当前位置:网站首页>Interviewer: please introduce cache penetration, cache null value, cache avalanche and cache breakdown, which are easy to understand
Interviewer: please introduce cache penetration, cache null value, cache avalanche and cache breakdown, which are easy to understand
2022-06-27 06:50:00 【xy29981】
An avalanche Is a professional term in back-end services , To understand it , Let's introduce... Step by step . Avalanches are cumulative problems , Under the avalanche , No snowflake is innocent .
today , To have a chat Cache penetration 、 Cache breakdown 、 cache An avalanche Related issues . I believe you will have a clearer understanding of these concepts .
For Internet developers , You will be familiar with the concept of avalanche , It seems that I feel a little pale when talking about Tiger . If the backend service avalanches , It would be GG 了 .
The topic written today , It's actually very basic , But there are several scenarios that are very important for high concurrency , I can't get around it , It is estimated that during the interview , Often .
Articles on this topic , There are a lot of them on the Internet , But I feel there is no suitable , Or the article is not refined enough , Or it's too lean , So I'd better write one by myself .
Although the content is basic , But I still stick to my previous writing style , After referring to many excellent blogs , I'm going to write an article that can be easily understood , Without losing a comprehensive article .
Preface
Let's first look at the normal query process :
First query Redis, If the query is successful , Go straight back to , Query does not exist , Go to query DB;
If DB The query is successful , Data write back Redis, Query does not exist , Go straight back to .

Cache penetration
Definition : When there is no data in the query database and cache , Because the database query has no data , For fault tolerance , The results will not be saved to the cache , therefore Every request will query the database , This is called cache penetration .
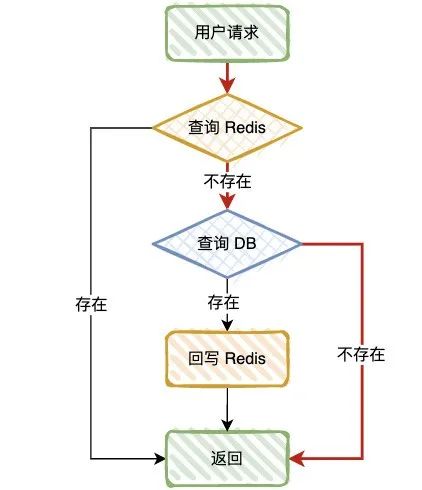
Red lines , This is the scene of cache penetration , When inquired Key In cache and DB When none of them exist , This will happen .
You can imagine , For example, there is an interface that needs to query product information , If a malicious user impersonates a non-existent product ID Initiate request , Instantaneous concurrency is very high , Estimate your DB I'll just hang up .
Maybe your first reaction is to perform regular verification on the input parameters , Filter out invalid requests , Yes ! The true , Is there any other better plan ?
Cache null
When we find a null value from the database , We can return a null value to the cache , In order to avoid the cache being occupied for a long time , You need to add a shorter expiration time to this null value , for example 3~5 minute .
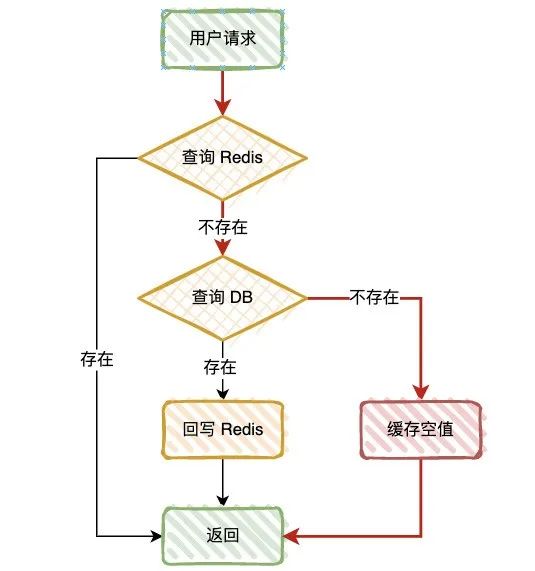
But there's a problem with this plan , When a large number of invalid requests penetrate , There will be a large number of null value caches in the cache , If the cache space is full , It will also eliminate some user information that has been cached , Instead, it will reduce the cache hit rate , So this program , Need to evaluate cache capacity .
If a cache null value is not desirable , At this time, you can consider using Bloom filter .
The bloon filter
The bloom filter is made up of a variable length N A binary array with a variable number M The hash function of , Be simple and rough , It's just one. Hash Map.
The principle is quite simple : Such as element key=#3, If through Hash The algorithm gets a value of 9 Value , There is this Hash Map Of the 9 Bit element , By marking 1 Indicates that there is already data in this bit , As shown in the figure below ,0 No data ,1 Yes, there are data .

