of text marquee
User control custom DependencyProperty
捕获数据包(Wireshark)
763. dividing alphabetic intervals
(15)Blender源码分析之闪屏窗口显示菜单功能
Prism framework project application - Navigation
ASP. Net core introduction
Restful API interface design standards and specifications
1.基础关
169. 多数元素
763. 划分字母区间
After four years of outsourcing, people are directly abandoned...
高性能算力中心 — RoCE — Overview
Three level menu applet
Analysis of updatechild principle of widget update mechanism of fluent
Uni app custom selection date 2 (September 16, 2021)