当前位置:网站首页>Basic data type and corresponding packing class
Basic data type and corresponding packing class
2022-06-23 12:23:00 【Hard working boy】
List of articles
It seems that I haven't fully understood the difference between basic data types and packaging classes .
Basic data type
6 Number types :byte、short、int、long、float、double
1 Types of characters :char
1 Middle Boolean :boolean
The corresponding packaging class Byte、Short、Integer、Long、Float、Double、Character、Boolean
Number of digits of basic type 、 byte 、 The default value is
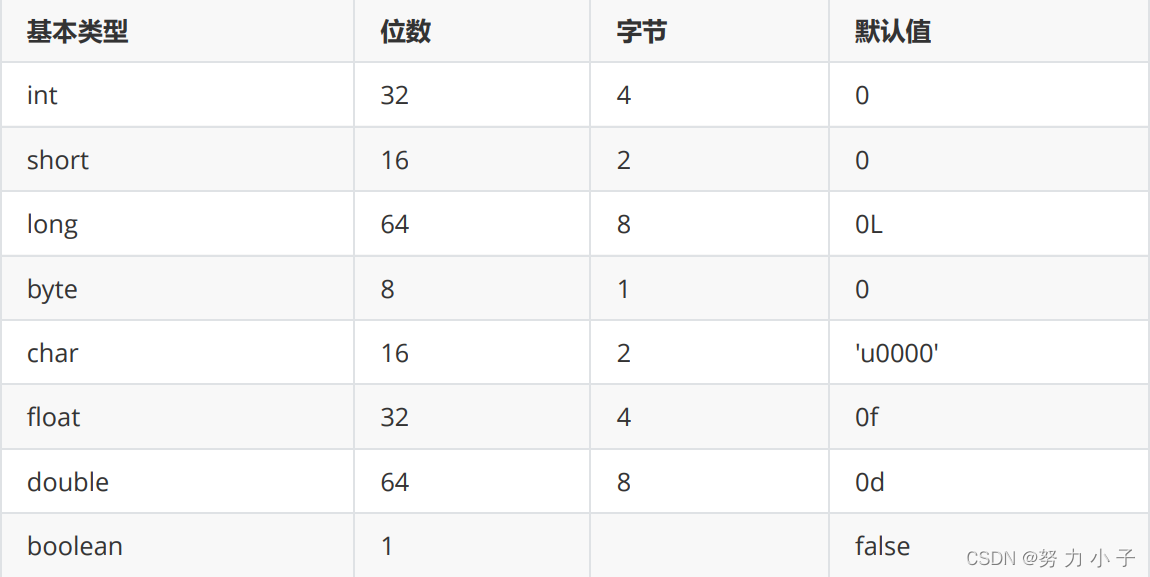
Java Use in long The type of data must be followed by the number L, Otherwise, it will be parsed as an integer .
Java Use in long The type of data must be followed by the number L, Otherwise, it will be parsed as an integer .
Packing
Wrap basic types with their corresponding reference types .
Unpacking
Convert wrapper type to base data type .
For example, use Integer Three objects are created abc,a=b+c, because + Cannot be used in Integer Inter object operation , It will unpack automatically .
Wrapper classes and constant pools
Java Most of the basic types of wrapper classes implement constant pool technology , namely Byte, Short, Integer, Long,Character,Boolean.Byte,Short,Integer,Long The default value is created [-128,127] The corresponding type of cached data ,Character Created values in [0,127] Range cache data ,Boolean Go straight back to True Or False. If it goes beyond the corresponding range, it will still create new objects .
Two types of floating-point wrapper classes Float,Double Constant pool technology is not implemented .
Integer i1=40//Java When compiling, it will directly encapsulate the code as Integer i1=Integer.valueOf(40);, To use the objects in the constant pool .
Integer i2 = new Integer(40)// In this case, a new object is created .
System.out.println(i1==i2)// Output false
边栏推荐
- Halcon knowledge: dyn_ Usage of threshold (scratch detection)
- Is there any regulation on the redemption time of financial products?
- Common fault analysis and Countermeasures of MySQL in go language
- @Dark horse fans, haven't you received this "high temperature subsidy"?
- Qt5 knowledge: some key points of signals and slots
- 面试题:举例说一下工作中你的接口测试是怎么做的?
- [no title] 2022 pressure pipeline patrol inspection and maintenance test questions and online simulation test
- ROS察微【57】:配置手臂机器人来抓东西
- Blue Bridge Cup single chip microcomputer (I) -- turn off peripherals and turn off led
- ROS2知识(6):坐标对象TF原理和实践
猜你喜欢
详解PyQt5信号与槽的关系
![Halcon principle: one dimensional function_ 1D type [2]](/img/54/570c6e739be1ab9caa9df805965b57.png)
Halcon principle: one dimensional function_ 1D type [2]
QT5知识:信号和槽的一些要点

Halcon knowledge: binocular_ Discrimination knowledge
![[cloud native & microservice viii] source code analysis of weightedresponsetimerule of ribbon load balancing strategy (response time weighting)](/img/cc/afad5b5d327416c809be3b661bcc13.png)
[cloud native & microservice viii] source code analysis of weightedresponsetimerule of ribbon load balancing strategy (response time weighting)

Localization information | aikesheng and China kefangde complete product compatibility and mutual certification
Getting started with redis - Chapter 4 - data structures and objects - jump table

这两所985大学,共享同一位校长!校方:属实

Getting started with redis - Chapter 2 - data structures and objects - linked lists

QT knowledge: using the qgraphicspixmapitem class
随机推荐
[zero foundation wechat applet] actual development of ID photo changing background color applet based on Baidu brain portrait segmentation
sql增加表记录的重复问题。
Qt5 knowledge: QT drawing graph
Capacitated Facility Location Problem容量有限设施选址问题
简历的项目经历,测试人员书写要注意的几个问题
09 -- 回文对
自己测试的范围内出现严重 BUG ,马上要上线,这种情况怎么办?
QT5知识:信号和槽的一些要点
Qt5 knowledge: DNS query
Meta 称英国安全法将“扫描所有私人信息”,有侵犯用户隐私风险
UI框架
10-- 根据中序遍历和后序遍历,构造二叉树
Qt知识:视图框架QGraphicsWidget详解
09 -- palindrome pair
QT5知识:DNS查询
ROS knowledge: reading point cloud data files
HMS Core 视频编辑服务开放模板能力,助力用户一键Get同款酷炫视频
DuPont analysis: what is the investment value of Anyang Iron and Steel Co., Ltd?
Hot spot of equity transfer: 93.75% equity transfer of Chongqing Jianke Construction Engineering Quality Inspection Co., Ltd
二维激光SLAM( 使用Laser Scan Matcher )