So through this method , There will be a conclusion : stay Hash Map in , Tagged data , Not necessarily , But unmarked data , There must be no .
Why? “ Tagged data , Not necessarily ” Well ? because Hash Conflict !
such as Hash Map The length of is 100, But you have 101 A request , If you're lucky enough to explode , this 100 Requests are typed evenly with a length of 100 Of Hash Map in , Your Hash Map All have been marked as 1.
When the first 101 When a request comes , Just 100% appear Hash Conflict , Although I didn't ask , But the mark is 1, The bloom filter did not intercept .
If you need to reduce miscalculation , Can increase Hash Map The length of , And choose a higher grade Hash function , For example, many times to key Conduct hash.
except Hash Conflict , The bloom filter can actually cause a fatal problem : Bloom filter update failed .
For example, there is a commodity ID First request , When DB When in , Need to be in Hash Map Mark in , But because of the Internet , Cause the tag to fail , So next time this product ID When the request is reissued , The request will be intercepted by the bloom filter , For example, this is a double 11 Stock of popular goods , There is clearly 10W Commodity , But you suggest that the inventory does not exist , Leaders may say “ You don't have to come tomorrow ”.
So if you use a bloom filter , In the face of Hash Map When updating data , It needs to be ensured that this data can 100% The update is successful , It can be done asynchronously 、 How to retry , Therefore, this scheme has certain implementation cost and risk .
Cache breakdown
Definition : A hotspot cache just fails at a certain time , Then there happens to be a large number of concurrent requests , At this point, these requests will put great pressure on the database , This is called cache breakdown .
This is actually the same as “ Cache penetration ” The flow chart is the same , But the starting point of this is “ A hotspot cache just fails at a certain time ”, For example, a very popular popular product , Cache suddenly fails , All the traffic directly reaches DB, This will cause excessive database requests at a certain time , More emphasis on instantaneity .
The main ways to solve the problem are 2 Kind of :
Distributed lock : Only the first thread that gets the lock requests the database , Then insert the cache , Of course, every time you get the lock, you have to check whether the cache has , In high concurrency scenarios , I don't recommend using distributed locks , It will affect the query efficiency ;
Settings never expire : For some hotspot caches , We can set it to never expire , This ensures the stability of the cache , But it should be noted that after the data changes , To update this hotspot cache in time , Otherwise, it will cause the error of query results , For example, popular goods , Preheat to the database first , Then go offline .
There are also “ Cache renewal ” The way , Such as caching 30 Minutes out , You can do a regular task , Every time 20 Run every minute , It feels like this way is neither fish nor fowl , For your reference only .
Cache avalanche
Definition : A large number of caches expire at the same time in a short time , Resulting in a large number of requests to query the database directly , This has caused great pressure on the database , In severe cases, the situation that may lead to database downtime is called cache avalanche .
if “ Cache breakdown ” It's individual resistance , that “ Cache avalanche ” It's a collective uprising , Then what happens to cache avalanche ?
A large number of caches expire at the same time in a short time ;
Cache service down , Cause a large-scale cache failure at a certain time .
So what are the solutions ?
Add random time to cache : Random time can be added when setting the cache , such as 0~60s, This can greatly avoid a large number of cache failures at the same time ;
Distributed lock : Add a distributed lock , The first request is to persist the data to the cache , Only other requests can enter ;
Current limiting and degradation : Through current limiting and degradation strategies , Reduce requested traffic ;
Cluster deployment :Redis Deploy through cluster 、 Master-slave strategy , After the primary node goes down , Will switch to the slave node , Guarantee the availability of services .
Example of adding random time to cache :
// Cache original expiration time
int exTime = 10 * 60;
// Random number generating class
Random random = new Random();
// Cache Settings
jedis.setex(cacheKey, exTime + random.nextInt(1000) , value);
In this way , It's much simpler . I'm sure you're right Cache penetration 、 Cache breakdown 、 cache An avalanche There must be a new understanding .
Please look forward to my next article , thank you .

more java Advanced information , Interview information , Official account
边栏推荐
- Scala函数柯里化(Currying)
- View functions in tidb
- [QT dot] realize the watchdog function to detect whether the external program is running
- IDEA中关于Postfix Completion代码模板的一些设置
- An Empirical Evaluation of In-Memory Multi-Version Concurrency Control
- Write an example of goroutine and practice Chan at the same time
- Convolution neural network -- Application of CNN model (ore prospecting prediction)
- Get the query parameter in the address URL specify the parameter method
- TiDB 数据库快速上手指南
- 分数阶PID控制
猜你喜欢

2022 CISP-PTE(一)文件包含

Yaml file encryption

面试官:你天天用 Lombok,说说它什么原理?我竟然答不上来…

Redis cache penetration, cache breakdown, cache avalanche

Redis 缓存穿透、缓存击穿、缓存雪崩

G1 and ZGC garbage collector

C Primer Plus Chapter 11_ Strings and string functions_ Codes and exercises

Inter thread wait and wake-up mechanism, singleton mode, blocking queue, timer

Yolov6's fast and accurate target detection framework is open source

2022 CISP-PTE(一)文件包含
随机推荐
记一次Spark报错:Failed to allocate a page (67108864 bytes), try again.
One year's experience of technical personnel in Entrepreneurship
ORA-00909: 参数个数无效,concat引起
MPC control of aircraft wingtip acceleration and control surface
主动学习(active learning)
分数阶PID控制
Tidb database Quick Start Guide
Scala函数柯里化(Currying)
面试官:请你介绍一下缓存穿透、缓存空值、缓存雪崩、缓存击穿的,通俗易懂
HTAP in depth exploration Guide
JVM common instructions
浅谈GPU:历史发展,架构
LeetCode 0086. Separate linked list
SQL injection bypass (I)
YOLOv6又快又准的目标检测框架 已开源
Assembly language - Wang Shuang Chapter 11 flag register - Notes
进程终止(你真的学会递归了吗?考验你的递归基础)
面试官:用分库分表如何做到永不迁移数据和避免热点问题?
Scala advanced_ Member access modifier
[QT dot] QT download link